- [Korean]
- Friction Stir Spot Welding Characteristics of Dissimilar Materials of Aluminum-Based Damping Composites and Steel Plates
-
Si-Seon Park, Young-Keun Jeong
-
J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):43-49. Published online February 28, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00010
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
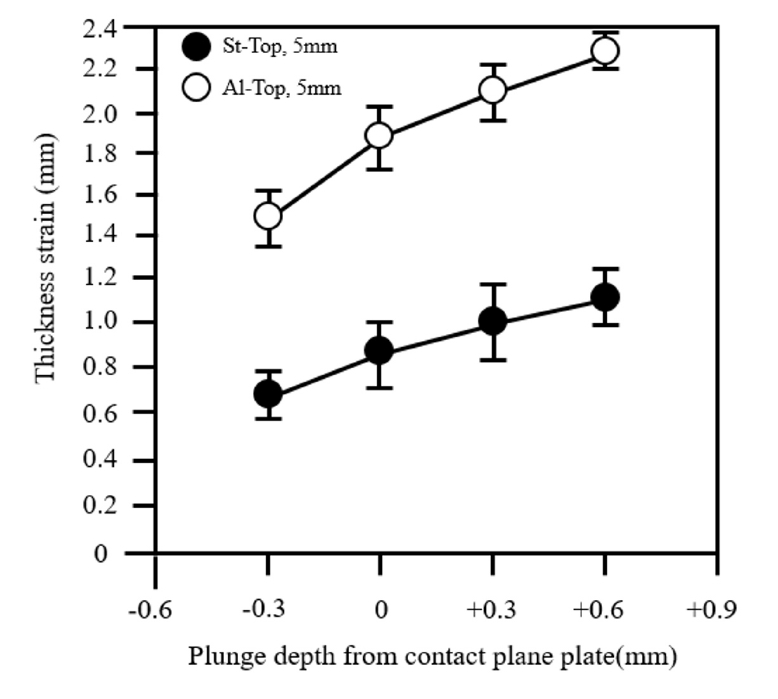
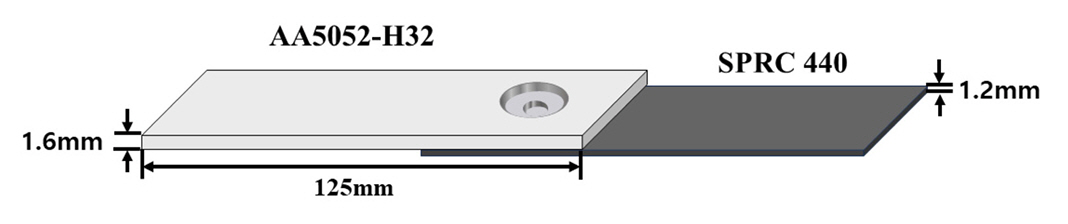
- Friction Stir Spot Welding (FSSW) is a solid-state welding technology that is rapidly growing in the automotive industry. Achieving superior welding characteristics requires the proper selection of tool geometry and process conditions. In this study, FSSW was performed on dissimilar materials comprising AA5052-HO/hot-melt aluminum alloy sheets and Steel Plate Cold Rolled for Deep Drawing Use(SPCUD) steel sheets. The effects of tool geometry, plate arrangement, and tool plunge depth on the welding process were investigated. At the joint interface between the aluminum alloy and the steel sheet, new intermetallic compounds (IMCs) were observed. As the plunge depth increased, thicker and more continuous IMC layers were formed. However, excessive plunge depth led to discontinuous layers and cracking defects. An analysis of the IMCs revealed a correlation between the IMC thickness and the shear tensile load. Furthermore, compared to the conventional Al-Top arrangement, the St-Top arrangement exhibited reduced deformation and superior shear tensile load values. These findings indicate that plate arrangement significantly influences the mechanical properties of the joint.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Tool Shape and Insertion Depth on Joining Properties in Friction Stir Spot Welding of Aluminum Alloy/high-strength Steel Sheets
-
Su-Ho An, Young-Keun Jeong
-
J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):37-42. Published online February 28, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.37
-
-
1,135
View
-
23
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 PDF PDF
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Friction Welding of Casted SCM440 and Sintered F-05-140 Dissimilar Steels and Their Joint Properties under Various Welding Conditions
Jisung Lee, Hansung Lee, Eunhyo Song, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 414. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Tungsten by Freeze Casting and Vacuum Drying of WO3/Tert-butyl Alcohol Slurry
-
Youn Ji Heo, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh, Young-Keun Jeong
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):118-122. Published online April 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.118
-
-
946
View
-
11
Download
-
3
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The synthesis of porous W by freeze-casting and vacuum drying is investigated. Ball-milled WO3 powders and tert-butyl alcohol were used as the starting materials. The tert-butyl alcohol slurry is frozen at –25°C and dried under vacuum at –25 and –10°C. The dried bodies are hydrogen-reduced at 800°C and sintered at 1000°C. The XRD analysis shows that WO3 is completely reduced to W without any reaction phases. SEM observations reveal that the struts and pores aligned in the tert-butyl alcohol growth direction, and the change in the powder content and drying temperature affects the pore structure. Furthermore, the struts of the porous body fabricated under vacuum are thinner than those fabricated under atmospheric pressure. This behavior is explained by the growth mechanism of tert-butyl alcohol and rearrangement of the powders during solidification. These results suggest that the pore structure of a porous body can be controlled by the powder content, drying temperature, and pressure. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  -
Fabrication of porous W by freeze-casting and hydrogen reduction of camphene-based WO
3
suspension
Ji Won Choi, Youngmin Kim, Ji Young Kim, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(3): 283. CrossRef - Preparation of Porous W-Cu by Freeze Casting of Tert-butyl Alcohol Slurry Mixed with WO3-CuO Powder
Youngmin Kim, Ji Young Kim, Minju Son, Wonyong Kwon, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 466. CrossRef - Fabrication of Porous TiO2 with Aligned Pores Using Tert-Butyl Alcohol Based Freeze Casting
Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2024; 62(12): 929. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Freeze Drying Process and Pore Structure Characteristics of Porous Cu with Various Sublimable Vehicles
-
Gyuhwi Lee, Sung-Tag Oh, Myung-Jin Suk, Young-Keun Jeong
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):198-202. Published online June 1, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.198
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The effect of sublimable vehicles on the pore structure of Cu fabricated by freeze drying is investigated. The 5 vol% CuO-dispersed slurries with camphene and various camphor-naphthalene compositions are frozen in a Teflon mold at -25°C, followed by sublimation at room temperature. After hydrogen reduction at 300°C and sintering at 600 °C, the green bodies of CuO are completely converted to Cu with various pore structures. The sintered samples prepared using CuO/camphene slurries show large pores that are aligned parallel to the sublimable vehicle growth direction. In addition, a dense microstructure is observed in the bottom section of the specimen where the solidification heat was released, owing to the difference in the solidification behavior of the camphene crystals. The porous Cu shows different pore structures, such as dendritic, rod-like, and plate shaped, depending on the composition of the camphornaphthalene system. The change in pore structure is explained by the crystal growth behavior of primary camphor and eutectic and primary naphthalene.
- [Korean]
- Nanostructure Construction of SiO2@Au Core-Shell by In-situ Synthesis
-
Mu-Jae Pyeon, Do Kyung Kim, Young-Keun Jeong
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):420-425. Published online October 1, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.420
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Core-shell structured nanoparticles are garnering attention because these nanoparticles are expected to have a wide range of applications. The objective of the present study is to improve the coating efficiency of gold shell formed on the surface of silica nanoparticles for SiO2@Au core-shell structure. For the efficient coating of gold shell, we attempt an in-situ synthesis method such that the nuclei of the gold nanoparticles are generated and grown on the surface of silica nanoparticles. This method can effectively form a gold shell as compared to the conventional method of attaching gold nanoparticles to silica particles. It is considered possible to form a dense gold shell because the problems caused by electrostatic repulsion between the gold nanoparticles in the conventional method are eliminated.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Powder Mixing Process on the Characteristics of Hybrid Structure Tungsten Powders with Nano-Micro Size
-
Na-Yeon Kwon, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):384-388. Published online October 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.384
-
-
894
View
-
3
Download
-
5
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The effect of the mixing method on the characteristics of hybrid-structure W powder with nano and micro sizes is investigated. Fine WO3 powders with sizes of ~0.6 μm, prepared by ball milling for 10 h, are mixed with pure W powder with sizes of 12 μm by various mixing process. In the case of simple mixing with ball-milled WO3 and micro sized W powders, WO3 particles are locally present in the form of agglomerates in the surface of large W powders, but in the case of ball milling, a relatively uniform distribution of WO3 particles is exhibited. The microstructural observation reveals that the ball milled WO3 powder, heat-treated at 750°C for 1 h in a hydrogen atmosphere, is fine W particles of ~200 nm or less. The powder mixture prepared by simple mixing and hydrogen reduction exhibits the formation of coarse W particles with agglomeration of the micro sized W powder on the surface. Conversely, in the powder mixture fabricated by ball milling and hydrogen reduction, a uniform distribution of fine W particles forming nano-micro sized hybrid structure is observed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Efficiency of Radiation Shielding Sheet to Reduce Radiation Exposure during C-arm Fluoroscopy
Hosang Jeon, Won Chul Shin, Hee Yun Seol, Yongkan Ki, Kyeong Baek Kim, Ki Seok Choo, Sang Don Lee, Suk-Woong Kang
Journal of the Korean Fracture Society.2023; 36(4): 111. CrossRef - Microstructure and Sintering Behavior of Fine Tungsten Powders Synthesized by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
Hyeonhui Jo, Jeong Hyun Kim, Young-In Lee, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2021; 59(5): 289. CrossRef - Facile phosphorus-embedding into SnS2 using a high-energy ball mill to improve the surface kinetics of P-SnS2 anodes for a Li-ion battery
Hongsuk Choi, Seungmin Lee, KwangSup Eom
Applied Surface Science.2019; 466: 578. CrossRef - Hydrogen reduction behavior and microstructural characteristics of WO3 and WO3-NiO powders
Hyunji Kang, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2019; 80: 69. CrossRef - Fabrication of Densified W-Ti by Reaction Treatment and Spark Plasma Sintering of WO3-TiH2 Powder Mixtures
Hyunji Kang, Heun Joo Kim, Ju-Yeon Han, Yunju Lee, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(9): 511. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Effect of Reaction Parameters on Silica Nanoparticles Synthesized by Sol-gel Method
-
Young-Hyun Lim, Do Kyung Kim, Young-Keun Jeong
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(6):442-446. Published online December 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.6.442
-
-
3,046
View
-
48
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
The sol-gel method is the simplest method for synthesizing monodispersed silica particles. The purpose of this study is to synthesize uniform, monodisperse spherical silica nanoparticles using tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) as the silica precursor, ethanol, and deionized water in the presence of ammonia as a catalyst. The reaction time and temperature and the concentration of the reactants are controlled to investigate the effect of the reaction parameters on the size of the synthesized particles. The size and morphology of the obtained silica particles are investigated using transmission electron microscopy and particle size analysis. The results show that monodispersed silica particles over a size range of 54-504 nm are successfully synthesized by the sol-gel method without using any additional process. The nanosized silica particles can be synthesized at higher TEOS/H2O ratios, lower ammonia concentrations, and especially, higher reaction temperatures. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - SYNTHESIS OF SILICA NANOPARTICLES FROM SUGARCANE WASTE: PRECIPITATION-BASED SIZE CONTROL AND CHARACTERIZATION
Mustapha Sulaiman, Naseer Inuwa Durumin Iya, Mamudu Aliyu
FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES.2024; 8(3): 222. CrossRef - Nanostructure Construction of SiO2@Au Core-Shell by In-situ Synthesis
Mu-Jae Pyeon, Do Kyung Kim, Young-Keun Jeong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(5): 420. CrossRef
- [Korean]
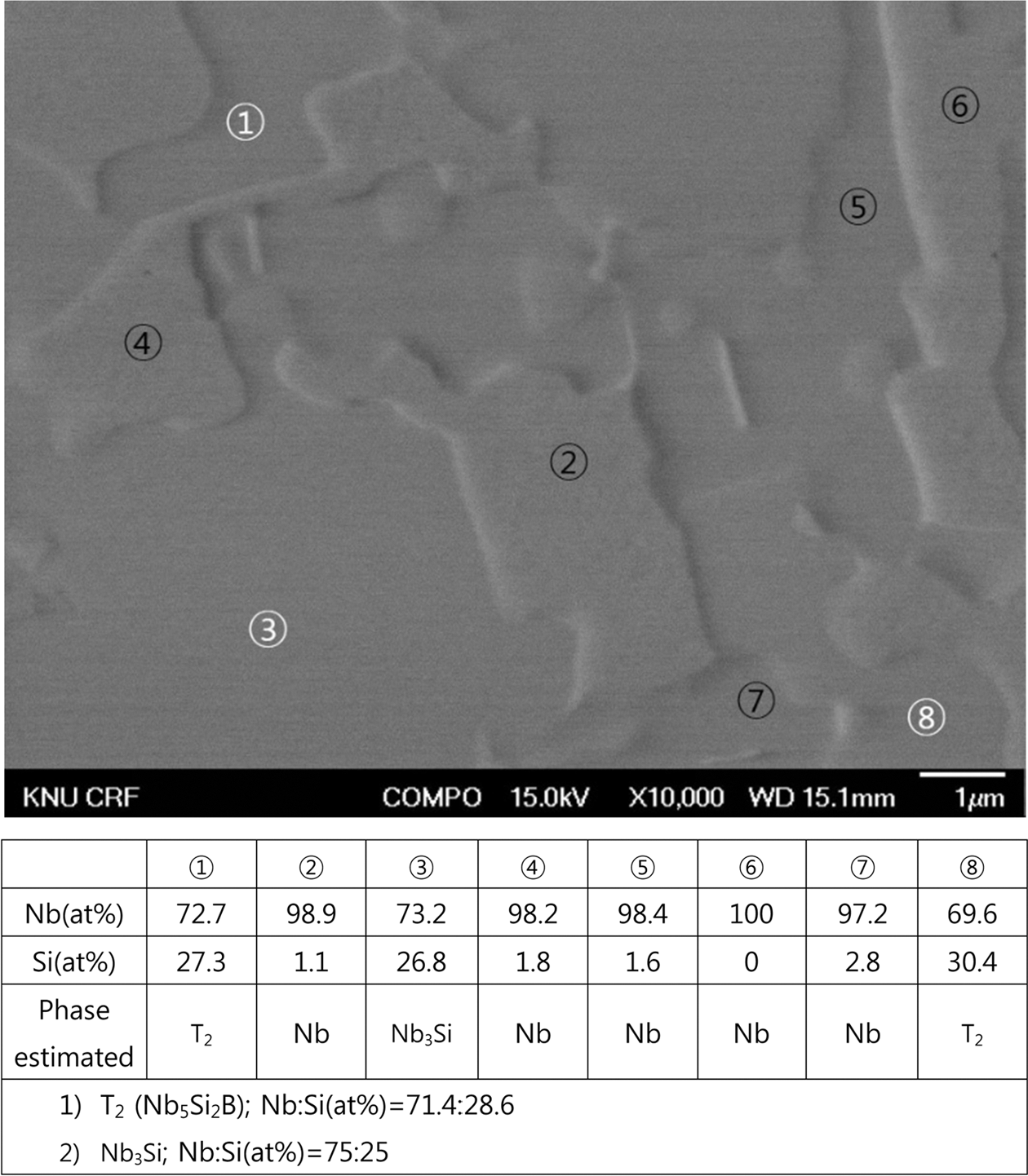
- Microstructure Characterization of Nb-Si-B alloys Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering Process
-
Sang-Hwan Kim, Nam-Woo Kim, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim, Seong Lee, Myung Jin Suk
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):426-431. Published online December 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.426
-
-
961
View
-
3
Download
-
5
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Microstructural examination of the Nb-Si-B alloys at Nb-rich compositions is performed. The Nb-rich corner of the Nb-Si-B system is favorable in that the constituent phases are Nb (ductile and tough phase with high melting temperature) and T2 phase (very hard intermetallic compound with favorable oxidation resistance) which are good combination for high temperature structural materials. The samples containing compositions near Nb-rich corner of the Nb- Si-B ternary system are prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS) process using T2 and Nb powders. T2 bulk phase is made in arc furnace by melting the Nb slug and the Si-B powder compact. The T2 bulk phase was subsequently ballmilled to powders. SPS is performed at 1300°C and 1400°C, depending on the composition, under 30 MPa for 600s, to produce disc-shaped specimen with 15 mm in diameter and 3 mm high. Hardness tests (Rockwell A-scale and micro Vickers) are carried out to estimate the mechanical property. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication of Nb-Si-B Alloys Using the Pulverized Nb-T2 Alloy Powder
Min-Ho Cho, Sung-Jun Kim, Hyun-Ji Kang, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim, Seong Lee, Myung Jin Suk
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(4): 299. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of Mo-Nb-Si-B quaternary alloy fabricated by powder metallurgical method
Jong Min Byun, Su-Ryong Bang, Se Hoon Kim, Won June Choi, Young Do Kim
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2017; 65: 14. CrossRef - Mechanical properties of Mo-Si-B alloys fabricated by using core-shell powder with dispersion of yttria nanoparticles
Jong Min Byun, Su-Ryong Bang, Won June Choi, Min Sang Kim, Goo Won Noh, Young Do Kim
Metals and Materials International.2017; 23(1): 170. CrossRef - Fabrication of Ta2O5 Dispersion-Strengthened Mo-Si-B Alloy by Powder Metallurgical Method
Jong Min Byun, Won June Choi, Su-Ryong Bang, Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim
JOM.2017; 69(4): 683. CrossRef - Rapid consolidation of nanostuctured WC-FeAl3 by pulsed current activated heating and its mechanical properties
In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2017; 65: 69. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Evaluation of Material Characteristics with Sintering Temperature in Ti2AlC MAX Phase Material using Spark Plasma Sintering Method
-
Chang-Hun Lee, Gyung Rae Baek, Hee Sang Jung, Young-Keun Jeong, Myung Chang Kang
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):175-180. Published online June 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.175
-
-
1,084
View
-
8
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
In this study, ternary compound Max Phase Ti2AlC material was mixed by 3D ball milling as a function of ball milling time. More than 99.5 wt% pure Ti2AlC was synthesized by using spark plasma sintering method at 1000, 1100, 1200, and 1300°C for 60 min. The material characteristics of synthesized samples were examined with relative density, hardness, and electrical conductivity as a function of sintering temperature. The phase composition of bulk was identified by X-ray diffraction. On the basis of FE-SEM result, a terraced structures which consists of several laminated layers were observed. And Ti2AlC bulk material obtained a vickers hardness of 5.1 GPa at the sintering temperature of 1100°C. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Synthesis and reaction path of Ti‐Al‐C MAX phases by reaction with Ti‐Al intermetallic compounds and TiC
Hojun Lee, Si Yeon Kim, Young‐In Lee, Jongmin Byun
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2023; 106(12): 7230. CrossRef
- [Korean]
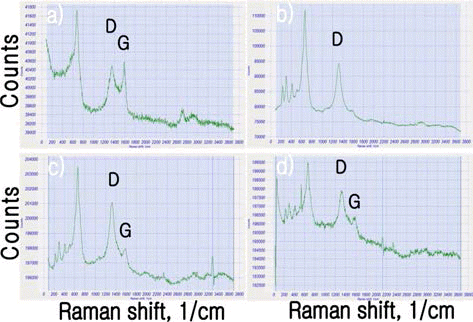
- Powder Sintering Characteristics of Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced SKD11 Tool Steel Sintered by Spark Plasma Sintering
-
Je-Se Moon, Sung-Sil Jung, Dae-Yeol Lee, Young-Keun Jeong, Myung Chang Kang, Chun-Dal Park, Kook-Tae Youn
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):157-162. Published online June 1, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.157
-
-
903
View
-
3
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
SKD11 (ASTM D2) tool steel is a versatile high-carbon, high-chromium, air-hardening tool steel that is characterized by a relatively high attainable hardness and numerous, large, chromium rich alloy carbide in the microstructure. SKD11 tool steel provides an effective combination of wear resistance and toughness, tool performance, price, and a wide variety of product forms. Adding of CNTs increased the performance of mechanical properties more. 1, 3 vol% CNTs was dispersed in SKD11 matrix by mechanical alloying. SKD11 carbon nanocomposite powder was sintered by spark plasma sintering process. FE-SEM, HR-TEM and Raman analysis were carried out for the SKD11 carbon nanocomposites. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Study on Effects of Mold Temperature on the Injection Molded Article
J.-H. Han, Y.-C. Kim
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1271. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Photocatalytic TiO2 prepared by Polymer Complex Solution Method
-
Jeong-Wook Jang, Young-Keun Jeong, Tae-Oh Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(4):249-254.
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.4.249
-
-
753
View
-
0
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Titanium dioxide was prepared by Polymer Complex Solution Method(PCSM) according to the mole ratio of Titanium (IV) isopropoxide(TTIP)/solvent and polymer(Poly Ethylene Glycol). Polymer electrolytes were usually made by dispersing preproduced ceramic nanoparticles in a polymer matrix. Using this method, pure and nano-sized TiO_2 powder was synthesized through a simple procedure and polymer entrapment route. At the optimum amount of the polymer, the titanium ions are dispersed in solution and a homogeneous polymeric network is formed. The maximum intensity of anatase phase of TiO_2 was achieved by calcining at 500°C for 2h. The synthesized TiO_2 powders were nano-sized and the average size was about 50nm. Anatase/Rutile ratio of the synthesized TiO_2 was 70%/30%.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Synthesis and characterization of N-doped TiO2/ZrO2 visible light photocatalysts
Ji Young Kim, Chan Soo Kim, Han Kwon Chang, Tae Oh Kim
Advanced Powder Technology.2011; 22(3): 443. CrossRef - Effects of ZrO2 addition on phase stability and photocatalytic activity of ZrO2/TiO2 nanoparticles
Ji-Young Kim, Chan-Soo Kim, Han-Kwon Chang, Tae-Oh Kim
Advanced Powder Technology.2010; 21(2): 141. CrossRef
|