- [English]
- Preparation of Flake-shape Cobalt Powders by High-Energy Ball Milling for rSOC Current Collectors
-
Poong-Yeon Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Hyeon Ju Kim, Su-Jin Yun, Si Young Chang, Jung-Yeul Yun
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):383-389. Published online October 31, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00241
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
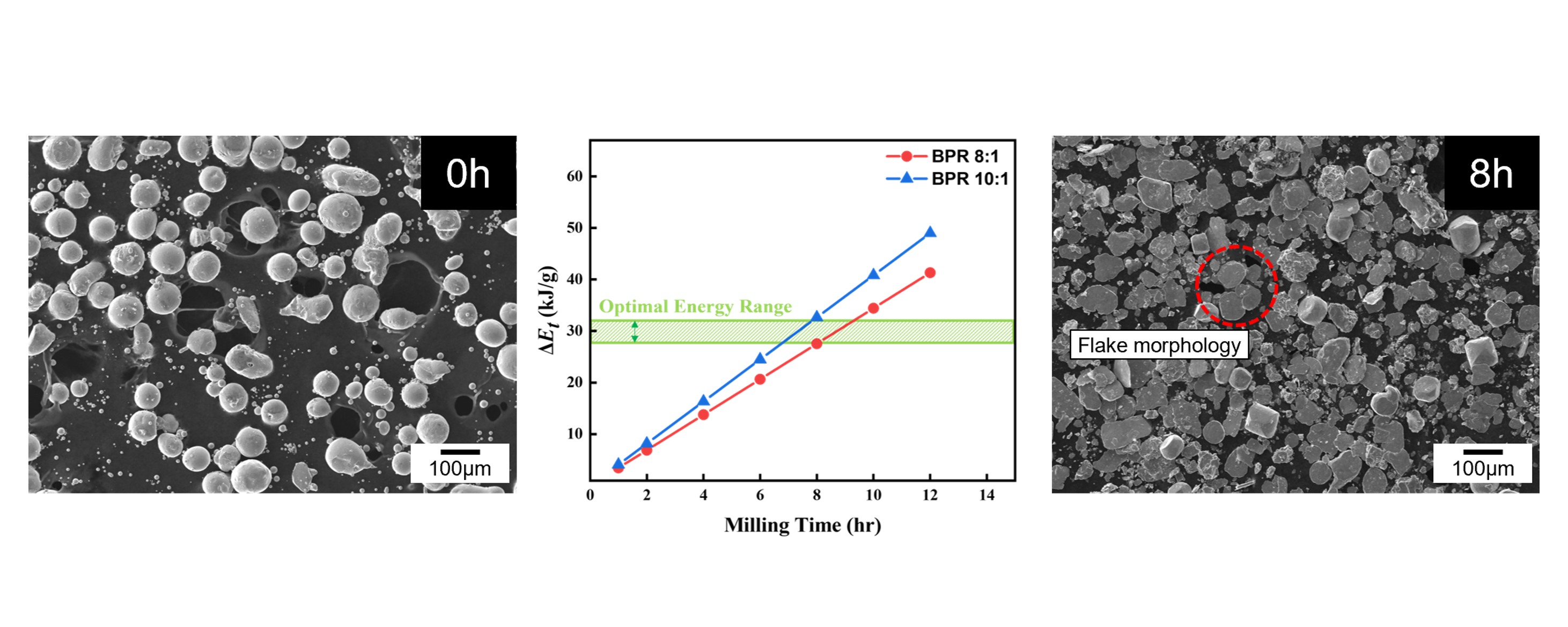
- Reversible solid oxide cells (rSOCs), which enable two-way conversion between electricity and hydrogen, have gained attention with the rise of hydrogen energy. However, foam-type current collectors in rSOC stacks exhibit poor structural controllability and limited electrode contact area. To address these limitations, this study aimed to convert spherical cobalt powders into flake-type morphology via high-energy ball milling, as a preliminary step toward fabricating flake-based current collectors.
Milling parameters—specifically, the ball-to-powder ratio (BPR), milling time, and process control agent (PCA) content—were varied. At an 8:1 BPR, over 90% of the powder became flake-shaped after 8 hours, while extended milling caused cold welding. In contrast, a 10:1 BPR resulted in dominant fragmentation. The Burgio–Rojac model quantified energy input and defined the optimal range for flake formation. Increasing the PCA to 4 wt% delayed flake formation to 16 hours and induced cold welding, as shown by bimodal particle size distributions. These results support the development of Co-based current collectors for use in rSOCs.
- [English]
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
-
Minji Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Su-Jin Yun, Poong-Yeon Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Juyong Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):299-308. Published online August 29, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00234
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
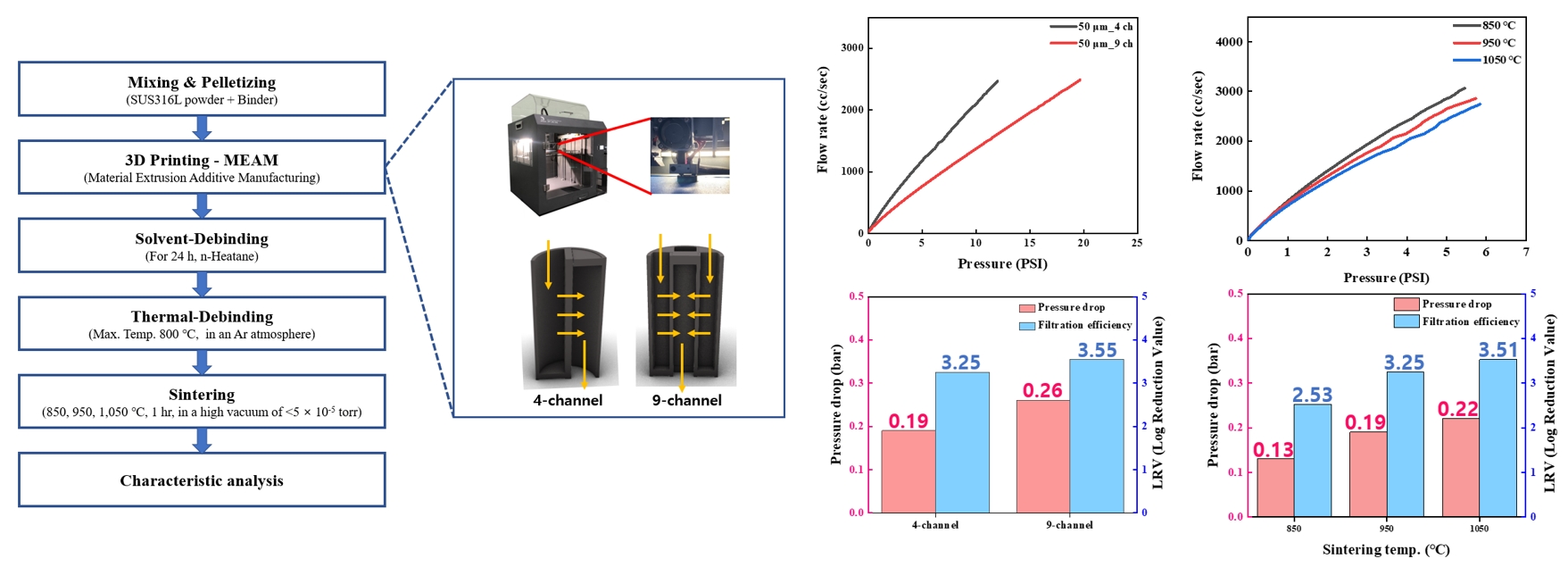
- The development of high-performance metal filters is essential for maintaining ultra-clean environments in semiconductor manufacturing. In this study, cross-sealed honeycomb filters were fabricated using STS316L powder via material extrusion additive manufacturing (MEAM) for semiconductor gas filtration. The effects of filter geometry (4 or 9 channels) and sintering temperature (850°C, 950°C, or 1,050°C) on performance were examined. First, 4-channel and 9-channel filters sintered at the same temperature (950°C) exhibited similar porosities of 50.08% and 50.57%, but the 9-channel filter showed a higher pressure-drop (0.26 bar) and better filtration-efficiency (3.55 LRV) than the 4-channel filter (0.19 bar and 3.25 LRV, respectively). Second, for filters with the same geometry (4-channel) increasing the sintering temperature reduced porosity from 64.52% to 40.33%, while the pressure-drop increased from 0.13 bar to 0.22 bar and filtration-efficiency improved from 2.53 LRV to 3.51 LRV. These findings demonstrate that filter geometry and sintering temperature are key factors governing the trade-off between air permeability, pressure-drop, and filtration efficiency. This work provides insights and data for optimizing MEAM-based high-performance metal powder filter design.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Ni-Cr-Al Metal Foam-Supported Catalysts for the Steam Methane Reforming (SMR), and its Mechanical Stability and Hydrogen Yield Efficiency
-
Kyu-Sik Kim, Tae-Hoon Kang, Man Sik Kong, Man-Ho Park, Jung-Yeul Yun, Ji Hye Ahn, Kee-Ahn Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):201-207. Published online June 1, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.201
-
-
1,293
View
-
19
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
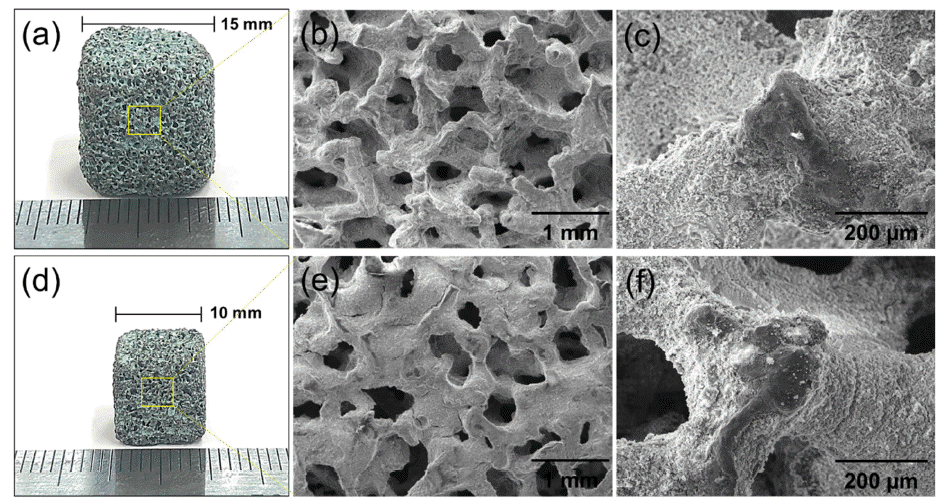
Ni–Cr–Al metal-foam-supported catalysts for steam methane reforming (SMR) are manufactured by applying a catalytic Ni/Al2O3 sol–gel coating to powder alloyed metallic foam. The structure, microstructure, mechanical stability, and hydrogen yield efficiency of the obtained catalysts are evaluated. The structural and microstructural characteristics show that the catalyst is well coated on the open-pore Ni–Cr–Al foam without cracks or spallation. The measured compressive yield strengths are 2–3 MPa at room temperature and 1.5–2.2 MPa at 750°C regardless of sample size. The specimens exhibit a weight loss of up to 9–10% at elevated temperature owing to the spallation of the Ni/Al2O3 catalyst. However, the metal-foam-supported catalyst appears to have higher mechanical stability than ceramic pellet catalysts. In SMR simulations tests, a methane conversion ratio of up to 96% is obtained with a high hydrogen yield efficiency of 82%. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Experimental Investigation of a 98% Hydrogen Peroxide Monopropellant Thruster Comprising the Metal-Foam-Supported Manganese Oxide Catalyst
Pawel Surmacz, Zbigniew Gut
Aerospace.2023; 10(3): 215. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Structural Characteristics, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-Cr-Al Metallic Foam Fabricated by Powder Alloying Process
-
Kyu-Sik Kim, Byeong-Hoon Kang, Man-Ho Park, Jung-Yeul Yun, Kee-Ahn Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):37-43. Published online February 1, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.37
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
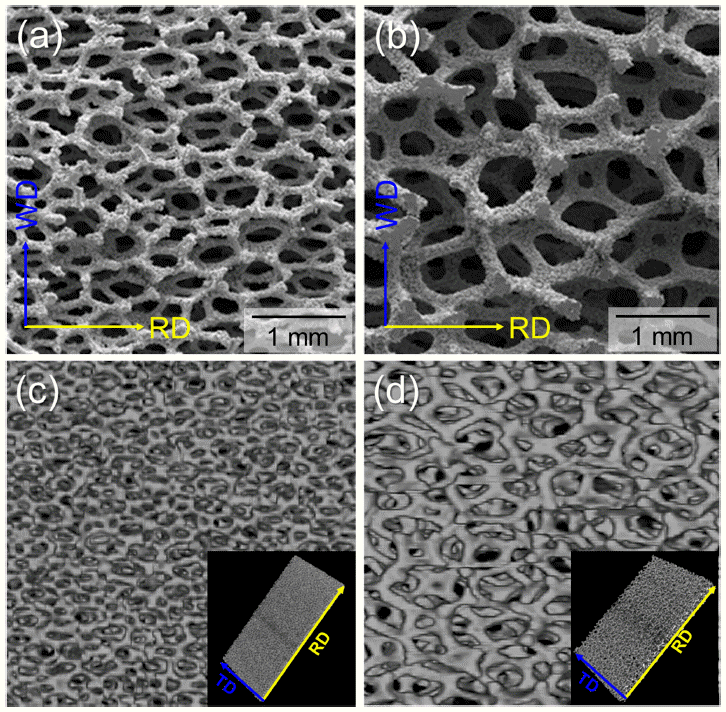
The Fe-22wt.%Cr-6wt.%Al foams were fabricated via the powder alloying process in this study. The structural characteristics, microstructure, and mechanical properties of Fe-Cr-Al foams with different average pore sizes were investigated. Result of the structural analysis shows that the average pore sizes were measured as 474 μm (450 foam) and 1220 μm (1200 foam). Regardless of the pore size, Fe-Cr-Al foams had a Weaire-Phelan bubble structure, and α-ferrite was the major constituent phase. Tensile and compressive tests were conducted with an initial strain rate of 10−3 /s. Tensile yield strengths were 3.4 MPa (450 foam) and 1.4 MPa (1200 foam). Note that the total elongation of 1200 foam was higher than that of 450 foam. Furthermore, their compressive yield strengths were 2.5 MPa (450 foam) and 1.1 MPa (1200 foam), respectively. Different compressive deformation behaviors according to the pore sizes of the Fe-Cr-Al foams were characterized: strain hardening for the 450 foam and constant flow stress after a slight stress drop for the 1200 foam. The effect of structural characteristics on the mechanical properties was also discussed.
- [Korean]
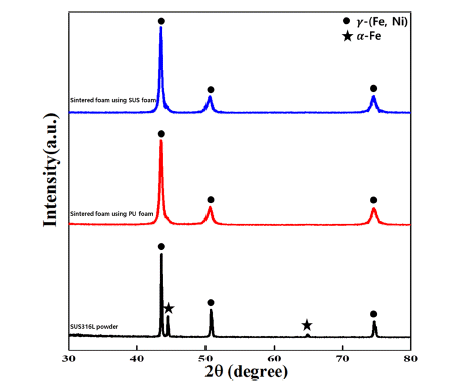
- A Study on Pore Properties of SUS316L Powder Porous Metal Fabricated by Electrostatic Powder Coating Process
-
Min-Jeong Lee, Yu-Jeong Yi, Hyeon-Ju Kim, Manho Park, Byoung-Kee Kim, Jung-Yeul Yun
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):415-419. Published online October 1, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.415
-
-
798
View
-
6
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Porous metals demonstrate not only excessively low densities, but also novel physical, thermal, mechanical, electrical, and acoustic properties. Thus, porous metals exhibit exceptional performance, which are useful for diesel particulate filters, heat exchangers, and noise absorbers. In this study, SUS316L foam with 90% porosity and 3,000 μm pore size is successfully manufactured using the electrostatic powder coating (ESPC) process. The mean size of SUS316L powders is approximately 12.33 μm. The pore properties are evaluated using SEM and Archimedes. As the quantity of powder coating increases, pore size decreases from 2,881 to 1,356 μm. Moreover, the strut thickness and apparent density increase from 423.7 to 898.3 μm and from 0.278 to 0.840 g/cm3, respectively. It demonstrates that pore properties of SUS316L powder porous metal are controllable by template type and quantity of powder coating. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
Minji Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Su-Jin Yun, Poong-Yeon Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Juyong Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 299. CrossRef
- [Korean]
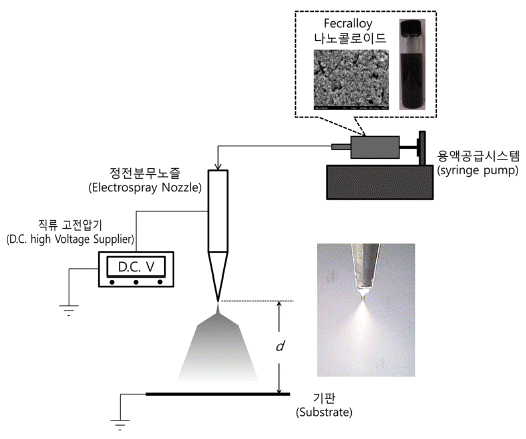
- Electrospray and Thermal Treatment Process for Enhancing Surface Roughness of Fecralloy Coating Layer on a Large Sized Substrate
-
Hye Moon Lee, Hye Young Koo, Sangsun Yang, Dahee Park, Sooho Jung, Jung-Yeul Yun
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):46-52. Published online February 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.46
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Fecralloy coating layer with large surface area is suitable for use as a filter media for efficient removal of hot gaseous pollutants exhausted from combustion processes. For uniform preparation of a Fecralloy coating layer with large surface area and strong adhesion to substrate, electrospray coating and thermal treatment processes are experimentally optimized in this study. A nano-colloidal solution with 0.05 wt% Fecralloy nanoparticles is successfully prepared. Optimized electrospraying conditions are experimentally discovered to prepare a uniform coating layer of Fecralloy nanocolloidal solution on a substrate. Drying the electrospray coated Fecralloy nano-colloidal solution layer at 120°C and subsequent heating at 600°C are the best post-treatment for enhancing the adhesion force and surface roughness of the Fecralloy coating layer on a substrate. An electrospray coating system, consisting of several multi-groove nozzles, is also experimentally confirmed as a reasonable device for uniform coating of Fecralloy nano-colloid on a large area substrate.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and High Temperature Oxidation Behaviors of Fe-Ni Alloys by Spark Plasma Sintering
-
Chae Hong Lim, Jong Seok Park, Sangsun Yang, Jung-Yeul Yun, Jin Kyu Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):53-57. Published online February 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.53
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
In this study, we report the microstructure and the high-temperature oxidation behavior of Fe-Ni alloys by spark plasma sintering. Structural characterization is performed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The oxidation behavior of Fe-Ni alloys is studied by means of a high-temperature oxidation test at 1000°C in air. The effect of Ni content of Fe-Ni alloys on the microstructure and on the oxidation characteristics is investigated in detail. In the case of Fe-2Ni and Fe-5Ni alloys, the microstructure is a ferrite (α) phase with body centered cubic (BCC) structure, and the microstructure of Fe-10Ni and Fe-20Ni alloys is considered to be a massive martensite (α’) phase with the same BCC structure as that of the ferrite phase. As the Ni content increases, the micro-Vickers hardness of the alloys also increases. It can also be seen that the oxidation resistance is improved by decreasing the thickness of the oxide film.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Fe-Cr-Al Porous Metal with Sintering Temperature and Times
-
Bon-Uk Koo, Su-in Lee, Dahee Park, Jung-Yeul Yun, Byoung-Kee Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):100-104. Published online April 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.100
-
-
809
View
-
4
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The porous metals are known as relatively excellent characteristic such as large surface area, light, lower heat capacity, high toughness and permeability. The Fe-Cr-Al alloys have high corrosion resistance, heat resistance and chemical stability for high temperature applications. And then many researches are developed the Fe-Cr-Al porous metals for exhaust gas filter, hydrogen reformer catalyst support and chemical filter. In this study, the Fe-Cr-Al porous metals are developed with Fe-22Cr-6Al(wt) powder using powder compaction method. The mean size of Fe-22Cr-6Al(wt) powders is about 42.69 μm. In order to control pore size and porosity, Fe-Cr-Al powders are sintered at 1200~1450°C and different sintering maintenance as 1~4 hours. The powders are pressed on disk shapes of 3 mm thickness using uniaxial press machine and sintered in high vacuum condition. The pore properties are evaluated using capillary flow porometer. As sintering temperature increased, relative density is increased from 73% to 96% and porosity, pore size are decreased from 27 to 3.3%, from 3.1 to 1.8 μm respectively. When the sintering time is increased, the relative density is also increased from 76.5% to 84.7% and porosity, pore size are decreased from 23.5% to 15.3%, from 2.7 to 2.08 μm respectively. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Synthesis and Magnetic Hysteresis Properties of an Aluminum-Doped Isotropic Hard-Magnetic Fe–Cr–Co Powder Alloy
A. S. Ustyukhin, V. A. Zelensky, I. M. Milyaev, M. I. Alymov, A. A. Ashmarin, A. B. Ankudinov, K. V. Sergienko
Inorganic Materials: Applied Research.2024; 15(2): 480. CrossRef - Fabrication of a Porous Ni-Based Metal with a Multi-pore Structure by a Screen Printing Process
Yu-Jeong Yi, Min-Jeong Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun, Byoung-Kee Kim
Metals and Materials International.2019; 25(5): 1272. CrossRef
- [English]
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Cu Foam by Slurry Coating Process
-
Dahee Park, Eun-Mi Jung, Sangsun Yang, Jung-Yeul Yun
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):87-92. Published online April 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.87
-
-
1,135
View
-
7
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Metallic porous materials have many interesting combinations of physical and geometrical properties with very low specific weight or high gas permeability. In this study, highly porous Cu foam is successfully fabricated by a slurry coating process. The Cu foam is fabricated specifically by changing the coating amount and the type of polyurethane foam used as a template. The processing parameters and pore characteristics are observed to identify the key parameters of the slurry coating process and the optimized morphological properties of the Cu foam. The pore characteristics of Cu foam are investigated by scanning electron micrographs and micro-CT analyzer, and air permeability of the Cu foam is measured by capillary flow porometer. We confirmed that the characteristics of Cu foam can be easily controlled in the slurry coating process by changing the microstructure, porosity, pore size, strut thickness, and the cell size. It can be considered that the fabricated Cu foams show tremendous promise for industrial application. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Preparation and comparative evolution of mechanical behavior of Fe and Fe2O3 foams and their polymer composites
Vemoori Raju, Roy Johnson, Asit Kumar Khanra
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2018; 750: 71. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- The Effect of Fe and Fe2O3 Powder Mixing Ratios on the Pore Properties of Fe Foam Fabricated by a Slurry Coating Process
-
Jin Ho Choi, Eun-Mi Jeong, Dahee Park, Sangsun Yang, Yoo-Dong Hahn, Jung-Yeul Yun
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):266-270. Published online August 1, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.266
-
-
1,343
View
-
4
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Metal foams have a cellular structure consisting of a solid metal containing a large volume fraction of pores. In particular, open, penetrating pores are necessary for industrial applications such as in high temperature filters and as a support for catalysts. In this study, Fe foam with above 90% porosity and 2 millimeter pore size was successfully fabricated by a slurry coating process and the pore properties were characterized. The Fe and Fe2O3 powder mixing ratios were controlled to produce Fe foams with different pore size and porosity. First, the slurry was prepared by uniform mixing with powders, distilled water and polyvinyl alcohol(PVA). After slurry coating on the polyurethane( PU) foam, the sample was dried at 80°C. The PVA and PU foams were then removed by heating at 700°C for 3 hours. The debinded samples were subsequently sintered at 1250°C with a holding time of 3 hours under hydrogen atmosphere. The three dimensional geometries of the obtained Fe foams with an open cell structure were investigated using X-ray micro CT(computed tomography) as well as the pore morphology, size and phase. The coated amount of slurry on the PU foam were increased with Fe2O3 mixing powder ratio but the shrinkage and porosity of Fe foams were decreased with Fe2O3 mixing powder ratio. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of STS316L Porous Metal for Vacuum Injection Mold
Se Hoon Kim, Sang Min Kim, Sang Ho Noh, Jin Pyeong Kim, Jae Hyuck Shin, Si-Young Sung, Jin Kwang Jin, Taean Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(3): 197. CrossRef
- [English]
- Effect of Debinding Conditions on the Microstructure of Sintered Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3
-
Jung-Yeul Yun, Jae-Ho Jeon, Suk-Joong L.Kang
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(4):261-265.
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.4.261
-
-
736
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- In order to fabricate complex-shaped polycrystalline ceramics by sintering, organic binders are usually pre-mixed with ceramic powders to enhance the formability during the shape forming process. These organic binders, however, must be eliminated before sintering so as to eliminate the possibilities of poor densification and unusual grain growth during sintering. The present work studies the effect of binder addition on grain growth behavior during sintering of 92(70Pb(Mg_1/3Nb_2/3)O_3-30PbTiO_3))-8PbO(mol%) piezoelectric ceramics. The microstructures of the sintered samples were examined for various heating profiles and debinding schedules of the binder removal process. Addition of Polyvinyl butyral(PVB) binder promoted abnormal grain growth especially in incompletely debinded regions. Residual carbon appears to change the grain shape from comer-rounded to faceted and enhance abnormal grain growth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Study on the Recovery Silver and Nanoparticles Synthesis from LTCC By-products of Lowly Concentrated Silver
Soyeong Joo, Nak-Kyoon Ahn, Chan Gi Lee, Jin-Ho Yoon
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 232. CrossRef
|