Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- The Recycling Process and Powderization Technology of Stellite 6 Scrap: A Thermodynamic and Heat Transfer Analysis
- YongKwan Lee, Hyun-chul Kim, Myungsuk Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kyoungtae Park, JaeJin Sim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):330-343. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00136
- 1,085 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
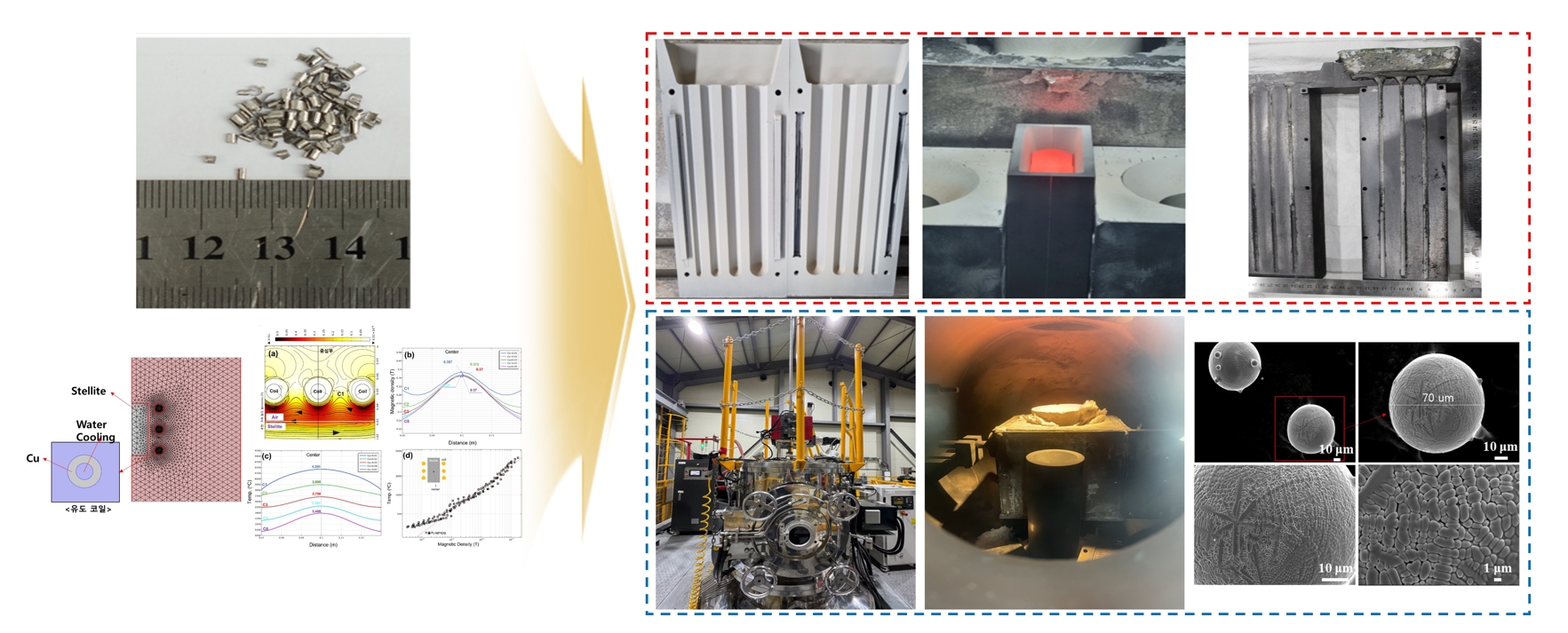
PDF - Co-Cr alloys are widely used in cutting tools and turbine components due to their high strength and resistance against wear and corrosion. However, scrap generated during hardfacing is often discarded due to impurities and oxidation, and research on its recycling remains limited. This study aimed to optimize the recycling process of Stellite 6 scrap to reduce waste and minimize costs while maintaining material quality. Melting, casting, and powdering processes were designed using HSC Chemistry, FactSage, and COMSOL Multiphysics, with optimization of key parameters such as the crucible material and temperature control. The recycled alloy and powder were analyzed using X-ray fluorescence analysis, inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy, and X-ray diffractometry, showing mechanical and chemical properties comparable to commercial Stellite 6. The Co and Cr contents were maintained, with a slight increase in Fe. These findings demonstrate the potential for producing high-quality recycled Stellite 6 materials, contributing to the sustainable utilization of metal resources in high-performance applications.
- [English]
- Selective Laser Sintering of Co-Cr Alloy Powders and Sintered Products Properties
- Dong-Wan Lee, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):7-12. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.7

- 1,457 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal-additive manufacturing techniques, such as selective laser sintering (SLS), are increasingly utilized for new biomaterials, such as cobalt-chrome (Co-Cr). In this study, Co-Cr gas-atomized powders are used as charge materials for the SLS process. The aim is to understand the consolidation of Co-Cr alloy powder and characterization of samples sintered using SLS under various conditions. The results clearly suggest that besides the matrix phase, the second phase, which is attributed to pores and oxidation particles, is observed in the sintered specimens. The as-built samples exhibit completely different microstructural features compared with the casting or wrought products reported in the literature. The microstructure reveals melt pools, which represent the characteristics of the scanning direction, in particular, or of the SLS conditions, in general. It also exposes extremely fine grain sizes inside the melt pools, resulting in an enhancement in the hardness of the as-built products. Thus, the hardness values of the samples prepared by SLS under all parameter conditions used in this study are evidently higher than those of the casting products.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of NiCo2O4/Ni Foam Electrode for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Water Splitting
- Minsol Kwon, Jaeseong Go, Yesol Lee, Sungmin Lee, Jisu Yu, Hyowon Lee, Sung Ho Song, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):411-417. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.411
- 1,112 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
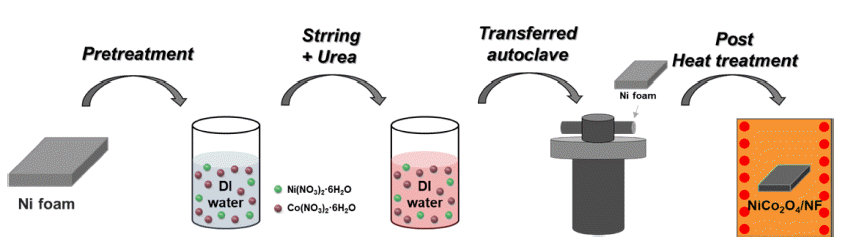
PDF Environmental issues such as global warming due to fossil fuel use are now major worldwide concerns, and interest in renewable and clean energy is growing. Of the various types of renewable energy, green hydrogen energy has recently attracted attention because of its eco-friendly and high-energy density. Electrochemical water splitting is considered a pollution-free means of producing clean hydrogen and oxygen and in large quantities. The development of non-noble electrocatalysts with low cost and high performance in water splitting has also attracted considerable attention. In this study, we successfully synthesized a NiCo2O4/NF electrode for an oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline water splitting using a hydrothermal method, which was followed by post-heat treatment. The effects of heat treatment on the electrochemical performance of the electrodes were evaluated under different heat-treatment conditions. The optimized NCO/NF-300 electrode showed an overpotential of 416 mV at a high current density of 50 mA/cm2 and a low Tafel slope (49.06 mV dec-1). It also showed excellent stability (due to the large surface area) and the lowest charge transfer resistance (12.59 Ω). The results suggested that our noble-metal free electrodes have great potential for use in developing alkaline electrolysis systems.
- [Korean]
- Extractive Metallurgy and Recycling of Cobalt
- Ho-Sang Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):252-261. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.252
- 1,203 View
- 16 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
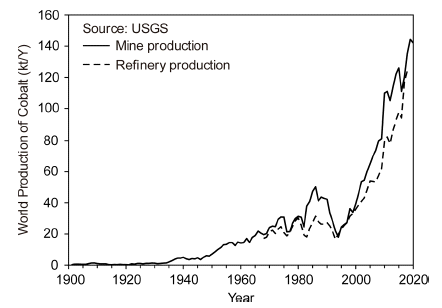
PDF Cobalt is a vital metal in the modern society because of its applications in lithium-ion batteries, super alloys, hard metals, and catalysts. Further, cobalt is a representative rare metal and is the 30th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust. This study reviews the current status of cobalt extraction and recycling processes, along with the trends in its production amount and use. Although cobalt occurs in a wide range of minerals, such as oxides and sulfides of copper and nickel ores, the amounts of cobalt in the minerals are too low to be extracted economically. The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) leads cobalt mining, and accounts for 68.9 % of the global cobalt reserves (142,000 tons in 2020). Cobalt is mainly extracted from copper–cobalt and nickel–cobalt concentrates and is occasionally extracted directly from the ore itself by hydro-, pyro-, and electro-metallurgical processes. These smelting methods are essential for developing new recycling processes to extract cobalt from secondary resources. Cobalt is mainly recycled from lithium-ion batteries, spent catalysts, and cobalt alloys. The recycling methods for cobalt also depend on the type of secondary cobalt resource. Major recycling methods from secondary resources are applied in pyro- and hydrometallurgical processes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reduction Behavior of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries by CO Gas
Sang-Yeop Lee, Jae-Ho Hwang, So-Yeong Lee, Ho-Sang Sohn
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2025; 63(10): 820. CrossRef - Recovering cobalt from cobalt oxide ore using suspension roasting and magnetic separation technique
Xinlei Wei, Yongsheng Sun, Yanjun Li, Peng Gao
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2023; 27: 3005. CrossRef
- Reduction Behavior of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries by CO Gas
- [Korean]
- Cobalt Recovery by Oxalic Acid and Hydroxide Precipitation from Waste Cemented Carbide Scrap Cobalt Leaching Solution
- Jaesung Lee, Mingoo Kim, Seulgi Kim, Dongju Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):497-501. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.497
- 1,307 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
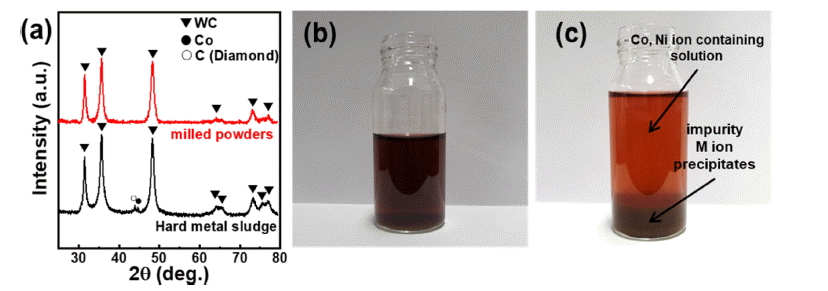
PDF Cobalt (Co) is mainly used to prepare cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) and binder metals for WC-Co hard metals. Developing an effective method for recovering Co from WC-Co waste sludge is of immense significance. In this study, Co is extracted from waste cemented carbide soft scrap via mechanochemical milling. The leaching ratio of Co reaches approximately 93%, and the leached solution, from which impurities except nickel are removed by pH titration, exhibits a purity of approximately 97%. The titrated aqueous Co salts are precipitated using oxalic acid and hydroxide precipitation, and the effects of the precipitating agent (oxalic acid and hydroxide) on the cobalt microstructure are investigated. It is confirmed that the type of Co compound and the crystal growth direction change according to the precipitation method, both of which affect the microstructure of the cobalt powders. This novel mechanochemical process is of significant importance for the recovery of Co from waste WC-Co hard metal. The recycled Co can be applied as a cemented carbide binder or a cathode material for lithium secondary batteries.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Cobalt Contents on the Microstructure and Charpy Impact Properties of Ferritic/martensitic Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel
- Daehyun Kwon, Sanghoon Noh, Jung Gu Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):311-317. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.311
- 908 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
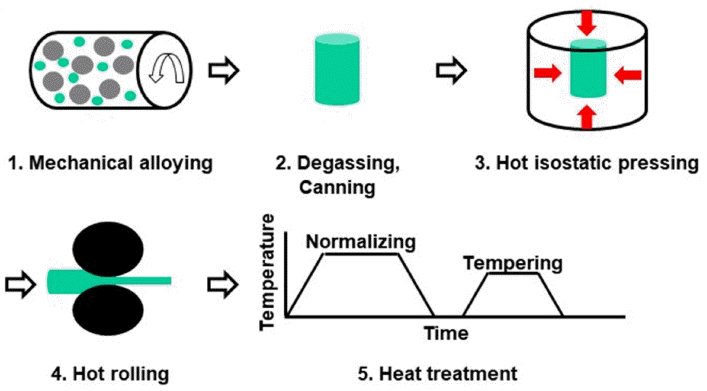
PDF In this study, the effects of Co content on the microstructure and Charpy impact properties of Fe-Cr-W ferritic/martensitic oxide dispersion strengthened (F/M ODS) steels are investigated. F/M ODS steels with 0–5 wt% Co are fabricated by mechanical alloying, followed by hot isostatic pressing, hot-rolling, and normalizing/tempering heat treatment. All the steels commonly exhibit two-phase microstructures consisting of ferrite and tempered martensite. The volume fraction of ferrite increases with the increase in the Co content, since the Co element considerably lowers the hardenability of the F/M ODS steel. Despite the lowest volume fraction of tempered martensite, the F/M ODS steel with 5 wt% Co shows the highest micro-Vickers hardness, owing to the solid solution-hardening effect of the alloyed Co. The high hardness of the steel improves the resistance to fracture initiation, thereby resulting in the enhanced fracture initiation energy in a Charpy impact test at – 40°C. Furthermore, the addition of Co suppresses the formation of coarse oxide inclusions in the F/M ODS steel, while simultaneously providing a high resistance to fracture propagation. Owing to these combined effects of Co, the Charpy impact energy of the F/M ODS steel increases gradually with the increase in the Co content.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Perforated Polygonal Cobalt Oxides using a Carbon Nanofiber Template
- Dong-Yo Sin, Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(5):350-355. Published online October 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.5.350
- 825 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
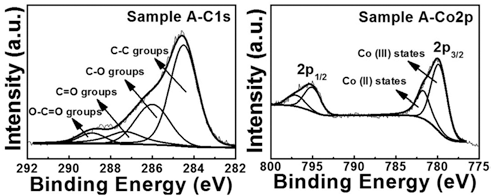
PDF Perforated polygonal cobalt oxide (CO3O4) is synthesized using electrospinning and a hydrothermal method followed by the removal of a carbon nanofiber (CNF) template. To investigate their formation mechanism, thermogravimetric analysis, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Xray photoelectron spectroscopy are examined. To obtain the optimum condition of perforated polygonal CO3O4, we prepare three different weight ratios of the Co precursor and the CNF template: sample A (Co precursor:CNF template- 10:1), sample B (Co precursor:CNF template-3.2:1), and sample C (Co precursor:CNF template-2:1). Among them, sample A exhibits the perforated polygonal CO3O4 with a thin carbon layer (5.7-6.2 nm) owing to the removal of CNF template. However, sample B and sample C synthesized perforated round CO3O4 and destroyed CO3O4 powders, respectively, due to a decreased amount of Co precursor. The increased amount of the CNF template prevents the formation of polygonal CO3O4. For sample A, the optimized weight ratio of the Co precursor and CNF template may be related to the successful formation of perforated polygonal CO3O4. Thus, perforated polygonal CO3O4 can be applied to electrode materials of energy storage devices such as lithium ion batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis of Nitrogen Doped Protein Based Carbon as Pt Catalysts Supports for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Young-geun Lee, Geon-hyeong An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(3): 182. CrossRef - Electrochemical Behavior of Well-dispersed Catalysts on Ruthenium Oxide Nanofiber Supports
Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 96. CrossRef
- Synthesis of Nitrogen Doped Protein Based Carbon as Pt Catalysts Supports for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
- [Korean]
- Preparation of Spherical Cobalt Fine Powders by New Liquid Reduction Method
- Dae Weon Kim, Ji-Hoon Kim, Yo-Han Choi, Hee Lack Choi, Jin-Ho Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):260-265. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.260
- 752 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
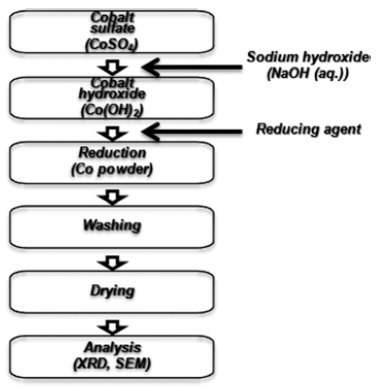
PDF Spherical fine cobalt powders were fabricated by new liquid reduction method. Commercial cobalt sufate heptahydrate was used as raw material. Also ethylene glycol was used as solvent and hydrazine-sodium hypophosphite mixture was used as reduction agent for the new liquid reduction method. A plate shaped cobalt powders with an approximately 300 nm were prepared by a traditional wet ruduction method using distilled water as solvent and hydrazine. Spherical fine cobalt powders with an average size of 1-3 μm were synthesized by a new liquid reduction method in 0.3M cobalt sulfate and 1.5M hydrazine-0.6M sodium hypophosphite mixture at 333K.
- [Korean]
- The Fabrication of Cobalt Nanopowder by Sonochemical Polyol Synthesis of Cobalt Hydroxide and Magnetic Separation Method
- Jong Min Byun, Myoung Hwan Choi, Chang Min Shim, Ji Young Kim, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):39-45. Published online February 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.39

- 812 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, cobalt nanopowder is fabricated by sonochemical polyol synthesis and magnetic separation method. First, sonochemical polyol synthesis is carried out at 220°C for up to 120 minutes in diethylene glycol (C4H10O3). As a result, when sonochemical polyol synthesis is performed for 50 minutes, most of the cobalt precursor (Co(OH)2) is reduced to spherical cobalt nanopowder of approximately 100 nm. In particular, aggregation and growth of cobalt particles are effectively suppressed as compared to common polyol synthesis. Furthermore, in order to obtain finer cobalt nanopowder, magnetic separation method using magnetic property of cobalt is introduced at an early reduction stage of sonochemical polyol synthesis when cobalt and cobalt precursor coexist. Finally, spherical cobalt nanopowder having an average particle size of 22 nm is successfully separated.
- [English]
- Materials Flow Analysis of Metallic Cobalt and Its Powder in Korea
- Hyun Seon Hong, Lee-Seung Kang, Hong-Yoon Kang, Han-Gil Suk
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):235-240. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.235

- 1,750 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The basis of the cobalt demand analysis by use was established via the investigation and analysis of the cobalt materials flow, and the overall cobalt metal material and parts industry structure in Korea was examined to determine the cobalt material flow. The markets of the cobalt material for machinery were studied, including their interrelations, via market and study trends, and relevant plans were examined. The results of the study indicated that the advanced core technology for advanced industry and technology-intensive industry development is required to structurally innovate the parts materials and basic materials industries and to upgrade the catch-up industry structure to the new frontier structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the potential for improving material utilization efficiency to secure lithium supply for China's battery supply chain
Xin Sun, Han Hao, Yong Geng, Zongwei Liu, Fuquan Zhao
Fundamental Research.2024; 4(1): 167. CrossRef - Trade structure and risk transmission in the international automotive Li-ion batteries trade
Xiaoqian Hu, Chao Wang, Xiangyu Zhu, Cuiyou Yao, Pezhman Ghadimi
Resources, Conservation and Recycling.2021; 170: 105591. CrossRef
- Exploring the potential for improving material utilization efficiency to secure lithium supply for China's battery supply chain
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


