- [Korean]
- Analysis on Milling Behavior of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Ni-based Atomizing Powder with Ni5Y Intermetallic Phase
-
Chun Woong Park, Jong Min Byun, Won June Choi, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):101-106. Published online April 1, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.101
-
-
989
View
-
3
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
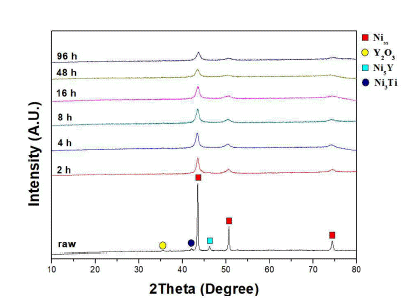
Ni-based oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) alloys have a higher usable temperature and better hightemperature mechanical properties than conventional superalloys. They are therefore being explored for applications in various fields such as those of aerospace and gas turbines. In general, ODS alloys are manufactured from alloy powders by mechanical alloying of element powders. However, our research team produces alloy powders in which the Ni5Y intermetallic phase is formed by an atomizing process. In this study, mechanical alloying was performed using a planetary mill to analyze the milling behavior of Ni-based oxide dispersions strengthened alloy powder in which the Ni5Y is the intermetallic phase. As the milling time increased, the Ni5Y intermetallic phase was refined. These results are confirmed by SEM and EPMA analysis on microstructure. In addition, it is confirmed that as the milling increased, the mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloy powder improve due to grain refinement by plastic deformation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Efficient prediction of corrosion behavior in ternary Ni-based alloy systems: Theoretical calculations and experimental verification
Xuelian Xiao, Keke Chang, Kai Xu, Ming Lou, Liping Wang, Qunji Xue
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2023; 167: 94. CrossRef - Effect of high-energy ball milling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloys fabricated using gas-atomized powder
Chun Woong Park, Won June Choi, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
Journal of Materials Science.2022; 57(38): 18195. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Research Trends of the Mo-Si-B Alloys as Next Generation Ultra-high-temperature Alloys
-
Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Jung Hyo Park, Young Do Kim, Jong Min Byun
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):156-165. Published online April 1, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.156
-
-
1,505
View
-
26
Download
-
4
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Over the last decade, the next generation’s ultra-high-temperature materials as an alternative to Nickel-based superalloys have been highlighted. Ultra-high-temperature materials based on refractory metals are one of several potential candidates. In particular, molybdenum alloys with small amounts of silicon and boron (Mo-Si-B alloys) have superior properties at high temperature. However, research related to Mo-Si-B alloys were mainly conducted by several developed countries but garnered little interest in Korea. Therefore, in this review paper, we introduce the development history of Mo-Si-B alloys briefly and discuss the properties, particularly the mechanical and oxidation properties of Mo-Si-B alloys. We also introduce the latest research trends of Mo-Si-B alloys based on the research paper. Finally, for domestic research related to this field, we explain why Mo-Si-B alloys should be developed and suggest the potential directions for Mo-Si-B alloys research. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
Minsu Kim, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 478. CrossRef - Preparation and Structure of Chromium Coatings Doped with Diamond Nanoparticles Deposited Directly on a Monolithic Composite of Molybdenum and Aluminum
V. P. Petkov, M. K. Aleksandrova, R. V. Valov, V. P. Korzhov, V. M. Kiiko, I. S. Zheltyakova
Protection of Metals and Physical Chemistry of Surfaces.2023; 59(3): 396. CrossRef - A Review of Mo-Si Intermetallic Compounds as Ultrahigh-Temperature Materials
Liang Jiang, Bin Zheng, Changsong Wu, Pengxiang Li, Tong Xue, Jiandong Wu, Fenglan Han, Yuhong Chen
Processes.2022; 10(9): 1772. CrossRef - Heat-Resistant Molybdenum Borosilicate Alloys Hardened with Titanium Carbides: Mo–Si–B–TiC (Survey)
I. L. Svetlov, O. G. Ospennikova, M. I. Karpov, Yu. V. Artemenko
Inorganic Materials: Applied Research.2021; 12(4): 866. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Molybdenum Silicide-based Composites with Uniformly Dispersed Silicon Carbide
-
Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim, Jong Min Byun
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):402-407. Published online October 1, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.402
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
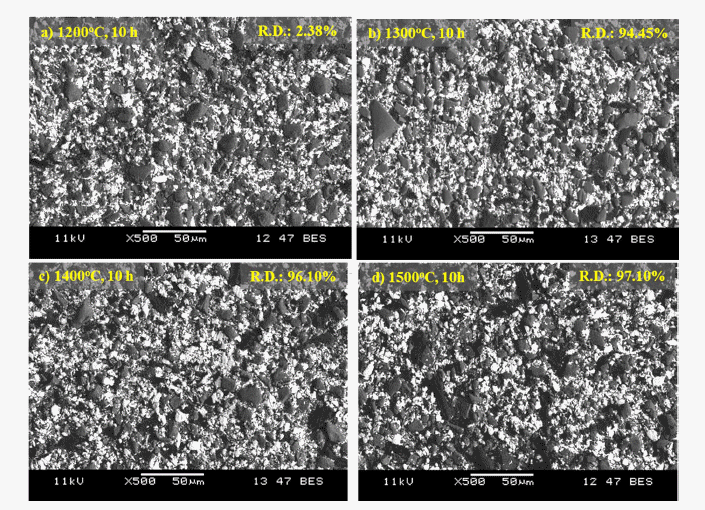
Molybdenum silicide has gained interest for high temperature structural applications. However, poor fracture toughness at room temperatures and low creep resistance at elevated temperatures have hindered its practical applications. This study uses a novel powder metallurgical approach applied to uniformly mixed molybdenum silicidebased composites with silicon carbide. The degree of powder mixing with different ball milling time is also demonstrated by Voronoi diagrams. Core-shell composite powder with Mo nanoparticles as the shell and β-SiC as the core is prepared via chemical vapor transport. Using this prepared core-shell composite powder, the molybdenum silicide-based composites with uniformly dispersed β-SiC are fabricated using pressureless sintering. The relative density of the specimens sintered at 1500°C for 10 h is 97.1%, which is similar to pressure sintering owing to improved sinterability using Mo nanoparticles.
- [Korean]
- Photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles using surfactant
-
Jong Min Byun, Chun Woong Park, Young In Kim, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):257-262. Published online June 1, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.257
-
-
1,153
View
-
9
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
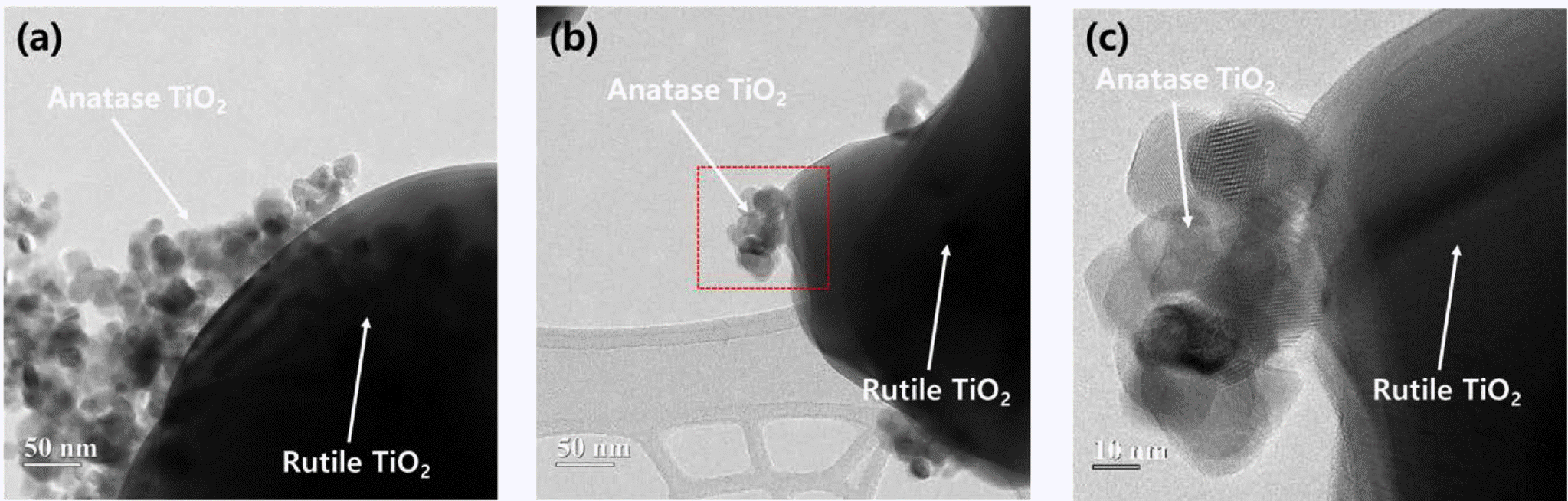
The coupling of two semiconducting materials is an efficient method to improve photocatalytic activity via the suppression of recombination of electron-hole pairs. In particular, the coupling between two different phases of TiO2, i.e., anatase and rutile, is particularly attractive for photocatalytic activity improvement of rutile TiO2 because these coupled TiO2 powders can retain the benefits of TiO2, one of the best photocatalysts. In this study, anatase TiO2 nanoparticles are synthesized and coupled on the surface of rutile TiO2 powders using a microemulsion method and heat treatment. Triton X-100, as a surfactant, is used to suppress the aggregation of anatase TiO2 nanoparticles and disperse anatase TiO2 nanoparticles uniformly on the surface of rutile TiO2 powders. Rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles are successfully prepared. Additionally, we compare the photocatalytic activity of these rutile-anatase coupled TiO2 powders under ultraviolet (UV) light and demonstrate that the reason for the improvement of photocatalytic activity is microstructural. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Refractory Metal Oxide–Doped Titanate Nanotubes: Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity under UV/Visible Light Range
Min-Sang Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi, Tohru Sekino, Young-Do Kim, Se-Hoon Kim
Catalysts.2021; 11(8): 987. CrossRef - Effect of Surfactant on the Dispersion Stability of Slurry for Semiconductor Silicon CMP
Hye Won Yun, Doyeon Kim, Do Hyung Han, Dong Wan Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(5): 395. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Ti Porous body with Improved Specific Surface Area by Synthesis of CNTs
-
Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):235-239. Published online June 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.235
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
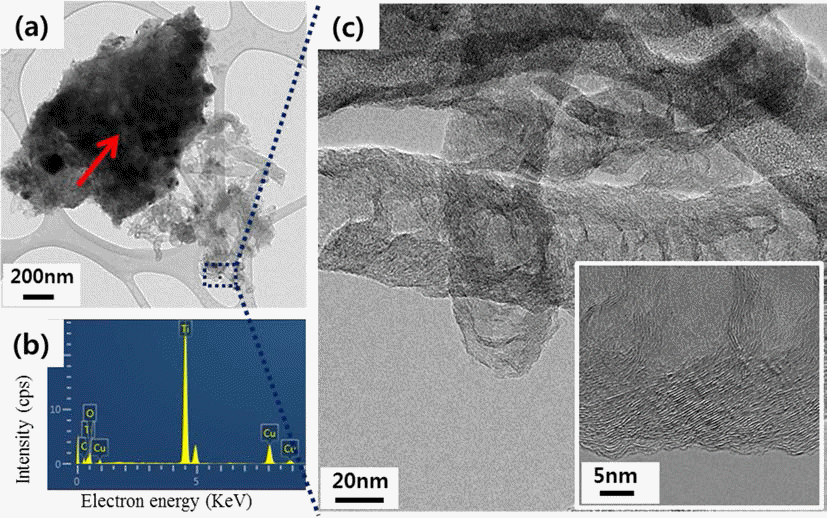
This study is performed to fabricate a Ti porous body by freeze drying process using titanium hydride (TiH2) powder and camphene. Then, the Ti porous body is employed to synthesize carbon nanotubes (CNTs) using thermal catalytic chemical vapor deposition (CCVD) with Fe catalyst and methane (CH4) gas to increase the specific surface area. The synthesized Ti porous body has 100 μm-sized macropores and 10-30 μm-sized micropores. The synthesized CNTs have random directions and are entangled with adjacent CNTs. The CNTs have a bamboo-like structure, and their average diameter is about 50 nm. The Fe nano-particles observed at the tip of the CNTs indicate that the tip growth model is applicable. The specific surface area of the CNT-coated Ti porous body is about 20 times larger than that of the raw Ti porous body. These CNT-coated Ti porous bodies are expected to be used as filters or catalyst supports.
- [English]
- Research Trend of Additive Manufacturing Technology
-
Hanshin Choi, Jong Min Byun, Wonsik Lee, Su-Ryong Bang, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):149-169. Published online April 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.149
-
-
3,114
View
-
8
Download
-
5
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Additive manufacturing (AM) is defined as the manufacture of three-dimensional tangible products by additively consolidating two-dimensional patterns layer by layer. In this review, we introduce four fundamental conceptual pillars that support AM technology: the bottom-up manufacturing factor, computer-aided manufacturing factor, distributed manufacturing factor, and eliminated manufacturing factor. All the conceptual factors work together; however, business strategy and technology optimization will vary according to the main factor that we emphasize. In parallel to the manufacturing paradigm shift toward mass personalization, manufacturing industrial ecology evolves to achieve competitiveness in economics of scope. AM technology is indeed a potent candidate manufacturing technology for satisfying volatile and customized markets. From the viewpoint of the innovation technology adoption cycle, various pros and cons of AM technology themselves prove that it is an innovative technology, in particular a disruptive innovation in manufacturing technology, as powder technology was when ingot metallurgy was dominant. Chasms related to the AM technology adoption cycle and efforts to cross the chasms are considered. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Extremely low temperature mechanical behavior of in-situ oxide containing 304L stainless steel fabricated by laser powder bed fusion
Kwangtae Son, Seung-Min Jeon, Brian K. Paul, Young-Sang Na, Kijoon Lee, Young-Kyun Kim
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - SiC-Si composite part fabrication via SiC powder binder jetting additive manufacturing and molten-Si infiltration
Ji-Won Oh, Jinsu Park, Sahn Nahm, Hanshin Choi
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2021; 101: 105686. CrossRef - Recent Trends and Application Status of the Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs)
Hyo-Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(2): 164. CrossRef - Metal Additive Manufacturing Cycle in Aerospace Industry: A Comprehensive Review
B. Barroqueiro, A. Andrade-Campos, R. A. F. Valente, V. Neto
Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing.2019; 3(3): 52. CrossRef - Technology Trend of the additive Manufacturing (AM)
Ji-Won Oh, Hyunwoong Na, Hanshin Choi
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(6): 494. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Research Trend of Fe/Ni Based Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Alloys
-
Chun Woong Park, Jong Min Byun, Jong Kwan Park, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):61-68. Published online February 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.61
-
-
1,803
View
-
27
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 PDF PDF
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of high-energy ball milling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloys fabricated using gas-atomized powder
Chun Woong Park, Won June Choi, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
Journal of Materials Science.2022; 57(38): 18195. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of CNT on a Camphene Impregnated Titanium Porous Body by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition
-
Hogyu Kim, Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):122-128. Published online April 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.122
-
-
786
View
-
1
Download
-
3
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
In this study, titanium(Ti) meshes and porous bodies are employed to synthesize carbon nanotubes(CNTs) using methane(CH4) gas and camphene solution, respectively, by chemical vapor deposition. Camphene is impregnated into Ti porous bodies prior to heating in a furnace. Various microscopic and spectroscopic techniques are utilized to analyze CNTs. It is found that CNTs are more densely and homogeneously populated on the camphene impregnated Ti-porous bodies as compared to CNTs synthesized with methane on Ti-porous bodies. It is elucidated that, when synthesized with methane, few CNTs are formed inside of Ti porous bodies due to methane supply limited by internal structures of Ti porous bodies. Ti-meshes and porous bodies are found to be multi-walled with high degree of structural disorders. These CNTs are expected to be utilized as catalyst supports in catalytic filters and purification systems. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Recent progress in additive manufacturing of porous titanium: From design to applications
Haoxin Song, Chen Wang, Wenzheng Yu, Mingsen Zhang, Jinqiang Shao, Hanwen Liang, Tingting Wu, Xiaoxiao Dong
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1026: 180451. CrossRef - Solvent induced surface modifications on hydrogen storage performance of ZnO nanoparticle decorated MWCNTs
Madhavi Konni, Anima S. Dadhich, Saratchandra Babu Mukkamala
Sustainable Energy & Fuels.2018; 2(2): 466. CrossRef - Influence of nickel nanoparticles on hydrogen storage behaviors of MWCNTs
Ye-Ji Han, Soo-Jin Park
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 85. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- The Fabrication of Cobalt Nanopowder by Sonochemical Polyol Synthesis of Cobalt Hydroxide and Magnetic Separation Method
-
Jong Min Byun, Myoung Hwan Choi, Chang Min Shim, Ji Young Kim, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):39-45. Published online February 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.39
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
In this study, cobalt nanopowder is fabricated by sonochemical polyol synthesis and magnetic separation method. First, sonochemical polyol synthesis is carried out at 220°C for up to 120 minutes in diethylene glycol (C4H10O3). As a result, when sonochemical polyol synthesis is performed for 50 minutes, most of the cobalt precursor (Co(OH)2) is reduced to spherical cobalt nanopowder of approximately 100 nm. In particular, aggregation and growth of cobalt particles are effectively suppressed as compared to common polyol synthesis. Furthermore, in order to obtain finer cobalt nanopowder, magnetic separation method using magnetic property of cobalt is introduced at an early reduction stage of sonochemical polyol synthesis when cobalt and cobalt precursor coexist. Finally, spherical cobalt nanopowder having an average particle size of 22 nm is successfully separated.
- [Korean]
- Enhancement of Coercivity for Nd-Fe-B Sintered Magnets
-
Se Hoon Kim, Jin Woo Kim, Jong Min Byun, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):60-67. Published online February 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.60
-
-
1,549
View
-
12
Download
-
3
Citations
-
 PDF PDF
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Study on the Demagnetization and Classification of NdFeB Magnets According to Different Heat Treatment Temperatures
Byeong Jun Kim, Ik Keun Park, Young Sung Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Technology Engineers.2021; 30(2): 119. CrossRef - Study on Demagnetization and Magnetization to Reuse NdFeB-based Magnets
Byeong Jun Kim, Young Sung Kim, Gi Tae Joo, Joon Hyun Kim, Ik Geun Park, Jae Yong Lee, Su Won Yang
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Technology Engineers.2021; 30(4): 269. CrossRef - Study on the Optimization of Reduction Conditions for Samarium-Cobalt Nanofiber Preparation
Jimin Lee, Jongryoul Kim, Yong-Ho Choa
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(4): 334. CrossRef
- [English]
- Powder Injection Molding of Translucent Alumina using Supercritical Fluid Debinding
-
Hyung Soo Kim, Jong Min Byun, Myung Jin Suk, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):407-414. Published online December 1, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.407
-
-
1,030
View
-
1
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The powder injection molding process having advantages in manufacturing three-dimensional precision parts essentially requires a debinding process before sintering to remove the binders used for preparing feedstock. In this study, powder injection molding of translucent alumina was performed, and carbon dioxide (CO2) is used as a supercritical fluid that makes it possible to remove a large amount of binder, which is paraffin wax. The relationship between the optical property of translucent alumina and the debinding condition (temperature and pressure) of supercritical CO2 was investigated. As temperature and pressure increased, extraction rate of the binder showed rising tendency and average grain size after sintering process was relatively fine. On the other hand, optical transmittance was reduced. As a result, the debinding condition at 50° and 20 MPa that represents the lowest extraction rate, 8.19 × 10−3 m2/sec, corresponds to the largest grain size of 14.7 μm and the highest optical transmittance of 45.2%. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Supercritical CO₂ debinding: A promising method for binder removal in ceramic fabrication with potential applications in additive manufacturing – A review
Adolor David Aiyeki
Journal of the European Ceramic Society.2026; 46(5): 117998. CrossRef - Experimental and numerical analysis of effects of supercritical carbon dioxide debinding on Inconel 718 MIM components
Dugauguez Olivier, Agne Aboubabky, Jimenez-Morales Antonia, Torralba José Manuel, Barriere Thierry
Powder Technology.2019; 355: 57. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- CNT Growth Behavior on Ti Substrate by Catalytic CVD Process with Temperature Gradient in Tube Furnace
-
Ju Hyuk Park, Jong Min Byun, Hyung Soo Kim, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):371-376. Published online October 1, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.371
-
-
1,056
View
-
2
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
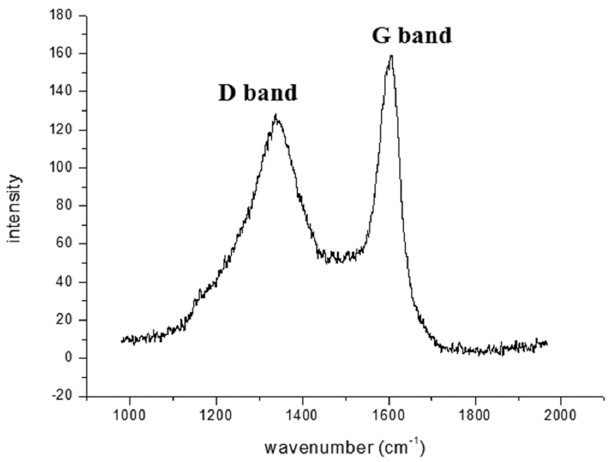
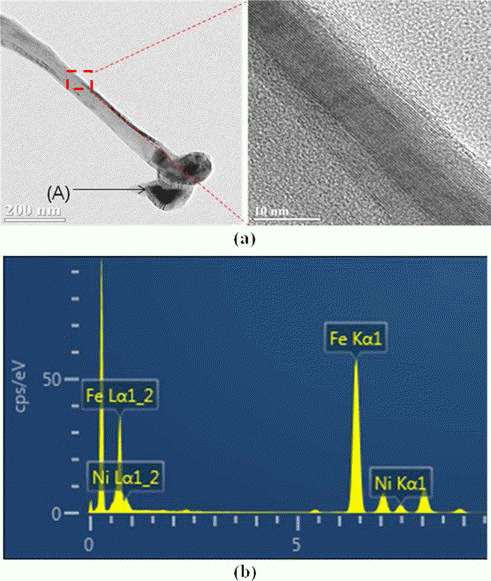
In this study, modified catalytic chemical vapor deposition (CCVD) method was applied to control the CNTs (carbon nanotubes) growth. Since titanium (Ti) substrate and iron (Fe) catalysts react one another and form a new phase (Fe2TiO5) above 700°C, the decrease of CNT yield above 800°C where methane gas decomposes is inevitable under common CCVD method. Therefore, we synthesized CNTs on the Ti substrate by dividing the tube furnace into two sections (left and right) and heating them to different temperatures each. The reactant gas flew through from the end of the right tube furnace while the Ti substrate was placed in the center of the left tube furnace. When the CNT growth temperature was set 700/950°C (left/right), CNTs with high yield were observed. Also, by examining the micro-structure of CNTs of 700/950°C, it was confirmed that CNTs show the bamboo-like structure. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication of Ti Porous body with Improved Specific Surface Area by Synthesis of CNTs
Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(3): 235. CrossRef - Synthesis of CNT on a Camphene Impregnated Titanium Porous Body by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition
Hogyu Kim, Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(2): 122. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- A study on the Powder Injection Molding of Translucent Alumina via Flowability Simulation of Powder/Binder Mixture
-
Hyung Soo Kim, Jong Min Byun, Se Hoon Kim, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):215-221. Published online June 1, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.215
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
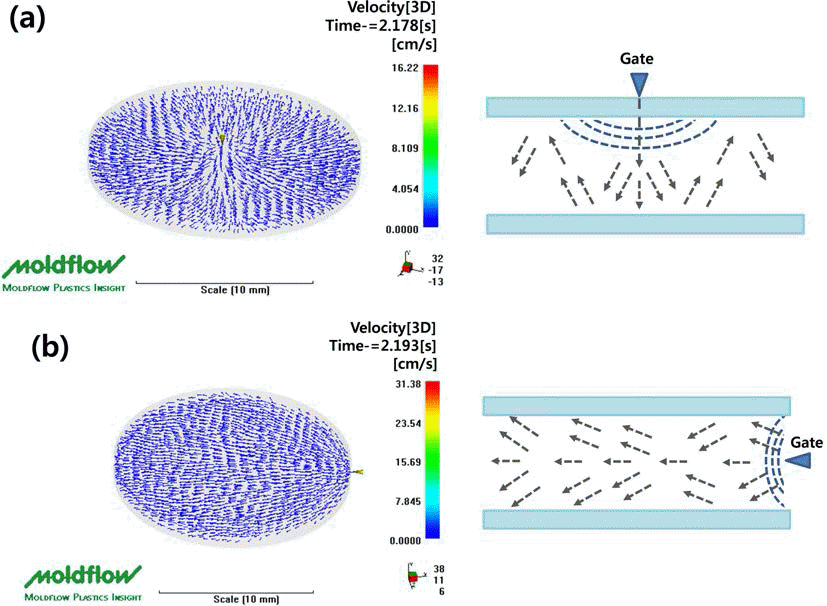
Translucent alumina is a potential candidate for high temperature application as a replacement of the glass or polymer. Recently, due to the increasing demand of high power light emitting diode (LED), there is a growing interest in the translucent alumina. Since the translucent property is very sensitive to the internal defect, such as voids inside or abnormal grain growth of sintered alumina, it is important to fabricate the defect-free product through the fabrication process. Powder injection molding (PIM) has been commonly applied for the fabrication of complex shaped products. Among the many parameters of PIM, the flowability of powder/binder mixture becomes more significant especially for the shape of the cavity with thin thickness. Two different positions of the gate were applied during PIM using the disc type of die. The binder was removed by solvent extraction method and the brown compact was sintered at 1750°C for 3 hours in a vacuum. The flowability was also simulated using moldflow (MPI 6.0) with two different types of gate. The effect of the flowability of powder/binder mixture on the microstructure of the sintered specimen was studied with the analysis of the simulation result.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Pt@TiO2 Nano-composite via Photochemical Reduction Method
-
Ji Young Kim, Jong Min Byun, Jin Woo Kim, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):119-123. Published online April 1, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.119
-
-
841
View
-
3
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
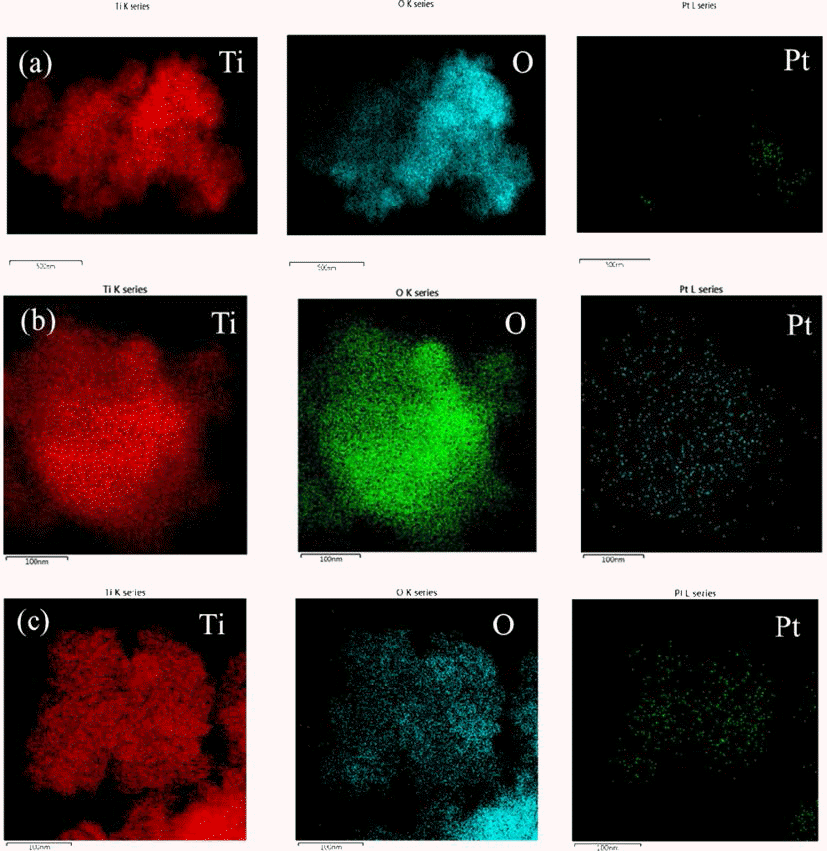
Pt has been widely used as catalyst for fuel cell and exhausted gas clean systems due to its high catalytic activity. Recently, there have been researches on fabricating composite materials of Pt as a method of reducing the amount of Pt due to its high price. One of the approaches for saving Pt used as catalyst is a core shell structure consisting of Pt layer on the core of the non-noble metal. In this study, the synthesis of Pt shell was conducted on the surface of TiO2 particle, a non-noble material, by applying ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. Anatase TiO2 particles with the average size of 20~30 nm were immersed in the ethanol dissolved with Pt precursor of H2PtCl6∙6H2O and exposed to UV irradiation with the wavelength of 365 nm. It was confirmed that Pt nano-particles were formed on the surface of TiO2 particles by photochemical reduction of Pt ion from the solution. The morphology of the synthesized Pt@TiO2 nano-composite was examined by TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles using surfactant
Jong Min Byun, Chun Woong Park, Young In Kim, Young Do Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 257. CrossRef - Synthesis and Photo Catalytic Activity of 10 wt%, 20 wt%Li-TiO2 Composite Powders
Hyeong-Chul Kim, Jae-Kil Han
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(1): 33. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Study on Surface Modification of Ti Substrate to Improve the Dispersion of Catalytic Metals on Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes
-
Seoung Yeol Kwak, Ho Gyu Kim, Jong Min Byun, Ju Hyuk Park, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):28-33. Published online February 1, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.28
-
-
893
View
-
0
Download
-
4
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
This paper describes the surface modification effect of a Ti substrate for improved dispersibility of the catalytic metal. Etching of a pure titanium substrate was conducted in 50% H2SO4, 50°C for 1 h-12 h to observe the surface roughness as a function of the etching time. At 1 h, the grain boundaries were obvious and the crystal grains were distinguishable. The grain surface showed micro-porosities owing to the formation of micro-pits less than 1 μm in diameter. The depths of the grain boundary and micro-pits appear to increase with etching time. After synthesizing the catalytic metal and growing the carbon nano tube (CNT) on Ti substrate with varying surface roughness, the distribution trends of the catalytic metal and grown CNT on Ti substrate are discussed from a micro-structural perspective. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Solvent induced surface modifications on hydrogen storage performance of ZnO nanoparticle decorated MWCNTs
Madhavi Konni, Anima S. Dadhich, Saratchandra Babu Mukkamala
Sustainable Energy & Fuels.2018; 2(2): 466. CrossRef - Influence of nickel nanoparticles on hydrogen storage behaviors of MWCNTs
Ye-Ji Han, Soo-Jin Park
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 85. CrossRef - Spontaneous Formation of Titanium Nitride on the Surface of a Ti Rod Induced by Electro-Discharge-Heat-Treatment in an N2 Atmosphere
W.H. Lee, Y.H. Yoon, Y.H. Kim, Y.K. Lee, J.Y. Kim, S.Y. Chang
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1281. CrossRef - Synthesis of CNT on a Camphene Impregnated Titanium Porous Body by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition
Hogyu Kim, Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(2): 122. CrossRef
|