- [English]
- SnF2-Induced LiF Interphase for Stable Lithium Metal Anodes with Suppressed Dendrite Growth
-
Yeong Hoon Jeon, Seul Ki Choi, Yun Seung Nah, Wonil Shin, Yong-Ho Choa, Minho Yang
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):212-221. Published online June 30, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00164
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Lithium (Li) metal is a promising anode for next-generation batteries due to its high capacity, low redox potential, and low density. However, dendrite growth and interfacial instability limit its use. In this study, an artificial solid electrolyte interphase layer of LiF and Li-Sn (LiF@Li-Sn) was fabricated by spray-coating SnF2 onto Li. The LiF@Li-Sn anode exhibited improved air stability and electrochemical performance. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy indicated a charge transfer resistance of 25.2 Ω after the first cycle. In symmetric cells, it maintained a low overpotential of 27 mV after 250 cycles at 2 mA/cm2, outperforming bare Li. In situ microscopy confirmed dendrite suppression during plating. Full cells with NMC622 cathodes and LiF@Li-Sn anodes delivered 130.8 mAh/g with 79.4% retention after 300 cycles at 1 C and 98.8% coulombic efficiency. This coating effectively stabilized the interface and suppressed dendrites, with promising implications for practical lithium metal batteries.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Cellulose Fiber Density Variation on Energy Harvesting Performance in a Hydrovoltaic Generator
-
Seung-Hwan Lee, So Hyun Baek, Hyun-Woo Lee, Yongbum Kwon, Kanghyuk Lee, Kee-Ryung Park, Yoseb Song, Bum Sung Kim, Ji Young Park, Yong-Ho Choa, Da-Woon Jeong
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):113-121. Published online April 30, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00052
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Energy harvesting has become a crucial technology for sustainable energy solutions; in particular, the utilization of ambient water movement in hydrovoltaic generators has emerged as a promising approach. However, optimizing performance requires an understanding of structural factors affecting energy harvesting, particularly capillary effects. This study aimed to improve hydrovoltaic generator performance by adjusting internal fiber density, which influences water transport and ion mobility. Using cold isostatic pressing, cellulose acetate (CA) loading in a urethane mold was varied to optimize internal density. As CA loading increased, the fiber arrangement became denser, narrowing capillary pathways and reducing proton mobility. While open-circuit voltage (VOC) remained stable, short-circuit current (ISC) decreased with higher CA mass. The sample with a loading of 0.3 g exhibited the highest energy harvesting efficiency, achieving ISC = 107.2 μA, VOC = 0.15 V, and power (P) = 16.7 μW. This study provides insights into methods of improving hydrovoltaic generator efficiency through internal structural modifications.
- [Korean]
- Research on the Manufacturing Technology for a PDMS Structure-Based Transpiration Generator Using Biomimetic Capillary Phenomenon
-
Seung-Hwan Lee, Jeungjai Yun, So Hyun Baek, Yongbum Kwon, Yoseb Song, Bum Sung Kim, Yong-Ho Choa, Da-Woon Jeong
-
J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):268-275. Published online June 1, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.268
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
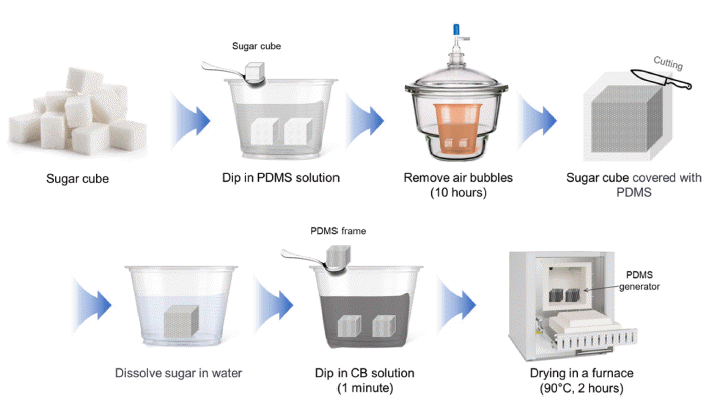
The demand for energy is steadily rising because of rapid population growth and improvements in living standards. Consequently, extensive research is being conducted worldwide to enhance the energy supply. Transpiration power generation technology utilizes the vast availability of water, which encompasses more than 70% of the Earth's surface, offering the unique advantage of minimal temporal and spatial constraints over other forms of power generation. Various principles are involved in water-based energy harvesting. In this study, we focused on explaining the generation of energy through the streaming potential within the generator component. The generator was fabricated using sugar cubes, PDMS, carbon black, CTAB, and DI water. In addition, a straightforward and rapid manufacturing method for the generator was proposed. The PDMS generator developed in this study exhibits high performance with a voltage of 29.6 mV and a current of 8.29 μA and can generate power for over 40h. This study contributes to the future development of generators that can achieve high performance and long-term power generation.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Tert-Butyl Alcohol Template on the Pore Structure of Porous Tungsten in Freeze Drying Process
-
Eui Seon Lee, Youn Ji Heo, Yun Taek Ko, Jin Gyeong Park, Yong-Ho Choa, Sung-Tag Oh
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):216-220. Published online June 1, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.216
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The effect of tert-butyl alcohol (TBA) as a freezing solvent on the pore structure of a porous tungsten body prepared by freeze-drying is analyzed. TBA slurries with a WO3 content of 10 vol% are prepared by mixing with a small amount of dispersant and binder at 30°C. The slurries are frozen at -25°C, and pores are formed in the frozen specimens by the sublimation of TBA during drying in air. After hydrogen reduction at 800°C and sintering at 1000°C, the green body of WO3 is completely converted to porous W with various pore structures. Directional pores from the center of the specimen to the outside are observed in the sintered bodies because of the columnar growth of TBA. A decrease in pore directionality and porosity is observed in the specimens prepared by long-duration drying and sintering. The change in pore structure is explained by the growth of the freezing solvent and densification.
- [Korean]
- Study on the Optimization of Reduction Conditions for Samarium-Cobalt Nanofiber Preparation
-
Jimin Lee, Jongryoul Kim, Yong-Ho Choa
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):334-339. Published online August 1, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.334
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
To meet the current demand in the fields of permanent magnets for achieving a high energy density, it is imperative to prepare nano-to-microscale rare-earth-based magnets with well-defined microstructures, controlled homogeneity, and magnetic characteristics via a bottom-up approach. Here, on the basis of a microstructural study and qualitative magnetic measurements, optimized reduction conditions for the preparation of nanostructured Sm-Co magnets are proposed, and the elucidation of the reduction-diffusion behavior in the binary phase system is clearly manifested. In addition, we have investigated the microstructural, crystallographic, and magnetic properties of the Sm-Co magnets prepared under different reduction conditions, that is, H2 gas, calcium, and calcium hydride. This work provides a potential approach to prepare high-quality Sm-Co-based nanofibers, and moreover, it can be extended to the experimental design of other magnetic alloys.
- [Korean]
- Study on the Optimization of Reduction Conditions for Samarium-Cobalt Nanofiber Preparation
-
Jimin Lee, Jongryoul Kim, Yong-Ho Choa
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):334-339. Published online August 1, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.334
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
To meet the current demand in the fields of permanent magnets for achieving a high energy density, it is imperative to prepare nano-to-microscale rare-earth-based magnets with well-defined microstructures, controlled homogeneity, and magnetic characteristics via a bottom-up approach. Here, on the basis of a microstructural study and qualitative magnetic measurements, optimized reduction conditions for the preparation of nanostructured Sm-Co magnets are proposed, and the elucidation of the reduction-diffusion behavior in the binary phase system is clearly manifested. In addition, we have investigated the microstructural, crystallographic, and magnetic properties of the Sm-Co magnets prepared under different reduction conditions, that is, H2 gas, calcium, and calcium hydride. This work provides a potential approach to prepare high-quality Sm-Co-based nanofibers, and moreover, it can be extended to the experimental design of other magnetic alloys.
- [English]
- The Synthesis Method of Tin Dioxide Nanoparticles by Plasma-Assisted Electrolysis Process and Gas Sensing Property
-
Tae Hyung Kim, Yoseb Song, Chan-Gi Lee, Yong-Ho Choa
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):351-356. Published online October 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.351
-
-
1,542
View
-
2
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
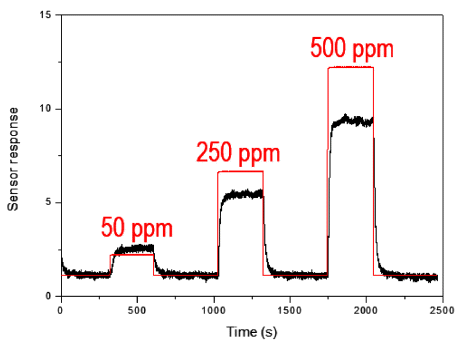
Tin dioxide nanoparticles are prepared using a newly developed synthesis method of plasma-assisted electrolysis. A high voltage is applied to the tin metal plate to apply a high pressure and temperature to the synthesized oxide layer on the metal surface, producing nanoparticles in a low concentration of sulfuric acid. The particle size, morphology, and size distribution is controlled by the concentration of electrolytes and frequency of the power supply. The as-prepared powder of tin dioxide nanoparticles is used to fabricate a gas sensor to investigate the potential application. The particle-based gas sensor exhibits a short response and recovery time. There is sensitivity to the reduction gas for the gas flowing at rates of 50, 250, and 500 ppm of H2S gas. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effects of porosity and particle size on the gas sensing properties of SnO2 films
Min Ah Han, Hyun-Jong Kim, Hee Chul Lee, Jin-Seong Park, Ho-Nyun Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 133. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- The Preparation and Growth Mechanism of the Recovered Bi2Te3 Particles with Respect to Surfactants
-
Hyeongsub So, Eunpil Song, Yong-Ho Choa, Kun-Jae Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):141-146. Published online April 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.141
-
-
1,199
View
-
9
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
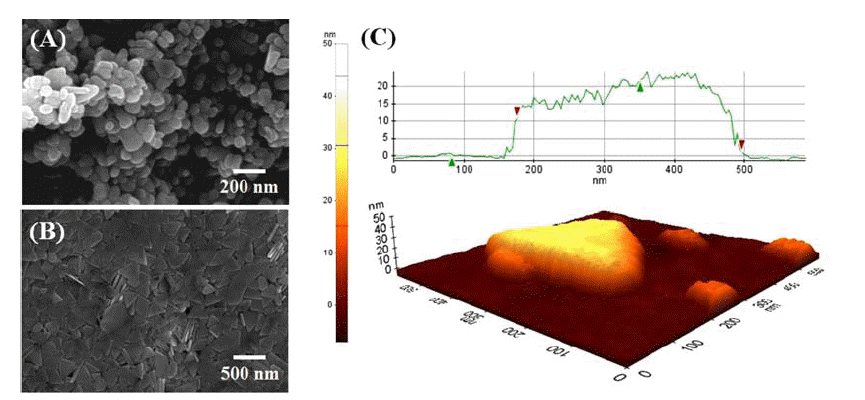
Bi2Te3 powders are recovered by wet chemical reduction for waste n-type thermoelectric chips, and the recovered particles with different morphologies are prepared using various surfactants such as cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (SDBS), and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). When citric acid is added as the surfactant, the shape of the aggregated particles shows no distinctive features. On the other hand, rod-shaped particles are formed in the sample with CTAB, and sheet-like particles are synthesized with the addition of SDBS. Further, particles with a tripod shape are observed when EDTA is added as the surfactant. The growth mechanism of the particle shapes depending on the surfactant is investigated, with a focus on the nucleation and growth phenomena. These results help to elucidate the intrinsic formation mechanism of the rod, plate, and tripod structures of the Bi2Te3 recovered by the wet reduction process. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Recovery of Barium, Nickel, and Titanium Powders from Waste MLCC
Haein Shin, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 374. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Investigation on Microstructure and Electrical Properties of Silver Conductive Features Using a Powder Composed of Silver
nanoparticles and Nanoplatelets
-
Yong-Sung Goo, Yong-Ho Choa, Young Hwangbo, Young-In Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):358-363. Published online October 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.358
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Noncontact direct-printed conductive silver patterns with an enhanced electrical resistivity are fabricated using a silver ink with a mixture of silver nanoparticles and nanoplates. The microstructure and electrical resistivity of the silver pattern are systematically investigated as a function of the mixing ratio of the nanoparticles and nanoplates. The pattern, which is fabricated using a mixture with a mixing ratio of 3(nanoparticles):7(nanoplates) and sintered at 200°C shows a highly dense and well-sintered microstructure and has a resistivity of 7.60 μΩ·cm. This originates a mutual synergistic effect through a combination of the sinterability of the nanoparticles and the packing ability of the nanoplates. This is a conductive material that can be used to fabricate noncontact direct-printed conductive patterns with excellent electrical conductivity for various flexible electronics applications, including solar cells, displays, RFIDs, and sensors.
- [Korean]
- Optical Characteristics of CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dot with Precursor Flow Rate Synthesized by using Microreactor
-
Ji Young Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Won Ju, Han Wook Seo, Yong-Ho Choa, Bum Sung Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):91-94. Published online April 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.91
-
-
1,281
View
-
6
Download
-
3
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
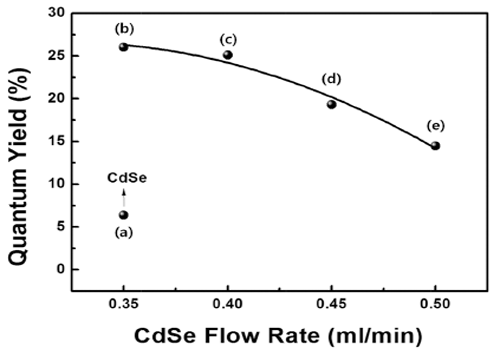
High-quality colloidal CdSe/ZnS (core/shell) is synthesized using a continuous microreactor. The particle size of the synthesized quantum dots (QDs) is a function of the precursor flow rate; as the precursor flow rate increases, the size of the QDs decreases and the band gap energy increases. The photoluminescence properties are found to depend strongly on the flow rate of the CdSe precursor owing to the change in the core size. In addition, a gradual shift in the maximum luminescent wave (λmax) to shorter wavelengths (blue shift) is found owing to the decrease in the QD size in accordance with the quantum confinement effect. The ZnS shell decreases the surface defect concentration of CdSe. It also lowers the thermal energy dissipation by increasing the concentration of recombination. Thus, a relatively high emission and quantum yield occur because of an increase in the optical energy emitted at equal concentration. In addition, the maximum quantum yield is derived for process conditions of 0.35 ml/min and is related to the optimum thickness of the shell material. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Quantum materials made in microfluidics - critical review and perspective
M. Wojnicki, V. Hessel
Chemical Engineering Journal.2022; 438: 135616. CrossRef - Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
Doyeon Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2019; 376: 206. CrossRef - Multimodal luminescence properties of surface-treated ZnSe quantum dots by Eu
Ji Young Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Kyoung-Mook Lim, Yong-Ho Choa, Woo-Byoung Kim, Bum Sung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 8. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Property of BaTiO3@Fe Nanofibers with Core-Shell Structure
-
Young-In Lee, Dae-Hwan Jang, Ki-Hoon Sung, Kyuman Lee, Yong-Ho Choa
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):38-42. Published online February 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.38
-
-
1,026
View
-
6
Download
-
4
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
BaTiO3-coated Fe nanofibers are synthesized via a three-step process. α-Fe2O3 nanofibers with an average diameter of approximately 200 nm are first prepared using an electrospinning process followed by a calcination step. The BaTiO3 coating layer on the nanofiber is formed by a sol-gel process, and a thermal reduction process is then applied to the core-shell nanofiber to selectively reduce the α-Fe2O3 to Fe. The thickness of the BaTiO3 shell is controlled by varying the reaction time. To evaluate the electromagnetic (EM) wave-absorbing abilities of the BaTiO3@Fe nanofiber, epoxy-based composites containing the nanofibers are fabricated. The composites show excellent EM wave absorption properties where the power loss increases to the high frequency region without any degradation. Our results demonstrate that the BaTiO3@Fe nanofibers obtained in this work are attractive candidates for electromagnetic wave absorption applications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Research on Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Based on Electrospinning Technology†
Baoding Li, Jing Qiao, Yue Liu, Haoyuan Tian, Wei Liu, Qilei Wu, Zhou Wang, Jiurong Liu, Zhihui Zeng
Chinese Journal of Chemistry.2024; 42(7): 777. CrossRef - Design, synthesis, and characterization of a porous ceramic-supported CeO2 nanocatalyst for CO -free H2 evolution
Jimin Lee, Minseob Lim, Tae Sung Kim, Kee-Ryung Park, Jong-Sik Lee, Hong-Baek Cho, Joo Hyun Park, Yong-Ho Choa
Applied Surface Science.2021; 548: 149198. CrossRef - Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Fe/MgO composites synthesized by a simple ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method
Hyo-Ryoung Lim, Seung-Jae Jung, Tae-Yeon Hwang, Jimin Lee, Ki Hyeon Kim, Hong-baek Cho, Yong-Ho Choa
Applied Surface Science.2019; 473: 1009. CrossRef - Study on the Optimization of Reduction Conditions for Samarium-Cobalt Nanofiber Preparation
Jimin Lee, Jongryoul Kim, Yong-Ho Choa
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(4): 334. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Characterization of Nickel Nanowires by an Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template-Based Electrodeposition
-
Hyo-Ryoung Lim, Yong-Ho Choa, Young-In Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):216-220. Published online June 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.216
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
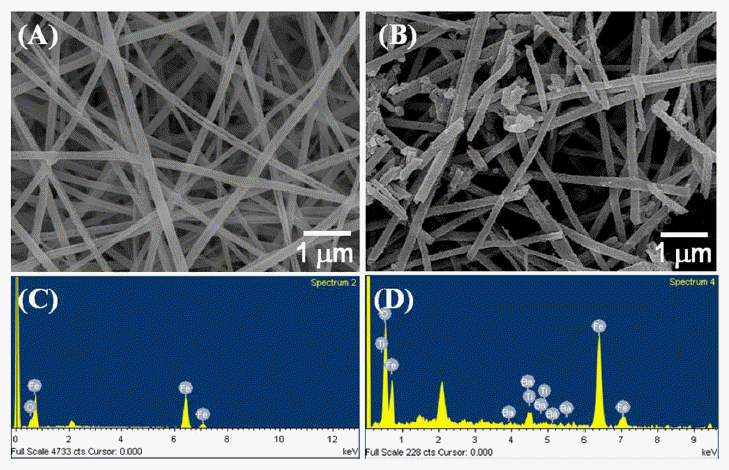
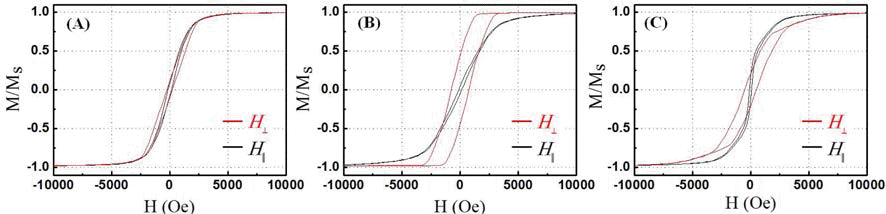
Vertically oriented nickel nanowire arrays with a different diameter and length are synthesized in porous anodic aluminium oxide templates by an electrodeposition method. The pore diameters of the templates are adjusted by controlling the anodization conditions and then they are utilized as templates to grow nickel nanowire arrays. The nickel nanowires have the average diameters of approximately 25 and 260 nm and the crystal structure, morphology and microstructure of the nanowires are systematically investigated using XRD, FE-SEM and TEM analysis. The nickel nanowire arrays show a magnetic anisotropy with the easy axis parallel to the nanowires and the coercivity and remanence enhance with decreasing a wire diameter and increasing a wire length.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Characterization of a Ceria Based Composite Electrolyte for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells by an Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
-
Young-In Lee, Yong-Ho Choa
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):222-228. Published online June 1, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.222
-
-
890
View
-
2
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
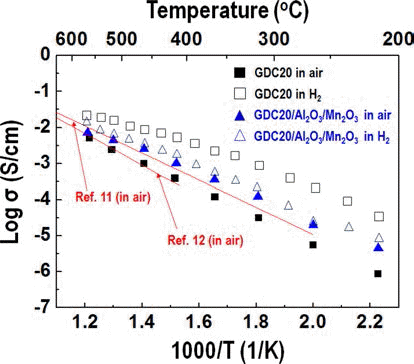
Much research into fuel cells operating at a temperature below 800°C. is being performed. There are significant efforts to replace the yttria-stabilized zirconia electrolyte with a doped ceria electrolyte that has high ionic conductivity even at a lower temperature. Even if the doped ceria electrolyte has high ionic conductivity, it also shows high electronic conductivity in a reducing environment, therefore, when used as a solid electrolyte of a fuel cell, the powergeneration efficiency and mechanical properties of the fuel cell may be degraded. In this study, gadolinium-doped ceria nanopowder with Al2O3 and Mn2O3 as a reinforcing and electron trapping agents were synthesized by ultrasonic pyrolysis process. After firing, their microstructure and mechanical and electrical properties were investigated and compared with those of pure gadolinium-doped ceria specimen. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - High growth-rate atomic layer deposition process of cerium oxide thin film for solid oxide fuel cell
Jin-Geun Yu, Byung Chan Yang, Jeong Woo Shin, Sungje Lee, Seongkook Oh, Jae-Ho Choi, Jaehack Jeong, Wontae Noh, Jihwan An
Ceramics International.2019; 45(3): 3811. CrossRef - Atomic-layer-deposited ZrO2-doped CeO2 thin film for facilitating oxygen reduction reaction in solid oxide fuel cell
Byung Chan Yang, Dohyun Go, Seongkook Oh, Jeong Woo Shin, Hyong June Kim, Jihwan An
Applied Surface Science.2019; 473: 102. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Sn and SnO2 Nanopowders by Low-Temperature Phase Transformation Method
-
Kun-Jae Lee, Yeon-Jun Joo, Yong-Dae So, Nam-Hoon Kim, Jai-Sung Lee, Yong-Ho Choa
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2006;13(1):46-51.
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2006.13.1.046
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Through the volume change of Sn in a low-temperature phase transformation, the Sn nanopowder with high, purity, was fabricated by an economic and eco-friendly process. The fine cracks were spontaneously generated. in, Sn ingot, which was reduced to powders in the repetition of phase transformation. The Sn nanopowder with 50 run in size was obtained by the 24th repetitions of phase transformation by low-temperature and ultrasonic treatments. Also, the SnO_2 powder was fabricated by the oxidation of the produced Sn powder to the ingot and milled by the ultrasonic milling method. The SnO_2 nanopowder of 20 nm in size was fabricated after the milling for 180 h.
- [Korean]
- Densification and Some Properties of Carbon Nanotubes-Dispersed Al2O3 Nanocomposite Powders
-
Seung-Hwa Yoo, Jae-Kyo Yang, Sung-Tag Oh, Kae-Myung Kang, Sung-Goon Kang, Yong-Ho Choa
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(6):393-398.
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.6.393
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- In-situ processing route was adopted to disperse carbon nanotubes (CNTs) into Al_2O_3 powders homogeneously. The Al_2O_3 composite powders with homogeneous dispersion of CNTs could be synthesized by a catalytic route for in-situ formation of CNTs on nano-sized Fe dispersed Al_2O_3 powders. CNTs/Fe/Al_2O_3 nanopowders were densified by spark plasma sintering (SPS). The hardness and bending strength as well as electrical conductivity increased with increasing sintering temperature. However, the electrical conductivity of the composites sintered at above 1500°C showed decreased value with increasing sintering temperature due to the oxidation of CNTs.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Characterization of CNTs/Metal/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Powders by Thermal CVD
-
Yong-Ho Choa, Seung-Hwa Yoo, Jae-Kyo Yang, Sung-Tag Oh, Sung-Goon Kang
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(2):146-150.
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.2.146
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- An optimum route to synthesize Al_2O_3-based composite powders with homogeneous dispersion of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) was investigated. CNTs/Metal/Al_2O_3 nanocomposite powders were fabricated by thermal chemical vapor deposition of C_2H_2 gas over metal/Al_2O_3 nanocomposite catalyst prepared by selective reduction of metal oxide/Al_2O_3 powders. The FT-Raman spectroscopy analysis revealed that the CNTs have single- and multi-walled structure. The CNTs with the diameter of 25-43 nm were homogeneously distributed in the metal/Al_2O_3 powders, and their characteristics were strongly affected by a kind of metal catalyst and catalyst size. The experimental results show that the composite powder with required size and dispersion of CNTs can be realized by control of synthesis condition.
|