Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
- [English]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Immiscible Fe-Cu Alloys using Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid
- Chu Dac Phuc, Nguyen Minh Thuyet, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):449-457. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.449

- 1,187 View
- 12 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Iron and copper are practically immiscible in the equilibrium state, even though their atomic radii are similar. As non-equilibrium solid solutions, the metastable Fe-Cu alloys can be synthesized using special methods, such as rapid quenching, vapor deposition, sputtering, ion-beam mixing, and mechanical alloying. The complexity of these methods (multiple steps, low productivity, high cost, and non-eco-friendliness) is a hinderance for their industrial applications. Electrical explosion of wire (EEW) is a well-known and effective method for the synthesis of metallic and alloy nanoparticles, and fabrication using the EEW is a simple and economic process. Therefore, it can be potentially employed to circumvent this problem. In this work, we propose the synthesis of Fe-Cu nanoparticles using EEW in a suitable solution. The powder shape, size distribution, and alloying state are analyzed and discussed according to the conditions of the EEW.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Identification of the reconstruction induced high-entropy spinel oxide nanosheets for boosting alkaline water oxygen evolution
Xuexue Wang, Runqing Lu, Shanhe Gong, Shaokang Yang, Wenbo Wang, Zhongti Sun, Xiaozhen Zhang, Jun Liu, Xiaomeng Lv
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 503: 158488. CrossRef - Trends in bimetallic nanomaterials and methods for the removal of p-nitrophenol and its derivatives from wastewater
M. S. Qatan, F. Arshad, M. Miskam, G. A. Naikoo
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology.2024; 21(5): 5247. CrossRef - Control of cluster coalescence during formation of bimetallic nanoparticles and nanoalloys obtained via electric explosion of two wires
K.V. Suliz, A.Yu. Kolosov, V.S. Myasnichenko, N.I. Nepsha, N.Yu. Sdobnyakov, A.V. Pervikov
Advanced Powder Technology.2022; 33(3): 103518. CrossRef
- Identification of the reconstruction induced high-entropy spinel oxide nanosheets for boosting alkaline water oxygen evolution
- [English]
- Interaction of Detonation Nanodiamonds with Hispidin
- Changkyu Rhee, Whungwhoe Kim, Andrey E. Burov, Alexey P. Puzyr, Vladimir S. Bondar
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):458-463. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.458
- 527 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
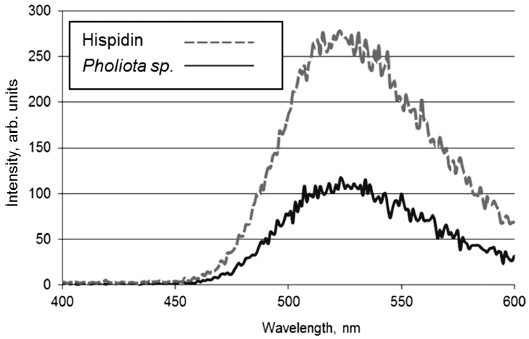
PDF Hispidin is a secondary metabolite found in numerous medicinal mushrooms that has attracted significant attention, owing to its distinct biological effects, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and cytoprotective properties. Experiments are being carried out to study the interaction of detonation nanodiamonds (DNDs) with synthetic and natural hispidin sourced from extracts of
Pholiota sp. fungus. The bioluminescence method is used to determine the adsorption/ desorption properties of DNDs toward hispidin. It is found that hispidin forms strong conjugates with DNDs, and the use of various eluents does not result in a significant release of the adsorbed hispidin molecules. DND-bovine serum albumin (BSA) complex, where DNDs serve as a carrier for the protein and the latter acts as a hispidin sorbent, has been developed and applied in hispidin adsorption/desorption tests. The results support the use of the DNDs as a carrier for hispidin in medical applications. They also advocate the application of the DND-BSA complex for isolating the substance from fungal extracts.
- [English]
- Features of Nickel Nanoparticles Structure Synthesized by the Spark Discharge Method
- C. K. Rhee, A. D. Maksimov, I. V. Beketov, A. I. Medvedev, A. M. Murzakaev
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):464-467. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.464
- 1,026 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
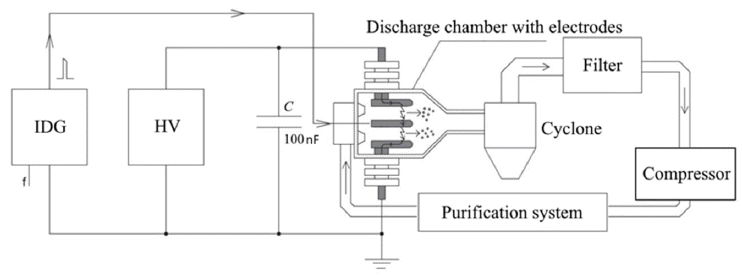
PDF Nickel nanopowders are obtained by the spark discharge method, which is based on the evaporation of the electrode surface under the action of the discharge current, followed by vapor condensation and the formation of nanoparticles. Nickel electrodes with a purity of 99.99% are used to synthesize the nickel nanoparticles in the setup. Nitrogen is used as the carrier gas with a purity of 99.998%. XRD, TEM, and EDX analyses of the nanopowders are performed. Moreover, HRTEM images with measured interplanar spacings are obtained. In the nickel nanopowder samples, a phase of approximately 90 wt% with an expanded crystal lattice of 6.5% on average is found. The results indicate an unusual process of nickel nanoparticle formation when the spark discharge method is employed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Study of Spots and Craters Formed during Spark Discharge in Air on Electrodes Made of Different Metals
A. D. Maksimov, E. I. Azarkevich, I. V. Beketov, D. S. Koleukh
Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics.2025; 89(10): 1941. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Craters Formed on Cathode and Anode Spots of a Spark Discharge in Air on Iron Electrodes
A. D. Maksimov, E. I. Azarkevich, I. V. Beketov, D. S. Koleukh
Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics.2023; 87(S2): S274. CrossRef
- Comparative Study of Spots and Craters Formed during Spark Discharge in Air on Electrodes Made of Different Metals
- [English]
- Effect of 50 μm class granules on the Injection Behavior of Brushite Bone Cement Prepared via Pre-dissolution Route
- Da Hye Mun, Sang Cheon Lee, Kyung-Sik Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):468-476. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.468

- 672 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The bone cement used for vertebroplasty must be sufficiently injectable. The introduction of granules reduces the amount of liquid required for liquefaction, implying that higher fluidity is achieved with the same amount of liquid. By employing β-tricalcium phosphate granules with an average diameter of 50 μm, changes in injectability are observed based on the paste preparation route and granular fraction. To obtain acceptable injectability, phase separation must be suppressed during injection, and sufficient capillary pressure to combine powder and liquid must work evenly throughout the paste. To achieve this, the granules should be evenly distributed. Reduced injection rates are observed for dry mixing and excessive granular content, owing to phase separation. All these correspond to conditions under which the clustered granules weakened the capillary pressure. The injected ratio of the paste formed by wet mixing displayed an inverted U-type shift with the granular fraction. The mixture of granules and powder resulted in an increase in the solid volume fraction, and a decrease in the liquid limit. This resulted in the enhancement of the liquidity, owing to the added liquid. It is inferred that the addition of granules improves the injectability, provided that the capillary pressure in the paste is maintained.
- [Korean]
- Photophysical Properties of Guest Molecules Confined in Nanopores
- Suhyeon Park, Juyeong Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):477-483. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.477
- 418 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
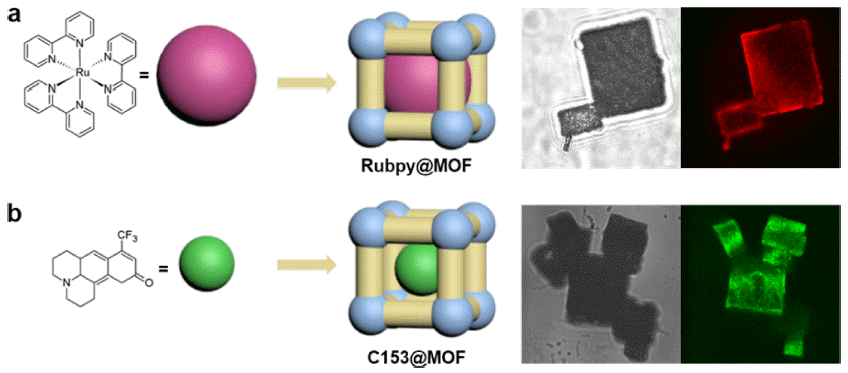
PDF Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are of significant interest because of their high porosity, which facilitates their utilization in gas storage and catalysis. To enhance their current properties in these applications, it is necessary to elucidate the interactions between molecules in a confined environment that differ from those in bulk conditions. Herein, we study the confined molecular interaction by investigating the solvent-dependent photophysical properties of two different-sized molecules inside MOF-5. Ruthenium
tris -bipyridine (Rubpy) and coumarin 153 (C153) are encapsulated in MOF-5. Rubpy with MOF-5 (Rubpy@MOF) is prepared by building MOF-5 around it, resulting in limited space for solvent molecules in the pores. The smaller C153 is encapsulated in the preformed MOF-5 (C153@MOF) by simply soaking the MOF in a concentrated C153 solution. C153@MOF permits more space for solvent molecules in the pore. Their characteristic absorption and emission spectra are examined to elucidate the confined molecular interactions. Rubpy@MOF and C153@MOF exhibit different spectral shifts compared to the guest molecules under bulk conditions. This discrepancy is attributed to the different micro-environments inside the pores, derived from confined host-guest interactions in the interplay of solvent molecules.
- [Korean]
- Real-time Collection and Correlation of Viscosity and Acoustic Data During Ball Milling Process
- Hyeondeok Jeong, Young-Beom Kim, Sung-Soo Ryu, Seiki Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):484-489. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.484

- 752 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, acoustic and viscosity data are collected in real time during the ball milling process and analyzed for correlation. After fast Fourier transformation (FFT) of the acoustic data, changes in the signals are observed as a function of the milling time. To analyze this quantitatively, the frequency band is divided into 1 kHz ranges to obtain an integral value. The integrated values in the 2–3 kHz range of the frequency band decrease linearly, confirming that they have a high correlation with changes in viscosity. The experiment is repeated four times to ensure the reproducibility of the data. The results of this study show that it is possible to estimate changes in slurry properties, such as viscosity and particle size, during the ball milling process using an acoustic signal.
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Debinding Process of High Purity Alumina Ceramic Fabricated by DLP 3D Printing
- Hyun-Been Lee, Hye-Ji Lee, Kyung-Ho Kim, Sung-Soo Ryu, Yoonsoo Han
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):490-497. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.490
- 1,099 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
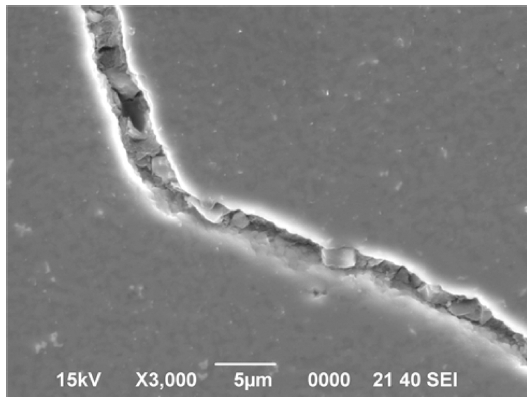
PDF The 3D printing process provides a higher degree of freedom when designing ceramic parts than the conventional press forming process. However, the generation and growth of the microcracks induced during heat treatment is thought to be due to the occurrence of local tensile stress caused by the thermal decomposition of the binder inside the green body. In this study, an alumina columnar specimen, which is a representative ceramic material, is fabricated using the digital light process (DLP) 3D printing method. DTG analysis is performed to investigate the cause of the occurrence of microcracks by analyzing the debinding process in which microcracks are mainly generated. HDDA of epoxy acrylates, which is the main binder, rapidly debinded in the range of 200 to 500°C, and microcracks are observed because of real-time microscopic image observation. For mitigating the rapid debinding process of HDDA, other types of acrylates PETA, PUA, and MMA are added, and the effect of these additives on the debinding rate is investigated. By analyzing the DTG in the 25 to 300°C region, it is confirmed that the PETA monomer and the PUA monomer can suppress the rapid decomposition rate of HDDA in this temperature range.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Optimization of Al2O3 Microchannels Using DLP-Based 3D Printing
Jun-Min Cho, Yong-Jun Seo, Yoon-Soo Han
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(1): 59. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Optimization of Al2O3 Microchannels Using DLP-Based 3D Printing
- [Korean]
- Effect of Morphological Control of Secondary Phase using Yb2O3 and Ca-Al-Si-O-based Glass on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of AlN
- Dong Kyu Choi, Shi Yeon Kim, Dong Hun Yeo, Hyo Soon Shin, Dae Yong Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):498-502. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.498
- 700 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
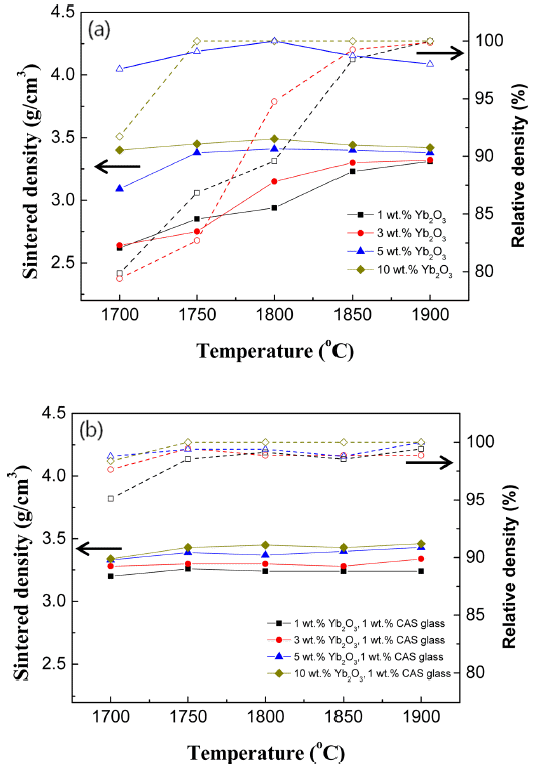
PDF We investigate the effects of Yb2O3 and calcium aluminosilicate (CAS) glass as sintering additives on the sintering behavior of AlN. The AlN specimens are sintered at temperatures between 1700°C and 1900°C for 2 h in a nitrogen atmosphere. When the Yb2O3 content is low (within 3 wt.%), an isolated shape of secondary phase is observed at the AlN grain boundary. In contrast, when 3 wt.% Yb2O3 and 1 wt.% CAS glass are added, a continuous secondary phase is formed at the AlN grain boundary. The thermal conductivity decreases when the CAS glass is added, but the sintering density does not decrease. In particular, when 10 wt.% Yb2O3 and 1 wt.% CAS glass are added to AlN, the flexural strength is the highest, at 463 MPa. These results are considered to be influenced by changes in the microstructure of the secondary phase of AlN.
- [Korean]
- Experimental Study on Improving Compressive Strength of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Reinforced Cement Composite
- Yomin Choi, Hyun‐Gyoo Shin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):503-508. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.503

- 481 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The mechanical properties and microstructures of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN)-reinforced cement composites are experimentally studied for three and seven curing days. Various sizes (5, 10, and 18 μm) and concentrations (0.1%, 0.25%, 0.5%, and 1.0%) of h-BN are dispersed by the tip ultrasonication method in water and incorporated into the cement composite. The compressive strength of the h-BN reinforced cements increases by 40.9%, when 0.5 wt% of 18 μm-sized h-BN is added. However, the compressive strength decreases when the 1.0 wt% cement composite is added, owing to the aggregation of the h-BNs in the cement composite. The microstructural characterization of the h-BN-reinforced cement composite indicates that the h-BNs act as bridges connecting the cracks, resulting in improved mechanical properties for the reinforced cement composite.
- [Korean]
- Review on Characterization Method and Recent Research Trend about Metal Powder for Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) Process
- Bin Lee, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Young Il Kim, Do Hoon Kim, Yong Son, Kyoung-Tae Park, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):509-519. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.509
- 956 View
- 8 Download
- 8 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
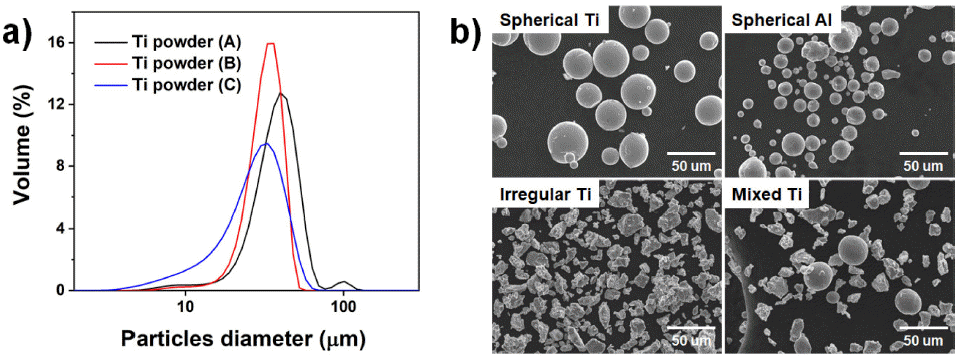
PDF A well-established characterization method is required in powder bed fusion (PBF) metal additive manufacturing, where metal powder is used. The characterization methods from the traditional powder metallurgy process are still being used. However, it is necessary to develop advanced methods of property evaluation with the advances in additive manufacturing technology. In this article, the characterization methods of powders for metal PBF are reviewed, and the recent research trends are introduced. Standardization status and specifications for metal powder for the PBF process which published by the ISO, ASTM, and MPIF are also covered. The establishment of powder characterization methods are expected to contribute to the metal powder industry and the advancement of additive manufacturing technology through the creation of related databases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
Enhanced flow properties of SiO
2
nanoparticles coated low-cost hydrogenation-dehydrogenation Ti-6Al-4V powder for powder bed fusion process
Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Tae hu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(2): 95. CrossRef -
SiO
2
nanoparticle-coated Ti-6Al-4V spherical powder for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process
Jongik Lee, Taehoo Kang, Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Sanghee Jung, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 333. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 288. CrossRef - A Study on Fabrication of PCD Endmill Holder using PBF Additive Manufacturing Technology
Min-Woo Sa, Ho-Min Son, Kyung-Hwan Park, Sang-Geun Lee, Dae-Ho Shin, Dong-Gyu Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2024; 23(6): 124. CrossRef - Rheological Characteristic Analysis Methods and Tests of Metal Powders for PBF Additive Manufacturing
Wan-Sik Woo, Ho-Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2023; 22(10): 1. CrossRef - Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
SangCheol Park, InYeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee, Bin Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(7): 534. CrossRef - Enhancing spreadability of hydrogenation-dehydrogenation titanium powder and novel method to characterize powder spreadability for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing
Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, InYeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Dongju Lee, Bin Lee
Materials & Design.2022; 223: 111247. CrossRef
-
Enhanced flow properties of SiO
2
nanoparticles coated low-cost hydrogenation-dehydrogenation Ti-6Al-4V powder for powder bed fusion process
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI




 First
First Prev
Prev


