Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and High-Temperature Performance Evaluation of Light-Weight Insulation Materials and Coatings for Reusable Thermal Protection Systems
- Min-Soo Nam, Jong-Il Kim, Jaesung Shin, Hyeonjun Kim, Bum-Seok Oh, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):521-529. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00318
- 1,549 View
- 54 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
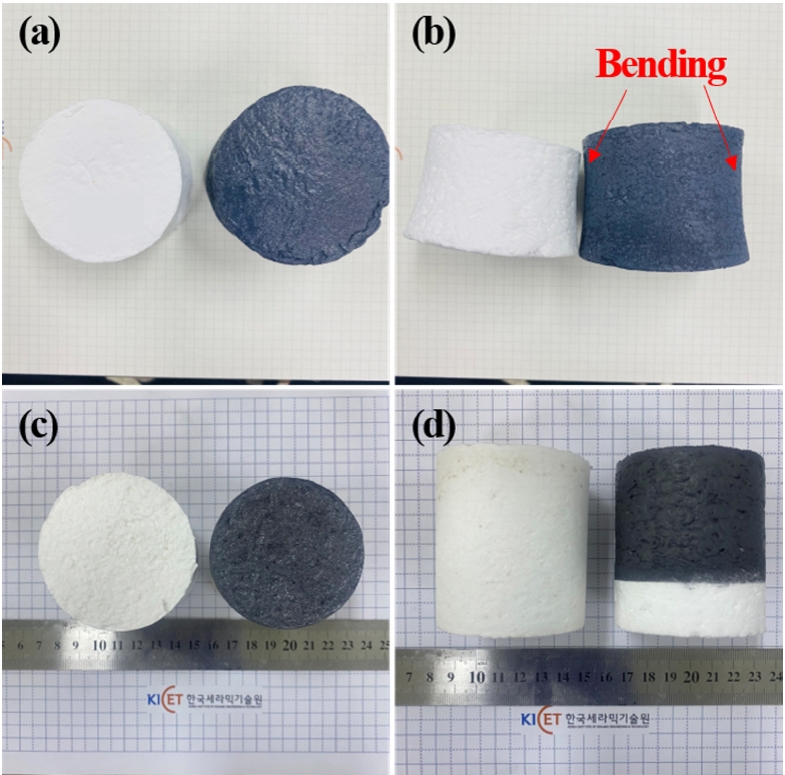
PDF - Light-weight ceramic insulation materials and high-emissivity coatings were fabricated for reusable thermal protection systems (TPS). Alumina-silica fibers and boric acid were used to fabricate the insulation, which was heat treated at 1250 °C. High-emissivity coating of borosilicate glass modified with TaSi2, MoSi2, and SiB6 was applied via dip-and-spray coating methods and heat-treated at 1100°C. Testing in a high-velocity oxygen fuel environment at temperatures over 1100 °C for 120 seconds showed that the rigid structures withstood the flame robustly. The coating effectively infiltrated into the fibers, confirmed by scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction analyses. Although some oxidation of TaSi2 occurred, thereby increasing the Ta2O5 and SiO2 phases, no significant phase changes or performance degradation were observed. These results demonstrate the potential of these materials for reusable TPS applications in extreme thermal environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Durability Assessment of Tile-Type Reusable Thermal Protection Materials
Minjeong Kim, Seong Man Choi
Materials.2026; 19(2): 303. CrossRef
- Durability Assessment of Tile-Type Reusable Thermal Protection Materials
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Al-Ni-Co-Y Bulk Metallic Glass fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
- Jeong Pyo Lee, Jin Kyu Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):41-46. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.41
- 925 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
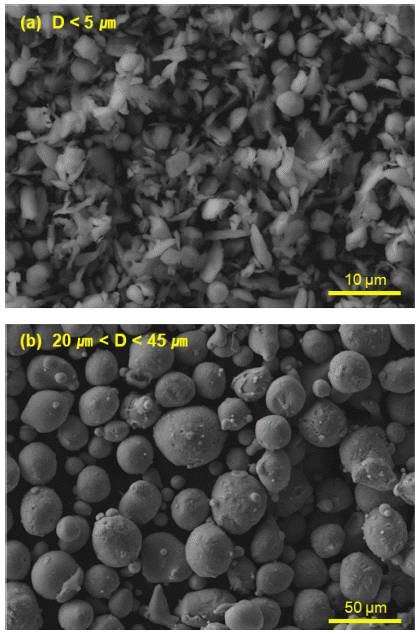
PDF In this study, an Al82Ni7Co3Y8 (at%) bulk metallic glass is fabricated using gas-atomized Al82Ni7Co3Y8 metallic glass powder and subsequent spark plasma sintering (SPS). The effect of powder size on the consolidation of bulk metallic glass is considered by dividing it into 5 μm or less and 20–45 μm. The sintered Al82Ni7Co3Y8 bulk metallic glasses exhibit crystallization behavior and crystallization enthalpy similar to those of the Al82Ni7Co3Y8 powder with 5 μm or less and it is confirmed that no crystallization occurred during the sintering process. From these results, we conclude that the Z-position-controlled spark plasma sintering process, using superplastic deformation by viscous flow in the supercooled liquid-phase region of amorphous powder, is an effective process for manufacturing bulk metallic glass.
- [Korean]
- Experimental Study on Improving Thermal Shock Resistance of Cement Composite Incorporating Hollow Glass Microspheres
- Yomin Choi, Hyun‐Gyoo Shin
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):505-510. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.505

- 759 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The thermal shock resistance of cement composites with hollow glass microspheres (HGM) is investigated. Cement composites containing various concentrations of HGM are prepared and their properties studied. The density, thermal conductivity, and coefficient of thermal expansion of the composites decrease with increasing HGM concentration. A thermal shock test is performed by cycling between -60 and 50ºC. After the thermal shock test, the compressive strength of the cement composite without HGM decreases by 28.4%, whereas the compressive strength of the cement composite with 30 wt% HGM decreases by 5.7%. This confirms that the thermal shock resistance of cement is improved by the incorporation of HGM. This effect is attributed to the reduction of the thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal expansion of the cement composite because of the incorporation of HGM, thereby reducing the occurrence of defects due to external temperature changes.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Light-weight Ceramic Insulation Materials by Using Oxide Ceramic Fibers for Reusable Thermal Protection Systems
- Seongwon Kim, Min-Soo Nam, Yoon-Suk Oh, Sahn Nahm, Jaesung Shin, Hyeonjun Kim, Bum-Seok Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):477-484. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.477
- 1,546 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Thermal protection systems (TPS) are a group of materials that are indispensable for protecting spacecraft from the aerodynamic heating occurring during entry into an atmosphere. Among candidate materials for TPS, ceramic insulation materials are usually considered for reusable TPS. In this study, ceramic insulation materials, such as alumina enhanced thermal barrier (AETB), are fabricated via typical ceramic processing from ceramic fiber and additives. Mixtures of silica and alumina fibers are used as raw materials, with the addition of B4C to bind fibers together. Reaction-cured glass is also added on top of AETB to induce water-proof functionality or high emissivity. Some issues, such as the elimination of clumps in the AETB, and processing difficulties in the production of reusable surface insulation are reported as well.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and High-Temperature Performance Evaluation of Light-Weight Insulation Materials and Coatings for Reusable Thermal Protection Systems
Min-Soo Nam, Jong-Il Kim, Jaesung Shin, Hyeonjun Kim, Bum-Seok Oh, Seongwon Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(6): 521. CrossRef
- Fabrication and High-Temperature Performance Evaluation of Light-Weight Insulation Materials and Coatings for Reusable Thermal Protection Systems
- [Korean]
- Effect of Morphological Control of Secondary Phase using Yb2O3 and Ca-Al-Si-O-based Glass on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of AlN
- Dong Kyu Choi, Shi Yeon Kim, Dong Hun Yeo, Hyo Soon Shin, Dae Yong Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):498-502. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.498
- 853 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
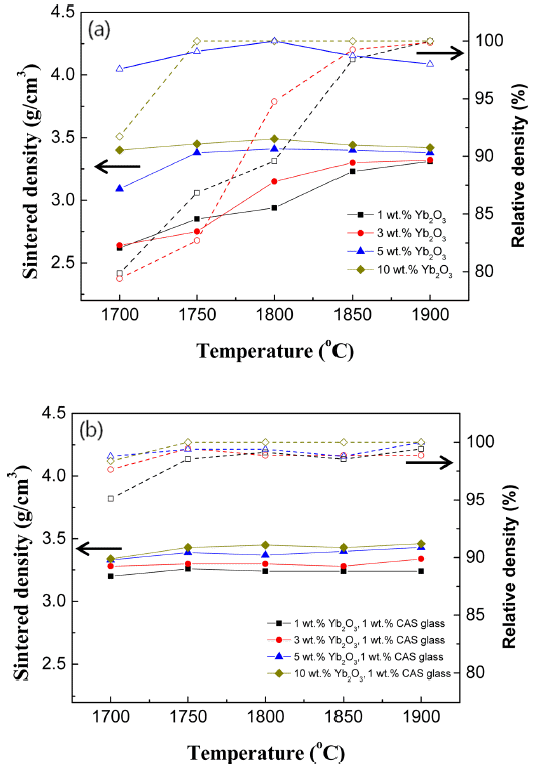
PDF We investigate the effects of Yb2O3 and calcium aluminosilicate (CAS) glass as sintering additives on the sintering behavior of AlN. The AlN specimens are sintered at temperatures between 1700°C and 1900°C for 2 h in a nitrogen atmosphere. When the Yb2O3 content is low (within 3 wt.%), an isolated shape of secondary phase is observed at the AlN grain boundary. In contrast, when 3 wt.% Yb2O3 and 1 wt.% CAS glass are added, a continuous secondary phase is formed at the AlN grain boundary. The thermal conductivity decreases when the CAS glass is added, but the sintering density does not decrease. In particular, when 10 wt.% Yb2O3 and 1 wt.% CAS glass are added to AlN, the flexural strength is the highest, at 463 MPa. These results are considered to be influenced by changes in the microstructure of the secondary phase of AlN.
- [Korean]
- Micro-deformation behavior of Brittle Hf-based Metallic Glass during Mechanical Milling
- Song-Yi Kim, A-Young Lee, Eun-Ji Cha, Do-Hun Kwon, Sung-Uk Hong, Min-Woo Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Min-Ha Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):246-250. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.246
- 675 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
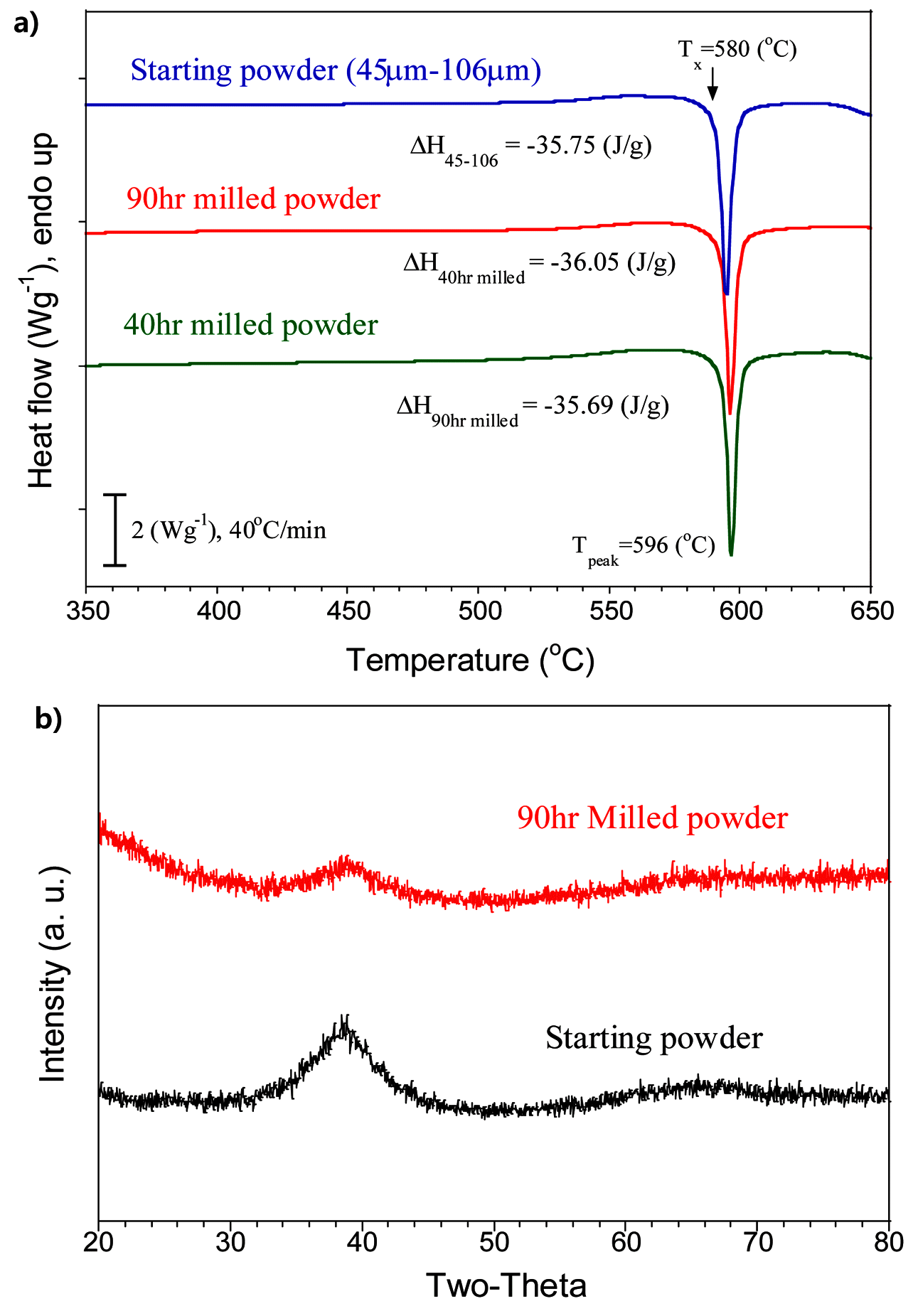
PDF In this study, we investigate the deformation behavior of Hf44.5Cu27Ni13.5Nb5Al10 metallic glass powder under repeated compressive strain during mechanical milling. High-density (11.0 g/cc) Hf-based metallic glass powders are prepared using a gas atomization process. The relationship between the mechanical alloying time and microstructural change under phase transformation is evaluated for crystallization of the amorphous phase. Planetary mechanical milling is performed for 0, 40, or 90 h at 100 rpm. The amorphous structure of the Hf-based metallic glass powders during mechanical milling is analyzed using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Microstructural analysis of the Hf-based metallic glass powder deformed using mechanical milling reveals a layered structure with vein patterns at the fracture surface, which is observed in the fracture of bulk metallic glasses. We also study the crystallization behavior and the phase and microstructure transformations under isothermal heat treatment of the Hf-based metallic glass.
- [English]
- Development of Powder Injection Molding Process for Fabrication of Glass Component
- Dongguo Lin, Junghyun Lee, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):26-32. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.26

- 2,415 View
- 22 Download
- 8 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Powder injection molding (PIM), which combines the advantages of powder metallurgy and plastic injection molding technologies, has become one of the most efficient methods for the net-shape production of both metal and ceramic components. In this work, plasma display panel glass bodies are prepared by the PIM process. After sintering, the hot isostatic pressing (HIP) process is adopted for improving the density and mechanical properties of the PIMed glass bodies. The mechanical and thermal behaviors of the prepared specimens are analyzed through bending tests and dilatometric analysis, respectively. After HIPing, the flexural strength of the prepared glass body reaches up to 92.17 MPa, which is 1.273 and 2.178 times that of the fused glass body and PIMed bodies, respectively. Moreover, a thermal expansion coefficient of 7.816 × 10−6/°C is obtained, which coincides with that of the raw glass powder (7.5-8.0 × 10−6/°C), indicating that the glass body is fully densified after the HIP process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and characteristics of Li2TiO3 pebbles manufactured by using powder injection molding (PIM) process
Young Ah Park, Yi-Hyun Park, Mu-Young Ahn, Young Soo Yoon
Journal of Nuclear Materials.2024; 597: 155140. CrossRef - Combined simulation of micro and nanoparticles in RF inductively coupled plasma torches with the variations of metallic species and feeding nozzle location
Cheongbin Cheon, Ho Jun Kim, Hae June Lee
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics.2023; 62(SA): SA1014. CrossRef - High-throughput injection molding of transparent fused silica glass
Markus Mader, Oliver Schlatter, Barbara Heck, Andreas Warmbold, Alex Dorn, Hans Zappe, Patrick Risch, Dorothea Helmer, Frederik Kotz, Bastian E. Rapp
Science.2021; 372(6538): 182. CrossRef - Controlling the sintering response in the development of multilayered components produced via powder injection molding route—a review
O. J. Ojo-kupoluyi, S. M. Tahir, T. T. Dele-Afolabi, M. S. Anuar
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2020; 107(9-10): 3755. CrossRef - Fabrication of pressureless sintered Si3N4 ceramic balls by powder injection molding
Chang Woo Gal, Gi Woung Song, Woon Hyung Baek, Hyung Kyu Kim, Dae Keun Lee, Ki Wook Lim, Seong Jin Park
Ceramics International.2019; 45(5): 6418. CrossRef - Thermal decomposition behavior and modeling of PMN-PZT ceramic feedstock with varying binder compositions
Jae Man Park, Jun Sae Han, Chang Woo Gal, Joo Won Oh, Dongguo Lin, Jaebum Noh, Kunal H Kate, Sundar V Atre, Youngmoo Kim, Seong Jin Park
Materials Research Express.2019; 6(6): 065316. CrossRef - Powder Injection Molding Process in Industrial Fields
Joo Won OH, Chang Woo GAL, Daseul SHIN, Jae Man PARK, Woo Seok YANG, Seong Jin PARK
Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy.2018; 65(9): 539. CrossRef - Optimization of Process Condition for Fe Nano Powder Injection Molding
Joo Won Oh, Won Sik Lee, Seong Jin Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(3): 223. CrossRef
- Fabrication and characteristics of Li2TiO3 pebbles manufactured by using powder injection molding (PIM) process
- [Korean]
- Formation of Nano-oxides on Porous Metallic Glass Compacts using Hydrothermal Synthesis
- H. J. Park, Y. S. Kim, S. H. Hong, J. T. Kim, J. Y. Cho, W. H. Lee, K. B. Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):229-233. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.229

- 760 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Porous metallic glass compact (PMGC) are developed by electro-discharge sintering (EDS) process of gas atomized Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 metallic glass powder under of 0.2 kJ generated by a 450 μF capacitor being charged to 0.94 kV. Functional iron-oxides are formed and growth on the surface of PMGCs via hydrothermal synthesis. It is carried out at 150°C for 48hr with distilled water of 100 mL containing Fe ions of 0.18 g/L. Consequently, two types of iron oxides with different morphology which are disc-shaped Fe2O3 and needle-shaped Fe3O4 are successfully formed on the surface of the PMGCs. This finding suggests that PMGC witih hydrothermal technique can be attractive for the practical technology as a new area of structural and functional materials. And they provide a promising road map for using the metallic glasses as a potential functional application.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced wear resistivity of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by high-pressure torsion under reciprocating dry conditions
Soo-Hyun Joo, Dong-Hai Pi, Jing Guo, Hidemi Kato, Sunghak Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(3): 383. CrossRef
- Enhanced wear resistivity of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by high-pressure torsion under reciprocating dry conditions
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


