Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
- [English]
- Microwave Absorbance of Polymer Composites Containing SiC Fibers Coated with Ni-Fe Thin Films
- Tian Liu, Sung-Soo Kim, Woo-cheal Choi, Byungil Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):375-378. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.375

- 1,094 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Conductive and dielectric SiC are fabricated using electroless plating of Ni–Fe films on SiC chopped fibers to obtain lightweight and high-strength microwave absorbers. The electroless plating of Ni–Fe films is achieved using a two-step process of surface sensitizing and metal plating. The complex permeability and permittivity are measured for the composite specimens with the metalized SiC chopped fibers dispersed in a silicone rubber matrix. The original noncoated SiC fibers exhibit considerable dielectric losses. The complex permeability spectrum does not change significantly with the Ni–Fe coating. Moreover, dielectric constant is sensitively increased with Ni–Fe coating, owing to the increase of the space charge polarization. The improvements in absorption capability (lower reflection loss and small matching thickness) are evident with Ni–Fe coating on SiC fibers. For the composite SiC fibers coated with Ni–Fe thin films, a -35 dB reflection loss is predicted at 7.6 GHz with a matching thickness of 4 mm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Magnetic sputtering of FeNi/C bilayer film on SiC fibers for effective microwave absorption in the low-frequency region
Tong Guo, Ben Huang, Changgeng Li, Yumin Lou, Xiu-Zhi Tang, Xiaozhong Huang, Jianling Yue
Ceramics International.2021; 47(4): 5221. CrossRef
- Magnetic sputtering of FeNi/C bilayer film on SiC fibers for effective microwave absorption in the low-frequency region
- [Korean]
- Study of Color Evolution by Silica Coating and Etching based Morphological Control of α-FeOOH
- NaRi Lee, Ri Yu, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):379-383. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.379
- 1,175 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
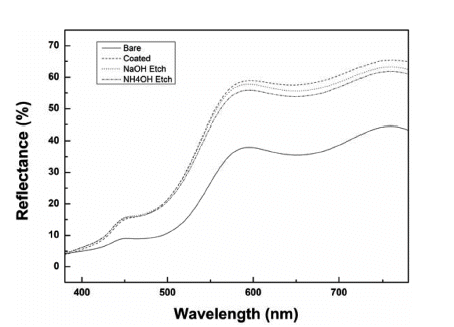
PDF Silica is used in shell materials to minimize oxidation and aggregation of nanoparticles. Particularly, porous silica has gained attention because of its performance in adsorption, catalysis, and medical applications. In this study, to investigate the effect of the density of the silica coating layer on the color of the pigment, we arbitrarily change the structure of a silica layer using an etchant. We use NaOH or NH4OH to etch the silica coating layer. First, we synthesize α-FeOOH for a length of 400 nm and coat it with TEOS to fabricate particles with a 50 nm coating layer. The coating thickness is then adjusted to 30–40 nm by etching the silica layer for 5 h. Four different shapes of α-FeOOH with different colors are measured using UV–vis light. From the color changes of the four different shapes of α-FeOOH features during coating or etching, the
L * value is observed to increase and brighten the overall color, and theb * value increases to impart a clear yellow color to the pigment. The brightest yellow color was that coated with silica; if the sample is etched with NaOH or NH4OH, theb * value can be controlled to study the yellow colors.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trend of Ceramic Nano Pigments
Ri Yu, YooJin Kim
Ceramist.2019; 22(3): 256. CrossRef
- Trend of Ceramic Nano Pigments
- [Korean]
- Thermoelectric Properties of PbTe Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering of Nano Powders
- Eun-Young Jun, Ho-Young Kim, Cham Kim, Kyung-Sik Oh, Tai-Joo Chung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):384-389. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.384
- 1,151 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
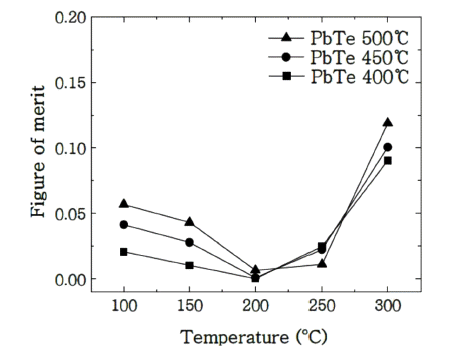
PDF Nanoparticles of PbTe are prepared via chemical reaction of the equimolar aqueous solutions of Pb(CH3COO)2 and Te at 120°C. The size of the obtained particles is 100 nm after calcination in a hydrogen atmosphere. Dense specimens for the thermoelectric characterization are produced by spark plasma sintering of prepared powders at 400°C to 500°C under 80 MPa for 5 min. The relative densities of the prepared specimens reach approximately 97% and are identified as cubic based on X-ray diffraction analyses. The thermoelectric properties are evaluated between 100°C and 300°C via electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity. Compared with PbTe ingot, the reduction of the thermal conductivities by more than 30% is verified via phonon scattering at the grain boundaries, which thus contributes to the increase in the figure of merit.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improved Thermoelectric Performance of Cu3Sb1−x−ySnxInySe4 Permingeatites Double-Doped with Sn and In
Ho-Jeong Kim, Il-Ho Kim
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(6): 422. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef
- Improved Thermoelectric Performance of Cu3Sb1−x−ySnxInySe4 Permingeatites Double-Doped with Sn and In
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Metallic Tantalum Powder by Magnesium-gas Reduction of Tantalum Oxide
- Dong-Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):390-394. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.390

- 825 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metallic tantalum powder is manufactured by reducing tantalum oxide (Ta2O5) with magnesium gas at 1,073–1,223 K in a reactor under argon gas. The high thermodynamic stability of magnesium oxide makes the reduction reaction from tantalum oxide into tantalum powder possible. The microstructure after the reduction reaction has the form of a mixture of tantalum and magnesium oxide, and the latter could be entirely eliminated by dissolving in weak hydrochloric acid. The powder size in SEM microstructure for the tantalum powder increases after acid leaching in the range of 50–300 nm, and its internal crystallite sizes are observed to be 11.5 to 24.7 nm with increasing reduction temperatures. Moreover, the optimized reduction temperature is found to be 1,173 K as the minimum oxygen concentration is approximately 1.3 wt.%.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A review of tantalum resources and its production
Xue WEI, Long-gong XIA, Zhi-hong LIU, Le-ru ZHANG, Qi-hou LI
Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China.2023; 33(10): 3132. CrossRef - Valuable metal recovery from waste tantalum capacitors via cryogenic crushing-alkaline calcination-leaching process
Longgong Xia, Xue Wei, Hongjun Wang, Fengchun Ye, Zhihong Liu
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2022; 16: 1637. CrossRef
- A review of tantalum resources and its production
- [Korean]
- Effect of Surfactant on the Dispersion Stability of Slurry for Semiconductor Silicon CMP
- Hye Won Yun, Doyeon Kim, Do Hyung Han, Dong Wan Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):395-401. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.395
- 2,118 View
- 46 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
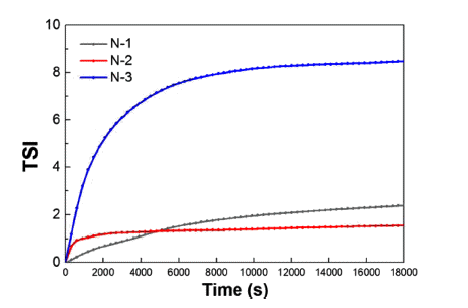
PDF The improvement of dispersion stability for the primary polishing slurry in a CMP process is achieved to prevent defects produced by agglomeration of the slurry. The dispersion properties are analyzed according to the physical characteristics of each silica sol sample. Further, the difference in the dispersion stability is confirmed as the surfactant content. The dispersibility results measured by Zeta potential suggest that the dispersion properties depend on the content and size of the abrasive in the primary polishing slurry. Moreover, the optimum ratio for high dispersion stability is confirmed as the addition content of the surfactant. Based on the aforementioned results, the long-term stability of each slurry is analyzed. Turbiscan analysis demonstrates that the agglomeration occurs depending on the increasing amount of surfactant. As a result, we demonstrate that the increased particle size and the decreased content of silica improve the dispersion stability and long-term stability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surface Defect Properties of Prime, Test-Grade Silicon Wafers
Seung-Hwan Oh, Hyeonmin Yim, Donghee Lee, Dong Hyeok Seo, Won Jin Kim, Ryun Na Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2022; 32(9): 396. CrossRef
- Surface Defect Properties of Prime, Test-Grade Silicon Wafers
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Molybdenum Silicide-based Composites with Uniformly Dispersed Silicon Carbide
- Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim, Jong Min Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):402-407. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.402
- 478 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
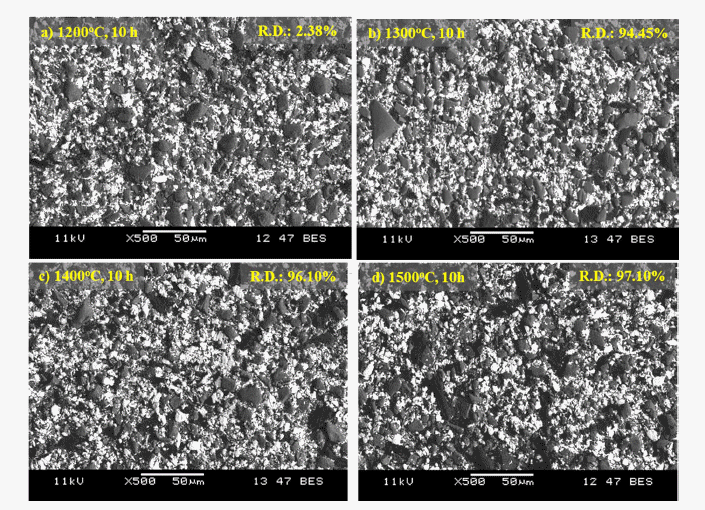
PDF Molybdenum silicide has gained interest for high temperature structural applications. However, poor fracture toughness at room temperatures and low creep resistance at elevated temperatures have hindered its practical applications. This study uses a novel powder metallurgical approach applied to uniformly mixed molybdenum silicidebased composites with silicon carbide. The degree of powder mixing with different ball milling time is also demonstrated by Voronoi diagrams. Core-shell composite powder with Mo nanoparticles as the shell and β-SiC as the core is prepared via chemical vapor transport. Using this prepared core-shell composite powder, the molybdenum silicide-based composites with uniformly dispersed β-SiC are fabricated using pressureless sintering. The relative density of the specimens sintered at 1500°C for 10 h is 97.1%, which is similar to pressure sintering owing to improved sinterability using Mo nanoparticles.
- [Korean]
- Microstructural and Wear Properties of WC-based and Cr3C2-based Cermet Coating Materials Manufactured with High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Process
- Yeon-Ji Kang, Gi-Su Ham, Hyung-Jun Kim, Sang-Hoon Yoon, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):408-414. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.408
- 880 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
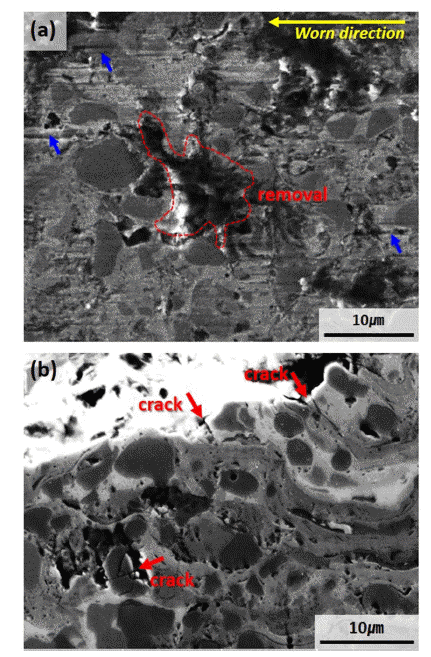
PDF This study investigates the microstructure and wear properties of cermet (ceramic + metal) coating materials manufactured using high velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) process. Three types of HVOF coating layers are formed by depositing WC-12Co, WC-20Cr-7Ni, and Cr3C2-20NiCr (wt.%) powders on S45C steel substrate. The porosities of the coating layers are 1 ± 0.5% for all three specimens. Microstructural analysis confirms the formation of second carbide phases of W2C, Co6W6C, and Cr7C3 owing to decarburizing of WC phases on WC-based coating layers. In the case of WC-12Co coating, which has a high ratio of W2C phase with high brittleness, the interface property between the carbide and the metal binder slightly decreases. In the Cr3C2-20CrNi coating layer, decarburizing almost does not occur, but fine cavities exist between the splats. The wear loss occurs in the descending order of Cr3C2-20NiCr, WC-12Co, and WC-20Cr-7Ni, where WC-20Cr-7Ni achieves the highest wear resistance property. It can be inferred that the ratio of the carbide and the binding properties between carbide–binder and binder–binder in a cermet coating material manufactured with HVOF as the primary factors determine the wear properties of the cermet coating material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tribological Behavior Analysis of WC-Ni-Cr + Cr3C2 and WC-Ni-Cr + YSZ Coatings Sprayed by HVOF
Tae-Jun Park, Gye-Won Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(5): 415. CrossRef - Effects of different HVOF thermal sprayed cermet coatings on tensile and fatigue properties of AISI 1045 steel
Gi-Su Ham, R. Kreethi, Hyung-jun Kim, Sang-hoon Yoon, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2021; 15: 6647. CrossRef
- Tribological Behavior Analysis of WC-Ni-Cr + Cr3C2 and WC-Ni-Cr + YSZ Coatings Sprayed by HVOF
- [Korean]
- A Study on Pore Properties of SUS316L Powder Porous Metal Fabricated by Electrostatic Powder Coating Process
- Min-Jeong Lee, Yu-Jeong Yi, Hyeon-Ju Kim, Manho Park, Byoung-Kee Kim, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):415-419. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.415
- 780 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Porous metals demonstrate not only excessively low densities, but also novel physical, thermal, mechanical, electrical, and acoustic properties. Thus, porous metals exhibit exceptional performance, which are useful for diesel particulate filters, heat exchangers, and noise absorbers. In this study, SUS316L foam with 90% porosity and 3,000 μm pore size is successfully manufactured using the electrostatic powder coating (ESPC) process. The mean size of SUS316L powders is approximately 12.33 μm. The pore properties are evaluated using SEM and Archimedes. As the quantity of powder coating increases, pore size decreases from 2,881 to 1,356 μm. Moreover, the strut thickness and apparent density increase from 423.7 to 898.3 μm and from 0.278 to 0.840 g/cm3, respectively. It demonstrates that pore properties of SUS316L powder porous metal are controllable by template type and quantity of powder coating.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
Minji Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Su-Jin Yun, Poong-Yeon Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Juyong Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 299. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
- [Korean]
- Nanostructure Construction of SiO2@Au Core-Shell by In-situ Synthesis
- Mu-Jae Pyeon, Do Kyung Kim, Young-Keun Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):420-425. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.420

- 923 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Core-shell structured nanoparticles are garnering attention because these nanoparticles are expected to have a wide range of applications. The objective of the present study is to improve the coating efficiency of gold shell formed on the surface of silica nanoparticles for SiO2@Au core-shell structure. For the efficient coating of gold shell, we attempt an in-situ synthesis method such that the nuclei of the gold nanoparticles are generated and grown on the surface of silica nanoparticles. This method can effectively form a gold shell as compared to the conventional method of attaching gold nanoparticles to silica particles. It is considered possible to form a dense gold shell because the problems caused by electrostatic repulsion between the gold nanoparticles in the conventional method are eliminated.
- [Korean]
- Sintering Behavior and Thermal Conductivity of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics with MgO–CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 Nano-glass Additive
- Su-Hyun Baik, Kyung Min Kim, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):426-434. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.426
- 1,174 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
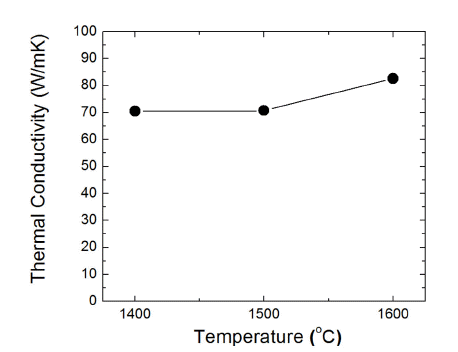
PDF In this study, MgO–CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 (MCAS) nanocomposite glass powder having a mean particle size of 50 nm and a specific surface area of 40 m2/g is used as a sintering additive for AlN ceramics. Densification behaviors and thermal properties of AlN with 5 wt% MCAS nano-glass additive are investigated. Dilatometric analysis and isothermal sintering of AlN-5wt% MCAS compact demonstrates that the shrinkage of the AlN specimen increases significantly above 1,300°C via liquid phase sintering of MCAS additive, and complete densification could be achieved after sintering at 1,600°C, which is a reduction in sintering temperature by 200°C compared to conventional AlN-Y2O3 systems. The MCAS glass phase is satisfactorily distributed between AlN particles after sintering at 1,600°C, existing as an amorphous secondary phase. The AlN specimen attained a thermal conductivity of 82.6 W/m·K at 1,600°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glass Additive Content on Properties of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
Kyung Min Kim, Su-Hyun Baik, Sung-Soo Ryu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(6): 494. CrossRef
- Effect of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glass Additive Content on Properties of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
- [Korean]
- Effects of Morphologies of Carbon Nanomaterials on Conductivity of Composites Containing Copper/Carbon Nanomaterial Hybrid Fillers
- Yeonjoo Lee, Sung-uk Hong, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):435-440. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.435
- 538 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
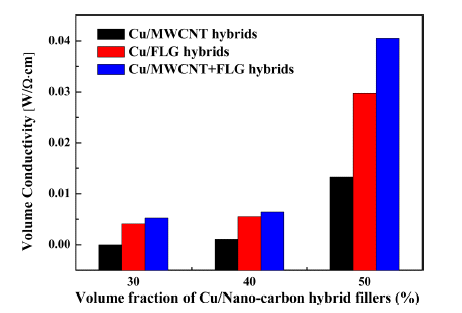
PDF In the present study, we develop a conductive copper/carbon nanomaterial additive and investigate the effects of the morphologies of the carbon nanomaterials on the conductivities of composites containing the additive. The conductive additive is prepared by mechanically milling copper powder with carbon nanomaterials, namely, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and/or few-layer graphene (FLG). During the milling process, the carbon nanomaterials are partially embedded in the surfaces of the copper powder, such that electrically conductive pathways are formed when the powder is used in an epoxy-based composite. The conductivities of the composites increase with the volume of the carbon nanomaterial. For a constant volume of carbon nanomaterial, the FLG is observed to provide more conducting pathways than the MWCNTs, although the optimum conductivity is obtained when a mixture of FLG and MWCNTs is used.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI




 First
First Prev
Prev


