Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Development of Composite-film-based Flexible Energy Harvester using Lead-free BCTZ Piezoelectric Nanomaterials
- Gwang Hyeon Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, Haksu Jang, Cheol Min Kim, Donghun Lee, Kwi-Il Park
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):16-22. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.16
- 1,833 View
- 32 Download
- 10 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
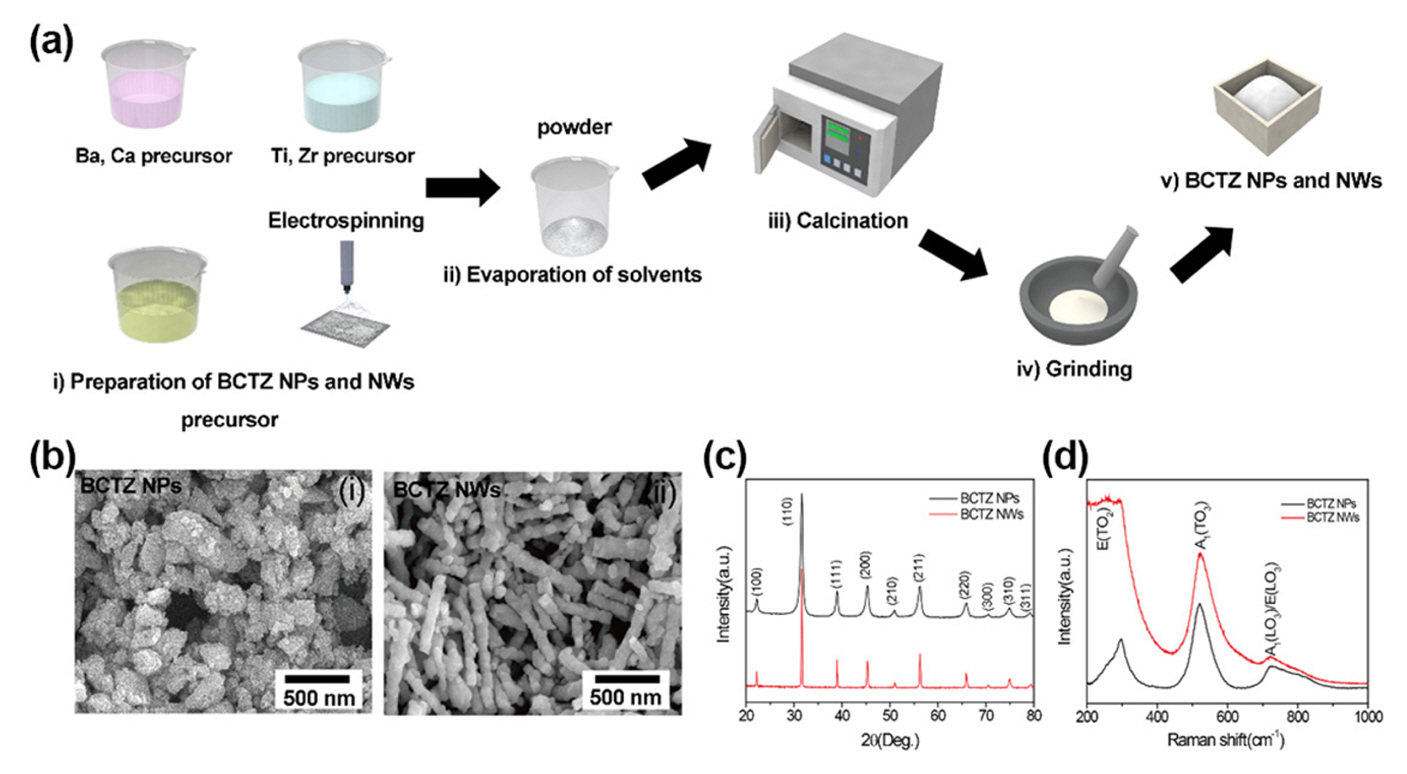
PDF - Composite-based piezoelectric devices are extensively studied to develop sustainable power supply and selfpowered devices owing to their excellent mechanical durability and output performance. In this study, we design a leadfree piezoelectric nanocomposite utilizing (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 (BCTZ) nanomaterials for realizing highly flexible energy harvesters. To improve the output performance of the devices, we incorporate porous BCTZ nanowires (NWs) into the nanoparticle (NP)-based piezoelectric nanocomposite. BCTZ NPs and NWs are synthesized through the solidstate reaction and sol-gel-based electrospinning, respectively; subsequently, they are dispersed inside a polyimide matrix. The output performance of the energy harvesters is measured using an optimized measurement system during repetitive mechanical deformation by varying the composition of the NPs and NWs. A nanocomposite-based energy harvester with 4:1 weight ratio generates the maximum open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current of 0.83 V and 0.28 A, respectively. In this study, self-powered devices are constructed with enhanced output performance by using piezoelectric energy harvesting for application in flexible and wearable devices.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unidirectional porous PVDF Piezoelectrets fabricated via gradient ice-templating for enhanced energy harvesting performance
HyoMin Jeon, Seo Young Yoon, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, HakSu Jang, Changyeon Baek, Tiandong Zhang, Geon-Tae Hwang, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Sustainable Materials and Technologies.2026; 47: e01888. CrossRef - In Situ Amidation‐Derived Interfacial Modulation for Homogeneous Ultra‐High Nanoparticle Loading Toward Robust and Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
HakSu Jang, In Beom Heo, Changyeon Baek, Dong Won Jeon, Donghun Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Hyejeong Choi, HyoMin Jeon, SungHoon Kim, Hyunseung Kim, Jihun Choi, Hyun‐Soo Chang, Chang Kyu Jeong, Min‐Ku Lee, Jun Mo Koo, Tiandong Zhang, Geon‐Tae Hwang, S
Advanced Functional Materials.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Long‐Lasting, Steady and Enhanced Energy Harvesting by Inserting a Conductive Layer into the Piezoelectric Polymer
HakSu Jang, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Dong Won Jeon, Hyeon Jun Park, BitNa Bae, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Cheol Min Kim, Changyeon Baek, Min‐Ku Lee, Sung Beom Cho, Gyoung‐Ja Lee, Kwi‐Il Park
Advanced Functional Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Flexible hybrid thermoelectric films made of bismuth telluride-PEDOT:PSS composites enabled by freezing-thawing process and simple chemical treatment
Cheol Min Kim, Seoha Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Bitna Bae, Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Gwang Hyun Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Haksu Jang, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Chemistry.2025; 44: 102532. CrossRef - Dual-controlled piezoelectric composite film with enhanced crystallinity and defect-free via solvent vapor treatment
HakSu Jang, Hyeon Jun Park, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, BitNa Bae, HyoMin Jeon, DongHun Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Nano Energy.2025; 136: 110705. CrossRef - Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(1): 16. CrossRef - Flexible Hybrid Energy Harvester based on Thermoelectric Composite Film and Electrospun Piezopolymer Membranes
Hyomin Jeon, Cheol Min Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, Hyejeong Choi, HakSu Jang, Kwi-Il Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(2): 104. CrossRef - Flexible Thermoelectric Energy Harvester with Stacked Structure of Thermoelectric Composite Films Made of PVDF and Bi2Te3-Based Particles
Da Eun Shin, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Kwi-Il Park
ACS Applied Energy Materials.2024; 7(19): 8288. CrossRef - Enhanced energy harvesting of fibrous composite membranes via plasma-piezopolymer interaction
Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, HakSu Jang, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Dong Hun Lee, Gwang Hyun Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Nano Energy.2024; 131: 110299. CrossRef - CoFe2O4-BaTiO3 core-shell-embedded flexible polymer composite as an efficient magnetoelectric energy harvester
Bitna Bae, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Cheol Min Kim, Jungho Ryu, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Geon-Tae Hwang, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Physics.2024; 48: 101567. CrossRef
- Unidirectional porous PVDF Piezoelectrets fabricated via gradient ice-templating for enhanced energy harvesting performance
- [Korean]
- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
- Jin-Kwon Kim, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Nahm Sahn, Sung-Soo Ryu, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):409-414. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.409
- 589 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF YSZ (Y2O3-stabilized zirconia)-based ceramics have excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength and wear resistance. In the application, YSZ is utilized in the bead mill, a fine-grinding process. YSZ-based parts, such as the rotor and pin, can be easily damaged by continuous application with high rpm in the bead mill process. In that case, adding WC particles improves the tribological and mechanical properties. YSZ-30 vol.% WC composite ceramics are manufactured via hot pressing under different pressures (10/30/60 MPa). The hot-pressed composite ceramics measure the physical properties, such as porosity and bulk density values. In addition, the phase formation of these composite ceramics is analyzed and discussed with those of physical properties. For the increased applied pressure of hot pressing, the tetragonality of YSZ and the crystallinity of WC are enhanced. The mechanical properties indicate an improved tendency with the increase in the applied pressure of hot pressing.
- [Korean]
- Effects of the Content of MgO Additive and Sintering Temperature on the Densification of Alumina Insulator
- Ri Joo Kim, Han Gyeol Jeong, Ye Ji Son, Sang Ki Ko, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):249-254. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.249

- 1,443 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The influence of MgO addition on the densification and microstructure of alumina (Al2O3) was studied. Compacted alumina specimens were manufactured using ball-milling and one-directional pressing followed by sintering at temperatures below 1700oC. Relative density, shrinkage, hardness, and microstructure were investigated using analytical tools such as FE-SEM, EDS, and XRD. When the MgO was added up to 5.0 wt% and sintered at 1500°C and 1600°C, the relative density exhibited an average value of 97% or more at both temperatures. The maximum density of 99.2% was with the addition of 0.5 wt% MgO at 1500°C. Meanwhile, the specimens showed significantly lower density values when sintered at 1400°C than at 1500°C and 1600°C owing to the relatively low sintering temperature. The hardness and shrinkage data also showed a similar trend in the change in density, implying that the addition of approximately 0.5 wt% MgO can promote the densification of Al2O3. Studying the microstructure confirmed the uniformity of the sintered alumina. These results can be used as basic compositional data for the development of MgOcontaining alumina as high-dielectric insulators.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hardness of Ultra-High-Density Alumina Fabricated using the Aerodynamic Levitation Process
Ye-Ji Son, Dong-Wook Kim, Seung-Wook Kim, Hyo-Min Kim, Hui-Woong Kang, Min-Yeong Ha, Dae-Yong Jeong
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2025; 35(9): 436. CrossRef
- Hardness of Ultra-High-Density Alumina Fabricated using the Aerodynamic Levitation Process
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characteristics of YSZ-TiC Ceramics Composite by Using Hot Pressing
- Jae-Hyung Choi, Ji-Young Choi, Seongwon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):381-388. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.381
- 1,515 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Zirconia has excellent mechanical properties, such as high fracture toughness, wear resistance, and flexural strength, which make it a candidate for application in bead mills as milling media as well as a variety of components. In addition, enhanced mechanical properties can be attained by adding oxide or non-oxide dispersing particles to zirconia ceramics. In this study, the densification and mechanical properties of YSZ-TiC ceramic composites with different TiC contents and sintering temperatures are investigated. YSZ - x vol.% TiC (x=10, 20, 30) system is selected as compositions of interest. The mixed powders are sintered using hot pressing (HP) at different temperatures of 1300, 1400, and 1500°C. The densification behavior and mechanical properties of sintered ceramics, such as hardness and fracture toughness, are examined.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
Jin-Kwon Kim, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Nahm Sahn, Sung-Soo Ryu, Seongwon Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(5): 409. CrossRef
- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
- [Korean]
- Multicomponent IGZO Ceramics for Transparent Electrode Target Fabricated from Oxides and Nitrates
- Hyun-Kwun Lee, Ji-Hye Yoon, Kyeong-Sik Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):375-382. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.375
- 583 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Homogeneous multicomponent indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) ceramics for transparent electrode targets are prepared from the oxides and nitrates as the source materials, and their properties are characterized. The selected compositions were In2O3:Ga2O3:ZnO = 1:1:2, 1:1:6, and 1:1:12 in mole ratio based on oxide. As revealed by X-ray diffraction analysis, calcination of the selected oxide or nitrides at 1200°C results in the formation of InGaZnO4, InGaZn3O6, and InGaZn5O8 phases. The 1:1:2, 1:1:6, and 1:1:12 oxide samples pressed in the form of discs exhibit relative densities of 96.9, 93.2, and 84.1%, respectively, after sintering at 1450°C for 12 h. The InGaZn3O6 ceramics prepared from the oxide or nitrate batches comprise large grains and exhibit homogeneous elemental distribution. Under optimized conditions, IGZO multicomponent ceramics with controlled phases, high densities, and homogeneous microstructures (grain and elemental distribution) are obtained.
- [English]
- Study of Fabrication and Improvement of Mechanical Properties of Mg-based Inorganic Fiber using Reflux Process and Silica Coating
- Ri Yu, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):195-200. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.195

- 1,210 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Whisker-type magnesium hydroxide sulfate hydrate (5Mg(OH)2·MgSO4·3H2O, abbreviated 513 MHSH), is used in filler and flame-retardant composites based on its hydrate phase and its ability to undergo endothermic dehydration in fire conditions, respectively. In general, the length of whiskers is determined according to various synthetic conditions in a hydrothermal reaction with high temperature (~180°C). In this work, high-quality 513 MHSH whiskers are synthesized by controlling the concentration of the raw material in ambient conditions without high pressure. Particularly, the concentration of the starting material is closely related to the length, width, and purity of MHSH. In addition, a ceramic-coating system is adopted to enhance the mechanical properties and thermal stability of the MHSH whiskers. The physical properties of the silica-coated MHSH are characterized by an abrasion test, thermogravimetric analysis, and transmission electron microscopy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and Morphology Control of Needle Type 513 MHSH and Mg(OH)2 from Dolomite
Jiyeon Kim, HyunSeung Shim, Seong-Ju Hwang, YooJin Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(5): 399. CrossRef - Effect of sulfate ion on synthesis of 5 Mg(OH)2·MgSO4·3H2O whiskers using non-hydrothermal method with acid catalyst
Areum Choi, Nuri Oh, YooJin Kim
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2022; 59(2): 224. CrossRef - Study of SiO2 coating and carboxylic surface-modification on Mg-based inorganic fiber by one-step reflux reaction
Minsol Park, Areum Choi, Seiki Kim, Wooyoung Shim, YooJin Kim
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2022; 59(6): 869. CrossRef - Effect of H2SO4 and Reaction Time on Synthesis of 5Mg(OH)2∙MgSO4∙3H2O Whiskers using Hydrothermal Reaction
Areum Choi, Nuri Oh, YooJin Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 401. CrossRef
- Synthesis and Morphology Control of Needle Type 513 MHSH and Mg(OH)2 from Dolomite
- [Korean]
- Effects of the Mixing Method and Sintering Temperature on the Characteristics of PZNN-PZT Piezoelectric Ceramic Materials
- So Won Kim, Yong Jeong Jeong, Hee Chul Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):487-493. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.487
- 968 View
- 6 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
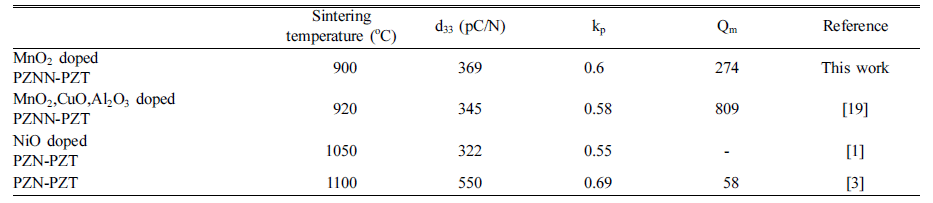
PDF The impact of different mixing methods and sintering temperatures on the microstructure and piezoelectric properties of PZNN-PZT ceramics is investigated. To improve the sinterability and piezoelectric properties of these ceramics, the composition of 0.13Pb((Zn0.8Ni0.2)1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.87Pb(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 (PZNN-PZT) containing a Pb-based relaxor component is selected. Two methods are used to create the powder for the PZNN-PZT ceramics. The first involves blending all source powders at once, followed by calcination. The second involves the preferential creation of columbite as a precursor, by reacting NiO with Nb2O5 powder. Subsequently, PZNN-PZT powder can be prepared by mixing the columbite powder, PbO, and other components, followed by an additional calcination step. All the PZNNPZT powder samples in this study show a nearly-pure perovskite phase. High-density PZNN-PZT ceramics can be fabricated using powders prepared by a two-step calcination process, with the addition of 0.3 wt% MnO2 at even relatively low sintering temperatures from 800°C to 1000°C. The grain size of the ceramics at sintering temperatures above 900°C is increased to approximately 3 μm. The optimized PZNN-PZT piezoelectric ceramics show a piezoelectric constant (d33) of 360 pC/N, an electromechanical coupling factor (kp) of 0.61, and a quality factor (Qm) of 275.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Analysis of Edge Chipping in LiTaO3 Wafer Grinding Using a Scratch Test and FEA Simulation
Haeseong Hwang, Seungho Han, Hyunseop Lee
Lubricants.2023; 11(7): 297. CrossRef - A generalized rule for phase transition generated by additives in piezoelectric ceramics
Jae-Min Cha, Young-Kook Moon, Jung-hwan Kim, Hyun-Ae Cha, Jong-Jin Choi, Byung-Dong Hahn, Seog-Young Yoon, Cheol-Woo Ahn
Materials Today Communications.2023; 37: 107290. CrossRef - Low-Temperature Sintering Properties of Bi2O3 Doped PZT-5H Piezoelectric Ceramics
Wanzi Mao, Qing Xu, Duanping Huang, Huajun Sun, Feng Zhang, Xiaobin Xie
Journal of Electronic Materials.2023; 52(5): 3334. CrossRef - Effect of LiBiO2 on low-temperature sintering of PZT-PZNN ceramics
Sung Cheul Hong, Shi Yeon Kim, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Zee Hoon Park, Sahn Nahm
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2022; 59(5): 638. CrossRef - Two-Stage De-binding for Cu Electrode Application to PZT-PZNN Multilayer Actuator
Sung Cheul Hong, Zeehoon Park, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Sahn Nahm
Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Materials.2022; 23(4): 348. CrossRef
- An Analysis of Edge Chipping in LiTaO3 Wafer Grinding Using a Scratch Test and FEA Simulation
- [English]
- Development of Powder Injection Molding Process for a Piezoelectric PAN-PZT Ceramics
- Jun Sae Han, Dong Yong Park, Dongguo Lin, Kwang Hyun Chung, Ravi Bollina, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):112-119. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.112

- 1,590 View
- 11 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A powder injection molding process is developed and optimized for piezoelectric PAN-PZT ceramics. Torque rheometer experiments are conducted to determine the optimal solids loading, and the rheological property of the feedstock is evaluated using a capillary rheometer. Appropriate debinding conditions are chosen using a thermal gravity analyzer, and the debound specimens are sintered using sintering conditions determined in a preliminary investigation. Piezoelectric performance measures, including the piezoelectric charge constant and dielectric constant, are measured to verify the developed process. The average values of the measured piezoelectric charge constant and dielectric constant are 455 pC/N and 1904, respectively. Powder injection molded piezoelectric ceramics produced by the optimized process show adequate piezoelectric performance compared to press-sintered piezoelectric ceramics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on Rheological Behavior and Mechanical Properties of PMN–PZT Ceramic Feedstock
Jae Man Park, Jun Sae Han, Joo Won Oh, Seong Jin Park
Metals and Materials International.2021; 27(5): 1069. CrossRef - Investigation of stainless steel 316L/zirconia joint part fabricated by powder injection molding
Chang Woo Gal, Sang Soo Han, Jun Sae Han, Dongguo Lin, Seong Jin Park
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2019; 16(1): 315. CrossRef - Fabrication of pressureless sintered Si3N4 ceramic balls by powder injection molding
Chang Woo Gal, Gi Woung Song, Woon Hyung Baek, Hyung Kyu Kim, Dae Keun Lee, Ki Wook Lim, Seong Jin Park
Ceramics International.2019; 45(5): 6418. CrossRef - Experimental analysis for fabrication of high-aspect-ratio piezoelectric ceramic structure by micro-powder injection molding process
Jun Sae Han, Chang Woo Gal, Jae Man Park, Jong Hyun Kim, Seong Jin Park
Materials Research Express.2018; 5(4): 046303. CrossRef
- Study on Rheological Behavior and Mechanical Properties of PMN–PZT Ceramic Feedstock
- [English]
- Processing Methods for the Preparation of Porous Ceramics
- Rizwan Ahmad, Jang-Hoon Ha, In-Hyuck Song
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):389-398. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.389
- 3,979 View
- 124 Download
- 22 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Macroporous ceramics with tailored pore size and shape could be used for well-established and emerging applications, such as molten metal filtration, biomaterial, catalysis, thermal insulation, hot gas filtration and diesel particulate filters. In these applications, unique properties of porous materials were required which could be achieved through the incorporation of macro-pores into ceramics. In this article, we reviewed the main processing techniques which can be used for the fabrication of macroporous ceramics with tailored microstructure. Partial sintering, replica templates, sacrificial fugutives, and direct foaming techniques was described here and compared in terms of micro-structures and mechanical properties that could be achieved. The main focus was given to the direct foaming technique which was simple and versatile approach that allowed the fabrication of macro-porous ceramics with tailored features and properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Contribution of microscale stochastic truss models to investigate the macroscale elasticity constants of porous ceramics
Thierry Canet, Gilles Dusserre, Thierry Cutard
European Journal of Mechanics - A/Solids.2025; 111: 105561. CrossRef - Synthesis and properties of high alumina cement-based porous composites in the ZrO2-CaO-Al2O3 system
Yesica L. Bruni, María F. Hernández, Susana Conconi, Gustavo Suárez
Ceramics International.2025; 51(23): 39794. CrossRef - Morphology and phase analysis of cordierite ceramic foams with Ag nanoparticles
J. Kupková, G. Kratošová, K. Čech Barabaszová, G. Simha Martynková
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering.2025; 1337(1): 012004. CrossRef - Organic waste-derived pore formers for macroporous ceramics fabrication: A review on synthesis, durability properties and potential applications
T.T. Dele-Afolabi, M.A. Azmah Hanim, A.A. Oyekanmi, M.N.M. Ansari, Surajudeen Sikiru, O.J. Ojo-Kupoluyi
Materials Today Sustainability.2024; 27: 100824. CrossRef - Chemistry and Physics of Wet Foam Stability for Porous Ceramics: A Review
Kamrun Nahar Fatema, Md Rokon Ud Dowla Biswas, Jung Gyu Park, Ik Jin Kim
Micro.2024; 4(4): 552. CrossRef - Investigating mass transfer coefficients in lean methane combustion reaction through the morphological and geometric analysis of structured open cell foam catalysts
Carmen W. Moncada Quintero, Hernan G. Mazzei, Marion Servel, Frédéric Augier, Yacine Haroun, Jean-François Joly, Stefania Specchia
Chemical Engineering Science.2023; 281: 119138. CrossRef - Composite PLGA–Nanobioceramic Coating on Moxifloxacin-Loaded Akermanite 3D Porous Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Regeneration
Georgia K. Pouroutzidou, Lambrini Papadopoulou, Maria Lazaridou, Konstantinos Tsachouridis, Chrysanthi Papoulia, Dimitra Patsiaoura, Ioannis Tsamesidis, Konstantinos Chrissafis, George Vourlias, Konstantinos M. Paraskevopoulos, Antonios D. Anastasiou, Dim
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(3): 819. CrossRef - Development of high strength large open porosity alumina ceramics using the sacrificial phase route: The role of the sacrificial phase fineness
Julian Alzukaimi, Rafi Jabrah
Ceramics International.2023; 49(2): 2923. CrossRef - Sustainable nanocomposite porous absorbent and membrane sieves: Definition, classification, history, properties, synthesis, applications, and future prospects
Sameer Ahmad, Weqar Ahmad Siddiqi, Sharif Ahmad
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2023; 11(2): 109367. CrossRef - Processing and characterization of porous composites based on CaAl4O7/CaZrO3
Yesica L. Bruni, María S. Conconi, María F. Hernández, Gustavo Suárez
Ceramics International.2023; 49(23): 37630. CrossRef - Trace addition of cellulose nanofiber in gel-casting system for structurally controlled porous ceramics towards superior thermal-insulating property
Yunzi Xin, Takashi Shirai
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan.2022; 130(5): 355. CrossRef - State-of-the-art review of fabrication, application, and mechanical properties of functionally graded porous nanocomposite materials
Ismail Barbaros, Yongmin Yang, Babak Safaei, Zhicheng Yang, Zhaoye Qin, Mohammed Asmael
Nanotechnology Reviews.2022; 11(1): 321. CrossRef - A review of petroleum emulsification types, formation factors, and demulsification methods
Ahmed Abdulrazzaq Hadi, Ali Abdulkhabeer Ali
Materials Today: Proceedings.2022; 53: 273. CrossRef - SLURRY OPTIMISATION FOR FAST FREEZE-DRYING OF POROUS ALUMINA
Kritkaew Somton
Ceramics - Silikaty.2021; : 368. CrossRef - Recycling food, agricultural, and industrial wastes as pore-forming agents for sustainable porous ceramic production: A review
Siti Zuliana Salleh, Afiqah Awang Kechik, Abdul Hafidz Yusoff, Mustaffa Ali Azhar Taib, Maryana Mohamad Nor, Mardawani Mohamad, Tse Guan Tan, Arlina Ali, Mohamad Najmi Masri, Julie Juliewatty Mohamed, Siti Koriah Zakaria, Jia Geng Boon, Faisal Budiman, Pa
Journal of Cleaner Production.2021; 306: 127264. CrossRef - Novel noble-metal-free ceramic filter with controlled pore structure for environmental cleaning
Yunzi Xin, Sohei Nakagawa, Harumitsu Nishikawa, Takashi Shirai
Ceramics International.2021; 47(8): 11819. CrossRef - Fabrication of porous titania sheet via tape casting: Microstructure and water permeability study
Saber Ghannadi, Hossein Abdizadeh, Alireza Babaei
Ceramics International.2020; 46(7): 8689. CrossRef - Farklı Bağlayıcı ve Sinterleme Katkılarının SiC Seramik Prefom Mikroyapısı Üzerine Etkisi
Ebru Yılmaz, Fatih Çalışkan
Academic Perspective Procedia.2019; 2(3): 1309. CrossRef - The preparation and characterization of porous alumina ceramics using an eco‐friendly pore‐forming agent
Julian Alzukaimi, Rafi Jabrah
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2019; 16(2): 820. CrossRef - Wet Foam Stability from Colloidal Suspension to Porous Ceramics: A Review
Ik Jin Kim, Jung Gyu Park, Young Han Han, Suk Young Kim, James F. Shackelford
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2019; 56(3): 211. CrossRef - Processing of porous alumina by foaming method-effect of foaming agent, solid loading and binder
Soumya Devavarapu, Paritosh Chaudhuri, Aroh Shrivastava, Santanu Bhattacharyya
Ceramics International.2019; 45(9): 12264. CrossRef - Macroporous flexible polyvinyl alcohol lithium adsorbent foam composite prepared via surfactant blending and cryo-desiccation
Grace M. Nisola, Lawrence A. Limjuco, Eleazer L. Vivas, Chosel P. Lawagon, Myoung Jun Park, Ho Kyong Shon, Neha Mittal, In Wook Nah, Hern Kim, Wook-Jin Chung
Chemical Engineering Journal.2015; 280: 536. CrossRef
- Contribution of microscale stochastic truss models to investigate the macroscale elasticity constants of porous ceramics
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


