Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Development of High-strength, High-temperature Nb-Si-Ti Alloys through Mechanical Alloying
- Jung-Joon Kim, Sang-Min Yoon, Deok-Hyun Han, Jongmin Byun, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):30-36. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.30
- 2,034 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and High Temperature Mechanical Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steels Manufactured by Combination Milling Process
- Jung-Uk Lee, Young-Kyun Kim, Jeoung Han Kim, Hwi-Jin Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):389-395. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.389
- 782 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
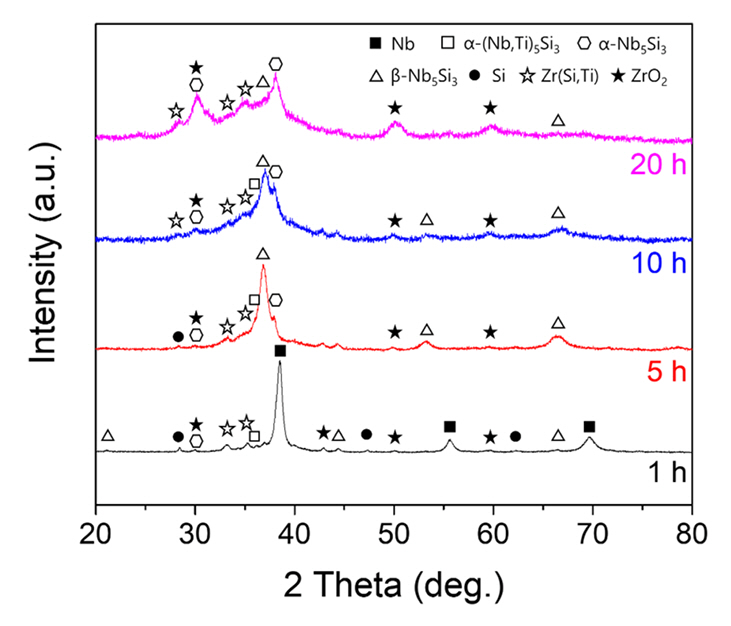
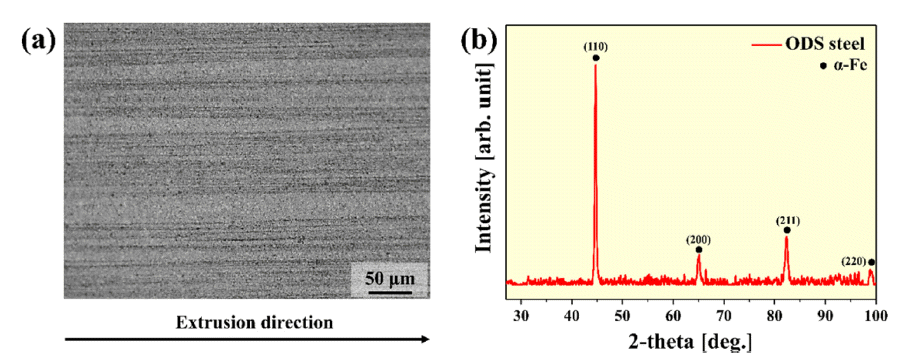
PDF Oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel has excellent high-temperature properties, corrosion resistance, and oxidation resistance, and is expected to be applicable in various fields. Recently, various studies on mechanical alloying (MA) have been conducted for the dispersion of oxide particles in ODS steel with a high number density. In this study, ODS steel is manufactured by introducing a complex milling process in which planetary ball milling, cryogenic ball milling, and drum ball milling are sequentially performed, and the microstructure and high-temperature mechanical properties of the ODS steel are investigated. The microstructure observation revealed that the structure is stretched in the extrusion direction, even after the heat treatment. In addition, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis confirmed the presence of oxide particles in the range of 5 to 10 nm. As a result of the room-temperature and high-temperature compression tests, the yield strengths were measured as 1430, 1388, 418, and 163 MPa at 25, 500, 700, and 900°C, respectively. Based on these results, the correlation between the microstructure and mechanical properties of ODS steel manufactured using the composite milling process is also discussed.
- [Korean]
- High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
- Yu-Jin Hwang, Dong-Yeol Wi, Kyu-Sik Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):110-119. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.110
- 1,138 View
- 26 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
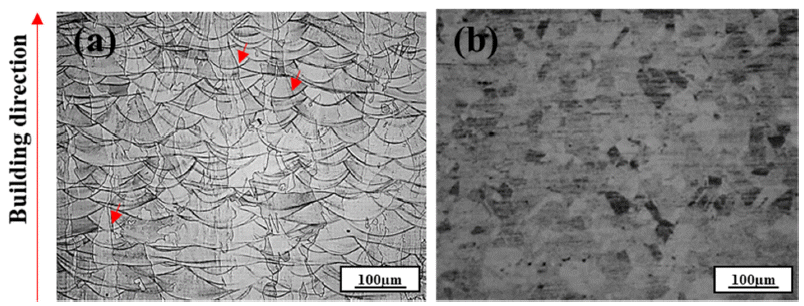
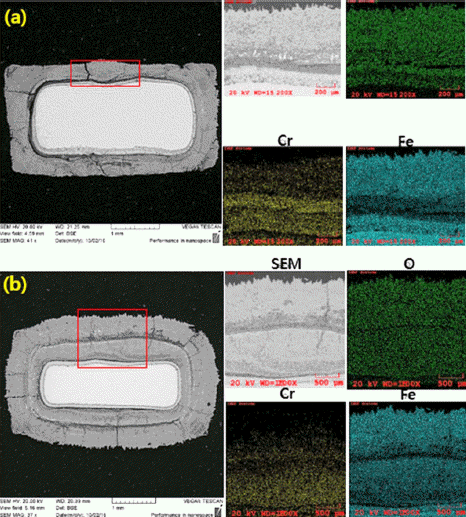
PDF In this study, the high-temperature oxidation properties of austenitic 316L stainless steel manufactured by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is investigated and compared with conventional 316L manufactured by hot rolling (HR). The initial microstructure of LPBF-SS316L exhibits a molten pool ~100 μm in size and grains grown along the building direction. Isotropic grains (~35 μm) are detected in the HR-SS316L. In high-temperature oxidation tests performed at 700°C and 900°C, LPBF-SS316L demonstrates slightly superior high-temperature oxidation resistance compared to HR-SS316L. After the initial oxidation at 700°C, shown as an increase in weight, almost no further oxidation is observed for both materials. At 900°C, the oxidation weight displays a parabolic trend and both materials exhibit similar behavior. However, at 1100°C, LPBF-SS316L oxidizes in a parabolic manner, but HR-SS316L shows a breakaway oxidation behavior. The oxide layers of LPBF-SS316L and HR-SS316L are mainly composed of Cr2O3, Febased oxides, and spinel phases. In LPBF-SS316L, a uniform Cr depletion region is observed, whereas a Cr depletion region appears at the grain boundary in HR-SS316L. It is evident from the results that the microstructure and the hightemperature oxidation characteristics and behavior are related.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Retention factor-based constitutive model of high-strength austenitic A4–80 bolts after fire exposure
Hui Wang, Bo Yang, Tao Sun, Weilai Yao, Wei Jiang
Journal of Constructional Steel Research.2025; 235: 109930. CrossRef - Study of structural stability at high temperature of pseudo-single tube with double layer as an alternative method for accident-tolerant fuel cladding
Jong Woo Kim, Hyeong Woo Min, Jaehwan Ko, Yonghee Kim, Young Soo Yoon
Journal of Nuclear Materials.2022; 566: 153800. CrossRef
- Retention factor-based constitutive model of high-strength austenitic A4–80 bolts after fire exposure
- [English]
- Effect of SiC and WC additon on Oxidation Behavior of Spark-Plasma-Sintered ZrB2
- Chang-Yeoul Kim, Jae-Seok Choi, Sung-Churl Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):455-462. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.455
- 1,093 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
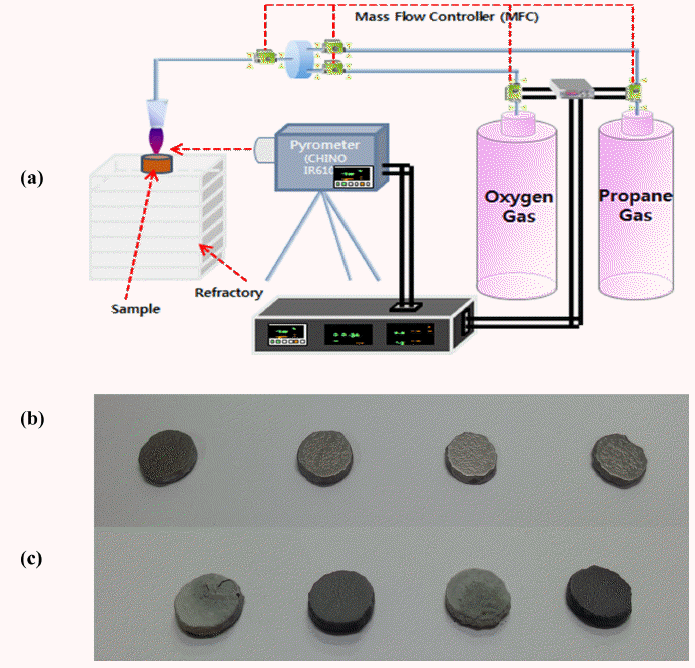
PDF ZrB2 ceramic and ZrB2 ceramic composites with the addition of SiC, WC, and SiC/WC are successfully synthesized by a spark plasma sintering method. During high-temperature oxidation, SiC additive form a SiO2 amorphous outer scale layer and SiC-deplete ZrO2 scale layer, which decrease the oxidation rate. WC addition forms WO3 during the oxidation process to result in a ZrO2/WO3 liquid sintering layer, which is known to improve the antioxidation effect. The addition of SiC and WC to ZrB2 reduces the oxygen effective diffusivity by one-fifth of that of ZrB2. The addition of both SiC and WC shows the formation of a SiO2 outer dense glass layer and ZrO2/WO3 layer so that the anti-oxidation effect is improved three times as much as that of ZrB2. Therefore, SiC- and WC-added ZrB2 has a lower two-order oxygen effective diffusivity than ZrB2; it improves the anti-oxidation performance 3 times as much as that of ZrB2.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role of TiC and WC Addition on the Mechanism and Kinetics of Isothermal Oxidation and High-Temperature Stability of ZrB2–SiC Composites
Pradyut Sengupta, Indranil Manna
High Temperature Corrosion of Materials.2024; 101(S1): 57. CrossRef
- Role of TiC and WC Addition on the Mechanism and Kinetics of Isothermal Oxidation and High-Temperature Stability of ZrB2–SiC Composites
- [Korean]
- Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
- Jae Jin Sim, Sang Hoon Choi, Ji Hwan Park, Il Kyu Park, Jae Hong Lim, Kyoung Tae Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):251-256. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.251
- 922 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
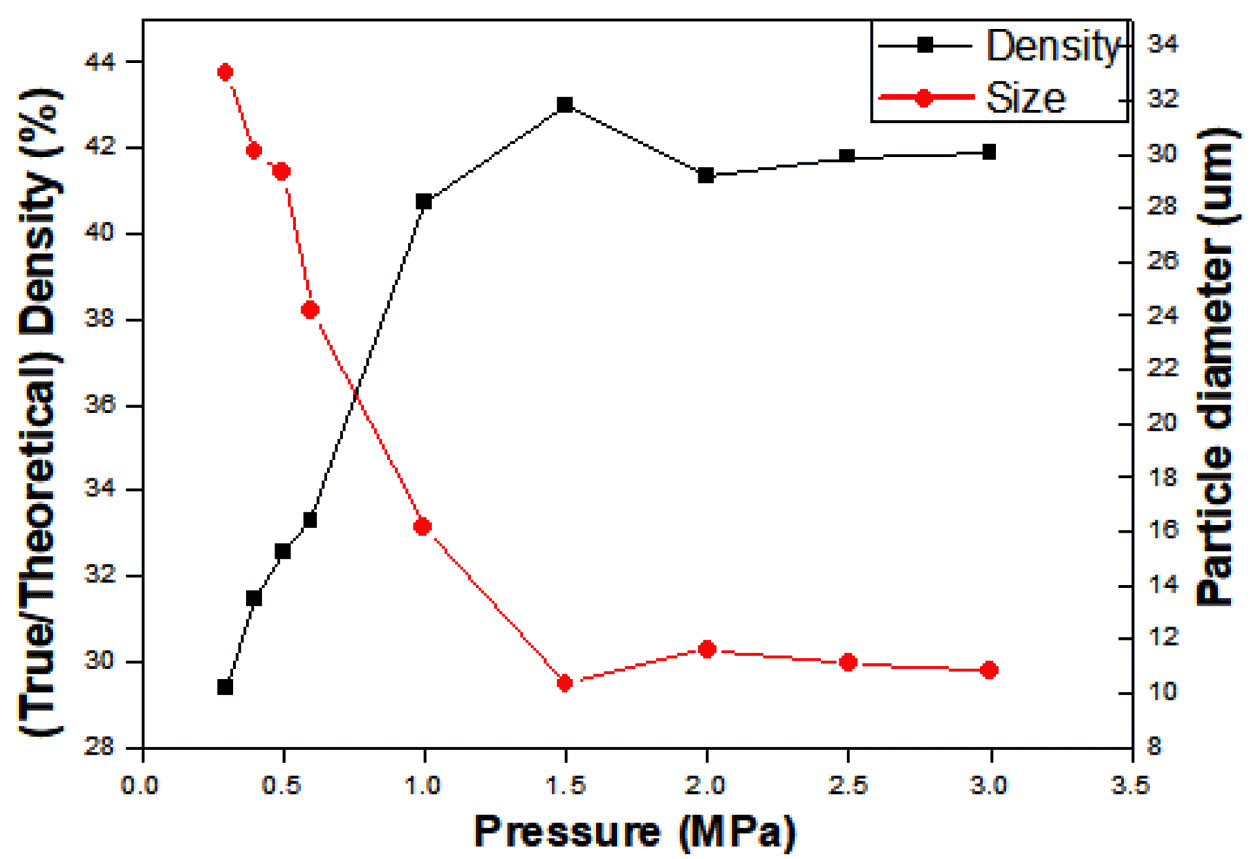
PDF We report the feasibility of TaC production via self-propagating high temperature synthesis, and the influence of the initial green compact density on the final composite particle size. Experiments are carried out from a minimum pressure of 0.3 MPa, the pressure at which the initial green body becomes self-standing, up to 3 MPa, the point at which no further combustion occurs. The green density of the pellets varies from 29.99% to 42.97%, as compared with the theoretical density. The increase in green density decreases the powder size of TaC, and the smallest particle size is observed with 1.5 MPa, at 10.36 μm. Phase analysis results confirm the presence of the TaC phase only. In the range of 0.3-0.5 MPa, traces of unreacted Ta and C residues are detected. However, results also show the presence of only C residue in the matrix within the pressure range of 0.6-3.0 MPa.
- [Korean]
- Manufacturing of Ni-Cr-B-Si + WC/12Co Composite Coating Layer Using Laser Cladding Process and its Mechanical Properties
- Gi-Su Ham, Chul-O Kim, Soon-Hong Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):370-376. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.370

- 704 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study we manufacture a Ni-Cr-B-Si +WC/12Co composite coating layer on a Cu base material using a laser cladding (LC) process, and investigate the microstructural and mechanical properties of the LC coating and Ni electroplating layers (reference material). The initial powder used for the LC coating layer is a powder feedstock with an average particle size of 125 μm. To identify the microstructural and mechanical properties, OM, SEM, XRD, room and high temperature hardness, and wear tests are implemented. Microstructural observation of the initial powder and LC coating layer confirm the layer is composed mainly of γ-Ni phases and WC and Cr23C6 carbides. The measured hardness of the LC coating and Ni electroplating layers are 653 and 154 Hv, respectively. The hardness measurement from room up to high temperatures of 700°C result in a hardness decrease as the temperature increases, but the hardness of the LC coating layer is higher for all temperature conditions. Room temperature wear results show that the wear loss of the LC coating layer is 1/12 of the wear level of the Ni electroplating layer. The measured bond strength is also greater in the LC coating than the Ni electroplating.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and Room Temperature Wear Properties of a Ni-Cr-B-Si-C Coating Layer Manufactured by the Laser Cladding Process
Tae-Hoon Kang, Kyu-Sik Kim, Soon-Hong Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2018; 56(6): 423. CrossRef - Microstructural and Wear Properties of WC-based and Cr3C2-based Cermet Coating Materials Manufactured with High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Process
Yeon-Ji Kang, Gi-Su Ham, Hyung-Jun Kim, Sang-Hoon Yoon, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(5): 408. CrossRef
- Microstructure and Room Temperature Wear Properties of a Ni-Cr-B-Si-C Coating Layer Manufactured by the Laser Cladding Process
- [Korean]
- High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Fe-14Cr Ferritic Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steels Manufactured by Mechanical Alloying Process
- Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Hwi-Jun Kim, Man-Sik Kong, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):133-140. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.133
- 655 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the oxidation properties of Fe-14Cr ferritic oxide-dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel at various high temperatures (900, 1000, and 1100°C for 24 h). The initial microstructure shows that no clear structural change occurs even under high-temperature heat treatment, and the average measured grain size is 0.4 and 1.1 μm for the as-fabricated and heat-treated specimens, respectively. Y–Ti–O nanoclusters 10–50 nm in size are observed. High-temperature oxidation results show that the weight increases by 0.27 and 0.29 mg/cm2 for the asfabricated and heat-treated (900°C) specimens, and by 0.47 and 0.50 mg/cm2 for the as-fabricated and heat-treated (1000°C) specimens, respectively. Further, after 24 h oxidation tests, the weight increases by 56.50 and 100.60 mg/cm2 for the as-fabricated and heat-treated (1100°C) specimens, respectively; the latter increase is approximately 100 times higher than that at 1000°C. Observation of the surface after the oxidation test shows that Cr2O3 is the main oxide on a specimen tested at 1000°C, whereas Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 phases also form on a specimen tested at 1100°C, where the weight increases rapidly. The high-temperature oxidation behavior of Fe-14Cr ODS steel is confirmed to be dominated by changes in the Cr2O3 layer and generation of Fe-based oxides through evaporation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(1): 36. CrossRef
- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and High Temperature Oxidation Behaviors of Fe-Ni Alloys by Spark Plasma Sintering
- Chae Hong Lim, Jong Seok Park, Sangsun Yang, Jung-Yeul Yun, Jin Kyu Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):53-57. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.53

- 500 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we report the microstructure and the high-temperature oxidation behavior of Fe-Ni alloys by spark plasma sintering. Structural characterization is performed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The oxidation behavior of Fe-Ni alloys is studied by means of a high-temperature oxidation test at 1000°C in air. The effect of Ni content of Fe-Ni alloys on the microstructure and on the oxidation characteristics is investigated in detail. In the case of Fe-2Ni and Fe-5Ni alloys, the microstructure is a ferrite (α) phase with body centered cubic (BCC) structure, and the microstructure of Fe-10Ni and Fe-20Ni alloys is considered to be a massive martensite (α’) phase with the same BCC structure as that of the ferrite phase. As the Ni content increases, the micro-Vickers hardness of the alloys also increases. It can also be seen that the oxidation resistance is improved by decreasing the thickness of the oxide film.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Diamond Particle Size on the Thermal Shock Property of High Pressure High Temperature Sintered Polycrystalline Diamond Compact
- Ji-Won Kim, Min-Seok Baek, Hee-Sub Park, Jin-Hyeon Cho, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):364-371. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.364

- 1,149 View
- 12 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the thermal shock property of a polycrystalline diamond compact (PDC) produced by a high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) sintering process. Three kinds of PDCs are manufactured by the HPHT sintering process using different particle sizes of the initial diamond powders: 8-16 μm (D50 = 4.3 μm), 10-20 μm (D50 = 6.92 μm), and 12-22 μm (D50 = 8.94 μm). The microstructure observation results for the manufactured PDCs reveal that elemental Co and W are present along the interface of the diamond particles. The fractions of Co and WC in the PDC increase as the initial particle size decreases. The manufactured PDCs are subjected to thermal shock tests at two temperatures of 780°C and 830°C. The results reveal that the PDC with a smaller particle size of diamond easily produces microscale thermal cracks. This is mainly because of the abundant presence of Co and WC phases along the diamond interface and the easy formation of Co-based (CoO, Co3O4) and W-based (WO2) oxides in the PDC using smaller diamond particles. The microstructural factors for controlling the thermal shock property of PDC material are also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of initial diamond particle size on the comprehensive mechanical properties of PDC
Xueqi Wang, Jianbo Tu, Baochang Liu
Ceramics International.2025; 51(8): 10433. CrossRef - High-impact-resistant polycrystalline diamond compact cutters with double working layers
Xueqi Wang, Jianbo Tu, Baochang Liu
Diamond and Related Materials.2025; 152: 111906. CrossRef - The Influence of the Binder Phase on the Properties of High-Pressure Sintered Diamond Polycrystals or Composites for Cutting Tool Applications
Lucyna Jaworska
Materials.2025; 18(3): 634. CrossRef - HPHT sintering and performance investigation of PDC with different interfacial geometry substrates for trimodal diamond particle size
Jianbo Tu, Xueqi Wang, Haibo Zhang, Baochang Liu
Ceramics International.2024; 50(11): 19074. CrossRef - HPHT sintering and performance investigation of PDC with high stacking density by dual particle size diamond formulations
Jianbo Tu, Xueqi Wang, Baochang Liu
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2024; 124: 106802. CrossRef
- Effects of initial diamond particle size on the comprehensive mechanical properties of PDC
- [Korean]
- A Study of the Sintering Behavior of Boron Carbide using In-situ High Temperature Dilatometer
- Hyukjae Lee, Bum-Sup Kim, Tai-Joo Chung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):102-107. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.102

- 802 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A high temperature dilatometer attached to a graphite furnace is built and used to study the sintering behavior of B4C. Pristine and carbon doped B4C compacts are sintered at various soaking temperatures and their shrinkage profiles are detected simultaneously using the dilatometer. Carbon additions enhance the sinterability of B4C with sintering to more than 97% of the theoretical density, while pristine B4C compacts could not be sintered above 91% due to particle coarsening. The shrinkage profiles of B4C reveal that the effect of carbon on the sinterability of B4C can be seen mostly below 1950°C. The high temperature dilatometer delivers very useful information which is impossible to obtain with conventional furnaces.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of rate-controlled sintering into the study of sintering behavior of boron carbide
Hyukjae Lee
Journal of the Korean Crystal Growth and Crystal Technology.2015; 25(1): 6. CrossRef
- Application of rate-controlled sintering into the study of sintering behavior of boron carbide
- [Korean]
- Effect of Cell Size on the High Temperature Oxidation Properties of Fe-Cr-Al Powder Porous Metal Manufactured by Electro-spray Process
- Jae-Sung Oh, Young-Min Kong, Byoung-Kee Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):55-61. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.55

- 956 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe-Cr-Al powder porous metal was manufactured by using new electro-spray process. First, ultra-fine fecralloy powders were produced by using the submerged electric wire explosion process. Evenly distributed colloid (0.05~0.5% powders) was dispersed on Polyurethane foam through the electro-spray process. And then degreasing and sintering processes were conduced. In order to examine the effect of cell size (200 μm, 450 μm, 500 μm) in process, pre-samples were sintered for two hours at temperature of 1450°C, in H2 atmospheres. A 24-hour thermo gravimetric analysis test was conducted at 1000°C in a 79% N2 + 21% O2 to investigate the high temperature oxidation behavior of powder porous metal. The results of the high temperature oxidation tests showed that oxidation resistance increased with increasing cell size. In the 200 μm porous metal with a thinner strut and larger specific surface area, the depletion of the stabilizing elements such as Al and Cr occurred more quickly during the high-temperature oxidation compared with the 450, 500 μm porous metals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Open‐Cell Austenitic Stainless Steel Foam by Electrostatic Powder Spraying Process
Tae-Hoon Kang, Kyu-Sik Kim, Jung-Yeul Yun, Min-Jeong Lee, Kee-Ahn Lee
Advanced Engineering Materials.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Microstructure and High Temperature Oxidation Behaviors of Fe-Ni Alloys by Spark Plasma Sintering
Chae Hong Lim, Jong Seok Park, Sangsun Yang, Jung-Yeul Yun, Jin Kyu Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(1): 53. CrossRef - Effect of Al2O3 Inter-Layer Grown on FeCrAl Alloy Foam to Improve the Dispersion and Stability of NiO Catalysts
유진 이, 본율 구, 성호 백, 만호 박, 효진 안
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2015; 25(8): 391~397. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Open‐Cell Austenitic Stainless Steel Foam by Electrostatic Powder Spraying Process
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


