Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effect of Building Orientation on Tensile Properties of Hastelloy X alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seong-June Youn, GooWon Noh, Seok Su Sohn, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):131-137. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00080
- 717 View
- 27 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
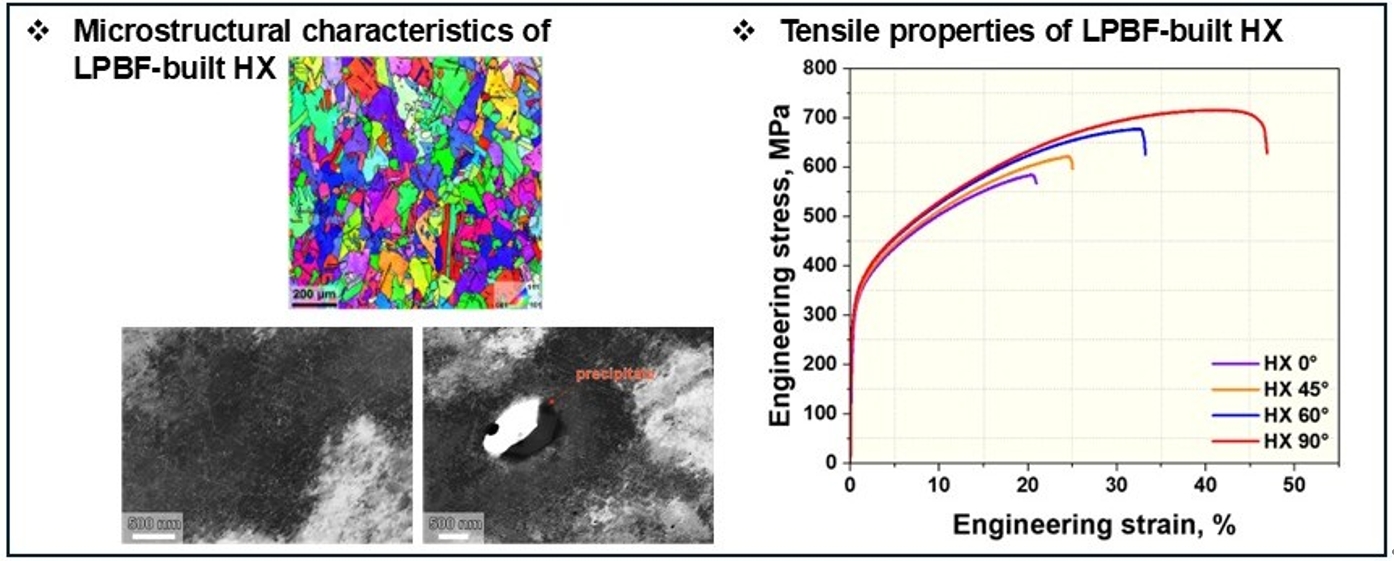
PDF - In this study, the effect of build orientation on the mechanical properties of Hastelloy X fabricated by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process was investigated. Initial microstructural analysis revealed an equiaxed grain structure with random crystallographic orientation and annealing twins. Intragranular precipitates identified as Cr-rich M23C6 and Mo-rich M6C carbides were observed, along with a dense dislocation network and localized dislocation accumulation around the carbides. Mechanical testing showed negligible variation in yield strength with respect to build orientation; however, both ultimate tensile strength and elongation exhibited a clear increasing trend with higher build angles. Notably, the specimen built at 90° exhibited approximately 22% higher tensile strength and more than twice the elongation compared to the 0° specimen.
- [English]
- Ultra-Low-Temperature (4.2 K) Tensile Properties and Deformation Mechanism of Stainless Steel 304L Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seung-Min Jeon, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):95-103. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00066

- 1,454 View
- 48 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the ultra-low-temperature (4.2 K) tensile properties and deformation mechanisms of stainless steel 304L manufactured via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). The tensile properties of LPBF 304L were compared to those of conventional 304L to assess its suitability for cryogenic applications. The results revealed that LPBF 304L exhibited a significantly higher yield strength but lower ultimate tensile strength and elongation than conventional 304L at 4.2 K. The temperature dependence of the yield strength also favored LPBF 304L. Microstructural analysis demonstrated that LPBF 304L features a high density of dislocation cells and nano-inclusions, contributing to its greater strength. Furthermore, strain-induced martensitic transformation was observed as a key deformation mechanism at cryogenic temperatures, where austenite transformed into both hexagonal-closed packed (HCP) and body-centered cubic (BCC) martensite. Notably, BCC martensite nucleation occurred within a single HCP band. These findings provide critical insights into the mechanical behavior of LPBF 304L at cryogenic temperatures and its potential for applications in extreme environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extremely low-temperature tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Heechan Jung, Min Young Sung, Young-Kyun Kim, Jaimyun Jung, Yoona Lee, Namhyun Kang, Kyung Tae Kim, Young-Sang Na, Seok Su Sohn, Jeong Min Park
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 950: 149460. CrossRef - Twinning- and transformation-induced high cryogenic strength and ductility of the CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy: Experiment and MD simulation
Yuze Wu, Zhide Li, Charlie Kong, M.W. Fu, Hailiang Yu
International Journal of Plasticity.2026; 196: 104553. CrossRef - Understanding the unique appearance behavior of shear bands during tensile deformation of α-brass at 4.2 K
Seon-Keun Oh, Sang-Hun Shim, Young-Kyun Kim, Young-Sang Na
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 945: 148989. CrossRef
- Extremely low-temperature tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
- [Korean]
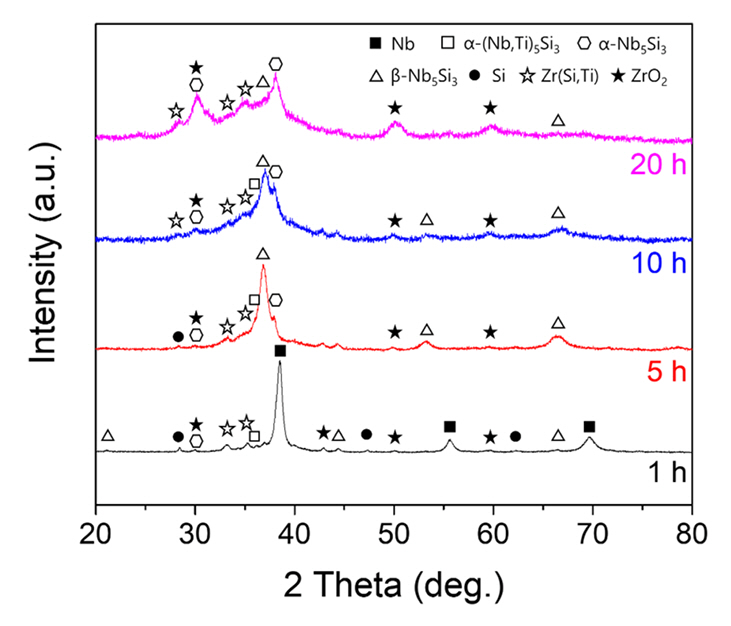
- Development of High-strength, High-temperature Nb-Si-Ti Alloys through Mechanical Alloying
- Jung-Joon Kim, Sang-Min Yoon, Deok-Hyun Han, Jongmin Byun, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):30-36. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.30
- 1,887 View
- 48 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and High Temperature Mechanical Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steels Manufactured by Combination Milling Process
- Jung-Uk Lee, Young-Kyun Kim, Jeoung Han Kim, Hwi-Jin Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):389-395. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.389
- 737 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
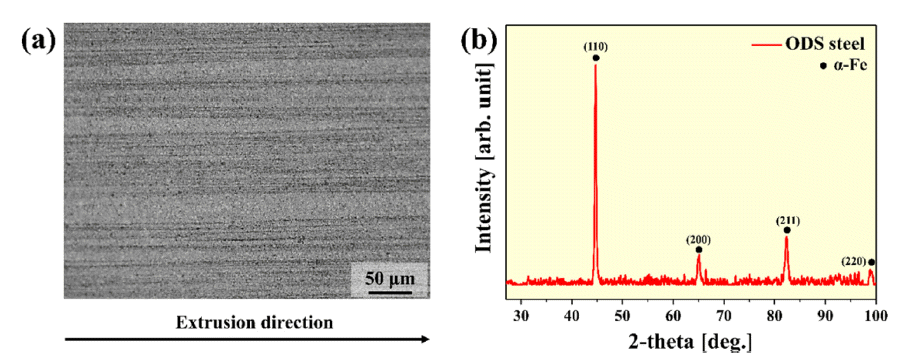
PDF Oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel has excellent high-temperature properties, corrosion resistance, and oxidation resistance, and is expected to be applicable in various fields. Recently, various studies on mechanical alloying (MA) have been conducted for the dispersion of oxide particles in ODS steel with a high number density. In this study, ODS steel is manufactured by introducing a complex milling process in which planetary ball milling, cryogenic ball milling, and drum ball milling are sequentially performed, and the microstructure and high-temperature mechanical properties of the ODS steel are investigated. The microstructure observation revealed that the structure is stretched in the extrusion direction, even after the heat treatment. In addition, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis confirmed the presence of oxide particles in the range of 5 to 10 nm. As a result of the room-temperature and high-temperature compression tests, the yield strengths were measured as 1430, 1388, 418, and 163 MPa at 25, 500, 700, and 900°C, respectively. Based on these results, the correlation between the microstructure and mechanical properties of ODS steel manufactured using the composite milling process is also discussed.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
- Seong-June Youn, Young-Kyun Kim, Jae-Sung Park, Joo-Hyun Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):333-338. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.333
- 629 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we fabricate a thin- and dense-BCuP-5 coating layer, one of the switching device multilayers, through a plasma spray process. In addition, the microstructure and macroscopic properties of the coating layer, such as hardness and bond strength, are investigated. Both the initial powder feedstock and plasma-sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer show the main Cu phase, Cu-Ag-Cu3P ternary phases, and Ag phase. This means that microstructural degradation does not occur during plasma spraying. The Vickers hardness of the coating layer was measured as 117.0 HV, indicating that the fine distribution of the three phases enables the excellent mechanical properties of the plasma-sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer. The pull-off strength of the plasma-sprayed BCuP-5 coating layer is measured as 16.5 kg/cm2. Based on the above findings, the applicability of plasma spray for the fabrication process of low-cost multi-layered electronic contact materials is discussed and suggested.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Dry-Electropolishing on the High Cycle Fatigue Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting
- Dong-Hoon Yang, Young-Kyun Kim, Yujin Hwang, Myoung-Se Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):471-476. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.471
- 610 View
- 8 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
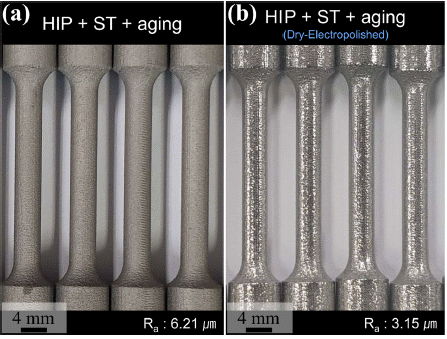
PDF Additively manufactured metallic components contain high surface roughness values, which lead to unsatisfactory high cycle fatigue resistance. In this study, high cycle fatigue properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy are investigated and the effect of dry-electropolishing, which does not cause weight loss, on the fatigue resistance is also examined. To reduce the internal defect in the as-built Ti-6Al-4V, first, hot isostatic pressing (HIP) is conducted. Then, to improve the mechanical properties, solution treatment and aging are also implemented. Selective laser melting (SLM)-built Ti64 shows a primary α and secondary α+β lamellar structure. The sizes of secondary α and β are approximately 2 μm and 100 nm, respectively. On the other hand, surface roughness
R a values of before and after dry-electropolishing are 6.21 μm and 3.15 μm, respectively. This means that dry-electropolishing is effective in decreasing the surface roughness of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The comparison of high cycle fatigue properties between before and after dry-electropolished samples shows that reduced surface roughness improves the fatigue limit from 150 MPa to 170 MPa. Correlations between surface roughness and high cycle fatigue properties are also discussed based on these findings.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-integrity diffusion bonding of laser powder bed fused, forged, and rolled Ti–6Al–4V alloys
Seoyeon Jeon, Hyunjong Ha, Dong Jun Lee, Hyeonil Park, Yong Nam Kwon, Hyunjoo Choi, Hyokyung Sung
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 35: 2108. CrossRef - Effect of Building Orientation on Tensile Properties of Hastelloy X alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seong-June Youn, GooWon Noh, Seok Su Sohn, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(2): 130. CrossRef - Surface finishing by shape-adaptive processes
Jiwang Yan, Brigid Mullany, Anthony Beaucamp, Daniel Meyer, Naohiko Sugita
CIRP Annals.2025; 74(2): 1019. CrossRef - High-Throughput Microstructural Characterization and Process Correlation Using Automated Electron Backscatter Diffraction
J. Elliott Fowler, Timothy J. Ruggles, Dale E. Cillessen, Kyle L. Johnson, Luis J. Jauregui, Robert L. Craig, Nathan R. Bianco, Amelia A. Henriksen, Brad L. Boyce
Integrating Materials and Manufacturing Innovation.2024; 13(3): 641. CrossRef - In-situ formed oxide enables extraordinary high-cycle fatigue resistance in additively manufactured CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy
Young-Kyun Kim, Min-Seok Baek, Sangsun Yang, Kee-Ahn Lee
Additive Manufacturing.2021; 38: 101832. CrossRef
- High-integrity diffusion bonding of laser powder bed fused, forged, and rolled Ti–6Al–4V alloys
- [Korean]
- Effect of Zone Annealing Velocity on the directional Recrystallization in a Ni base Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Alloys
- Young-Kyun Kim, Seong-June Yoon, Jong-Kwan Park, Hwi-Jun Kim, Man-Sik Kong, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):331-335. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.331
- 568 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
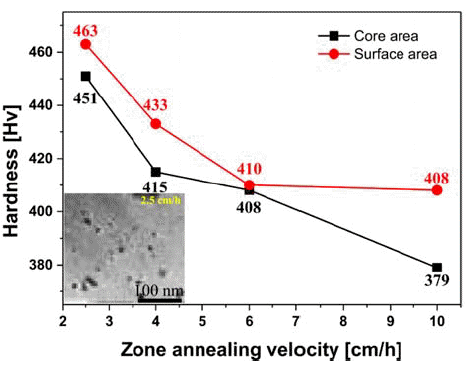
PDF This study investigates the directional recrystallization behavior of Ni based oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) alloy according to the zone annealing velocity. The zone annealing temperature is set as 1390°C, while the zone velocities are set as 2.5, 4, 6, and 10 cm/h, respectively. The initial microstructure observation of the as-extruded sample shows equiaxed grains of random orientation, with an average grain size of 530 nm. On the other hand, the zone annealed samples show a large deviation in grain size depending on the zone velocities. In particular, grains with a size of several millimeters are observed at 2.5-cm/h zone velocity. It is also found that the preferred orientation varies with the zone annealing velocity. On the basis of these results, this study discusses the role of zone velocities in the directional recrystallization of Ni base ODS alloy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Directional recrystallisation processing: a review
Chao Yang, Ian Baker
International Materials Reviews.2021; 66(4): 256. CrossRef
- Directional recrystallisation processing: a review
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
- Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):36-42. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.1.36
- 738 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
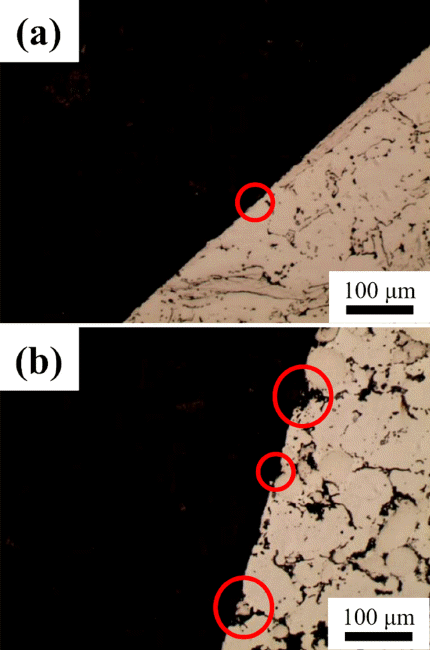
PDF In order to expand the application of oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel, a composite material is manufactured by adding mechanically alloyed ODS steel powder to conventional steel and investigated in terms of microstructure and wear properties. For comparison, a commercial automobile part material is also tested. Initial microstructural observations confirm that the composite material with added ODS steel contains i) a pearlitic Fe matrix area and ii) an area with Cr-based carbides and ODS steel particles in the form of a Fe-Fe3C structure. In the commercial material, various hard Co-, Fe-Mo-, and Cr-based particles are present in a pearlitic Fe matrix. Wear testing using the VSR engine simulation wear test confirms that the seatface widths of the composite material with added ODS steel and the commercial material are increased by 24% and 47%, respectively, with wear depths of 0.05 mm and 0.1 mm, respectively. The ODS steel-added composite material shows better wear resistance. Post-wear-testing surface and cross-sectional observations show that particles in the commercial material easily fall off, while the ODS steel-added material has an even, smooth wear surface.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- First principles determination of formation of a Cr shell on the interface between Y–Ti–O nanoparticles and a ferritic steel matrix
Ki-Ha Hong, Jae Bok Seol, Jeoung Han Kim
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 69. CrossRef - Thermal Properties and Microstructural Changes of Fe-Co System Valve Seat Alloy by High Densification Process
In-Shup Ahn, Dong-Kyu Park, Kwang-Bok Ahn, Seoung-Mok Shin
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(2): 112. CrossRef
- First principles determination of formation of a Cr shell on the interface between Y–Ti–O nanoparticles and a ferritic steel matrix
- [Korean]
- High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Fe-14Cr Ferritic Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steels Manufactured by Mechanical Alloying Process
- Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Hwi-Jun Kim, Man-Sik Kong, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):133-140. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.133
- 582 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
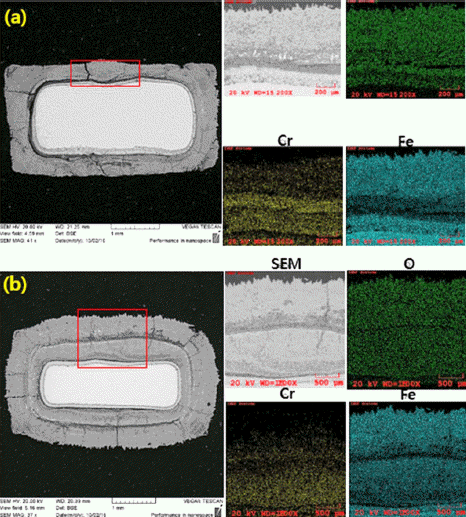
PDF This study investigates the oxidation properties of Fe-14Cr ferritic oxide-dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel at various high temperatures (900, 1000, and 1100°C for 24 h). The initial microstructure shows that no clear structural change occurs even under high-temperature heat treatment, and the average measured grain size is 0.4 and 1.1 μm for the as-fabricated and heat-treated specimens, respectively. Y–Ti–O nanoclusters 10–50 nm in size are observed. High-temperature oxidation results show that the weight increases by 0.27 and 0.29 mg/cm2 for the asfabricated and heat-treated (900°C) specimens, and by 0.47 and 0.50 mg/cm2 for the as-fabricated and heat-treated (1000°C) specimens, respectively. Further, after 24 h oxidation tests, the weight increases by 56.50 and 100.60 mg/cm2 for the as-fabricated and heat-treated (1100°C) specimens, respectively; the latter increase is approximately 100 times higher than that at 1000°C. Observation of the surface after the oxidation test shows that Cr2O3 is the main oxide on a specimen tested at 1000°C, whereas Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 phases also form on a specimen tested at 1100°C, where the weight increases rapidly. The high-temperature oxidation behavior of Fe-14Cr ODS steel is confirmed to be dominated by changes in the Cr2O3 layer and generation of Fe-based oxides through evaporation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(1): 36. CrossRef
- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


