Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
- [Korean]
- Phase Formation and Physical Properties of SiAlON Ceramics Fabricated by Gas-Pressure Reactive Sintering
- Soyul Lee, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Yoonsoo Han, Sung-Min Lee, Seongwon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):431-436. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.431
- 946 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
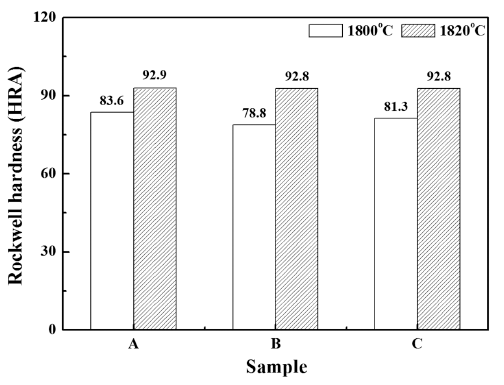
PDF SiAlON-based ceramics are some of the most typical oxynitride ceramic materials, which can be used as cutting tools for heat-resistant super-alloys (HRSA). SiAlON can be fabricated by using gas-pressure reactive sintering from the raw materials, nitrides and oxides such as Si3N4, AlN, Al2O3, and Yb2O3. In this study, we fabricate Ybm/3Si12-(m+n)Alm+nOnN16-n (m=0.3, n=1.9, 2.3, 2.7) ceramics by using gas-pressure sintering at different sintering temperatures. Then, the densification behavior, phase formation, microstructure, and hardness of the sintered specimens are characterized. We obtain a fully densified specimen with β- SiAlON after gas-pressure sintering at 1820°C for 90 min. under 10 atm N2 pressure. These SiAlON ceramic materials exhibited hardness values of ~92.9 HRA. The potential of these SiAlON ceramics for cutting tool application is also discussed.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Deposition Parameter and Mixing Process of Raw Materials on the Phase and Structure of Ytterbium Silicate Environmental Barrier Coatings by Suspension Plasma Spray Method
- Ho-lim Ryu, Seon-A Choi, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Soo Han, Kyun Choi, Sahn Nahm, Yoon-Suk Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):437-443. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.437

- 819 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF SiC-based composite materials with light weight, high durability, and high-temperature stability have been actively studied for use in aerospace and defense applications. Moreover, environmental barrier coating (EBC) technologies using oxide-based ceramic materials have been studied to prevent chemical deterioration at a high temperature of 1300°C or higher. In this study, an ytterbium silicate material, which has recently been actively studied as an environmental barrier coating because of its high-temperature chemical stability, is fabricated on a sintered SiC substrate. Yb2O3 and SiO2 are used as the raw starting materials to form ytterbium disilicate (Yb2Si2O7). Suspension plasma spraying is applied as the coating method. The effect of the mixing method on the particle size and distribution, which affect the coating formation behavior, is investigated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), an energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. It is found that the originally designed compounds are not effectively formed because of the refinement and vaporization of the raw material particles, i.e., SiO2, and the formation of a porous coating structure. By changing the coating parameters such as the deposition distance, it is found that a denser coating structure can be formed at a closer deposition distance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
Seong-June Youn, Young-Kyun Kim, Jae-Sung Park, Joo-Hyun Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(4): 333. CrossRef
- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
- [Korean]
- Insulating Behavior of Sintered AlN Ceramics Prepared by High-Energy Bead Milling of AlN Powder
- Sung-Soo Ryu, Sung-Min Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):444-449. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.444
- 782 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
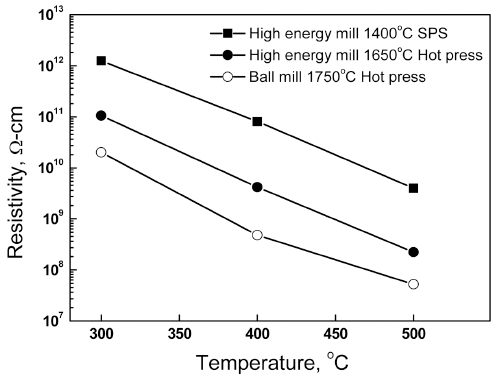
PDF Aluminum nitride (AlN) powder specimens are treated by high-energy bead milling and then sintered at various temperatures. Depending on the solvent and milling time, the oxygen content in the AlN powder varies significantly. When isopropyl alcohol is used, the oxygen content increases with the milling time. In contrast, hexane is very effective at suppressing the oxygen content increase in the AlN powder, although severe particle sedimentation after the milling process is observed in the AlN slurry. With an increase in the milling time, the primary particle size remains nearly constant, but the particle agglomeration is reduced. After spark plasma sintering at 1400°C, the second crystalline phase changes to compounds containing more Al2O3 when the AlN raw material with an increased milling time is used. When the sintering temperature is decreased from 1750°C to 1400°C, the DC resistivity increases by approximately two orders of magnitude, which implies that controlling the sintering temperature is a very effective way to improve the DC resistivity of AlN ceramics.
- [Korean]
- Mechanical Strength Values of Reaction-Bonded-Silicon-Carbide Tubes with Different Sample Size
- Seongwon Kim, Soyul Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Sung-Min Lee, Yoonsoo Han, Hyun-Ick Shin, Youngseok Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):450-456. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.450
- 513 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
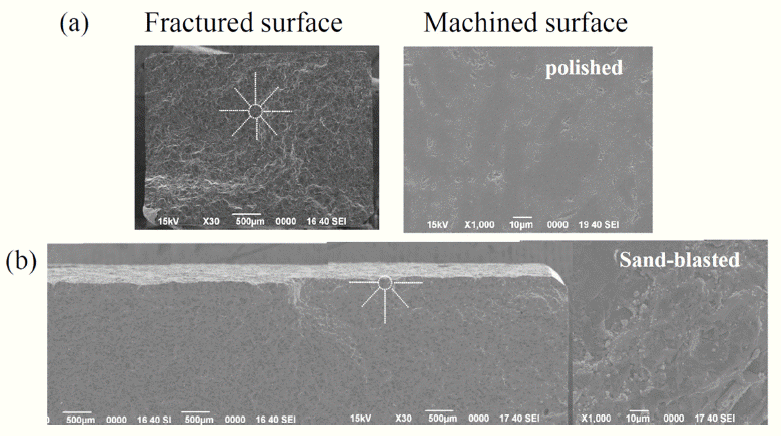
PDF Reaction-bonded silicon carbide (RBSC) is a SiC-based composite ceramic fabricated by the infiltration of molten silicon into a skeleton of SiC particles and carbon, in order to manufacture a ceramic body with full density. RBSC has been widely used and studied for many years in the SiC field, because of its relatively low processing temperature for fabrication, easy use in forming components with a near-net shape, and high density, compared with other sintering methods for SiC. A radiant tube is one of the most commonly employed ceramics components when using RBSC materials in industrial fields. In this study, the mechanical strengths of commercial RBSC tubes with different sizes are evaluated using 3-point flexural and C-ring tests. The size scaling law is applied to the obtained mechanical strength values for specimens with different sizes. The discrepancy between the flexural and C-ring strengths is also discussed.
- [Korean]
- Preparation of Nanosized Gd2O3:Eu3+ Red Phosphor Coated on Mica Flake and Its Luminescent Property
- Se-Min Ban, Jeong Min Park, Kyeong Youl Jung, Byung-Ki Choi, Kwang-Jung Kang, Myung Chang Kang, Dae-Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):457-463. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.457

- 968 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nanosized Gd2O3:Eu3+ red phosphor is prepared using a template method from metal salt impregnated into a crystalline cellulose and is dispersed using a bead mill wet process. The driving force of the surface coating between Gd2O3:Eu3+ and mica is induced by the Coulomb force. The red phosphor nanosol is effectively coated on mica flakes by the electrostatic interaction between positively charged Gd2O3:Eu3+ and negatively charged mica above pH 6. To prepare Gd2O3:Eu3+-coated mica (Gd2O3:Eu/mica), the coating conditions are optimized, including the stirring temperature, pH, calcination temperature, and coating amount (wt%) of Gd2O3:Eu3+. In spite of the low luminescence of the Gd2O3:Eu/mica, the luminescent property is recovered after calcination above 600°C and is enhanced by increasing the Gd2O3:Eu3+ coating amount. The Gd2O3:Eu/mica is characterized using X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, zeta potential measurements, and fluorescence spectrometer analysis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimization of dispersed LaPO4:Tb nanosol and their photoluminescence properties
Mahboob Ullah, Se-Min Ban, Dae-Sung Kim
Optical Materials.2019; 97: 109366. CrossRef
- Optimization of dispersed LaPO4:Tb nanosol and their photoluminescence properties
- [Korean]
- Filling and Wiping Properties of Silver Nano Paste in Trench Layer of Metal Mesh Type Transparent Conducting Electrode Films for Touch Screen Panel Application
- Gi-Dong Kim, Hyun-Min Nam, Sangsun Yang, Lee-Soon Park, Su-Yong Nam
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):464-471. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.464

- 1,139 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A metal mesh TCE film is fabricated using a series of processes such as UV imprinting of a transparent trench pattern (with a width of 2-5 μm) onto a PET film, filling it with silver paste, wiping of the surface, and heatcuring the silver paste. In this work nanosized (40-50 nm) silver particles are synthesized and mixed with submicron (250-300 nm)-sized silver particles to prepare silver paste for the fabrication of metal mesh-type TCE films. The filling of these silver pastes into the patterned trench layer is examined using a specially designed filling machine and the rheological testing of the silver pastes. The wiping of the trench layer surface to remove any residual silver paste or particles is tested with various mixture solvents, and ethyl cellosolve acetate (ECA):DI water = 90:10 wt% is found to give the best result. The silver paste with 40-50 nm Ag:250-300 nm Ag in a 10:90 wt% mixture gives the highest electrical conductance. The metal mesh TCE film obtained with this silver paste in an optimized process exhibits a light transmittance of 90.4% and haze at 1.2%, which is suitable for TSP application.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Silver and epoxy binder-based printed electrodes and the effect of silver nanoparticles on stretchability
Suk Hun Hyun, Se-Hoon Park, Sung-Hoon Choa, Hyun Jin Nam, Heejoon Ahn
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics.2019; 30(19): 17591. CrossRef - Electro-mechanical Properties of Stretchable Ag Paste by the Difference of Ag Particles
Sun-Young Kang, Min-Young Park, Dong-Young Jang
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Technology Engineers.2019; 28(3): 188. CrossRef
- Silver and epoxy binder-based printed electrodes and the effect of silver nanoparticles on stretchability
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous W-Ti by Freeze-Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of WO3-TiH2 Powder Mixtures
- Hyunji Kang, Sung Hyun Park, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):472-476. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.472

- 605 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Porous W-10 wt% Ti alloys are prepared by freeze-drying a WO3-TiH2/camphene slurry, using a sintering process. X-ray diffraction analysis of the heat-treated powder in an argon atmosphere shows the WO3 peak of the starting powder and reaction-phase peaks such as WO2.9, WO2, and TiO2 peaks. In contrast, a powder mixture heated in a hydrogen atmosphere is composed of the W and TiW phases. The formation of reaction phases that are dependent on the atmosphere is explained by a thermodynamic consideration of the reduction behavior of WO3 and the dehydrogenation reaction of TiH2. To fabricate a porous W-Ti alloy, the camphene slurry is frozen at -30°C, and pores are generated in the frozen specimens by the sublimation of camphene while drying in air. The green body is hydrogen-reduced and sintered at 1000°C for 1 h. The sintered sample prepared by freeze-drying the camphene slurry shows large and aligned parallel pores in the camphene growth direction, and small pores in the internal walls of the large pores. The strut between large pores consists of very fine particles with partial necking between them.
- [Korean]
- Preparation and Characterization of Visible Light-Sensitive N-doped TiO2 Using a Sol-gel Method
- NaRi Lee, Ri Yu, Tae Kwan Kim, Jae-Hwan Pee, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):477-482. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.477

- 1,176 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide (N-doped TiO2) is attracting continuously increasing attention as a material for environmental photocatalysis. The N-atoms can occupy both interstitial and substitutional positions in the solid, with some evidence of a preference for interstitial sites. In this study, N-doped TiO2 is prepared by the sol–gel method using NH4OH and NH4Cl as N ion doping agents, and the physical and photocatalytic properties with changes in the synthesis temperature and amount of agent are analyzed. The photocatalytic activities of the N-doped TiO2 samples are evaluated based on the decomposition of methylene blue (MB) under visible-light irradiation. The addition of 5 wt% NH4Cl produces the best physical properties. As per the UV-vis analysis results, the N-doped TiO2 exhibits a higher visible-light activity than the undoped TiO2. The wavelength of the N-doped TiO2 shifts to the visible-light region up to 412 nm. In addition, this sample shows MB removal of approximately 81%, with the whiteness increasing to +97 when the synthesis temperature is 600oC. The coloration and phase structure of the N-doped TiO2 are characterized in detail using UV-vis, CIE
Lab color parameter measurements, and powder X-ray diffraction (XRD).
- [Korean]
- Photocatalytic and Adsorption Properties of WO3 Nanorods Prepared by Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Su-Yeol Yu, Chunghee Nam
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):483-488. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.483
- 1,145 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
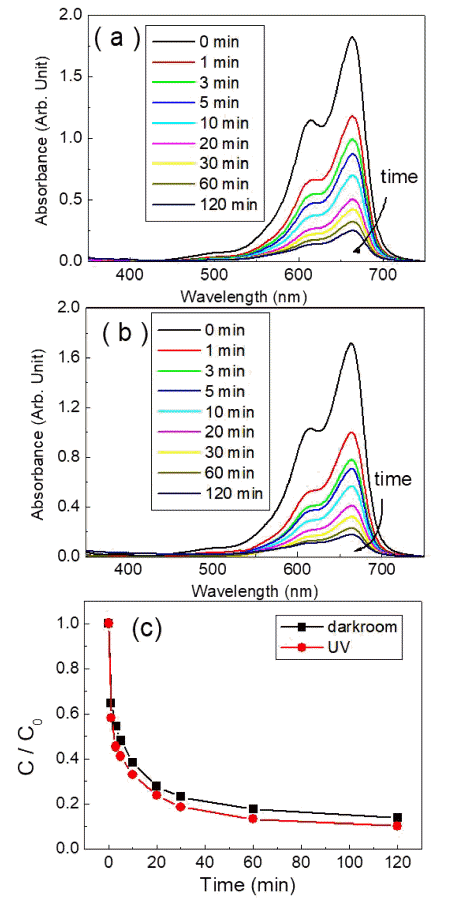
PDF Transition-metal oxide semiconductors have various band gaps. Therefore, many studies have been conducted in various application fields. Among these, methods for the adsorption of organic dyes and utilization of photocatalytic properties have been developed using various metal oxides. In this study, the adsorption and photocatalytic effects of WO3 nanomaterials prepared by hydrothermal synthesis are investigated, with citric acid added in the hydrothermal process as a structure-directing agent. The nanostructures of WO3 are studied using transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy images. The crystal structure is investigated using X-ray diffraction patterns, and the changes in the dye concentrations adsorbed on WO3 nanorods are measured with a UV-visible absorption spectrophotometer based on Beer-Lambert’s law. The methylene blue (MB) dye solution is subjected to acid or base conditions to monitor the change in the maximum adsorption amount in relation to the pH. The maximum adsorption capacity is observed at pH 3. In addition to the dye adsorption, UV irradiation is carried out to investigate the decomposition of the MB dye as a result of photocatalytic effects. Significant photocatalytic properties are observed and compared with the adsorption effects for dye removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Photocatalytic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Prepared by Electrodeposition Method
Kwang-Mo Kang, Ji-Hye Jeong, Ga-In Lee, Jae-Min Im, Hyun-Jeong Cheon, Deok-Hyeon Kim, Yoon-Chae Nah
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(1): 40. CrossRef - Photocatalysis of TiO<sub>2</sub>/WO<sub>3</sub> Composites Synthesized by Ball Milling
Su-Yeol Yu, Chunghee Nam
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(4): 316. CrossRef
- Photocatalytic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Prepared by Electrodeposition Method
- [Korean]
- Study on Surface-defect Passivation of InP System Quantum Dots by Photochemical Method
- Doyeon Kim, Hyun-Su Park, Hye Mi Cho, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):489-493. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.489
- 1,595 View
- 12 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
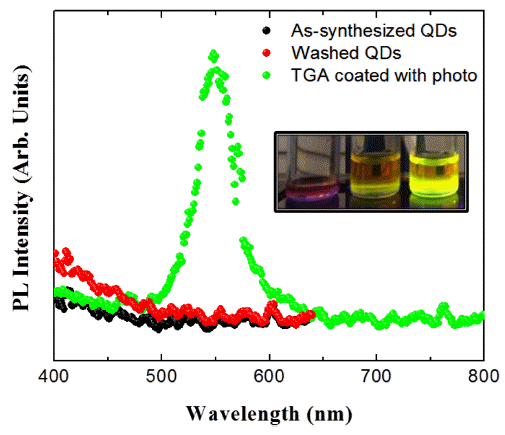
PDF In this study, the surface passivation process for InP-based quantum dots (QDs) is investigated. Surface coating is performed with poly(methylmethacrylate) (PMMA) and thioglycolic acid. The quantum yield (QY) of a PMMA-coated sample slightly increases by approximately 1.3% relative to that of the as-synthesized InP/ZnS QDs. The QYs of the uncoated and PMMA-coated samples drastically decrease after 16 days because of the high defect state density of the InP-based QDs. PMMA does not have a significant effect on the defect passivation. Thioglycolic acid is investigated in this study for the effective surface passivation of InP-based QDs. Surface passivation with thioglycolic acid is more effective than that with the PMMA coating, and the QY increases from 1.7% to 11.3%. ZnS formed on the surface of the InP QDs and S in thioglycolic acid show strong bonding property. Additionally, the QY is further increased up to 21.0% by the photochemical reaction. Electron–hole pairs are formed by light irradiation and lead to strong bonding between the inorganic and thioglycolic acid sulfur. The surface of the InP core QDs, which does not emit light, is passivated by the irradiated light and emits green light after the photochemical reaction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
Doyeon Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2019; 376: 206. CrossRef
- Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
- [Korean]
- Technology Trend of the additive Manufacturing (AM)
- Ji-Won Oh, Hyunwoong Na, Hanshin Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):494-507. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.494
- 1,898 View
- 11 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A three-dimensional physical part can be fabricated from a three-dimensional digital model in a layer-wise manner via additive manufacturing (AM) technology, which is different from the conventional subtractive manufacturing technology. Numerous studies have been conducted to take advantage of the AM opportunities to penetrate bespoke custom product markets, functional engineering part markets, volatile low-volume markets, and spare part markets. Nevertheless, materials issues, machines issues, product issues, and qualification/certification issues still prevent the AM technology from being extensively adopted in industries. The present study briefly reviews the standard classification, technological structures, industrial applications, technological advances, and qualification/certification activities of the AM technology. The economics, productivity, quality, and reliability of the AM technology should be further improved to pass through the technology adoption lifecycle of innovation technology. The AM technology is continuously evolving through the introduction of PM materials, hybridization of AM and conventional manufacturing technologies, adoption of process diagnostics and control systems, and enhanced standardization of the whole lifecycle qualification and certification methodology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Convolutional LSTM based melt-pool prediction from images of laser tool path strategy in laser powder bed fusion for additive manufacturing
Joung Min Park, Minho Choi, Jumyung Um
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2024; 130(3-4): 1871. CrossRef - Color evaluation by thickness of interim restorative resin produced by digital light processing 3D printer
Wol Kang, Won-Gi Kim
Journal of Korean Acedemy of Dental Technology.2021; 43(3): 77. CrossRef - Optimization of Metal Powder Particle Size Distribution for Powder Bed Fusion Process via Simulation
Hwaseon Lee, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Young Il Kim, Jieun Nam, Yong Son, Taek-Soo Kim, Bin Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(1): 44. CrossRef - Technology Trend of Additive Manufacturing Standardization
Hanshin Choi, Jinsu Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 420. CrossRef - Multi-step Metals Additive Manufacturing Technologies
Ji-Won Oh, Jinsu Park, Hanshin Choi
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 256. CrossRef - Anisotropy in Green Body Bending Strength due to Additive Direction in the Binder-Jetting Additive Manufacturing Process
Ji-Won Oh, Sahn Nahm, Byoungmoon Kim, Hanshin Choi
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2019; 57(4): 227. CrossRef - Effect of Porosity on Mechanical Anisotropy of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Additively Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting
Jeong Min Park, Jin Myoung Jeon, Jung Gi Kim, Yujin Seong, Sun Hong Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(6): 475. CrossRef
- Convolutional LSTM based melt-pool prediction from images of laser tool path strategy in laser powder bed fusion for additive manufacturing
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI




 First
First Prev
Prev


