Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Smelting and Recycling of Niobium
- Ho-Sang Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):517-528. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00367
- 717 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
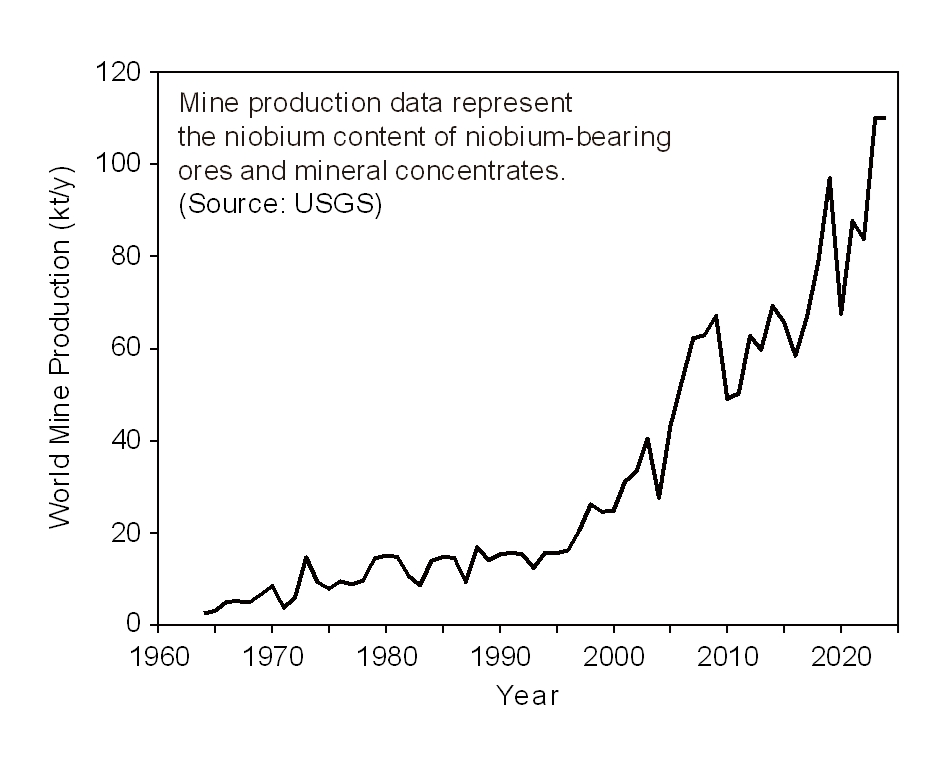
PDF - Global annual production of niobium is only around 100,000 tonnes; however, it is a critical metal for modern industry and is mined in only a limited number of regions. This study reviews the current status of niobium smelting and recycling technologies. Approximately 90% of niobium is produced as ferroniobium (FeNb) for use in steel alloys, although niobium is also utilized in superalloys, superconductors, capacitors, semiconductors, and other applications. Niobium coexists with tantalum in columbite and tantalite ores. These ores are decomposed by hydrofluoric acid digestion or alkali fusion, followed by solvent extraction to separate Nb2O5 and Ta2O5. Niobium metal and FeNb are produced from Nb2O5 primarily via aluminothermic reduction, although metallic niobium can also be manufactured by thermal reduction using Mg, Ca, or C, as well as by molten salt electrolysis. Crude niobium is subsequently refined into high-purity niobium through molten salt electrolytic refining, high-temperature vacuum treatment, and electron beam melting. Because most niobium is used as an alloying element in stainless steel and high-strength low-alloy steel, recycling practices for niobium remain poorly documented.
- [Korean]
- Flexible Hybrid Energy Harvester based on Thermoelectric Composite Film and Electrospun Piezopolymer Membranes
- Hyomin Jeon, Cheol Min Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, Hyejeong Choi, HakSu Jang, Kwi-Il Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):104-112. Published online March 4, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00458

- 972 View
- 32 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A hybrid energy harvester that consisted of thermoelectric (TE) composite film and electrospun piezoelectric (PE) polymeric membranes was constructed. TE composites were fabricated by dispersing inorganic TE powders inside polyvinylidene fluoride elastomer using a drop-casting technique. The polyvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene, which was chosen due to its excellent chemical resistance, mechanical stability, and biocompatibility, was electrospun onto an aluminum foil to fabricate the ultra-flexible PE membranes. To create a hybrid energy harvester that can simultaneously convert heat and mechanical energy resources into electricity, the TE composite films attached to the PE membrane were encapsulated with protective polydimethylsiloxane. The fabricated energy harvester converted the outputs with a maximum voltage of 4 V (PE performance) and current signals of 0.2 μA (TE performance) under periodical heat input and mechanical bending in hybrid modes. This study demonstrates the potential of the hybrid energy harvester for powering flexible and wearable electronics, offering a sustainable and reliable power source.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unidirectional porous PVDF Piezoelectrets fabricated via gradient ice-templating for enhanced energy harvesting performance
HyoMin Jeon, Seo Young Yoon, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, HakSu Jang, Changyeon Baek, Tiandong Zhang, Geon-Tae Hwang, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Sustainable Materials and Technologies.2026; 47: e01888. CrossRef
- Unidirectional porous PVDF Piezoelectrets fabricated via gradient ice-templating for enhanced energy harvesting performance
- [English]
- Effect of Calcium Addition on the High-Temperature Recovery of Nd and Dy from Nd-Fe-B Scrap Using Mg-Based Extractants
- Hyoseop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):493-499. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00283
- 1,694 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
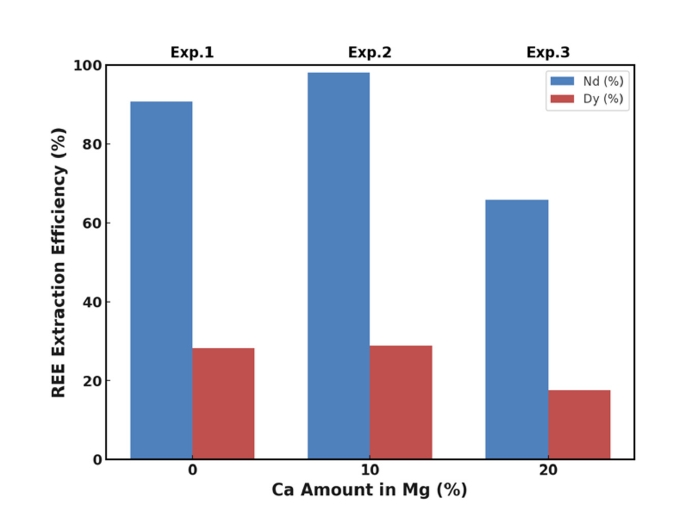
PDF - This study investigated whether calcium (Ca) addition improved the recovery of neodymium (Nd) and dysprosium (Dy) from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap using magnesium (Mg)-based liquid metal extraction (LME). Traditional LME processes are limited to temperatures up to 850 °C due to oxidation issues, reducing the efficiency of rare earth element (REE) recovery, especially for Dy. By adding 10 wt.% Ca to Mg and increasing the processing temperature to 1,000 °C, we achieved nearly 100% Nd and approximately 38% Dy recovery, compared to 91% and 28%, respectively, with pure Mg at 850 °C. However, excessive Ca addition (20 wt.%) decreased the recovery efficiency due to the formation of stable intermetallic compounds. These results highlight the critical role of Ca in optimizing REE recycling from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap.
- [Korean]
- Friction Welding of Casted SCM440 and Sintered F-05-140 Dissimilar Steels and Their Joint Properties under Various Welding Conditions
- Jisung Lee, Hansung Lee, Eunhyo Song, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):414-421. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00311
- 923 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
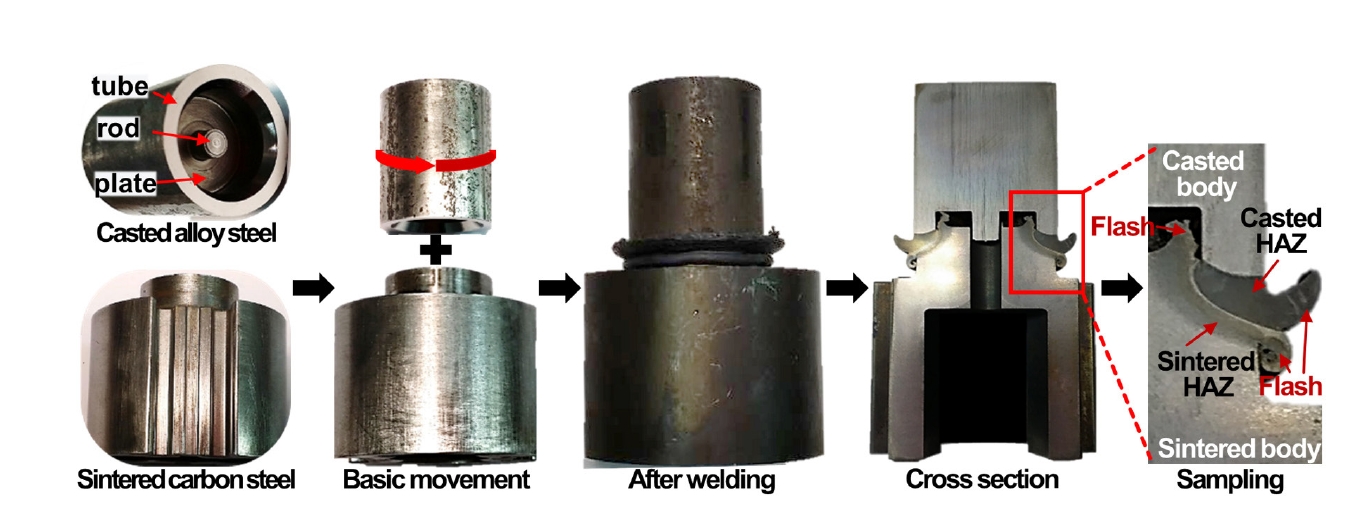
PDF - Friction welding, which uses heat and plastic flow to join metals, is expanding across industries due to its ability to weld heterogeneous alloys and simple process. However, process research is essential for materials with complex geometries, and limited research has been conducted on friction welding between cast and sintered metals. This study analyzed the mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of the joint by controlling the rotational speed and friction pressure, which affect the removal of the heat-affected zone in friction welding of casted SCM440 and sintered F-05-140. Hardness mapping and microstructure observations with material transition were performed to investigate the correlation between phase behavior and welding conditions. These results are anticipated to reduce costs and improve the mechanical properties of key mobility components.
- [English]
- Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
- Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):119-125. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00045
- 3,180 View
- 81 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
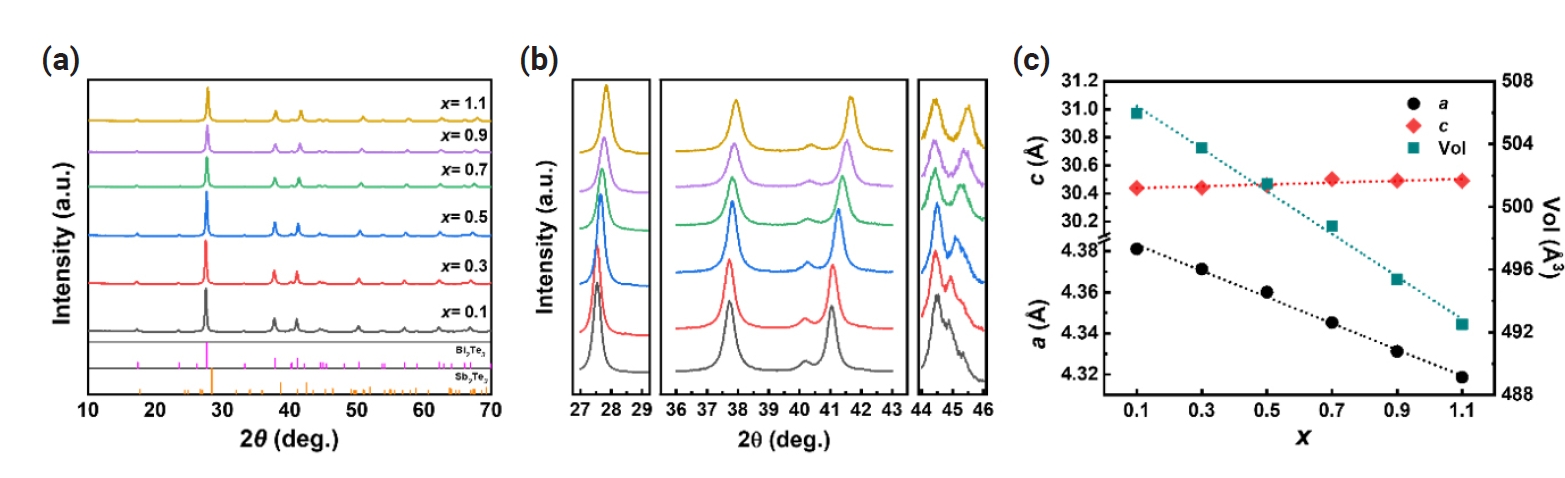
PDF - The n-type Bi2-xSbxTe3 compounds have been of great interest due to its potential to achieve a high thermoelectric performance, comparable to that of p-type Bi2-xSbxTe3. However, a comprehensive understanding on the thermoelectric properties remains lacking. Here, we investigate the thermoelectric transport properties and band characteristics of n-type Bi2-xSbxTe3 (x = 0.1 – 1.1) based on experimental and theoretical considerations. We find that the higher power factor at lower Sb content results from the optimized balance between the density of state effective mass and nondegenerate mobility. Additionally, a higher carrier concentration at lower x suppresses bipolar conduction, thereby reducing thermal conductivity at elevated temperatures. Consequently, the highest zT of ~ 0.5 is observed at 450 K for x = 0.1 and, according to the single parabolic band model, it could be further improved by ~70 % through carrier concentration tuning.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef - Enhanced energy harvesting performance of bendable thermoelectric generator enabled by trapezoidal-shaped legs
Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Cheol Min Kim, Hyejeong Choi, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Journal of Power Sources.2025; 631: 236254. CrossRef - Flexible hybrid thermoelectric films made of bismuth telluride-PEDOT:PSS composites enabled by freezing-thawing process and simple chemical treatment
Cheol Min Kim, Seoha Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Bitna Bae, Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Gwang Hyun Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Haksu Jang, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Chemistry.2025; 44: 102532. CrossRef - Enhanced Electrical Properties of 3D Printed Bi2Te3-Based Thermoelectric Materials via Hot Isostatic Pressing
Seungki Jo
Ceramist.2025; 28(1): 126. CrossRef - Hot isostatic pressing-driven fine-tuning of electrical properties in p- and n-type (Bi,Sb)2Te3 thermoelectric materials
Seungki Jo, Jeong Min Park, Linh Ba Vu, Haeum Park, Soo Ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Jungho Choe, Kyung Tae Kim
Ceramics International.2025; 51(26): 51107. CrossRef - Compensation of increased carrier concentration and thermal conductivity in enhancing thermoelectric efficiency in Sn-doped Sb-In-Te alloys
Yunjae Kim, Seungwoo Ha, Gyujin Chang, Gwan Hyeong Lee, Jaewoo Park, Chanwoo Ju, Se Yun Kim, TaeWan Kim, Sang-il Kim
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
- [English]
- Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):8-15. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.8
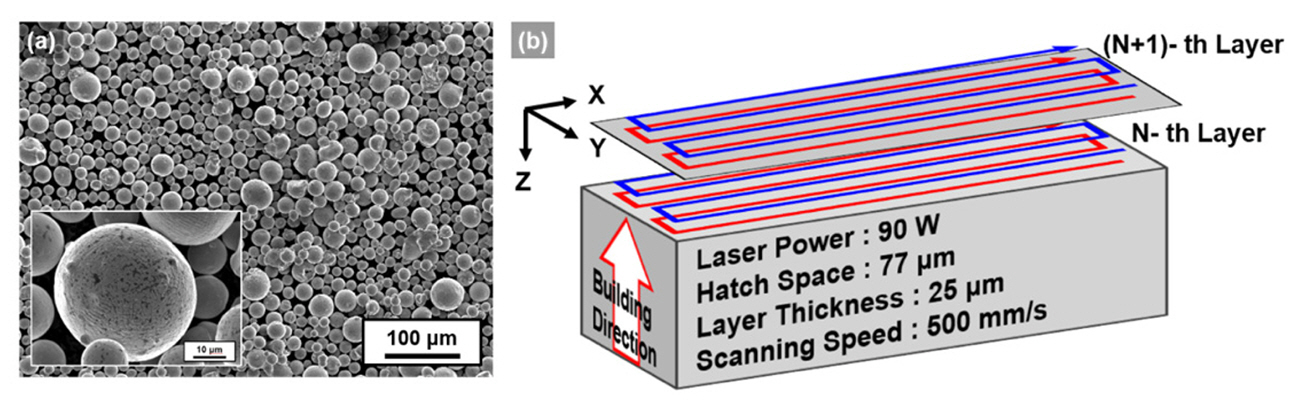
- 4,530 View
- 139 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The emergence of ferrous-medium entropy alloys (FeMEAs) with excellent tensile properties represents a potential direction for designing alloys based on metastable engineering. In this study, an FeMEA is successfully fabricated using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), a metal additive manufacturing technology. Tensile tests are conducted on the LPBF-processed FeMEA at room temperature and cryogenic temperatures (77 K). At 77 K, the LPBF-processed FeMEA exhibits high yield strength and excellent ultimate tensile strength through active deformation-induced martensitic transformation. Furthermore, due to the low stability of the face-centered cubic (FCC) phase of the LPBF-processed FeMEA based on nano-scale solute heterogeneity, stress-induced martensitic transformation occurs, accompanied by the appearance of a yield point phenomenon during cryogenic tensile deformation. This study elucidates the origin of the yield point phenomenon and deformation behavior of the FeMEA at 77 K.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stronger weld than base metal in face-centered cubic alloy through multi-scale heterogeneity
Yoona Lee, Sangwon Park, Dongwon Shin, Marcia Myung Hye Ahn, Wei Xiong, Nokeun Park, Hyoung Seop Kim, Je In Lee, Wookjin Lee, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park, Namhyun Kang
Materials Research Letters.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Effect of Building Orientation on Tensile Properties of Hastelloy X alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seong-June Youn, GooWon Noh, Seok Su Sohn, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(2): 130. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Cryogenic tensile behavior of carbon-doped CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Hyeonseok Kwon, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Jungho Choe, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jung Gi Kim, Jeong Min Park
Additive Manufacturing.2024; 86: 104223. CrossRef - Recent progress in high-entropy alloys for laser powder bed fusion: Design, processing, microstructure, and performance
Asker Jarlöv, Zhiguang Zhu, Weiming Ji, Shubo Gao, Zhiheng Hu, Priyanka Vivegananthan, Yujia Tian, Devesh Raju Kripalani, Haiyang Fan, Hang Li Seet, Changjun Han, Liming Tan, Feng Liu, Mui Ling Sharon Nai, Kun Zhou
Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports.2024; 161: 100834. CrossRef
- Stronger weld than base metal in face-centered cubic alloy through multi-scale heterogeneity
- [Korean]
- Effect of Substrate Pre-heating on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnet Manufactured by L-PBF
- Yeon Woo Kim, Haeum Park, Tae-Hoon Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):116-122. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.116
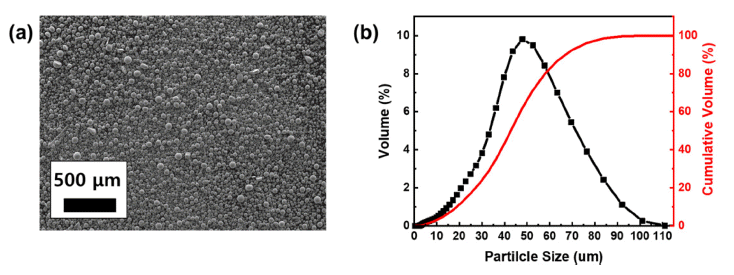
- 1,159 View
- 17 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Because magnets fabricated using Nd-Fe-B exhibit excellent magnetic properties, this novel material is used in various high-tech industries. However, because of the brittleness and low formability of Nd-Fe-B magnets, the design freedom of shapes for improving the performance is limited based on conventional tooling and postprocessing. Laserpowder bed fusion (L-PBF), the most famous additive manufacturing (AM) technique, has recently emerged as a novel process for producing geometrically complex shapes of Nd-Fe-B parts owing to its high precision and good spatial resolution. However, because of the repeated thermal shock applied to the materials during L-PBF, it is difficult to fabricate a dense Nd-Fe-B magnet. In this study, a high-density (>96%) Nd-Fe-B magnet is successfully fabricated by minimizing the thermal residual stress caused by substrate heating during L-PBF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Linkage between process-induced microstructure and magnetic property of Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Yeon Woo Kim, Sujin Lee, Yoona Lee, Jae Bok Seol, Namhyun Kang, Yoon Suk Choi, Ji-Hun Yu, Jung-Goo Lee, Tae-Hoon Kim, Jeong Min Park
Materials & Design.2025; 259: 114929. CrossRef
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- [Korean]
- Effect of Mo Addition on the Austenite Stability of Nanocrystalline Fe-7wt.%Mn Alloy Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
- Woochul Shin, Seung Bae Son, Jae-Gil Jung, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):517-522. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.517
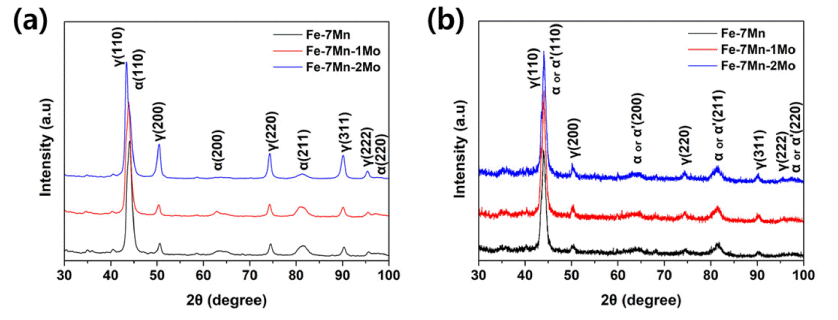
- 893 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We investigate the austenite stability in nanocrystalline Fe-7%Mn-X%Mo (X = 0, 1, and 2) alloys fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Mo is known as a ferrite stabilizing element, whereas Mn is an austenite stabilizing element, and many studies have focused on the effect of Mn addition on austenite stability. Herein, the volume fraction of austenite in nanocrystalline Fe-7%Mn alloys with different Mo contents is measured using X-ray diffraction. Using a disk compressive test, austenite in Fe–Mn–Mo alloys is confirmed to transform into strain-induced martensite during plastic deformation by a disk d. The variation in austenite stability in response to the addition of Mo is quantitatively evaluated by comparing the k-parameters of the kinetic equation for the strain-induced martensite transformation.
- [English]
- Optimization of VIGA Process Parameters for Power Characteristics of Fe-Si-Al-P Soft Magnetic Alloy using Machine Learning
- Sung-Min Kim, Eun-Ji Cha, Do-Hun Kwon, Sung-Uk Hong, Yeon-Joo Lee, Seok-Jae Lee, Kee-Ahn Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):459-467. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.459

- 885 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Soft magnetic powder materials are used throughout industries such as motors and power converters. When manufacturing Fe-based soft magnetic composites, the size and shape of the soft magnetic powder and the microstructure in the powder are closely related to the magnetic properties. In this study, Fe-Si-Al-P alloy powders were manufactured using various manufacturing process parameter sets, and the process parameters of the vacuum induction melt gas atomization process were set as melt temperature, atomization gas pressure, and gas flow rate. Process variable data that records are converted into 6 types of data for each powder recovery section. Process variable data that recorded minute changes were converted into 6 types of data and used as input variables. As output variables, a total of 6 types were designated by measuring the particle size, flowability, apparent density, and sphericity of the manufactured powders according to the process variable conditions. The sensitivity of the input and output variables was analyzed through the Pearson correlation coefficient, and a total of 6 powder characteristics were analyzed by artificial neural network model. The prediction results were compared with the results through linear regression analysis and response surface methodology, respectively.
- [English]
- Nitric Oxide Detection of Fe(DTC)3-hybrizided CdSe Quantum Dots Via Fluorescence Energy Transfer
- Chang-Yeoul Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):453-458. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.453
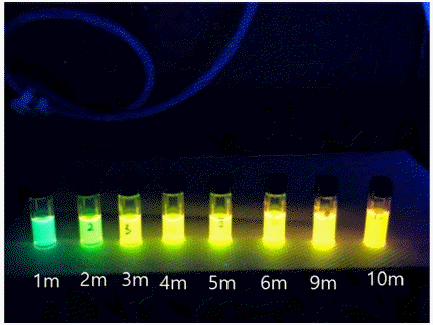
- 1,152 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We successfully synthesize water-dispersible CTAB-capped CdSe@ZnS quantum dots with the crystal size of the CdSe quantum dots controlled from green to orange colors. The quenching effect of Fe(DTC)3 is very efficient to turn off the emission light of quantum dots at four molar ratios of the CdSe quantum dots, that is, the effective covering the surface of quantum dots with Fe(DTC)3. However, the reaction with Fe(DTC)3 for more than 24 h is required to completely realize the quenching effect. The highly quenched quantum dots efficiently detect nitric oxide at nano-molar concentration of 110nM of NO with 34% of recovery of emission light intensity. We suggest that Fe(DTC)3-hybridized CdSe@ZnS quantum dots are an excellent fluorescence resonance energy transfer probe for the detection of nitric oxide in biological systems.
- [Korean]
- Gradient Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-6%Mn Alloy by Different Sized Powder Stacking
- Namhyuk Seo, Junho Lee, Woocheol Shin, Junhyub Jeon, Jungbin Park, Seung Bae Son, Jae-Gil Jung, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):382-389. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.382

- 750 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A typical trade-off relationship exists between strength and elongation in face-centered cubic metals. Studies have recently been conducted to enhance strength without ductility reduction through surface-treatment-based ultrasonic nanocrystalline surface modification (UNSM), which creates a gradient microstructure in which grains become smaller from the inside to the surface. The transformation-induced plasticity effect in Fe-Mn alloys results in excellent strength and ductility due to their high work-hardening rate. This rate is achieved through strain-induced martensitic transformation when an alloy is plastically deformed. In this study, Fe-6%Mn powders with different sizes were prepared by high-energy ball milling and sintered through spark plasma sintering to produce Fe-6%Mn samples. A gradient microstructure was obtained by stacking the different-sized powders to achieve similar effects as those derived from UNSM. A compressive test was performed to investigate the mechanical properties, including the yielding behavior. The deformed microstructure was observed through electron backscatter diffraction to determine the effects of gradient plastic deformation.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Iron Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Mo-Fe P/M Alloys
- HyoWoon Hwang, YongJae Lee, JiHwan Park, Dong-Geun Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):325-331. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.325
- 1,189 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Beta-titanium alloys are used in many industries due to their increased elongation resulting from their BCC structure and low modulus of elasticity. However, there are many limitations to their use due to the high cost of betastabilizer elements. In this study, biocompatible Ti-Mo-Fe beta titanium alloys are designed by replacing costly betastabilizer elements (e.g., Nb, Zr, or Ta) with inexpensive Mo and Fe elements. Additionally, Ti-Mo-Fe alloys designed with different Fe contents are fabricated using powder metallurgy. Fe is a strong, biocompatible beta-stabilizer element and a low-cost alloying element. The mechanical properties of the Ti-Mo-Fe metastable beta titanium alloys are analyzed in relation to the microstructural changes. When the Fe content increases, the tensile strength and elongation decrease due to brittle fracture despite a decreasing pore fraction. It is confirmed that the hardness and tensile strength of Ti-5Mo-2Fe P/M improve to more than 360 Hv and 900 MPa, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 288. CrossRef - Fabrication of Ti-Mo Core-shell Powder and Sintering Properties for Application as a Sputtering Target
Won Hee Lee, Chun Woong Park, Heeyeon Kim, Yuncheol Ha, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 43. CrossRef - Effect of Strain Rate on Deformation Behaviors of Ti-12.1Mo -1Fe Metastable Beta Alloy
In Kyeong Jin, Dong-Geun Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(10): 741. CrossRef
- Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
- [Korean]
- Manufacturing of Fe-Mn-Al-C Based Low Mn Lightweight Steel Via Direct Energy Deposition
- Kwang Kyu Ko, Han Sol Son, Cha Hee Jung, Hyo Ju Bae, Eun Hye Park, Jung Gi Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Jae Bok Seol
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):320-324. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.320
- 1,291 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Lightweight steel is a crucial material that is being actively studied because of increased carbon emissions, tightening regulations regarding fuel efficiency, and the emergence of UAM, all of which have been recently labeled as global issues. Hence, new strategies concerning the thickness and size reduction of steel are required. In this study, we manufacture lightweight steel of the Fe-Mn-Al-C system, which has been recently studied using the DED process. By using 2.8 wt.% low-Mn lightweight steel, we attempt to solve the challenge of joining steel parts with a large amount of Mn. Among the various process variables, the laser scan power is set at 600 and 800W, and the laser scan speed is fixed at 16.67 mm/s before the experiments. Several pores and cracks are observed under both conditions, and negligibly small pores of approximately 0.5 μm are observed.
- [Korean]
- Porosity Prediction of the Coating Layer Based on Process Conditions of HVOF Thermal Spray Coating
- Junhyub Jeon, Namhyuk Seo, Jong Jae Lee, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):478-482. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.478

- 443 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The effect of the process conditions of high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) thermal spray coating on the porosity of the coating layer is investigated. HVOF coating layers are formed by depositing amorphous FeMoCrBC powder. Oxygen pressure varies from 126 to 146 psi and kerosene pressure from 110 to 130 psi. The Microstructural analysis confirms its porosity. Data analysis is performed using experimental data. The oxygen pressure-kerosene pressure ratio is found to be a key contributor to the porosity. An empirical model is proposed using linear regression analysis. The proposed model is then validated using additional test data. We confirm that the oxygen pressure-kerosene pressure ratio exponentially increases porosity. We present a porosity prediction model relationship for the oxygen pressure-kerosene pressure ratio.
- [Korean]
- Preparation of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticle Decorated on Electrospun Carbon Nanofiber Composite Electrodes for Supercapacitors
- Hyewon Hwang, Seoyeon Yuk, Minsik Jung, Dongju Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):470-477. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.470
- 749 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
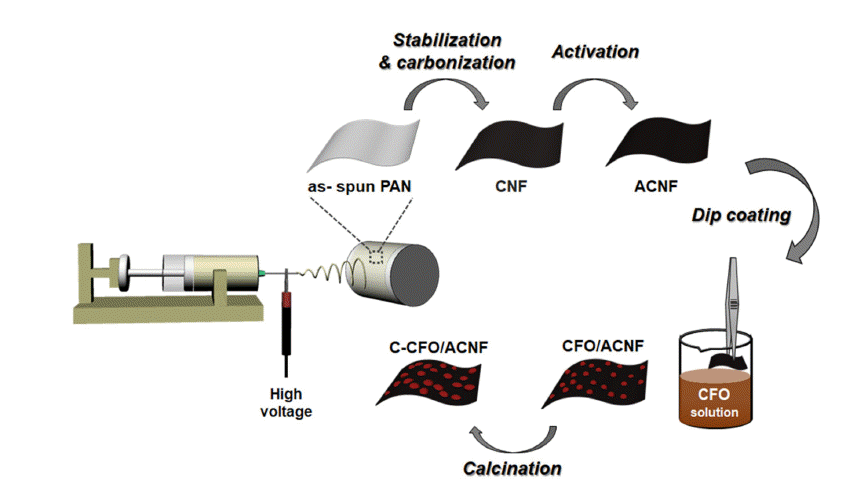
PDF Energy storage systems should address issues such as power fluctuations and rapid charge-discharge; to meet this requirement, CoFe2O4 (CFO) spinel nanoparticles with a suitable electrical conductivity and various redox states are synthesized and used as electrode materials for supercapacitors. In particular, CFO electrodes combined with carbon nanofibers (CNFs) can provide long-term cycling stability by fabricating binder-free three-dimensional electrodes. In this study, CFO-decorated CNFs are prepared by electrospinning and a low-cost hydrothermal method. The effects of heat treatment, such as the activation of CNFs (ACNFs) and calcination of CFO-decorated CNFs (C-CFO/ACNFs), are investigated. The C-CFO/ACNF electrode exhibits a high specific capacitance of 142.9 F/g at a scan rate of 5 mV/s and superior rate capability of 77.6% capacitance retention at a high scan rate of 500 mV/s. This electrode also achieves the lowest charge transfer resistance of 0.0063 Ω and excellent cycling stability (93.5% retention after 5,000 cycles) because of the improved ion conductivity by pathway formation and structural stability. The results of our work are expected to open a new route for manufacturing hybrid capacitor electrodes containing the C-CFO/ACNF electrode that can be easily prepared with a low-cost and simple process with enhanced electrochemical performance.
- [Korean]
- Austenite Stability and Mechanical Properties of Nanocrystalline FeNiCrMoMnSiC Alloy Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
- Jungbin Park, Junhyub Jeon, Namhyuk Seo, Gwanghun Kim, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(4):336-341. Published online August 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.4.336
- 933 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, a nanocrystalline FeNiCrMoMnSiC alloy was fabricated, and its austenite stability, microstructure, and mechanical properties were investigated. A sintered FeNiCrMoMnSiC alloy sample with nanosized crystal was obtained by high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. The sintering behavior was investigated by measuring the displacement according to the temperature of the sintered body. Through microstructural analysis, it was confirmed that a compact sintered body with few pores was produced, and cementite was formed. The stability of the austenite phase in the sintered samples was evaluated by X-ray diffraction analysis and electron backscatter diffraction. Results revealed a measured value of 51.6% and that the alloy had seven times more austenite stability than AISI 4340 wrought steel. The hardness of the sintered alloy was 60.4 HRC, which was up to 2.4 times higher than that of wrought steel.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and mechanical behavior of AISI 4340 steel fabricated via spark plasma sintering and post-heat treatment
Jungbin Park, Junhyub Jeon, Namhyuk Seo, Singon Kang, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2023; 862: 144433. CrossRef
- Microstructure and mechanical behavior of AISI 4340 steel fabricated via spark plasma sintering and post-heat treatment
- [Korean]
- Measurement Method of Prior Austenite Grain Size of Nb-added Fe-based Alloys
- Kwang Kyu Ko, Hyo Ju Bae, Sin Woo Jung, Hyo Kyung Sung, Jung Gi Kim, Jae Bok Seol
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(4):317-324. Published online August 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.4.317

- 1,102 View
- 12 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels show excellent toughness when trace amounts of transition elements are added. In steels, prior austenite grain size (PAGS), which is often determined by the number of added elements, is a critical factor in determining the mechanical properties of the material. In this study, we used two etching methods to measure and compare the PAGS of specimens with bainitic HSLA steels having different Nb contents These two methods were nital etching and picric acid etching. Both methods confirmed that the sample with high Nb content exhibited smaller PAGS than its low Nb counterpart because of Nb’s ability to hinder austenite recrystallization at high temperatures. Although both etching approaches are beneficial to PAGS estimation, the picric acid etching method has the advantage of enabling observation of the interface containing Nb precipitate. By contrast, the nital etching method has the advantage of a very short etching time (5 s) in determining the PAGS, with the picric acid etching method being considerably longer (5 h).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Austempering vs. Q&P: Comparative effects on microstructure and mechanical properties of complex-alloyed TRIP-assisted steel
V.G. Efremenko, Yu.G. Chabak, I. Petryshynets, I. Sili, T.M. Kovbasiuk, A.V. Efremenko, M.N. Brykov, M. Dabalá, M. Franceschi, H. Halfa, A.G. Lekatou
Materials Today Communications.2025; 47: 113179. CrossRef
- Austempering vs. Q&P: Comparative effects on microstructure and mechanical properties of complex-alloyed TRIP-assisted steel
- [Korean]
- Improvement of Mechanical Properties of Nanocrystalline FeCrC Alloy via Strain-Induced Martensitic Transformation
- Gwanghun Kim, Junhyub Jeon, Namhyuk Seo, Jungbin Park, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):246-252. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.246

- 532 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The effect of sintering conditions on the austenite stability and strain-induced martensitic transformation of nanocrystalline FeCrC alloy is investigated. Nanocrystalline FeCrC alloys are successfully fabricated by spark plasma sintering with an extremely short densification time to obtain the theoretical density value and prevent grain growth. The nanocrystallite size in the sintered alloys contributes to increased austenite stability. The phase fraction of the FeCrC sintered alloy before and after deformation according to the sintering holding time is measured using X-ray diffraction and electron backscatter diffraction analysis. During compressive deformation, the volume fraction of strain-induced martensite resulting from austenite decomposition is increased. The transformation kinetics of the strain-induced martensite is evaluated using an empirical equation considering the austenite stability factor. The hardness of the S0W and S10W samples increase to 62.4-67.5 and 58.9-63.4 HRC before and after deformation. The hardness results confirmed that the mechanical properties are improved owing to the effects of grain refinement and strain-induced martensitic transformation in the nanocrystalline FeCrC alloy.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Sintering Condition on Tensile Strength of Fe-based Non-equiatomic High Entropy Alloy
- Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jeon, Gwanghun Kim, Jungbin Park, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):221-226. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.221

- 985 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We fabricate the non-equiatomic high-entropy alloy (NE-HEA) Fe49.5Mn30Co10Cr10C0.5 (at.%) using spark plasma sintering under various sintering conditions. Each elemental pure powder is milled by high-energy ball milling to prepare NE-HEA powder. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the sintered samples are investigated using various methods. We use the X-ray diffraction (XRD) method to investigate the microstructural characteristics. Quantitative phase analysis is performed by direct comparison of the XRD results. A tensile test is used to compare the mechanical properties of small samples. Next, electron backscatter diffraction analysis is performed to analyze the phase fraction, and the results are compared to those of XRD analysis. By combining different sintering durations and temperature conditions, we attempt to identify suitable spark plasma sintering conditions that yield mechanical properties comparable with previously reported values. The samples sintered at 900 and 1000°C with no holding time have a tensile strength of over 1000 MPa.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
- [Korean]
- Mn-doping Effect on the Blackness and NIR Reflectance of Fe2O3 Cool Pigments
- Jin Soo Hwang, Kyeong Youl Jung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):38-43. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.38

- 809 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A high NIR-reflective black pigment is developed by Mn doping of Fe2O3. The pigment powders are prepared by spray pyrolysis, and the effect of the Mn concentration on the blackness and optical properties is investigated. Mn doping into the crystal lattice of α-Fe2O3 is found to effectively change the powder color from red to black, lowering the NIR reflectance compared to that of pure Fe2O3. The pigment doped with 10% Mn, i.e., Fe1.8Mn0.2O3, exhibits a black color with an optical bandgap of 1.3 eV and a Chroma value of 1.14. The NIR reflectance of the prepared Fe1.8Mn0.2O3 black pigment is 2.2 times higher than that of commercially available carbon black, and this material is proven to effectively work as a cool pigment in a temperature rise experiment under near-infrared illumination.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced near-infrared reflectance of TiO2/(Fe,Mn)2O3 composite black pigments synthesized by spray pyrolysis
Jin Soo Hwang, Kyeong Youl Jung
Ceramics International.2026; 52(1): 1041. CrossRef
- Enhanced near-infrared reflectance of TiO2/(Fe,Mn)2O3 composite black pigments synthesized by spray pyrolysis
- [Korean]
- Analysis of Wafer Cleaning Solution Characteristics and Metal Dissolution Behavior according to the Addition of Chelating Agent
- Myungsuk Kim, Keunhyuk Ryu, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):25-30. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.25

- 1,016 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The surface of silicon dummy wafers is contaminated with metallic impurities owing to the reaction with and adhesion of chemicals during the oxidation process. These metallic impurities negatively affect the device performance, reliability, and yield. To solve this problem, a wafer-cleaning process that removes metallic impurities is essential. RCA (Radio Corporation of America) cleaning is commonly used, but there are problems such as increased surface roughness and formation of metal hydroxides. Herein, we attempt to use a chelating agent (EDTA) to reduce the surface roughness, improve the stability of cleaning solutions, and prevent the re-adsorption of impurities. The bonding between the cleaning solution and metal powder is analyzed by referring to the Pourbaix diagram. The changes in the ionic conductivity, H2O2 decomposition behavior, and degree of dissolution are checked with a conductivity meter, and the changes in the absorbance and particle size before and after the reaction are confirmed by ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) analyses. Thus, the addition of a chelating agent prevents the decomposition of H2O2 and improves the life of the silicon wafer cleaning solution, allowing it to react smoothly with metallic impurities.
- [Korean]
- Austenite Stability of Sintered Fe-based Alloy
- Seunggyu Choi, Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jun, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):414-419. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.414

- 1,308 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the present study, we investigated the austenite stability of a sintered Fe-based nanocrystalline alloy. The volume fraction of austenite was measured based on the X-ray diffraction data of sintered Fe-based nanocrystalline alloys, which were prepared by high-energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering. The sintered alloy samples showed a higher volume fraction of austenite at room temperature as compared to the equilibrium volume fraction of austenite obtained using thermodynamic calculations, which resulted from the nanosized crystalline structure of the sintered alloy. It was proved that the austenite stability of the sintered Fe-based alloy increased with a rise in the amount of austenite stabilizing elements such as Mn, Ni, and C; however, it increased more effectively with a decrease in the actual grain size. Furthermore, we proposed a new equation to predict the martensite starting temperature for sintered Fe-based alloys.
- [Korean]
- Partially Dry-Transferred Graphene Electrode with Zinc Oxide Nanopowder and Its Application on Organic Solar Cells
- Yeongsu Jo, Chae Young Woo, Soon Kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):305-310. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.305
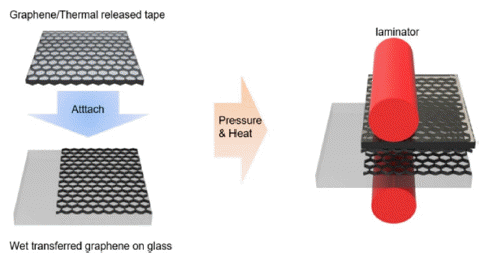
- 557 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, partially dry transfer is investigated to solve the problem of fully dry transfer. Partially dry transfer is a method in which multiple layers of graphene are dry-transferred over a wet-transferred graphene layer. At a wavelength of 550 nm, the transmittance of the partially dry-transferred graphene is seen to be about 3% higher for each layer than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene. Furthermore, the sheet resistance of the partially drytransferred graphene is relatively lower than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene, with the minimum sheet resistance being 179 Ω/sq. In addition, the fully dry-transferred graphene is easily damaged during the solution process, so that the performance of the organic photovoltaics (OPV) does not occur. In contrast, the best efficiency achievable for OPV using the partially dry-transferred graphene is 2.37% for 4 layers.
- [Korean]
- Study on the Compaction Properties of Fe-Si-Al-Graphite Powder Mixtures
- Jun Hyeok Jeong, Jinnil Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):300-304. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.300
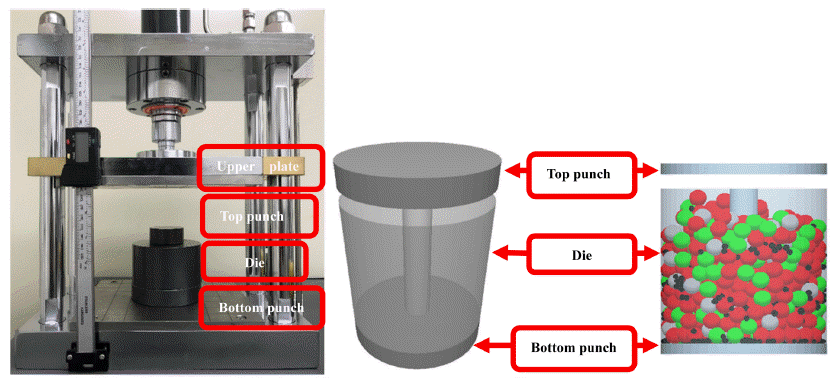
- 579 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this paper, a durability study is presented to enhance the mechanical properties of an Fe-Si-Al powderbased magnetic core, through the addition of graphite. The compressive properties of Fe-Si-Al-graphite powder mixtures are explored using discrete element method (DEM), and a powder compaction experiment is performed under identical conditions to verify the reliability of the DEM analysis. Important parameters for powder compaction of Fe-Si-Algraphite powder mixtures are identified. The compressibility of the powders is observed to increase as the amount of graphite mixture increases and as the size of the graphite powders decreases. In addition, the compaction properties of the Fe-Si-Al-graphite powder mixtures are further explored by analyzing the transmissibility of stress between the top and bottom punches as well as the distribution of the compressive force. The application of graphite powders is confirmed to result in improved stress transmission and compressive force distribution, by 24% and 51%, respectively.
- [Korean]
- Fluorescent Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications
- Y. K. Kim, B. K. Song, J. G. Lee, Y. K. Baek
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):154-163. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.154
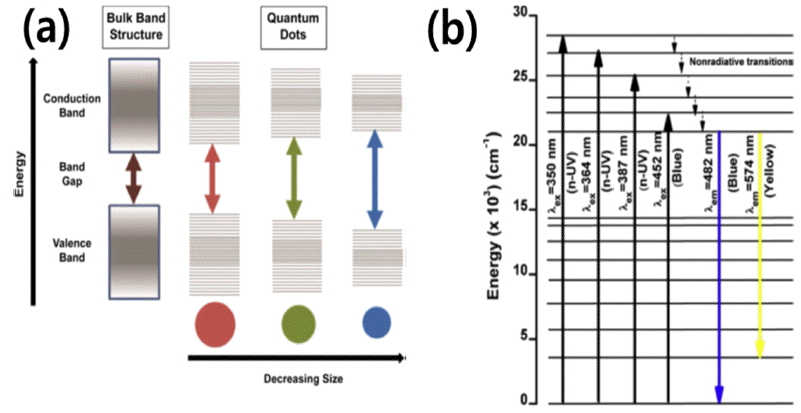
- 2,921 View
- 12 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fluorescent nanoparticles are characterized by their unique properties such as luminescence, optical transparency, and sensitivity to various chemical environments. For example, semiconductor nanocrystals (quantum dots), which are nanophosphors doped with transition metal or rare earth ions, can be classified as fluorescent nanoparticles. Tuning their optical and physico-chemical properties can be carried out by considering and taking advantage of nanoscale effects. For instance, quantum confinement causes a much higher fluorescence with nanoparticles than with their bulk counterparts. Recently, various types of fluorescent nanoparticles have been synthesized to extend their applications to other fields. In this study, State-of-the-art fluorescent nanoparticles are reviewed with emphasis on their analytical and anti-counterfeiting applications and synthesis processes. Moreover, the fundamental principles behind the exceptional properties of fluorescent nanoparticles are discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation and Analysis of High Functional Silicone Hydrogel Lens Containing Metal Oxide Nanoparticles by Photopolymerizaion
Ji-Won Heo, A-Young Sung
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2022; 32(4): 193. CrossRef
- Preparation and Analysis of High Functional Silicone Hydrogel Lens Containing Metal Oxide Nanoparticles by Photopolymerizaion
- [Korean]
- Sintering Behavior of M-type Sr-Hexaferrite by MnCO3 Addition
- MinSeok Jeong, Changjae You, Jung Young Cho, Kyoung-Seok Moon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):126-131. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.126
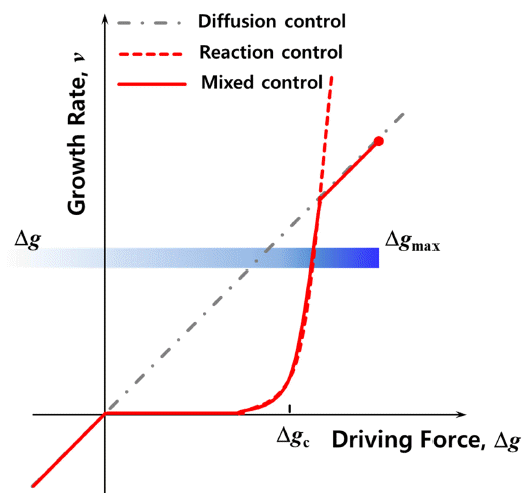
- 589 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The grain growth behavior of M-type Sr hexaferrite (SrM) grains is investigated with the addition of MnCO3. First, the SrM powder is synthesized by a conventional solid-state reaction. The powder compacts of SrM are sintered at 1250°C for 2 h with various amounts of MnCO3 (0, 0.5, 1.0, and 4.0 mol%). There is no secondary solid phase in any of the sintered samples. Relative density increases when MnCO3 is added to the SrM. Obvious abnormal grain growth does not appear in any of the SrM samples with MnCO3. The average grain size increases when 0.5 mol% MnCO3 is added to the SrM. However, as the amount of MnCO3 increase to over 0.5 mol%, the average grain size decreases. These observations allow us to conclude that the growth of SrM grains is governed by the two-dimensional nucleation grain growth mechanism, and the critical driving force for the growth of a grain decreases as the amount of MnCO3 increases.
- [Korean]
- Optimization of Metal Powder Particle Size Distribution for Powder Bed Fusion Process via Simulation
- Hwaseon Lee, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Young Il Kim, Jieun Nam, Yong Son, Taek-Soo Kim, Bin Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):44-51. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.44
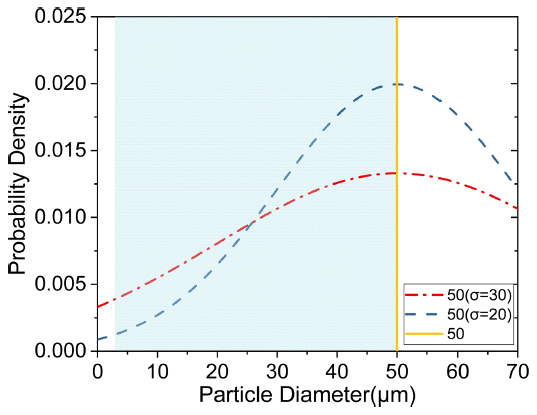
- 1,529 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Powder characteristics, such as density, size, shape, thermal properties, and surface area, are of significant importance in the powder bed fusion (PBF) process. The powder required is exclusive for an efficient PBF process. In this study, the particle size distribution suitable for the powder bed fusion process was derived by modeling the PBF product using simulation software (GeoDict). The modeling was carried out by layering sintered powder with a large particle size distribution, with 50 μm being the largest particle size. The results of the simulation showed that the porosity decreased when the mean particle size of the powder was reduced or the standard deviation increased. The particle size distribution of prepared titanium powder by the atomization process was also studied. This study is expected to offer direction for studies related to powder production for additive manufacturing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the International Symposium on Innovation in Materials Processing (ISIMP, 26–29 October 2021)”
Hyunjoo Choi, Jungjoon Kim, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung Seop Kim
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2023; 64(10): 2542. CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the International Symposium on Innovation in Materials Processing (ISIMP, 26–29 October 2021)”
- [Korean]
- Structural Characteristics, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-Cr-Al Metallic Foam Fabricated by Powder Alloying Process
- Kyu-Sik Kim, Byeong-Hoon Kang, Man-Ho Park, Jung-Yeul Yun, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):37-43. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.37
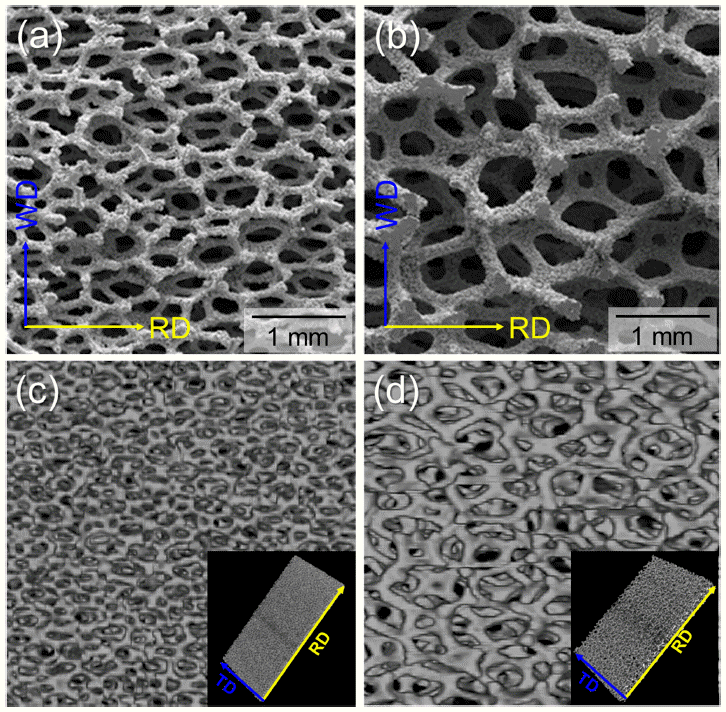
- 651 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The Fe-22wt.%Cr-6wt.%Al foams were fabricated via the powder alloying process in this study. The structural characteristics, microstructure, and mechanical properties of Fe-Cr-Al foams with different average pore sizes were investigated. Result of the structural analysis shows that the average pore sizes were measured as 474 μm (450 foam) and 1220 μm (1200 foam). Regardless of the pore size, Fe-Cr-Al foams had a Weaire-Phelan bubble structure, and α-ferrite was the major constituent phase. Tensile and compressive tests were conducted with an initial strain rate of 10−3 /s. Tensile yield strengths were 3.4 MPa (450 foam) and 1.4 MPa (1200 foam). Note that the total elongation of 1200 foam was higher than that of 450 foam. Furthermore, their compressive yield strengths were 2.5 MPa (450 foam) and 1.1 MPa (1200 foam), respectively. Different compressive deformation behaviors according to the pore sizes of the Fe-Cr-Al foams were characterized: strain hardening for the 450 foam and constant flow stress after a slight stress drop for the 1200 foam. The effect of structural characteristics on the mechanical properties was also discussed.
- [Korean]
- Synthesize of Nd2Fe14B Powders from 1-D Nd2Fe14B Wires using Electrospinning Process
- Nu Si A Eom, Su Noh, Muhammad Aneeq Haq, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):477-480. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.477

- 896 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Magnetic 0-D Nd2Fe14B powders are successfully fabricated using 1-D Nd2Fe14B nanowire formed by an efficient and facile electrospinning process approach. The synthesized Nd-Fe-B fibers and powders are investigated for their microstructural, crystallographic, and magnetic properties according to a series of subsequent heat treatments. Each heat-treatment process leads to the removal of organic impurities and the formation of the respective oxides/composites of Nd, Fe, and B, resulting in the formation of Nd2Fe14B powders. Nd-Fe-B fibers exhibit the following magnetic properties: The coercivity (Hci) of 3260 Oe, a maximum magnetization at 3T of 109.44 emu/g, and a magnetization remanence (Mr) of 44.11 emu/g. This process easily mass produces hard magnetic Nd2Fe14B powders using a 1-D synthesis process and can be extended to the experimental design of other magnetic materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nd2Fe14B/FeCo Core–Shell Nanoparticle Synthesis Using Galvanic Substitution Based Electroless Plating
Muhammad Aneeq Haq, Han-Saem Lee, Mi Hye Lee, Da-Woon Jeong, Eom Nu Si A, Bin Lee, Yoseb Song, Bum Sung Kim
Coatings.2022; 12(3): 389. CrossRef
- Nd2Fe14B/FeCo Core–Shell Nanoparticle Synthesis Using Galvanic Substitution Based Electroless Plating
- [Korean]
- The Influence of Fe Particle Size on the Critical Properties of MgB2 Superconductor
- Hyeondeok Jeong, Dong-Gun Lee, Sung-Soo Ryu, Hai-Woong Park, Chan-Joong Kim, Byung-Hyuk Jun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):432-436. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.432
- 555 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study demonstrates the effect of addition of Fe particles of different sizes on the critical properties of the superconductor MgB2. Bulk MgB2 is synthesized by ball milling Mg and B powders with Fe particles at 900°C. When Fe particles with size less than 10 μm are added in MgB2, they easily react with B and form the FeB phase, resulting in a reduction in the amount of the MgB2 phase and deterioration of the crystallinity. Accordingly, both the critical temperature and the critical current density are significantly reduced. On the other hand, when larger Fe particles are added, the Fe2B phase forms instead of FeB due to the lower reactivity of Fe toward B. Accordingly, negligible loss of B occurs, and the critical properties are found to be similar to those of the intact MgB2.
- [Korean]
- Austenite Stability of Nanocrystalline FeMnNiC Alloy
- Seung-Jin Oh, Junhyub Jeon, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):389-394. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.389
- 914 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the present study, we have investigated the effect of sintering process conditions on the stability of the austenite phase in the nanocrystalline Fe-5wt.%Mn-0.2wt.%C alloy. The stability and volume fraction of the austenite phase are the key factors that determine the mechanical properties of FeMnC alloys, because strain-induced austenitemartensite transformation occurs under the application of an external stress at room temperature. Nanocrystalline Fe-5wt.%Mn-0.2wt.%C samples are fabricated using the spark plasma sintering method. The stability of the austenite phase in the sintered samples is evaluated by X-ray diffraction analysis and hardness test. The volume fraction of austenite at room temperature increases as the sample is held for 10 min at the sintering temperature, because of carbon diffusion in austenite. Moreover, water quenching effectively prevents the formation of cementite during cooling, resulting in a higher volume fraction of austenite. Furthermore, it is found that the hardness is influenced by both the austenite carbon content and volume fraction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Cobalt Content on Austenite Stability and Strain-Induced Martensite Transformation of Nanocrystalline Fe-7Mn Alloy Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
Sungjin Kim, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(7): 811. CrossRef - Austenite Stability of Sintered Fe-based Alloy
Seunggyu Choi, Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jun, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 414. CrossRef
- Influence of Cobalt Content on Austenite Stability and Strain-Induced Martensite Transformation of Nanocrystalline Fe-7Mn Alloy Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
- [Korean]
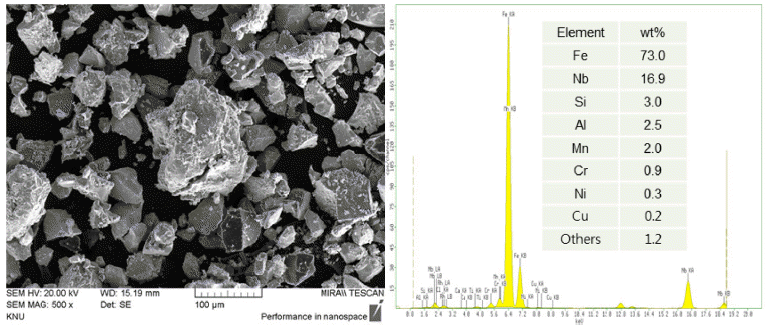
- Microstructure and Characterization of Overlay Welding Layer using Fe-based Composite Powders
- Hong Min, Jong-Jae Lee, Jin Kyu Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):214-219. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.214
- 757 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, the microstructure and characterization of an overlay welding layer using Fe-based composite powders are reported. The effects of the number of passes and composition of powders on the microstructure and mechanical properties are investigated in detail. The welding wire and powders are deposited twice on a stainless-steel rod using a laser overlay welding process. The microstructure and structural characterization are performed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The mechanical properties of the first and second overlay layers are analyzed through the micro-Vickers-hardness tester and abrasion wear tester. In the second overlay layer, the hardness and specific wear are approximately 840 Hv and 2.0 × 10−5 mm3/Nm, respectively. It is suggested that the increase of the volume fractions of (Cr,Fe)7C3 and NbC phases in the second welding layer enhances the hardness and wear resistance.
- [Korean]
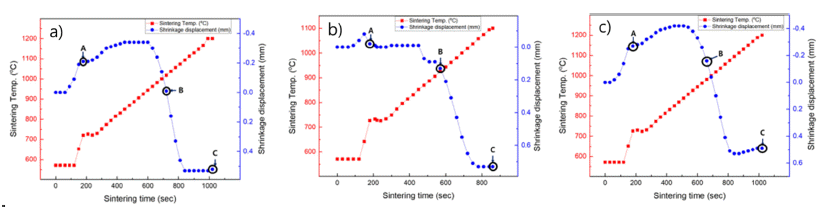
- Property Evaluation of Tungsten-Carbide Hard Materials as a Function of Binder
- Ju-Hun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Jeong-Han Lee, Sung-Kil Hong, Hyun-Kuk Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):132-137. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.132
- 1,074 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten carbide (WC) hard materials are used in various industries and possess a superior hardness compared to other hard materials. They have particularly high melting points, high strength, and abrasion resistance. Accordingly, tungsten carbide hard materials are used for wear-resistant tools, cutting tools, machining tools, and other tooling materials. In this study, the WC-5wt.%Co, Fe, Ni hard materials are densified using the horizontal ball milled WC-Co, WC-Fe, and WC-Ni powders by a spark plasma sintering process. The WC-5Co, WC-5Fe, and WC-5Ni hard materials are almost completely densified with a relative density of up to 99.6% after simultaneous application of a pressure of 60 MPa and an electric current for about 15 min without any significant change in the grain size. The average grain size of WC-5Co, WC-5Fe, and WC-5Ni that was produced through SPS was about 0.421, 0.779, and 0.429 μm, respectively. The hardness and fracture toughness of the dense WC-5Co, WC-5Fe, WC-5Ni hard materials were also investigated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing Mechanical Properties via Grain Growth Suppression and High Densification in WC Compacts
Jong Min Gwak, Min Soo Park, Gook Hyun Ha, Nam Hyun Kang
Metals and Materials International.2025; 31(12): 3733. CrossRef - Synthesis of W2C by Spark Plasma Sintering of W-WC Powder Mixture and Its Etching Property
Gyu-Sang Oh, Sung-Min Lee, Sung-Soo Ryu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(4): 293. CrossRef - Fabrication and Properties of Densified Tungsten by Magnetic Pulse Compaction and Spark Plasma Sintering
Eui Seon Lee, Jongmin Byun, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2020; 30(6): 321. CrossRef
- Enhancing Mechanical Properties via Grain Growth Suppression and High Densification in WC Compacts
- [Korean]
- Thermal Properties and Microstructural Changes of Fe-Co System Valve Seat Alloy by High Densification Process
- In-Shup Ahn, Dong-Kyu Park, Kwang-Bok Ahn, Seoung-Mok Shin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):112-118. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.112

- 892 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Infiltration is a popular technique used to produce valve seat rings and guides to create dense parts. In order to develop valve seat material with a good thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient, Cu-infiltrated properties of sintered Fe-Co-M(M=Mo,Cr) alloy systems are studied. It is shown that the copper network that forms inside the steel alloy skeleton during infiltration enhances the thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient of the steel alloy composite. The hard phase of the CoMoCr and the network precipitated FeCrC phase are distributed homogeneously as the infiltrated Cu phase increases. The increase in hardness of the alloy composite due to the increase of the Co, Ni, Cr, and Cu contents in Fe matrix by the infiltrated Cu amount increases. Using infiltration, the thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient were increased to 29.5 W/mK and 15.9 um/m°C, respectively, for tempered alloy composite.
- [Korean]
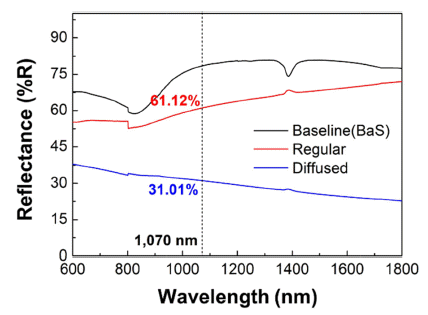
- Reflectance Characteristics of Al-Si based Alloys according to Powder Size and Composition
- Gwang Mook Choi, Hong Jun Chae
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):22-27. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.22
- 834 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, the effects of powder size and composition on the reflectance of Al-Si based alloys are presented. First, the reflectance of Al-Si bulk and powder are analyzed to confirm the effect of powder size. Results show that the bulk has a higher reflectance than that of powder because the bulk has lower surface defects. In addition, the larger the particle size, the higher is the reflectance because the interparticle space decreases. Second, the effect of composition on the reflectance by the changing composition of Al-Si-Mg is confirmed. Consequently, the reflectance of the alloy decreases with the addition of Si and Mg because dendrite Si and Mg2Si are formed, and these have lower reflectance than pure Al. Finally, the reflectance of the alloy is due to the scattering of free electrons, which is closely related to electrical conductivity. Measurements of the electrical conductivity based on the composition of the Al-Si-Mg alloy confirm the same tendency as the reflectance.
- [Korean]
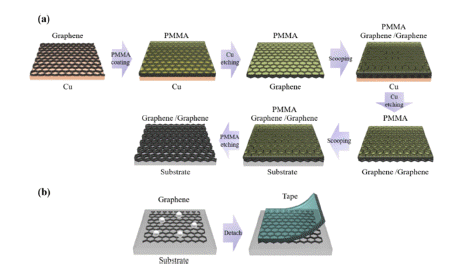
- A Study on Residual Powder Removing Technique of Multi-Layered Graphene Based on Graphene One-Step Transfer Process
- Chae-young Woo, Yeongsu Jo, Soon-kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):11-15. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.11
- 1,527 View
- 15 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, a method to remove residual powder on a multi-layered graphene and a new approach to transfer multi-layered graphene at once are studied. A graphene one-step transfer (GOST) method is conducted to minimize the residual powder comparison with a layer-by-layer transfer. Furthermore, a residual powder removing process is investigated to remove residual powder at the top of a multi-layered graphene. After residual powder is removed, the sheet resistance of graphene is decreased from 393 to 340 Ohm/sq in a four-layered graphene. In addition, transmittance slightly increases after residual powder is removed from the top of the multi-layered graphene. Optical and atomic-force microscopy images are used to analyze the graphene surface, and the Ra value is reduced from 5.2 to 3.7 nm following residual powder removal. Therefore, GOST and residual powder removal resolve the limited application of graphene electrodes due to residual powder.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Partially Dry-Transferred Graphene Electrode with Zinc Oxide Nanopowder and Its Application on Organic Solar Cells
Yeongsu Jo, Chae Young Woo, Soon Kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(4): 305. CrossRef
- Partially Dry-Transferred Graphene Electrode with Zinc Oxide Nanopowder and Its Application on Organic Solar Cells
- [English]
- A Separator with Activated Carbon Powder Layer to Enhance the Performance of Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
- Duc-Luong Vu, Jae-Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):466-474. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.466
- 1,124 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The high theoretical energy density (2600 Wh kg−1) of Lithium-sulfur batteries and the high theoretical capacity of elemental sulfur (1672 mAh g−1) attract significant research attention. However, the poor electrical conductivity of sulfur and the polysulfide shuttle effect are chronic problems resulting in low sulfur utilization and poor cycling stability. In this study, we address these problems by coating a polyethylene separator with a layer of activated carbon powder. A lithium-sulfur cell containing the activated carbon powder-coated separator exhibits an initial specific discharge capacity of 1400 mAh g−1 at 0.1 C, and retains 63% of the initial capacity after 100 cycles at 0.2 C, whereas the equivalent cell with a bare separator exhibits a 1200 mAh g−1 initial specific discharge capacity, and 50% capacity retention under the same conditions. The activated carbon powder-coated separator also enhances the rate capability. These results indicate that the microstructure of the activated carbon powder layer provides space for the sulfur redox reaction and facilitates fast electron transport. Concurrently, the activated carbon powder layer traps and reutilizes any polysulfides dissolved in the electrolyte. The approach presented here provides insights for overcoming the problems associated with lithium-sulfur batteries and promoting their practical use.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A one-step deposition method to prepare separators with carbon soot loading for lithium-sulfur battery
Yueting Zhu, Jingjing Wang, Yanshu Wang, Ying Zhu, Yixuan Li, Shicheng Zhao
Ionics.2022; 28(4): 1693. CrossRef - High thermal stability multilayered electrolyte complexes via layer-by-layer for long-life lithium-sulfur battery
Jing Wang, Yufan Li, Xianmei Deng, Lei Yan, Zhiqiang Shi
Ionics.2020; 26(11): 5481. CrossRef
- A one-step deposition method to prepare separators with carbon soot loading for lithium-sulfur battery
- [Korean]
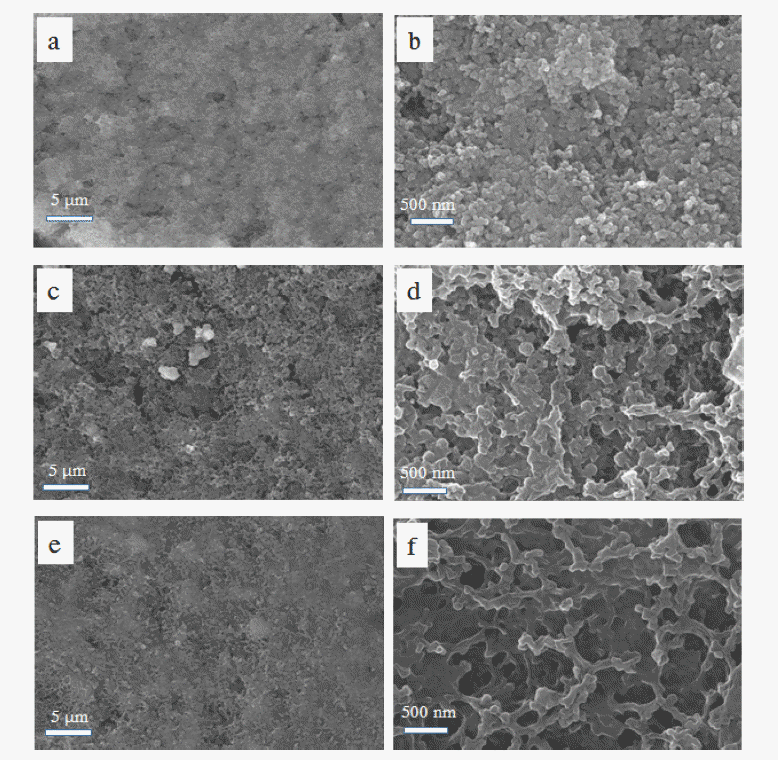
- Study of Color Evolution by Silica Coating and Etching based Morphological Control of α-FeOOH
- NaRi Lee, Ri Yu, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):379-383. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.379
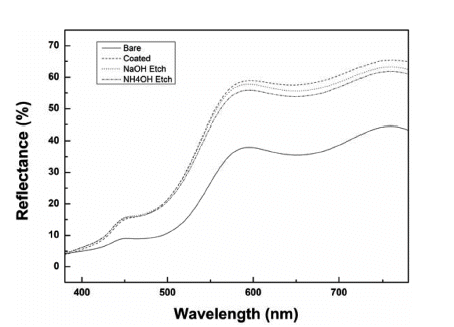
- 1,196 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Silica is used in shell materials to minimize oxidation and aggregation of nanoparticles. Particularly, porous silica has gained attention because of its performance in adsorption, catalysis, and medical applications. In this study, to investigate the effect of the density of the silica coating layer on the color of the pigment, we arbitrarily change the structure of a silica layer using an etchant. We use NaOH or NH4OH to etch the silica coating layer. First, we synthesize α-FeOOH for a length of 400 nm and coat it with TEOS to fabricate particles with a 50 nm coating layer. The coating thickness is then adjusted to 30–40 nm by etching the silica layer for 5 h. Four different shapes of α-FeOOH with different colors are measured using UV–vis light. From the color changes of the four different shapes of α-FeOOH features during coating or etching, the
L * value is observed to increase and brighten the overall color, and theb * value increases to impart a clear yellow color to the pigment. The brightest yellow color was that coated with silica; if the sample is etched with NaOH or NH4OH, theb * value can be controlled to study the yellow colors.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trend of Ceramic Nano Pigments
Ri Yu, YooJin Kim
Ceramist.2019; 22(3): 256. CrossRef
- Trend of Ceramic Nano Pigments
- [Korean]
- Photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles using surfactant
- Jong Min Byun, Chun Woong Park, Young In Kim, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):257-262. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.257
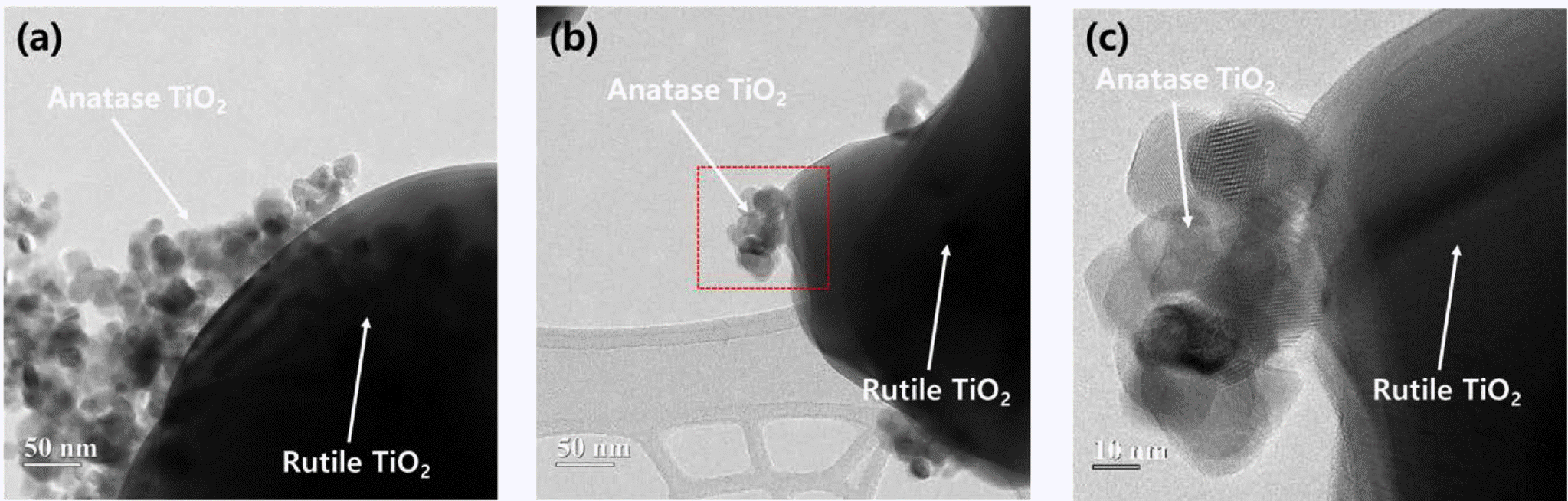
- 1,154 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The coupling of two semiconducting materials is an efficient method to improve photocatalytic activity via the suppression of recombination of electron-hole pairs. In particular, the coupling between two different phases of TiO2, i.e., anatase and rutile, is particularly attractive for photocatalytic activity improvement of rutile TiO2 because these coupled TiO2 powders can retain the benefits of TiO2, one of the best photocatalysts. In this study, anatase TiO2 nanoparticles are synthesized and coupled on the surface of rutile TiO2 powders using a microemulsion method and heat treatment. Triton X-100, as a surfactant, is used to suppress the aggregation of anatase TiO2 nanoparticles and disperse anatase TiO2 nanoparticles uniformly on the surface of rutile TiO2 powders. Rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles are successfully prepared. Additionally, we compare the photocatalytic activity of these rutile-anatase coupled TiO2 powders under ultraviolet (UV) light and demonstrate that the reason for the improvement of photocatalytic activity is microstructural.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Refractory Metal Oxide–Doped Titanate Nanotubes: Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity under UV/Visible Light Range
Min-Sang Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi, Tohru Sekino, Young-Do Kim, Se-Hoon Kim
Catalysts.2021; 11(8): 987. CrossRef - Effect of Surfactant on the Dispersion Stability of Slurry for Semiconductor Silicon CMP
Hye Won Yun, Doyeon Kim, Do Hyung Han, Dong Wan Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(5): 395. CrossRef
- Refractory Metal Oxide–Doped Titanate Nanotubes: Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity under UV/Visible Light Range
- [Korean]
- Effect of Milling Time and Addition of PCA on Austenite Stability of Fe-7%Mn Alloy
- Seung-Jin Oh, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):126-131. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.126
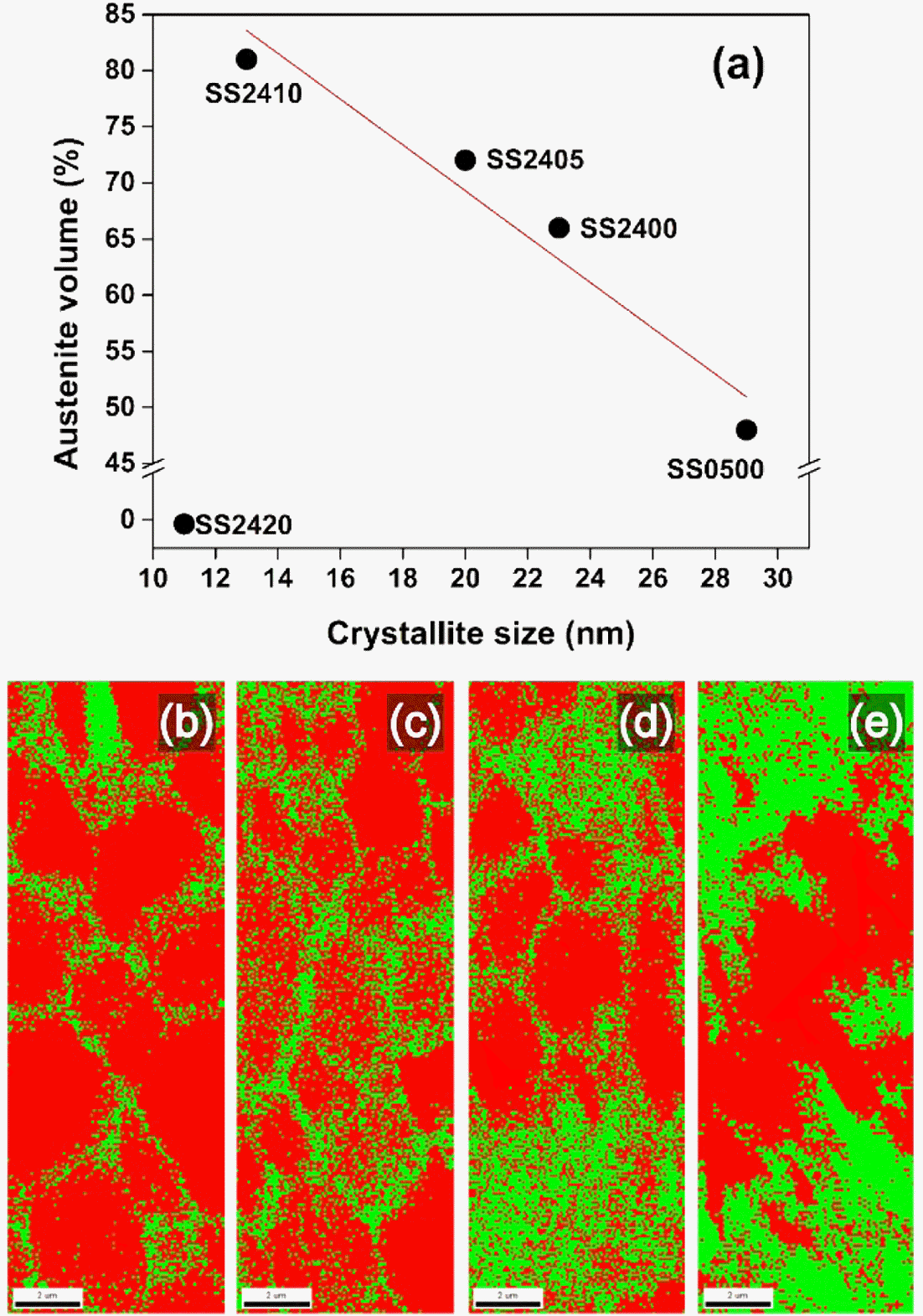
- 777 View
- 9 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the present study, we investigate the effects of milling time and the addition of a process control agent (PCA) on the austenite stability of a nanocrystalline Fe-7%Mn alloy by XRD analysis and micrograph observation. Nanocrystalline Fe-7%Mn alloys samples are successfully fabricated by spark plasma sintering. The crystallite size of ball-milled powder and the volume fraction of austenite in the sintered sample are calculated using XRD analysis. Changes in the shape and structure of alloyed powder according to milling conditions are observed through FE-SEM. It is found that the crystallite size is reduced with increasing milling time and amount of PCA addition due to the variation in the balance between the cold-welding and fracturing processes. As a result, the austenite stability increased, resulting in an exceptionally high volume fraction of austenite retained at room temperature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of mechanical milling on microstructure and mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy fabricated via spark plasma sintering
Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Eunjoo Shin, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 39: 4854. CrossRef - Effect of Cooling Rate on Microstructure and Hardness during Solution Treatment and Aging Process of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy for Aerospace Components
Seongji Seo, Hojoon Choi, Geeyoung Lee, Kee-Ahn Lee, Jeongho Han, Minsu Jung
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2021; 30(5): 3406. CrossRef - Development of Fe-Mn-based Hybrid Materials Containing Nano-scale Oxides by a Powder Metallurgical Route
Jonggyu Jeon, Jungjoon Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 203. CrossRef - Austenite Stability of Sintered Fe-based Alloy
Seunggyu Choi, Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jun, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 414. CrossRef - Austenite Stability of Nanocrystalline FeMnNiC Alloy
Seung-Jin Oh, Junhyub Jeon, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(5): 389. CrossRef
- Effects of mechanical milling on microstructure and mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy fabricated via spark plasma sintering
- [English]
- Microstructural Characterization of Gas Atomized Copper-Iron Alloys with Composition and Powder Size
- Sardar Farhat Abbas, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):19-24. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.25.1.19

- 683 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Cu-Fe alloys (CFAs) are much anticipated for use in electrical contacts, magnetic recorders, and sensors. The low cost of Fe has inspired the investigation of these alloys as possible replacements for high-cost Cu-Nb and Cu-Ag alloys. Here, alloys of Cu and Fe having compositions of Cu100-xFex (x = 10, 30, and 50 wt.%) are prepared by gas atomization and characterized microstructurally and structurally based on composition and powder size with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Grain sizes and Fe-rich particle sizes are measured and relationships among composition, powder size, and grain size are established. Same-sized powders of different compositions yield different microstructures, as do differently sized powders of equal composition. No atomic-level alloying is observed in the CFAs under the experimental conditions.
- [Korean]
- Sintering behavior of Fe-(Mo-Mn-P)-xSi alloys according to the Green Density
- Woo-Young Jung, Jin-Uk Ok, Dong-Kyu Park, In-Shup Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):400-405. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.400
- 1,217 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
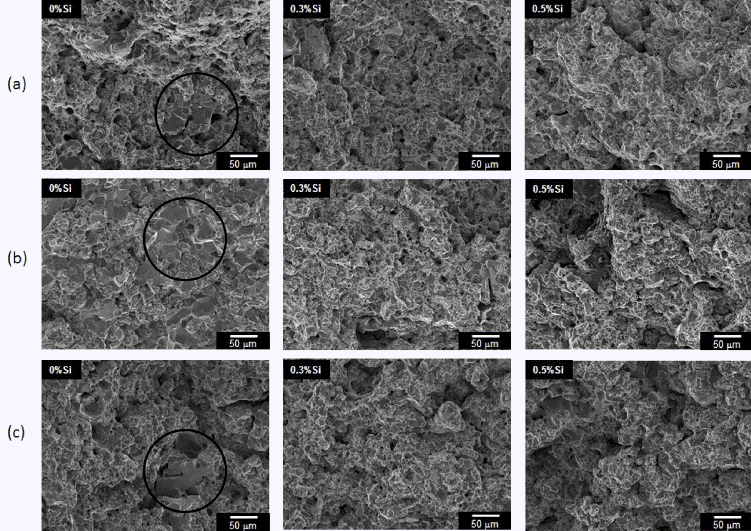
PDF The addition of a large amount of alloying elements reduces the compactibility and increases the compacting pressure, thereby shortening the life of the compacting die and increasing the process cost of commercial PM steel. In this study, the characteristic changes of Fe-Mo-P, Fe-Mn-P, and Fe-Mo-Mn-P alloys are investigated according to the Si contents to replace the expensive elements, such as Ni. All compacts with different Si contents are fabricated with the same green densities of 7.0 and 7.2 g/cm3. The transverse rupture strength (TRS) and sintered density are measured using the specimens obtained through the sintering process. The sintered density tends to decrease, whereas the TRS increases as the Si content increases. The TRS of the sintered specimen compacted with 7.2 g/cm3 is twice as high as that compacted with 7.0 g/cm3.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Si or Sn on the Sintered Properties of Fe-(Mo,Mn)-P Lean alloy
Woo-Young Jung, Jin-Uk Ok, Dong-Kyu Park, In-Shup Ahn
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(4): 302. CrossRef
- The Effects of Si or Sn on the Sintered Properties of Fe-(Mo,Mn)-P Lean alloy
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Fe3O4/Fe/Graphene nanocomposite powder by Electrical Wire Explosion in Liquid Media and its Electrochemical Properties
- Yoo-Young Kim, Ji-Seub Choi, Hoi-Jin Lee, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):308-314. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.308
- 1,022 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
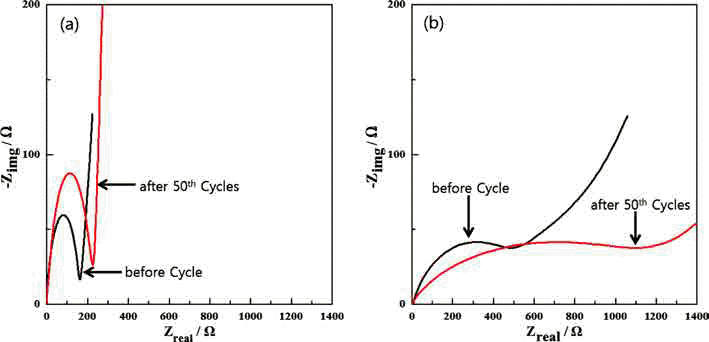
PDF Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is synthesized by electrical wire explosion of Fe wire and dispersed graphene in deionized water at room temperature. The structural and electrochemical characteristics of the powder are characterized by the field-emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, field-emission transmission electron microscopy, cyclic voltammetry, and galvanometric discharge-charge method. For comparison, Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposites are fabricated under the same conditions. The Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite particles, around 15-30 nm in size, are highly encapsulated in a graphene matrix. The Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder exhibits a high initial charge specific capacity of 878 mA/g and a high capacity retention of 91% (798 mA/g) after 50 cycles. The good electrochemical performance of the Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is clearly established by comparison of the results with those obtained for Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite powder and is attributed to alleviation of volume change, good distribution of electrode active materials, and improved electrical conductivity upon the addition of graphene.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
Kyunbae Lee, Joonsik Lee, Byung Mun Jung, Byeongjin Park, Taehoon Kim, Sang Bok Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 478: 733. CrossRef
- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
- [Korean]
- The Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Y2O3-Dispersed Fe-C and Fe-CNT Sintered Steels
- Jin Young Lim, Jung-Ho Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):298-301. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.298
- 626 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
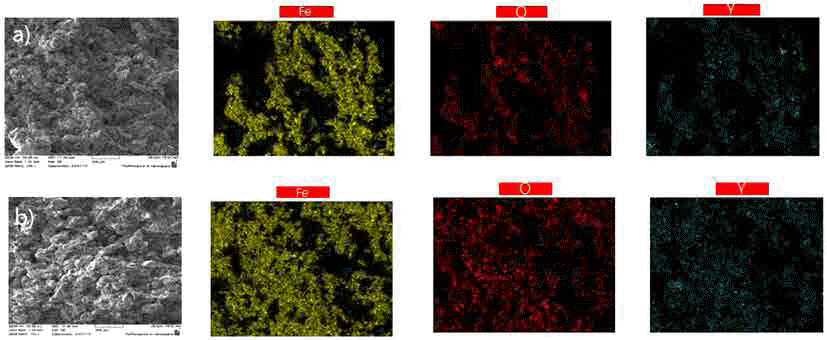
PDF In the present work, we use multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) as the starting material for the fabrication of sintered carbon steel. A comparison is made with conventionally sintered carbon steel, where graphite is used as the starting material. Milling is performed using a horizontal mill sintered in a vacuum furnace. We analyze the grain size, number of pores, X-ray diffraction patterns, and microstructure. Changes in the physical properties are determined by using the Archimedes method and Vickers hardness measurements. The result shows that the use of MWCNTs instead of graphite significantly reduces the size and volume of the pores as well as the grain size after sintering. The addition of Y2O3.to the Fe-MWCNT samples further inhibits the growth of grains.
- [Korean]
- The Effect of SiO2 addition on Oxidation and Electrical Resistance Stability at High-temperature of P/M Fecralloy Compact
- Jin-Woo Park, Jin-Uk Ok, Woo-young Jung, Dong-kyu Park, In-Shup Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):292-297. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.292
- 645 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
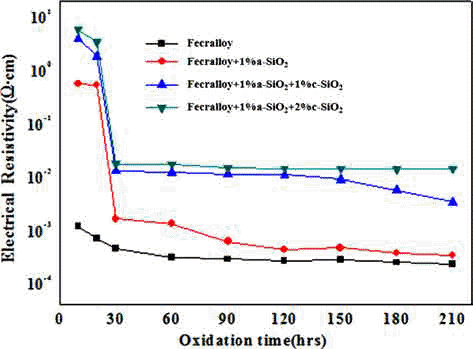
PDF A metallic oxide layer of a heat-resistant element contributes to the high-temperature oxidation resistance by delaying the oxidation and has a positive effect on the increase in electrical resistivity. In this study, green compacts of Fecralloy powder mixed with amorphous and crystalline silica are oxidized at 950°C for up to 210 h in order to evaluate the effect of metal oxide on the oxidation and electrical resistivity. The weight change ratio increases as per a parabolic law, and the increase is larger than that observed for Fecralloy owing to the formation of Fe-Si, Fe-Cr composite oxide, and Al2O3 upon the addition of Si oxide. Si oxides promote the formation of Al2O3 and Cr oxide at the grain boundary, and obstruct neck formation and the growth of Fecralloy particles to ensure stable electrical resistivity.
- [English]
- Magnetically Driven Assemblies of γ-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles into Well-Ordered Permanent Structures
- Myunghwan Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(3):229-234. Published online June 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.229
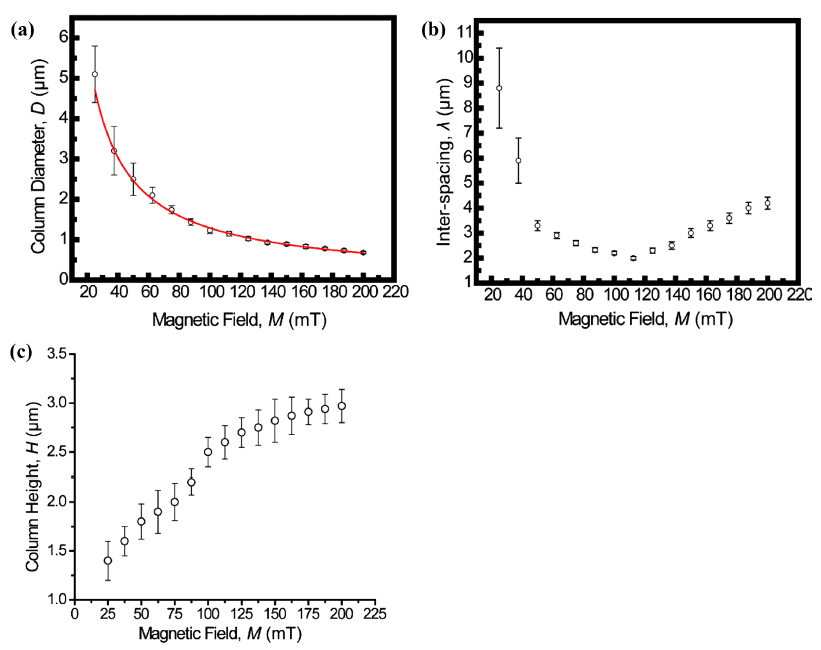
- 857 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We report on a simple and robust route to the spontaneous assembly of well-ordered magnetic nanoparticle superstructures by irreversible evaporation of a sessile single droplet of a mixture of a ferrofluid (FF) and a nonmagnetic fluid (NF). The resulting assembled superstructures are seen to form well-packed, vertically arranged columns with diameters of 5~0.7 μm, interparticle spacings of 9~2 μm, and heights of 1.3~3 μm. The assembled superstructures are strongly dependent on both the magnitude of magnetic field and the mixing ratio of the mixture. As the magnitude of the externally applied magnetic field and the mixing ratio of the mixture increase gradually, the size and interspacing of the magnetic nanoparticle aggregations decrease. Without an externally applied magnetic field, featureless patterns are observed for the γ-Fe3O4 nanoparticle aggregations. The proposed approach may lead to a versatile, cost-effective, fast, and scalable fabrication process based on the field-induced self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles.
- [English]
- Optimization of Process Condition for Fe Nano Powder Injection Molding
- Joo Won Oh, Won Sik Lee, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(3):223-228. Published online June 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.223

- 1,166 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nanopowders provide better details for micro features and surface finish in powder injection molding processes. However, the small size of such powders induces processing challenges, such as low solid loading, high feedstock viscosity, difficulty in debinding, and distinctive sintering behavior. Therefore, the optimization of process conditions for nanopowder injection molding is essential, and it should be carefully performed. In this study, the powder injection molding process for Fe nanopowder has been optimized. The feedstock has been formulated using commercially available Fe nanopowder and a wax-based binder system. The optimal solid loading has been determined from the critical solid loading, measured by a torque rheometer. The homogeneously mixed feedstock is injected as a cylindrical green body, and solvent and thermal debinding conditions are determined by observing the weight change of the sample. The influence of the sintering temperature and holding time on the density has also been investigated. Thereafter, the Vickers hardness and grain size of the sintered samples have been measured to optimize the sintering conditions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of stainless steel 316L/zirconia joint part fabricated by powder injection molding
Chang Woo Gal, Sang Soo Han, Jun Sae Han, Dongguo Lin, Seong Jin Park
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2019; 16(1): 315. CrossRef - Fabrication and properties of Si3N4 based ceramics using combustion synthesized powders
Chang Woo Gal, Gi Woung Song, Woon Hyung Baek, Hyung Kyu Kim, Dae Keun Lee, Ki Wook Lim, Seong Jin Park
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2019; 81: 325. CrossRef - Powder Injection Molding Process in Industrial Fields
Joo Won OH, Chang Woo GAL, Daseul SHIN, Jae Man PARK, Woo Seok YANG, Seong Jin PARK
Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy.2018; 65(9): 539. CrossRef
- Investigation of stainless steel 316L/zirconia joint part fabricated by powder injection molding
- [English]
- Lithium-silicate coating on Lithium Nickel Manganese Oxide (LiNi0.7Mn0.3O2) with a Layered Structure
- Dong-jin Kim, Da-ye Yoon, Woo-byoung Kim, Jae-won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):87-95. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.87
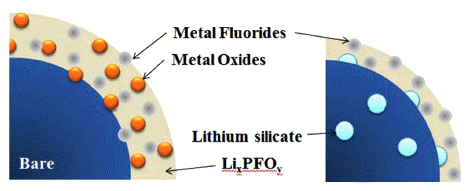
- 1,315 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Lithium silicate, a lithium-ion conducting ceramic, is coated on a layer-structured lithium nickel manganese oxide (LiNi0.7Mn0.3O2). Residual lithium compounds (Li2CO3 and LiOH) on the surface of the cathode material and SiO2 derived from tetraethylorthosilicate are used as lithium and silicon sources, respectively. Powder X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive spectroscopy analyses show that lithium silicate is coated uniformly on the cathode particles. Charge and discharge tests of the samples show that the coating can enhance the rate capability and cycle life performance. The improvements are attributed to the reduced interfacial resistance originating from suppression of solid-electrolyte interface (SEI) formation and dissolution of Ni and Mn due to the coating. An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of the cycled electrodes shows that nickel oxide and manganese oxide particles are formed on the surface of the electrode and that greater decomposition of the electrolyte occurs for the bare sample, which confirms the assumption that SEI formation and Ni and Mn dissolution can be reduced using the coating process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Artificial cathode-electrolyte interphases on nickel-rich cathode materials modified by silyl functional group
Hye Ji Song, Seol Heui Jang, Juhyeon Ahn, Si Hyoung Oh, Taeeun Yim
Journal of Power Sources.2019; 416: 1. CrossRef
- Artificial cathode-electrolyte interphases on nickel-rich cathode materials modified by silyl functional group
- [Korean]
- High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of Fe-14Cr Ferritic Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steels Manufactured by Mechanical Alloying Process
- Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Hwi-Jun Kim, Man-Sik Kong, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):133-140. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.133
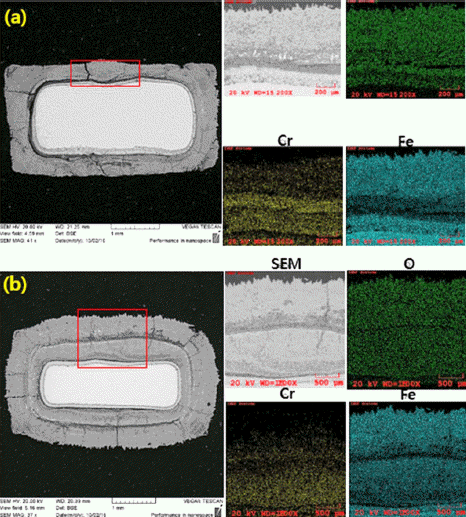
- 686 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the oxidation properties of Fe-14Cr ferritic oxide-dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel at various high temperatures (900, 1000, and 1100°C for 24 h). The initial microstructure shows that no clear structural change occurs even under high-temperature heat treatment, and the average measured grain size is 0.4 and 1.1 μm for the as-fabricated and heat-treated specimens, respectively. Y–Ti–O nanoclusters 10–50 nm in size are observed. High-temperature oxidation results show that the weight increases by 0.27 and 0.29 mg/cm2 for the asfabricated and heat-treated (900°C) specimens, and by 0.47 and 0.50 mg/cm2 for the as-fabricated and heat-treated (1000°C) specimens, respectively. Further, after 24 h oxidation tests, the weight increases by 56.50 and 100.60 mg/cm2 for the as-fabricated and heat-treated (1100°C) specimens, respectively; the latter increase is approximately 100 times higher than that at 1000°C. Observation of the surface after the oxidation test shows that Cr2O3 is the main oxide on a specimen tested at 1000°C, whereas Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 phases also form on a specimen tested at 1100°C, where the weight increases rapidly. The high-temperature oxidation behavior of Fe-14Cr ODS steel is confirmed to be dominated by changes in the Cr2O3 layer and generation of Fe-based oxides through evaporation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(1): 36. CrossRef
- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
- [English]
- Microstructure and Soft Magnetic Properties of Fe-6.5 wt.%Si Sheets Fabricated by Powder Hot Rolling
- Myung Shin Kim, Do Hun Kwon, Won Sik Hong, Hwi Jun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):122-127. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.122
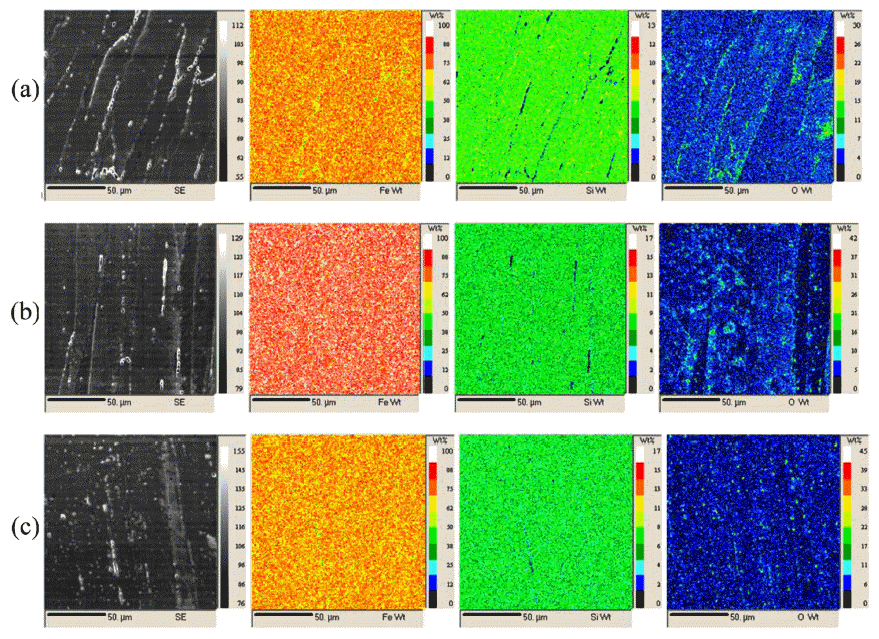
- 945 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe-6.5 wt.% Si alloys are widely known to have excellent soft magnetic properties such as high magnetic flux density, low coercivity, and low core loss at high frequency. In this work, disc-shaped preforms are prepared by spark plasma sintering at 1223 K after inert gas atomization of Fe-6.5 wt.% Si powders. Fe-6.5 wt.% Si sheets are rolled by a powder hot-rolling process without cracking, and their microstructure and soft magnetic properties are investigated. The microstructure and magnetic properties (saturation magnetization and core loss) of the hot-rolled Fe-6.5 wt.% Si sheets are examined by scanning electron microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction, vibration sample magnetometry, and AC
B–H analysis. The Fe-6.5 wt.% Si sheet rolled at a total reduction ratio of 80% exhibits good soft magnetic properties such as a saturation magnetization of 1.74 T and core loss (W5/1000) of 30.7 W/kg. This result is caused by an increase in the electrical resistivity resulting from an increased particle boundary density and the oxide layers between the primary particle boundaries.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


