Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Interaction of Detonation Nanodiamonds with Hispidin
- Changkyu Rhee, Whungwhoe Kim, Andrey E. Burov, Alexey P. Puzyr, Vladimir S. Bondar
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):458-463. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.458
- 719 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
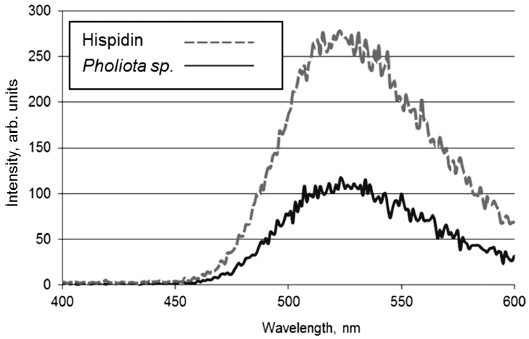
PDF Hispidin is a secondary metabolite found in numerous medicinal mushrooms that has attracted significant attention, owing to its distinct biological effects, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and cytoprotective properties. Experiments are being carried out to study the interaction of detonation nanodiamonds (DNDs) with synthetic and natural hispidin sourced from extracts of
Pholiota sp. fungus. The bioluminescence method is used to determine the adsorption/ desorption properties of DNDs toward hispidin. It is found that hispidin forms strong conjugates with DNDs, and the use of various eluents does not result in a significant release of the adsorbed hispidin molecules. DND-bovine serum albumin (BSA) complex, where DNDs serve as a carrier for the protein and the latter acts as a hispidin sorbent, has been developed and applied in hispidin adsorption/desorption tests. The results support the use of the DNDs as a carrier for hispidin in medical applications. They also advocate the application of the DND-BSA complex for isolating the substance from fungal extracts.
- [English]
- Nanodiamonds Conjugated with Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs for Transdermal Delivery
- Changkyu Rhee, Alexey P. Puzyr, Andrey E. Burov, Olga G. Burova, Whungwhoe Kim, Vladimir S. Bondar
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):459-465. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.459
- 806 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
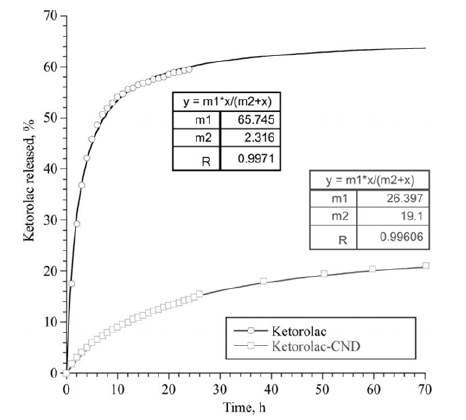
PDF Most commercially available detonation nanodiamonds (DNDs) require further processing to qualify for use in biomedical applications, as they often contain many impurities and exhibit poor dispersibility in aqueous media. In this work, DNDs are modified to improve purity and impart a high colloidal stability to the particles. The dispersive and adsorption properties of modified DNDs are evaluated in terms of the suitability of DNDs as carriers for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in transdermal delivery. The study of adsorption on strongly positively and strongly negatively charged DNDs showed their high loading capacity for NSAIDs, and a pronounced relationship between the drugs and the particles’ charges. Experiments on long-term desorption carried out with DND/NSAID complexes indicate that the nanoparticles exert a sustained effect on the drug release process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unveiling the trending paradigms of synthesis and theranostic biomedical potentials of nano-diamonds (NDs) - a state-of-the-art update
Sagnik Nag, Kedlaya Srikrishna H. Damodar, Swayambhik Mukherjee, Dinesh R. Rao, Ipsita Debnath, Sree Haryini, Sourav Mohanto, Mohammed Gulzar Ahmed, Vetriselvan Subramaniyan
Inorganic Chemistry Communications.2025; 177: 114313. CrossRef
- Unveiling the trending paradigms of synthesis and theranostic biomedical potentials of nano-diamonds (NDs) - a state-of-the-art update
- [English]
- Dispersion Behavior and Size Analysis of Thermally Purified High Pressure-high Temperature Synthesized Nanodiamond Particles
- Hansang Kwon, Jehong Park, Marc Leparoux
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(3):216-222. Published online June 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.216

- 1,384 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Synthesized monocrystalline nanodiamond (nD) particles are heat-treated at various temperatures to produce highly structured diamond crystals. The heat-treated nDs show different weight loss ratios during thermogravimetric analysis. The crystallinities of the heat-treated nDs are analyzed using Raman spectroscopy. The average particle sizes of the heat-treated nDs are measured by a dynamic light scattering (DLS) system and direct imaging observation methods. Moreover, individual dispersion behaviors of the heat-treated nD particles are investigated based on ultrasonic dispersion methods. The average particle sizes of the dispersed nDs according to the two different measurement methods show very similar size distributions. Thus, it is possible to produce highly crystallized nD powder particles by a heattreatment process, and the nD particles are relatively easy to disperse individually without any dispersant. The heattreated nDs can lead to potential applications such as in nanocomposites, quantum dots, and biomedical materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Two extreme crystal size scales of diamonds, large single crystal and nanocrystal diamonds: Synthesis, properties and their mutual transformation
Yang Wang, Wei-hua Wang, Shi-lin Yang, Guo-yang Shu, Bing Dai, Jia-qi Zhu
New Carbon Materials.2021; 36(3): 512. CrossRef
- Two extreme crystal size scales of diamonds, large single crystal and nanocrystal diamonds: Synthesis, properties and their mutual transformation
- [Korean]
- Effect of Diamond Particle Size on the Thermal Shock Property of High Pressure High Temperature Sintered Polycrystalline Diamond Compact
- Ji-Won Kim, Min-Seok Baek, Hee-Sub Park, Jin-Hyeon Cho, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):364-371. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.364

- 1,199 View
- 12 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the thermal shock property of a polycrystalline diamond compact (PDC) produced by a high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) sintering process. Three kinds of PDCs are manufactured by the HPHT sintering process using different particle sizes of the initial diamond powders: 8-16 μm (D50 = 4.3 μm), 10-20 μm (D50 = 6.92 μm), and 12-22 μm (D50 = 8.94 μm). The microstructure observation results for the manufactured PDCs reveal that elemental Co and W are present along the interface of the diamond particles. The fractions of Co and WC in the PDC increase as the initial particle size decreases. The manufactured PDCs are subjected to thermal shock tests at two temperatures of 780°C and 830°C. The results reveal that the PDC with a smaller particle size of diamond easily produces microscale thermal cracks. This is mainly because of the abundant presence of Co and WC phases along the diamond interface and the easy formation of Co-based (CoO, Co3O4) and W-based (WO2) oxides in the PDC using smaller diamond particles. The microstructural factors for controlling the thermal shock property of PDC material are also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- From abrasion to spallation: Stress-dependent transition of wear mechanisms in polycrystalline diamond governed by grain architecture
Di Xu, Lifen Deng, Xiwei Cui, Shuai Hou, Jialin Li, Xiaoling Li, Nan Jiang
Diamond and Related Materials.2026; 163: 113417. CrossRef - Effects of initial diamond particle size on the comprehensive mechanical properties of PDC
Xueqi Wang, Jianbo Tu, Baochang Liu
Ceramics International.2025; 51(8): 10433. CrossRef - High-impact-resistant polycrystalline diamond compact cutters with double working layers
Xueqi Wang, Jianbo Tu, Baochang Liu
Diamond and Related Materials.2025; 152: 111906. CrossRef - The Influence of the Binder Phase on the Properties of High-Pressure Sintered Diamond Polycrystals or Composites for Cutting Tool Applications
Lucyna Jaworska
Materials.2025; 18(3): 634. CrossRef - HPHT sintering and performance investigation of PDC with different interfacial geometry substrates for trimodal diamond particle size
Jianbo Tu, Xueqi Wang, Haibo Zhang, Baochang Liu
Ceramics International.2024; 50(11): 19074. CrossRef - HPHT sintering and performance investigation of PDC with high stacking density by dual particle size diamond formulations
Jianbo Tu, Xueqi Wang, Baochang Liu
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2024; 124: 106802. CrossRef
- From abrasion to spallation: Stress-dependent transition of wear mechanisms in polycrystalline diamond governed by grain architecture
- [Korean]
- Effect of Molding Pressure on the Microstructure and Wear Resistance Property of Polycrystalline Diamond Compact
- Ji-Won Kim, Hee-Sub Park, Jin-Hyeon Cho, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):203-207. Published online June 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.203
- 898 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
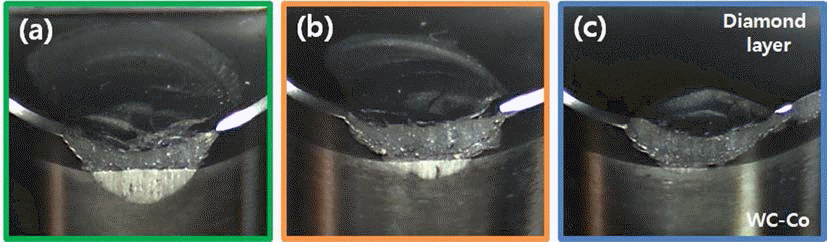
PDF This study investigated the microstructure and wear resistance property of HPHT (high pressure high temperature) sintered PDC (polycrystalline diamond compact) in accordance with initial molding pressure. After quantifying an identical amount of diamond powder, the powder was inserted in top of WC-Co sintered material, and molded under four different pressure conditions (50, 100, 150, 200 kgf/cm2). The obtained diamond compact underwent sintering in high pressure, high temperature conditions. In the case of the 50 kgf/cm2 initial molding pressure condition, cracks were formed on the surface of PDC. On the other hand, PDCs obtained from 100~200 kgf/cm2 initial molding pressure conditions showed a meticulous structure. As molding pressure increased, low Co composition within PDC was detected. A wear resistance test was performed on the PDC, and the 200 kgf/cm2 condition PDC showed the highest wear resistance property.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Co Leaching on the Vertical Turning Lathe Wear Properties of Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Manufactured by High Temperature and High Pressure Sintering Process
Min-Seok Baek, Ji-Won Kim, Bae-Gun Park, Hee-Sub Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2020; 58(7): 480. CrossRef - Enhanced wear resistivity of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by high-pressure torsion under reciprocating dry conditions
Soo-Hyun Joo, Dong-Hai Pi, Jing Guo, Hidemi Kato, Sunghak Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(3): 383. CrossRef
- Effect of Co Leaching on the Vertical Turning Lathe Wear Properties of Polycrystalline Diamond Compact Manufactured by High Temperature and High Pressure Sintering Process
- [Korean]
- Machining Characteristics of Micro Structure using Single-Crystal Diamond Tool on Cu-plated Mold
- Chang-Eui Kim, Eun-chae Jeon, Tae-Jin Je, Myung Chang Kang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):169-174. Published online June 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.169
- 1,026 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
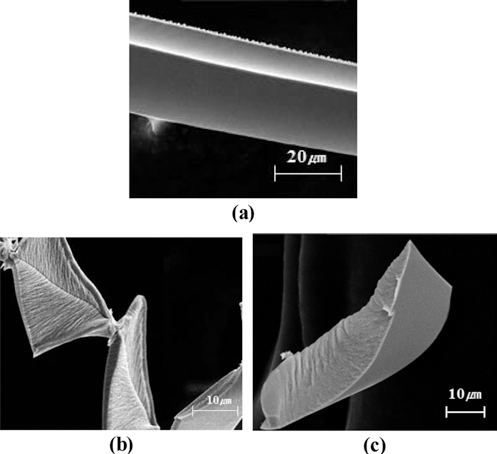
PDF The optical film for light luminance improvement of back light unit that is used in light emitting diode/liquid crystal display and retro-reflective film is used as luminous sign consist of square and triangular pyramid structure pattern based on V-shape micro prism pattern. In this study, we analyzed machining characteristics of Cu-plated flat mold by shaping with diamond tool. First, cutting conditions were optimized as V-groove machining for the experiment of micro prism structure mold machining with prism pattern shape, cutting force and roughness. Second, the micro prism structure such as square and triangular pyramid pattern were machined by cross machining method with optimizing cutting conditions. Variation of Burr and chip shape were discussed by material properties and machining method.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of ultra-precision planing process to fabricate high luminance retroreflector based on cutting force and tool vibration analysis
Ji-Young Jeong, Jun Sae Han, Chung-Mo Kang, Eun-Ji Gwak, Doo-Sun Choi, Tae-Jin Je
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Precision Cutting of the Molds of an Optical Functional Texture Film with a Triangular Pyramid Texture
Huang Li, Zhilong Xu, Jun Pi, Fei Zhou
Micromachines.2020; 11(3): 248. CrossRef
- Investigation of ultra-precision planing process to fabricate high luminance retroreflector based on cutting force and tool vibration analysis
- [Korean]
- Thermal Properties of Diamond Aligned Electroless Ni Plating Layer/Oxygen Free Cu Substrates
- Da-Woon Jeong, Song-Yi Kim, Kyoung-Tae Park, Seok-Jun Seo, Taek Soo Kim, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):134-137. Published online April 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.134
- 1,020 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
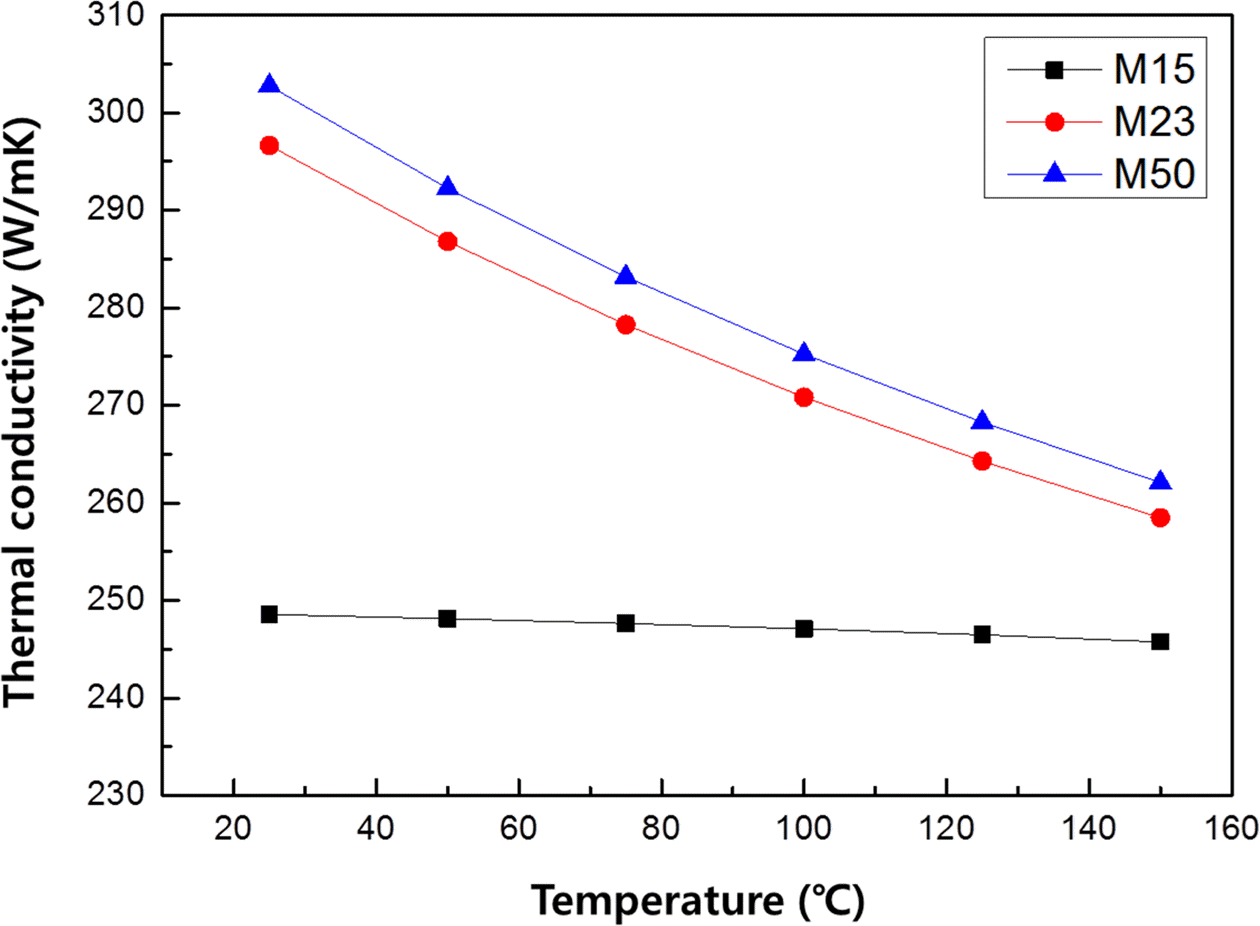
PDF The monolayer engineering diamond particles are aligned on the oxygen free Cu plates with electroless Ni plating layer. The mean diamond particle sizes of 15, 23 and 50 μm are used as thermal conductivity pathway for fabricating metal/carbon multi-layer composite material systems. Interconnected void structure of irregular shaped diamond particles allow dense electroless Ni plating layer on Cu plate and fixing them with 37-43% Ni thickness of their mean diameter. The thermal conductivity decrease with increasing measurement temperature up to 150°C in all diamond size conditions. When the diamond particle size is increased from 15 μm to 50 μm (Max. 304 W/mK at room temperature) tended to increase thermal conductivity, because the volume fraction of diamond is increased inside plating layer.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Diamond Particle Ratio on the Microstructure and Thermal Shock Property of HPHT Sintered Polycrystalline Diamond Compact (PDC)
- Ji-Won Kim, Hee-Sub Park, Jin-Hyeon Cho, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):111-115. Published online April 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.111
- 1,060 View
- 11 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
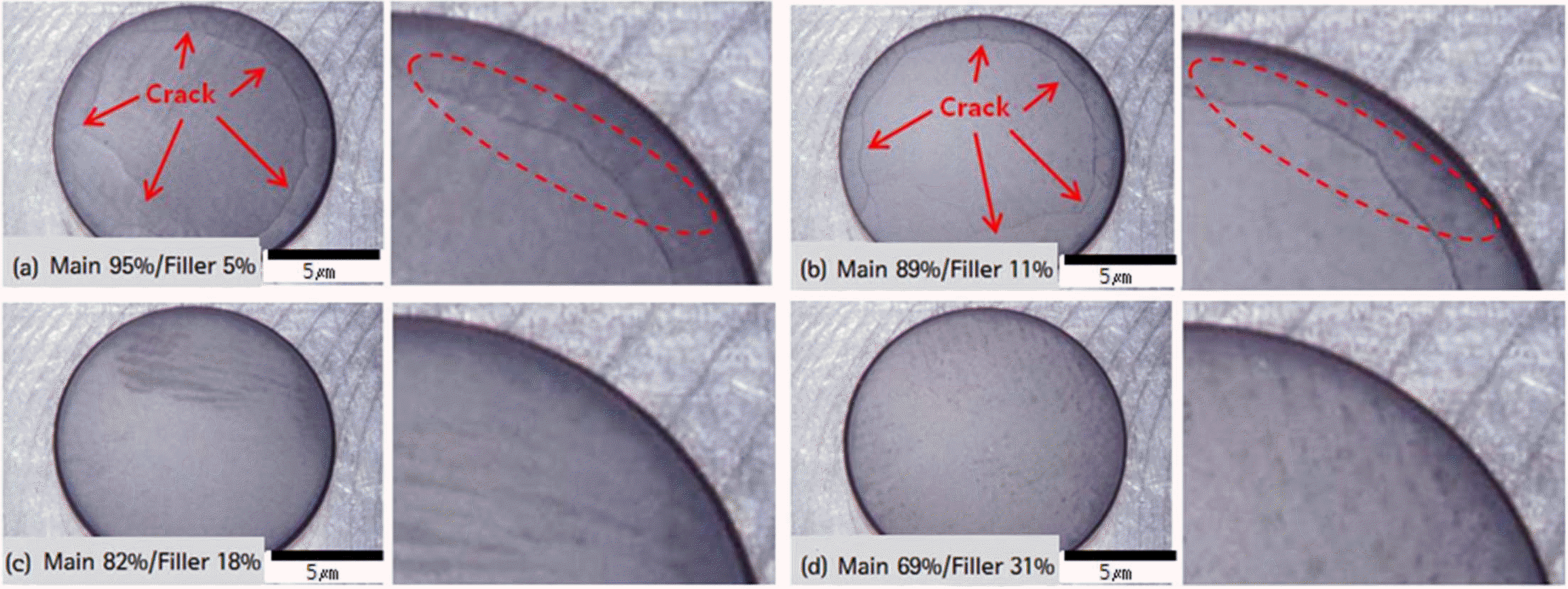
PDF This study investigates the microstructure and thermal shock properties of polycrystalline diamond compact (PDC) produced by the high-temperature, high-pressure (HPHT) process. The diamond used for the investigation features a 12~22 μm- and 8~16 μm-sized main particles, and 1~2 μm-sized filler particles. The filler particle ratio is adjusted up to 5~31% to produce a mixed particle, and then the tap density is measured. The measurement finds that as the filler particle ratio increases, the tap density value continuously increases, but at 23% or greater, it reduces by a small margin. The mixed particle described above undergoes an HPHT sintering process. Observation of PDC microstructures reveals that the filler particle ratio with high tap density value increases direct bonding among diamond particles, Co distribution becomes even, and the Co and W fraction also decreases. The produced PDC undergoes thermal shock tests with two temperature conditions of 820 and 830, and the results reveals that PDC with smaller filler particle ratio and low tap density value easily produces cracks, while PDC with high tap density value that contributes in increased direct bonding along with the higher diamond content results in improved thermal shock properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of initial diamond particle size on the comprehensive mechanical properties of PDC
Xueqi Wang, Jianbo Tu, Baochang Liu
Ceramics International.2025; 51(8): 10433. CrossRef - HPHT sintering and performance investigation of PDC with different interfacial geometry substrates for trimodal diamond particle size
Jianbo Tu, Xueqi Wang, Haibo Zhang, Baochang Liu
Ceramics International.2024; 50(11): 19074. CrossRef - HPHT sintering and performance investigation of PDC with high stacking density by dual particle size diamond formulations
Jianbo Tu, Xueqi Wang, Baochang Liu
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2024; 124: 106802. CrossRef
- Effects of initial diamond particle size on the comprehensive mechanical properties of PDC
- [Korean]
- Study on Hardness and Corrosion Resistance of Magnesium by Anodizing and Sealing Treatment With Nano-diamond Powder
- Soo Young Kang, Dae Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):260-265. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.260

- 1,061 View
- 7 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, in order to increase surface ability of hardness and corrosion of magnesium alloy, anodizing and sealing with nano-diamond powder was conducted. A porous oxide layer on the magnesium alloy was successfully made at 85°C through anodizing. It was found to be significantly more difficult to make a porous oxide layer in the magnesium alloy compared to an aluminum alloy. The oxide layer made below 73°C by anodizing had no porous layer. The electrolyte used in this study is DOW 17 solution. The surface morphology of the magnesium oxide layer was investigated by a scanning electron microscope. The pores made by anodizing were sealed by water and aqueous nanodiamond powder respectively. The hardness and corrosion resistance of the magnesium alloy was increased by the anodizing and sealing treatment with nano-diamond powder.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of different turbulent flow on failure behavior in secondary loop of the pressurized water reactor
Y. Hu, L. Zhao, Y.H. Lu, T. Shoji
Nuclear Engineering and Design.2020; 368: 110812. CrossRef - Effect of heat treatment on corrosion resistance and adhesion property in Zn-Mg-Zn multi-layer coated steel prepared by PVD process
Jong Min Byun, Su-Ryong Bang, Hyun Woo Kim, Tae-Yeob Kim, Suk-Jun Hong, Young Do Kim
Surface and Coatings Technology.2017; 309: 1010. CrossRef - Convergent Study of Aluminum Anodizing Method on the Thermal Fatigue
Soo Young Kang
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(5): 169. CrossRef - Convergent Study of Texture on the Mechanical Properties of Electrodeposits
Soo Young Kang
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(6): 193. CrossRef
- The effect of different turbulent flow on failure behavior in secondary loop of the pressurized water reactor
- [Korean]
- Study on Anodizing at Constant Current for Sealing Treatment of Nano-diamond Powder
- Soo Young Kang, Dae Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):114-118. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.114
- 889 View
- 7 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
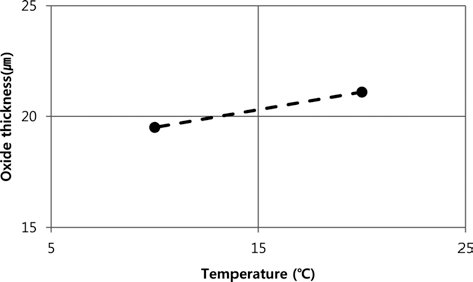
PDF In this study, an aluminum oxide layer for sealing treatment of nano-diamond powder was synthesized by anodizing under constant current. The produced pore size and oxide thickness were investigated using scanning electron microscopy. The pore size increased as the treatment time increased, current density increased, sulfuric acid concentration decreased, which is different from the results under constant voltage, due to a dissolution of the oxide layers. The oxide layer thickness by the anodizing increased as temperature, time, and current density increased. The results of this study can be applied to optimize the sealing treatment process of nano-diamond particles of 4-10 nm to enhance the resistances of corrosion and wear of the matrix.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Convergent Study of Aluminum Anodizing Method on the Thermal Fatigue
Soo Young Kang
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(5): 169. CrossRef - Convergent Study of Texture on the Mechanical Properties of Electrodeposits
Soo Young Kang
Journal of the Korea Convergence Society.2016; 7(6): 193. CrossRef - Study on Improvement of Corrosion Resistance and Wear Resistance by Anodizing and Sealing Treatment with Nano-diamond Powder on aluminum
Soo Young Kang, Dae Won Lee
Journal of the Korean institute of surface engineering.2014; 47(3): 121. CrossRef - Study on Hardness and Corrosion Resistance of Magnesium by Anodizing and Sealing Treatment With Nano-diamond Powder
Soo Young Kang, Dae Won Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(4): 260. CrossRef
- Convergent Study of Aluminum Anodizing Method on the Thermal Fatigue
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


