Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
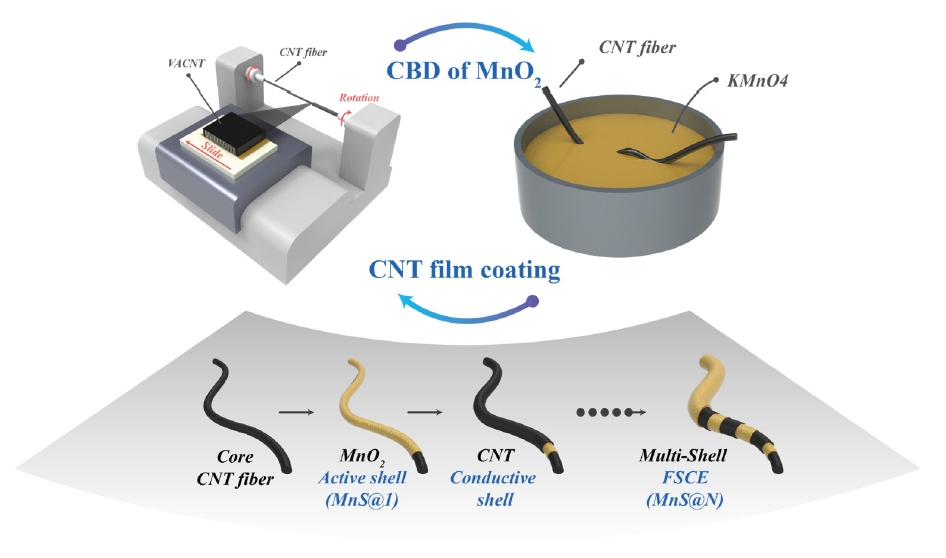
- The Effect of a CNT/MnO2 Nanoparticle Composite–Based Multi-Shell Typed Electrode for a Fiber Supercapacitor (FSC)
- Yeonggwon Kim, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):30-36. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00416
- 1,140 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fiber supercapacitors have attracted significant interest as potential textile energy storage devices due to their remarkable flexibility and rapid charge/discharge capabilities. This study describes the fabrication of a composite fiber supercapacitor (FSC) electrode through a multi-shell architecture, featuring layers of carbon nanotube (CNT) conductive shells and MnO₂ nanoparticle active shells. The number of layers was adjusted to assess their impact on FSC energy storage performance. Increasing the number of shells reduced electrode resistance and enhanced pseudocapacitive characteristics. Compared to the MnS@1 electrode, the MnS@5 electrode exhibited a high areal capacitance of 301.2 mF/cm², a 411% increase, but showed a higher charge transfer resistance (RCT) of 701.6 Ω. This is attributed to reduced ion diffusion and charge transfer ability resulting from the thicker multi-shell configuration. These results indicate that fine-tuning the quantity of shells is crucial for achieving an optimal balance between energy storage efficiency and stability.
- [English]
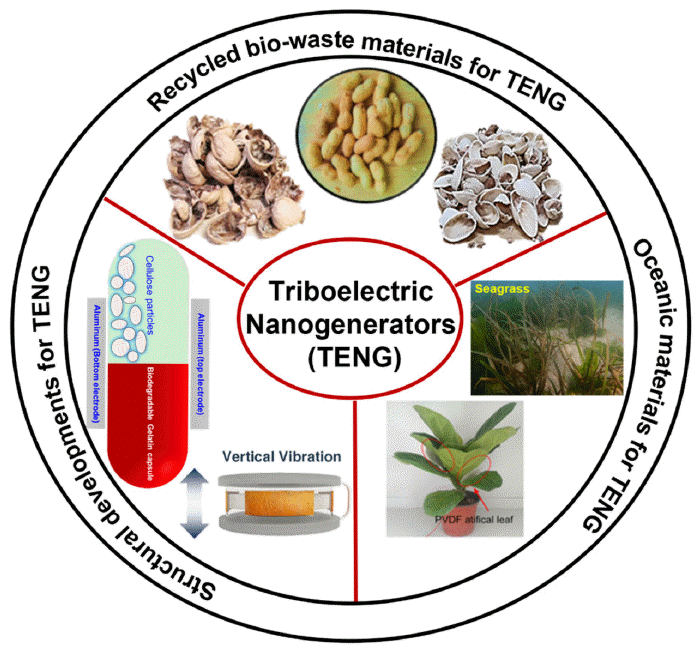
- Eco-Friendly Powder and Particles-Based Triboelectric Energy Harvesters
- Rayyan Ali Shaukat, Jihun Choi, Chang Kyu Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):528-535. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.528
- 2,052 View
- 38 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Since their initial development in 2012, triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) have gained popularity worldwide as a desired option for harnessing energy. The urgent demand for TENGs is attributed to their novel structural design, low cost, and use of large-scale materials. The output performance of a TENG depends on the surface charge density of the friction layers. Several recycled and biowaste materials have been explored as friction layers to enhance the output performance of TENGs. Natural and oceanic biomaterials have also been investigated as alternatives for improving the performance of TENG devices. Moreover, structural innovations have been made in TENGs to develop highly efficient devices. This review summarizes the recent developments in recycling and biowaste materials for TENG devices. The potential of natural and oceanic biowaste materials is also discussed. Finally, future outlooks for the structural developments in TENG devices are presented.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Future Space Missions
Rayyan Ali Shaukat, Muhammad Muqeet Rehman, Maryam Khan, Rui Chang, Carlo Saverio Iorio, Yarjan Abdul Samad, Yijun Shi
Nano-Micro Letters.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Fabrication and Characterization of a Flexible Polyurethane-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for a Harvesting Energy System
Saba Ejaz, Imran Shah, Shahid Aziz, Gul Hassan, Ahmed Shuja, Muhammad Asif Khan, Dong-Won Jung
Micromachines.2025; 16(2): 230. CrossRef - Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(1): 16. CrossRef - Sustainable Triboelectric Nanogenerator from Abalone Shell Powder for Self-Powered Humidity Sensing
Yunsook Yang, Farhan Akhtar, Shahzad Iqbal, Muhammad Muqeet Rehman, Woo Young Kim
Sensors.2025; 25(24): 7584. CrossRef - Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 529. CrossRef
- Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Future Space Missions
- [Korean]
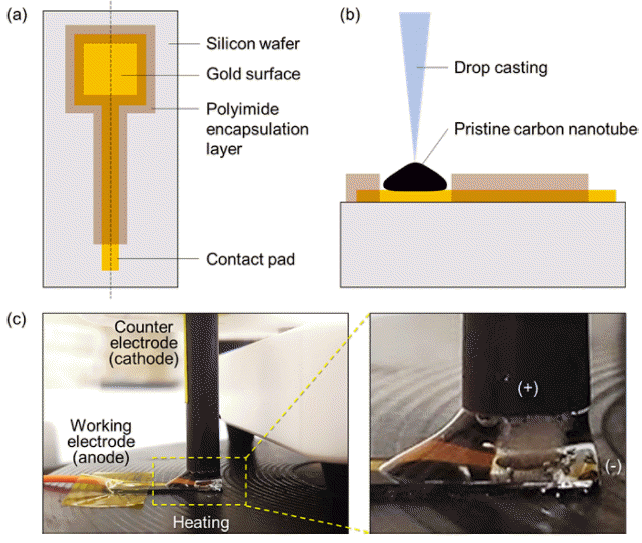
- Capacitance Enhancement and Evaluation of Gold-Deposited Carbon Nanotube Film Ion-Selective Electrode
- Do Youn Kim, Hanbyeol Son, Hyo-Ryoung Lim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):310-317. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.310
- 964 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Small-film-type ion sensors are garnering considerable interest in the fields of wearable healthcare and home-based monitoring systems. The performance of these sensors primarily relies on electrode capacitance, often employing nanocomposite materials composed of nano- and sub-micrometer particles. Traditional techniques for enhancing capacitance involve the creation of nanoparticles on film electrodes, which require cost-intensive and complex chemical synthesis processes, followed by additional coating optimization. In this study, we introduce a simple one-step electrochemical method for fabricating gold nanoparticles on a carbon nanotube (Au NP–CNT) electrode surface through cyclic voltammetry deposition. Furthermore, we assess the improvement in capacitance by distinguishing between the electrical double-layer capacitance and diffusion-controlled capacitance, thereby clarifying the principles underpinning the material design. The Au NP–CNT electrode maintains its stability and sensitivity for up to 50 d, signifying its potential for advanced ion sensing. Additionally, integration with a mobile wireless data system highlights the versatility of the sensor for health applications.
- [Korean]
- Controlling the Heat Generation Capability of Iron Oxide-Base Nanoparticles
- Jin-sil Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):518-526. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.518

- 694 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This review summarizes the recent progress in iron-oxide-based heat generators. Cancer treatment using magnetic nanoparticles as a heat generator, termed magnetic fluid hyperthermia, is a promising noninvasive approach that has gained significant interest. Most previous studies on improving the hyperthermia effect have focused on the construction of dopant-containing iron oxides. However, their applications in a clinical application can be limited due to extra dopants, and pure iron oxide is the only inorganic material approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Several factors that influence the heat generation capability of iron-oxide-based nanoparticles are summarized by reviewing recent studies on hyperthermia agents. Thus, our paper will provide the guideline for developing pure iron oxide-based heat generators with high heat dissipation capabilities.
- [English]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Immiscible Fe-Cu Alloys using Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid
- Chu Dac Phuc, Nguyen Minh Thuyet, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):449-457. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.449

- 1,587 View
- 12 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Iron and copper are practically immiscible in the equilibrium state, even though their atomic radii are similar. As non-equilibrium solid solutions, the metastable Fe-Cu alloys can be synthesized using special methods, such as rapid quenching, vapor deposition, sputtering, ion-beam mixing, and mechanical alloying. The complexity of these methods (multiple steps, low productivity, high cost, and non-eco-friendliness) is a hinderance for their industrial applications. Electrical explosion of wire (EEW) is a well-known and effective method for the synthesis of metallic and alloy nanoparticles, and fabrication using the EEW is a simple and economic process. Therefore, it can be potentially employed to circumvent this problem. In this work, we propose the synthesis of Fe-Cu nanoparticles using EEW in a suitable solution. The powder shape, size distribution, and alloying state are analyzed and discussed according to the conditions of the EEW.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Scaling up plasma-derived metallic nanoalloys: A comprehensive review of production bottlenecks, manufacturing readiness, and AI-driven pathways to viability
Hugues Nkomba Museba, BongJu Lee
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2026; 1054: 185926. CrossRef - Identification of the reconstruction induced high-entropy spinel oxide nanosheets for boosting alkaline water oxygen evolution
Xuexue Wang, Runqing Lu, Shanhe Gong, Shaokang Yang, Wenbo Wang, Zhongti Sun, Xiaozhen Zhang, Jun Liu, Xiaomeng Lv
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 503: 158488. CrossRef - Trends in bimetallic nanomaterials and methods for the removal of p-nitrophenol and its derivatives from wastewater
M. S. Qatan, F. Arshad, M. Miskam, G. A. Naikoo
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology.2024; 21(5): 5247. CrossRef - Control of cluster coalescence during formation of bimetallic nanoparticles and nanoalloys obtained via electric explosion of two wires
K.V. Suliz, A.Yu. Kolosov, V.S. Myasnichenko, N.I. Nepsha, N.Yu. Sdobnyakov, A.V. Pervikov
Advanced Powder Technology.2022; 33(3): 103518. CrossRef
- Scaling up plasma-derived metallic nanoalloys: A comprehensive review of production bottlenecks, manufacturing readiness, and AI-driven pathways to viability
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Nucleation Behavior of MoO3 Nano Particles with Concentration of Precursors
- Seyoung Lee, Namhun Kwon, Jaeseok Roh, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):394-400. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.394

- 1,540 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) is used in various applications including sensors, photocatalysts, and batteries owing to its excellent ionic conductivity and thermal properties. It can also be used as a precursor in the hydrogen reduction process to obtain molybdenum metals. Control of the parameters governing the MoO3 synthesis process is extremely important because the size and shape of MoO3 in the reduction process affect the shape, size, and crystallization of Mo metal. In this study, we fabricated MoO3 nanoparticles using a solution combustion synthesis (SCS) method that utilizes an organic additive, thereby controlling their morphology. The nucleation behavior and particle morphology were confirmed using ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). The concentration of the precursor (ammonium heptamolybdate tetrahydrate) was adjusted to be 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 M. Depending on this concentration, different nucleation rates were obtained, thereby resulting in different particle morphologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterization of Compacted and Pressureless Sintered Parts for Molybdenum Oxide Powder according to Hydrogen Reduction Temperature
Jong Hoon Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(4): 336. CrossRef
- Characterization of Compacted and Pressureless Sintered Parts for Molybdenum Oxide Powder according to Hydrogen Reduction Temperature
- [Korean]
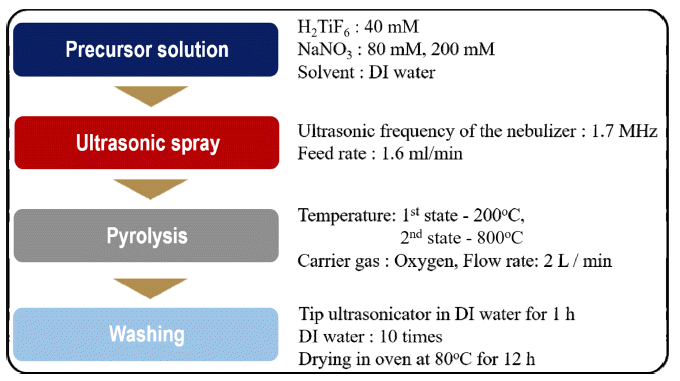
- Effect of Pyrolysis temperature on TiO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Salt-assisted Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
- Jae-Hyun Yoo, Myeong-Jun Ji, Woo-Young Park, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):237-242. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.237

- 837 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, ultrasonic spray pyrolysis combined with salt-assisted decomposition, a process that adds sodium nitrate (NaNO3) into a titanium precursor solution, is used to synthesize nanosized titanium dioxide (TiO2) particles. The added NaNO3 prevents the agglomeration of the primary nanoparticles in the pyrolysis process. The nanoparticles are obtained after a washing process, removing NaNO3 and NaF from the secondary particles, which consist of the salts and TiO2 nanoparticles. The effects of pyrolysis temperature on the size, crystallographic characteristics, and bandgap energy of the synthesized nanoparticles are systematically investigated. The synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles have a size of approximately 2–10 nm a bandgap energy of 3.1–3.25 eV, depending on the synthetic temperature. These differences in properties affect the photocatalytic activities of the synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and Sintering Behavior of Fine Tungsten Powders Synthesized by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
Hyeonhui Jo, Jeong Hyun Kim, Young-In Lee, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2021; 59(5): 289. CrossRef
- Microstructure and Sintering Behavior of Fine Tungsten Powders Synthesized by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Optical Property of TiO2 Nanoparticles Using a Salt-assisted Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
- Myeong-Jun Ji, Woo-Young Park, Jae-Hyun Yoo, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):34-39. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.34
- 835 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Current synthesis processes for titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles require expensive precursors or templates as well as complex steps and long reaction times. In addition, these processes produce highly agglomerated nanoparticles. In this study, we demonstrate a simple and continuous approach to synthesize TiO2 nanoparticles by a salt-assisted ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method. We also investigate the effect of salt content in a precursor solution on the morphology and size of synthesized products. The synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles are systematically characterized by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron micrograph, and UV-Vis spectroscopy. These nanoparticles appear to have a single anatase phase and a uniform particle-size distribution with an average particle size of approximately 10 nm. By extrapolating the plots of the transformed Kubelka-Munk function versus the absorbed light energy, we determine that the energy band gap of the synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles is 3.25 eV.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Pyrolysis temperature on TiO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Salt-assisted Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
Jae-Hyun Yoo, Myeong-Jun Ji, Woo-Young Park, Young-In Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(3): 237. CrossRef
- Effect of Pyrolysis temperature on TiO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Salt-assisted Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Nanopowders by Hydrothermal Method and their Application to Dye-sentisized Solar Cell Materials
- JinYoung Lim, Jeongseok Ahn, Jung-Ho Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):309-315. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.309
- 688 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
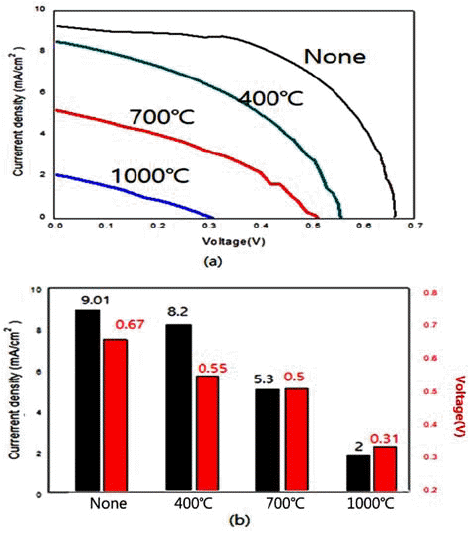
PDF In the present work, we synthesize nano-sized ZnO, SnO2, and TiO2 powders by hydrothermal reaction using metal chlorides. We also examine the energy-storage characteristics of the resulting materials to evaluate the potential application of these powders to dye-sensitized solar cells. The control of processing parameters such as pressure, temperature, and the concentration of aqueous solution results in the formation of a variety of powder morphologies with different sizes. Nano-rod, nano-flower, and spherical powders are easily formed with the present method. Heat treatment after the hydrothermal reaction usually increases the size of the powder. At temperatures above 1000°C, a complete collapse of the shape occurs. With regard to the capacity of DSSC materials, the hydrothermally synthesized TiO2 results in the highest current density of 9.1 mA/cm2 among the examined oxides. This is attributed to the fine particle size and morphology with large specific surface area.
- [Korean]
- Technology Trend of Luminescent Nanomaterials
- Hyewon Jeong, Jae Sung Son
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):170-177. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.170
- 1,103 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
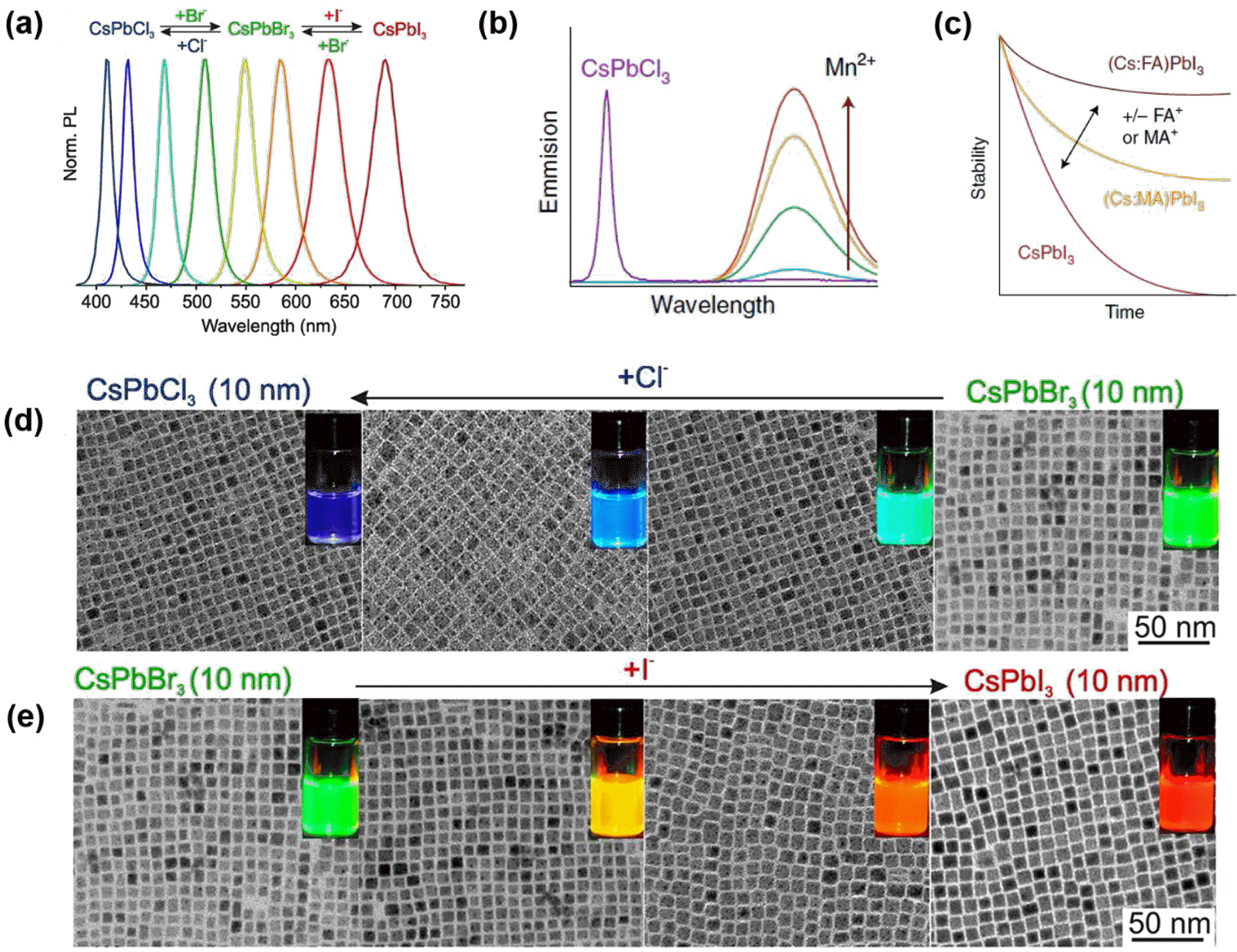
PDF Colloidally synthesized luminescent nanocrystals (NCs) have attracted tremendous attention due to their unique nanoscale optical and electronic properties. The emission properties of these NCs can be precisely tuned by controlling their size, shape, and composition as well as by introducing appropriate dopant impurities. Nowadays, these NCs are actively utilized for various applications such as optoelectronic devices including light emitting diodes (LEDs), lasers, and solar cells, and bio-medical applications such as imaging agents and bio-sensors. In this review, we classify luminescent nanomaterials into quantum dots (QDs), upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs), and perovskite NCs and present their intrinsic emission mechanism. Furthermore, the recently emerging issues of efficiency, toxicity, and durability in these materials are discussed for better understanding of industry demands. As well, the future outlook will be offered for researchers to guide the direction of future research.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Structural Relationship between University Dance Students’ Emotional Regulation, Emotion Response, and Engagement in Classes
Jinhee Gong
The Journal of Korean Institute of Information Technology.2020; 18(4): 121. CrossRef
- A Structural Relationship between University Dance Students’ Emotional Regulation, Emotion Response, and Engagement in Classes
- [English]
- The Synthesis Method of Tin Dioxide Nanoparticles by Plasma-Assisted Electrolysis Process and Gas Sensing Property
- Tae Hyung Kim, Yoseb Song, Chan-Gi Lee, Yong-Ho Choa
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):351-356. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.351
- 1,537 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
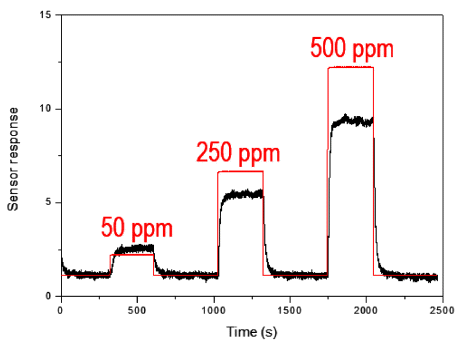
PDF Tin dioxide nanoparticles are prepared using a newly developed synthesis method of plasma-assisted electrolysis. A high voltage is applied to the tin metal plate to apply a high pressure and temperature to the synthesized oxide layer on the metal surface, producing nanoparticles in a low concentration of sulfuric acid. The particle size, morphology, and size distribution is controlled by the concentration of electrolytes and frequency of the power supply. The as-prepared powder of tin dioxide nanoparticles is used to fabricate a gas sensor to investigate the potential application. The particle-based gas sensor exhibits a short response and recovery time. There is sensitivity to the reduction gas for the gas flowing at rates of 50, 250, and 500 ppm of H2S gas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of porosity and particle size on the gas sensing properties of SnO2 films
Min Ah Han, Hyun-Jong Kim, Hee Chul Lee, Jin-Seong Park, Ho-Nyun Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 133. CrossRef
- Effects of porosity and particle size on the gas sensing properties of SnO2 films
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Optical Property of BaTiO3 Nanoparticles Using a Salt-assisted Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
- Young Hwangbo, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):326-331. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.326
- 904 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
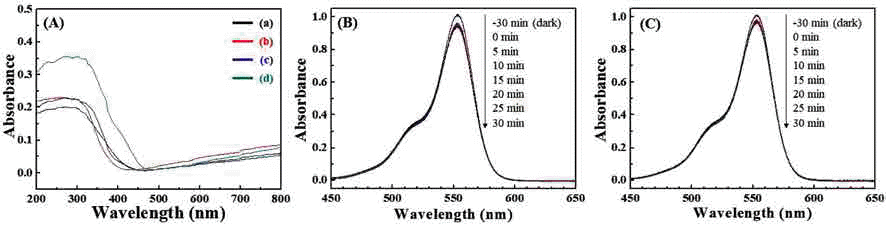
PDF The structural formation of inorganic nanoparticles dispersed in polymer matrices is a key technology for producing advanced nanocomposites with a unique combination of optical, electrical, and mechanical properties. Barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanoparticles are attractive for increasing the refractive index and dielectric constant of polymer nanocomposites. Current synthesis processes for BaTiO3 nanoparticles require expensive precursors or organic solvents, complicated steps, and long reaction times. In this study, we demonstrate a simple and continuous approach for synthesizing BaTiO3 nanoparticles based on a salt-assisted ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method. This process allows the synthesis of BaTiO3 nanoparticles with diameters of 20-50 nm and a highly crystalline tetragonal structure. The optical properties and photocatalytic activities of the nanoparticles show that they are suitable for use as fillers in various nanocomposites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sr doping effects on La(1-x)SrxMnO3-BaTiO3 nanocomposites: A comprehensive analysis of structural, optical, magnetic, and dielectric properties
Milad Karamzadeh-Jahromi, Morteza Izadifard, Mohammad Ebrahim Ghazi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2024; 1006: 176272. CrossRef
- Sr doping effects on La(1-x)SrxMnO3-BaTiO3 nanocomposites: A comprehensive analysis of structural, optical, magnetic, and dielectric properties
- [Korean]
- Recovery and Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaching Solution of LTCC Electrode By-Products
- Juyeon Yoo, Yubin Kang, Jinju Park, Hojin Ryu, Jin-Ho Yoon, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):315-320. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.315

- 507 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF There has been much interest in recycling electronic wastes in order to mitigate environmental problems and to recover the large amount of constituent metals. Silver recovery from electronic waste is extensively studied because of environmental and economic benefits and the use of silver in fabricating nanodevices. Hydrometallurgical processing is often used for silver recovery because it has the advantages of low cost and ease of control. Research on synthesis recovered silver into nanoparticles is needed for application to transistors and solar cells. In this study, silver is selectively recovered from the by-product of electrodes. Silver precursors are prepared using the dissolution characteristics of the leaching solution. In the liquid reduction process, silver nanoparticles are synthesized under various surfactant conditions and then analyzed. The purity of the recovered silver is 99.24%, and the average particle size of the silver nanoparticles is 68 nm.
- [English]
- Magnetically Driven Assemblies of γ-Fe3O4 Nanoparticles into Well-Ordered Permanent Structures
- Myunghwan Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(3):229-234. Published online June 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.229
- 857 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
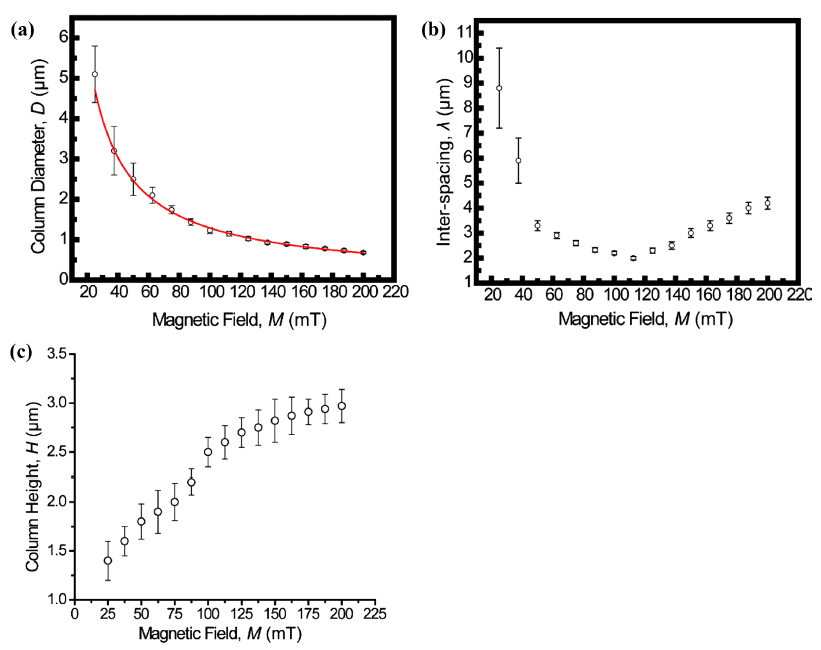
PDF We report on a simple and robust route to the spontaneous assembly of well-ordered magnetic nanoparticle superstructures by irreversible evaporation of a sessile single droplet of a mixture of a ferrofluid (FF) and a nonmagnetic fluid (NF). The resulting assembled superstructures are seen to form well-packed, vertically arranged columns with diameters of 5~0.7 μm, interparticle spacings of 9~2 μm, and heights of 1.3~3 μm. The assembled superstructures are strongly dependent on both the magnitude of magnetic field and the mixing ratio of the mixture. As the magnitude of the externally applied magnetic field and the mixing ratio of the mixture increase gradually, the size and interspacing of the magnetic nanoparticle aggregations decrease. Without an externally applied magnetic field, featureless patterns are observed for the γ-Fe3O4 nanoparticle aggregations. The proposed approach may lead to a versatile, cost-effective, fast, and scalable fabrication process based on the field-induced self-assembly of magnetic nanoparticles.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Properties of InP/ZnS core/shell Nanoparticles with One-pot process
- So Yeong Joo, Myung Hwan Hong, Leeseung Kang, Tae Hyung Kim, Chan Gi Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):11-16. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.11
- 1,037 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
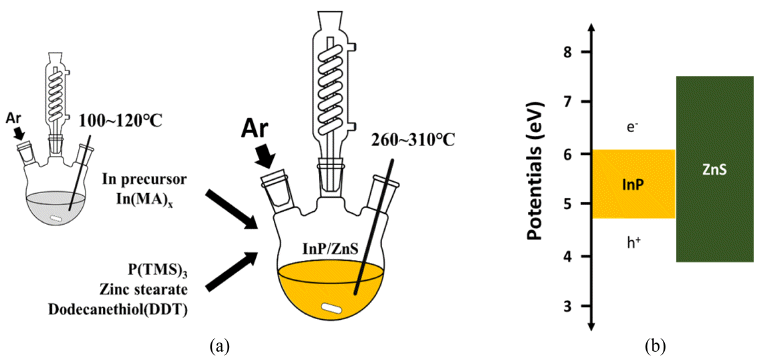
PDF In this study, simple chemical synthesis of green emitting Cd-free InP/ZnS QDs is accomplished by reacting In, P, Zn, and S precursors by one-pot process. The particle size and the optical properties were tailored, by controlling various experimental conditions, including [In]/[MA] (MA: myristic acid) mole ratio, reaction temperature and reaction time. The results of ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy (UV-vis), and of photoluminescence (PL), reveal that the exciton emission of InP was improved by surface coating, with a layer of ZnS. We report the correlation between each experimental condition and the luminescent properties of InP/ZnS core/shell QDs. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) techniques were used to characterize the as-synthesized QDs. In contrast to core nanoparticles, InP/ZnS core/shell treated with surface coating shows a clear ultraviolet peak. Besides this work, we need to study what clearly determines the shell kinetic growth mechanism of InP/ZnS core shell QDs.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Reaction Parameters on Silica Nanoparticles Synthesized by Sol-gel Method
- Young-Hyun Lim, Do Kyung Kim, Young-Keun Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(6):442-446. Published online December 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.6.442
- 3,047 View
- 49 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
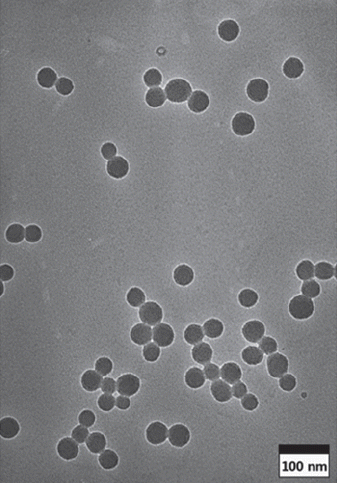
PDF The sol-gel method is the simplest method for synthesizing monodispersed silica particles. The purpose of this study is to synthesize uniform, monodisperse spherical silica nanoparticles using tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) as the silica precursor, ethanol, and deionized water in the presence of ammonia as a catalyst. The reaction time and temperature and the concentration of the reactants are controlled to investigate the effect of the reaction parameters on the size of the synthesized particles. The size and morphology of the obtained silica particles are investigated using transmission electron microscopy and particle size analysis. The results show that monodispersed silica particles over a size range of 54-504 nm are successfully synthesized by the sol-gel method without using any additional process. The nanosized silica particles can be synthesized at higher TEOS/H2O ratios, lower ammonia concentrations, and especially, higher reaction temperatures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SYNTHESIS OF SILICA NANOPARTICLES FROM SUGARCANE WASTE: PRECIPITATION-BASED SIZE CONTROL AND CHARACTERIZATION
Mustapha Sulaiman, Naseer Inuwa Durumin Iya, Mamudu Aliyu
FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES.2024; 8(3): 222. CrossRef - Nanostructure Construction of SiO2@Au Core-Shell by In-situ Synthesis
Mu-Jae Pyeon, Do Kyung Kim, Young-Keun Jeong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(5): 420. CrossRef
- SYNTHESIS OF SILICA NANOPARTICLES FROM SUGARCANE WASTE: PRECIPITATION-BASED SIZE CONTROL AND CHARACTERIZATION
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Ag Particles by Polyol Process and Wet Chemical Process
- Juyeon Yoo, Hyosung Jang, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):297-302. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.297
- 809 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
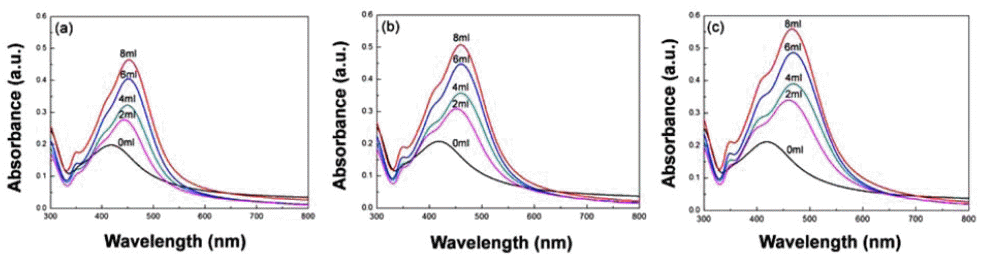
PDF Ag nanoparticles are extensively studied and utilized due to their excellent catalysis, antibiosis and optical properties. They can be easily synthesized by chemical reduction methods and it is possible to prepare particles of uniform size and high purity. These methods are divided into vapor methods and liquid phase reduction methods. In the present study, Ag particles are prepared and analyzed through two chemical reduction methods using solvents containing a silver nitrate precursor. When Ag ions are reduced using a reductant in the aqueous solution, it is possible to control the Ag particle size by controlling the formic acid ratio. In addition, in the Polyol process, Ag nanoparticles prepared at various temperatures and reaction time conditions have multiple twinned and anisotropic structures, and the particle size variation can be confirmed using field emissions scanning electron microscopy and by analyzing the UV-vis spectrum.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recovery and Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaching Solution of LTCC Electrode By-Products
Juyeon Yoo, Yubin Kang, Jinju Park, Hojin Ryu, Jin-Ho Yoon, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(4): 315. CrossRef
- Recovery and Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaching Solution of LTCC Electrode By-Products
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Copper Nanoparticles by a Chemical Reduction Method
- Min Woo Choi, Min Hwan Bae, Jung-Ho Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):228-234. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.228
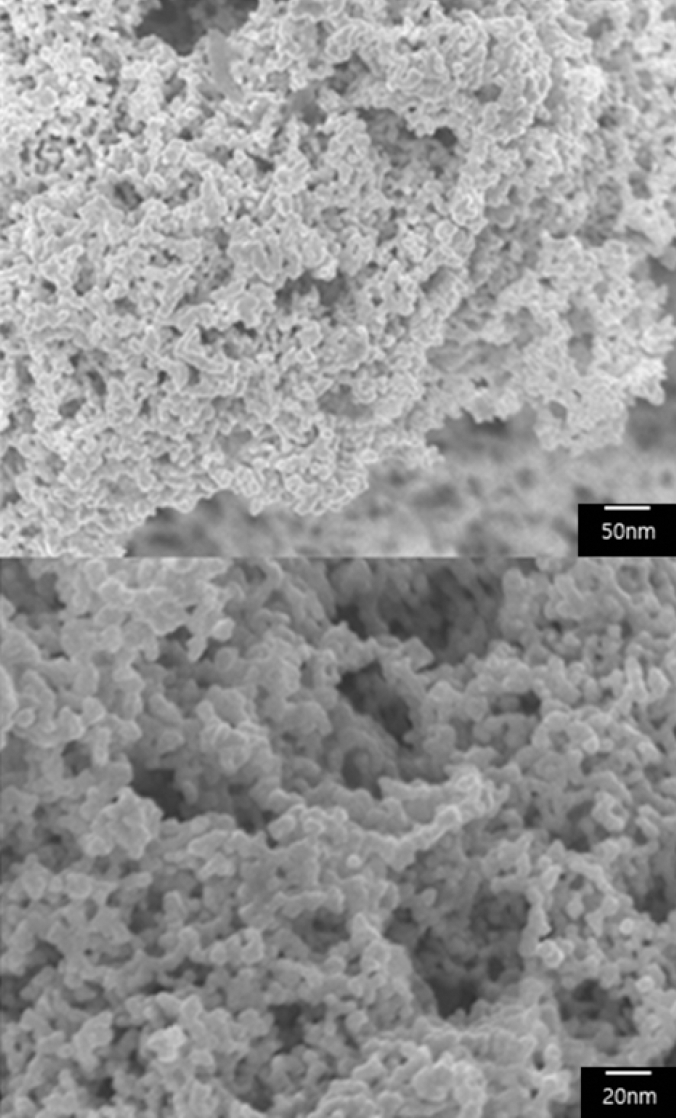
- 2,153 View
- 42 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Copper nanoparticles attract much attention as substitutes of noble metals such as silver and can help reduce the manufacturing cost of electronic products due to their lower cost and good conductivity. In the present work, the chemical reduction is examined to optimize the synthesis of nano-sized copper particles from copper sulfate. Sodium borohydride and ascorbic acid are used as reducing and antioxidant agents, respectively. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is used as a size-control and capping agent. An appropriate dose of PEG inhibits the abnormal growth of copper nanoparticles, maintaining chemical stability. The addition of ascorbic acid prevents the oxidation of nanoparticles during synthesis and storage. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) are used to investigate the size of the synthesized nanoparticles and the coordination between copper nanoparticles and PEG. For chemical reduction, copper nanoparticles less than 100 nm in size without oxidized layers are successfully obtained by the present method.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Correlation between electrical conductivity and antibacterial activity of chitosan-stabilized copper and silver nanoparticles
C.Raja Mohan, Ruckmani Kandasamy, J. Kabiriyel
Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications.2024; 7: 100503. CrossRef - Green Synthesis and Characterization of Natural Magnetic Particles/Chitosan Composite Material Impregnated with Copper Nanoparticles
Defia Indah Permatasari, Bambang Rusdiarso, Nuryono Nuryono
Solid State Phenomena.2022; 339: 19. CrossRef - Copper Nanoparticle(CuNP’s)Synthesis: A review of the various ways with Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activity
Israfil Alam Tito, Sahab Uddin, Shafiul Islam, Snahasish Bhowmik
Oriental Journal Of Chemistry.2021; 37(5): 1030. CrossRef
- Correlation between electrical conductivity and antibacterial activity of chitosan-stabilized copper and silver nanoparticles
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Highly Dispersible Metal Nanoparticles in P3HT:PCBM Layers and Their Effects on the Performance of Polymer Solar Cells
- Min-Ji Kim, Gyu-Chae Choi, Young-Kuk Kim, Yang-Do Kim, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):179-184. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.179

- 479 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we prepare polymer solar cells incorporating organic ligand-modified Ag nanoparticles (OAgNPs) highly dispersed in the P3HT:PCBM layer. Ag nanoparticles decorated with water-dispersible ligands (WAgNPs) were also utilized as a control sample. The existence of the ligands on the Ag surface was confirmed by FTIR spectra. Metal nanoparticles with different surface chemistries exhibited different dispersion tendencies. O-AgNPs were highly dispersed even at high concentrations, whereas W-AgNPs exhibited significant aggregation in the polymer layer. Both dispersion and blending concentration of the Ag nanoparticles in P3HT:PCBM matrix had critical effects on the device performance as well as light absorption. The significant changes in short-circuit current density (JSC) of the solar cells seemed to be related to the change in the polymer morphology according to the concentration of AgNPs introduced. These findings suggested the importance of uniform dispersion of plasmonic metal nanoparticles and their blending concentration conditions in order to boost the solar cell performance.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


