Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
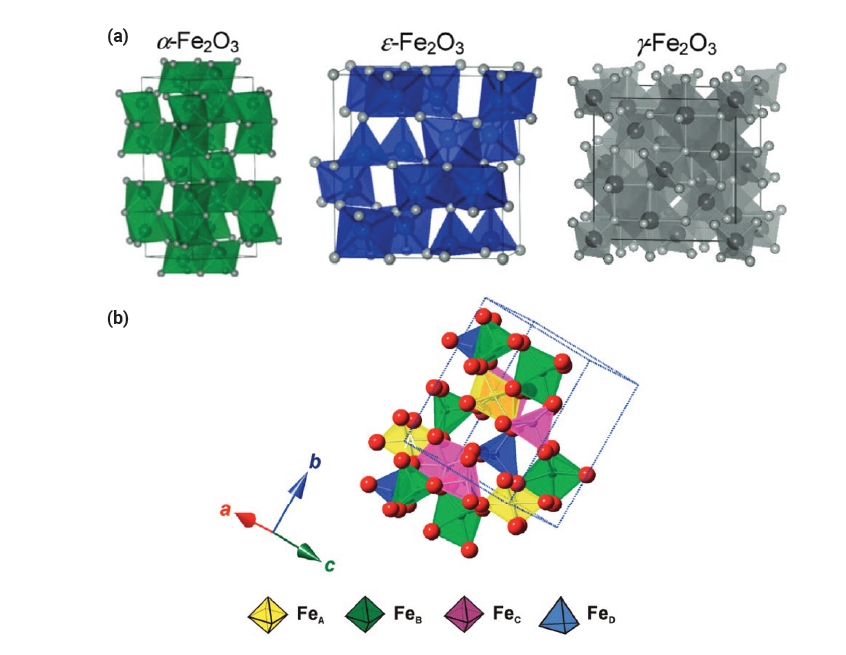
- Epsilon Iron Oxide (ε-Fe2O3) as an Electromagnetic Functional Material: Properties, Synthesis, and Applications
- Ji Hyeong Jeong, Hwan Hee Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):465-479. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00290
- 3,461 View
- 90 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Iron oxide (ε-Fe₂O₃) is emerging as a promising electromagnetic material due to its unique magnetic and electronic properties. This review focuses on the intrinsic properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, particularly its high coercivity, comparable to that of rare-earth magnets, which is attributed to its significant magnetic anisotropy. These properties render it highly suitable for applications in millimeter wave absorption and high-density magnetic storage media. Furthermore, its semiconducting behavior offers potential applications in photocatalytic hydrogen production. The review also explores various synthesis methods for fabricating ε-Fe₂O₃ as nanoparticles or thin films, emphasizing the optimization of purity and stability. By exploring and harnessing the properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, this study aims to contribute to the advancement of next-generation electromagnetic materials with potential applications in 6G wireless telecommunications, spintronics, high-density data storage, and energy technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
Babak Enami Alamdari, Yu Tang, Danilo Erricolo, Lesley H. Sneed
Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical Pressure Induced Strain Control of Magnetic Anisotropy in the Simple Perovskite ϵ-Fe2O3
Subir Roy, Gurleen K. Uppal, Alberto Acosta, Rachel Nickel, Charles A. Roberts, Johan van Lierop
Nano Letters.2026; 26(1): 34. CrossRef - Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling
Petr Kharitonskii, Andrei Krasilin, Nadezhda Belskaya, Svetlana Yanson, Nikita Bobrov, Andrey Ralin, Kamil Gareev, Nikita Zolotov, Dmitry Zaytsev, Elena Sergienko
Magnetochemistry.2025; 11(12): 103. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
- [Korean]
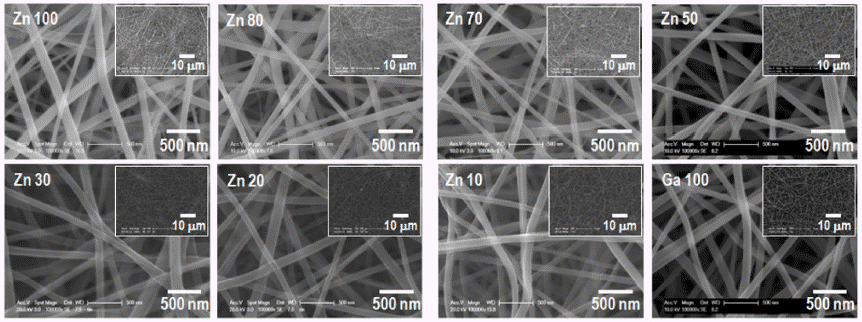
- A Study on Morphology Control of (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) Nanofibers according to the Composition and Crystallinity of Oxide Nanofibers Synthesized by Electrospinning
- Jeong Hyun Kim, Sung-Tag Oh, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):259-266. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.259
- 651 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) solid solution is attracting extensive attention for photocatalytic water splitting and wastewater treatment owing to its narrow and controllable band gap. To optimize the photocatalytic performance of the solid solution, the key points are to decrease its band gap and recombination rate. In this study, (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) nanofibers with various Zn fractions are prepared by electrospinning followed by calcination and nitridation. The effect of the composition and crystallinity of electrospun oxide nanofibers on the morphology and optical properties of the obtained solid-solution nanofibers are systematically investigated. The results show that the final shape of the (Ga1-xZnx) (N1-xOx) material is greatly affected by the crystallinity of the oxide nanofibers before nitridation. The photocatalytic properties of (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) with different Ga:Zn atomic ratios are investigated by studying the degradation of rhodamine B under visible light irradiation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Nanowire by Electrospinning Process Using Nickel Oxide Particle Recovered from MLCC
Haein Shin, Jongwon Bae, Minsu Kang, Kun-Jae Lee
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 502. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Nanowire by Electrospinning Process Using Nickel Oxide Particle Recovered from MLCC
- [Korean]
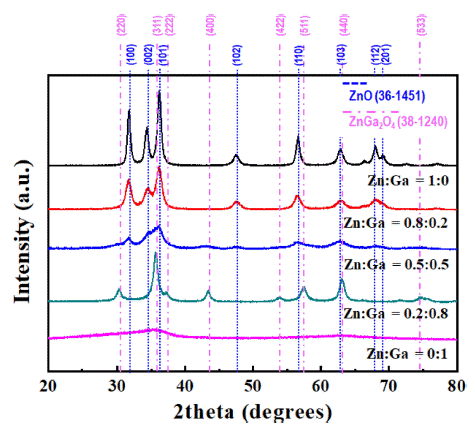
- Synthesis and Optical Property of (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x Nanoparticles Using an Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process and Subsequent Chemical Transformation
- Jeong Hyun Kim, Cheol-Hui Ryu, Myungjun Ji, Yomin Choi, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):143-149. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.143
- 783 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x solid solution nanoparticles with a high zinc content are prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis and subsequent nitridation. The structure and morphology of the samples are investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field-emission scanning electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The characterization results show a phase transition from the Zn and Ga-based oxides (ZnO or ZnGa2O4) to a (GaN)1-x (ZnO)x solid solution under an NH3 atmosphere. The effect of the precursor solution concentration and nitridation temperature on the final products are systematically investigated to obtain (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x nanoparticles with a high Zn concentration. It is confirmed that the powder synthesized from the solution in which the ratio of Zn and Ga was set to 0.8:0.2, as the initial precursor composition was composed of about 0.8-mole fraction of Zn, similar to the initially set one, through nitriding treatment at 700°C. Besides, the synthesized nanoparticles exhibited the typical XRD pattern of (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x, and a strong absorption of visible light with a bandgap energy of approximately 2.78 eV, confirming their potential use as a hydrogen production photocatalyst.
- [Korean]
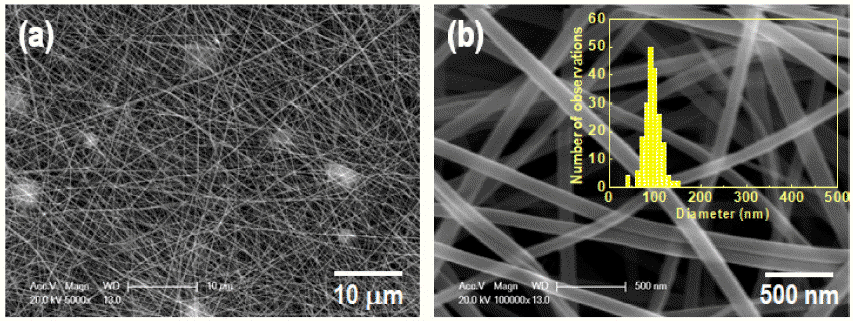
- Effect of Calcination Temperature on the Microstructure and Photocatalytic Activity of Electrospun BiVO4 Nanofiber
- Myeongjun Ji, Jeong Hyun Kim, Cheol-Hui Ryu, Yun Taek Ko, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):226-232. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.226
- 1,216 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) is considered a potentially attractive candidate for the visible-light-driven photodegradation of organic pollutants. In an effort to enhance their photocatalytic activities, BiVO4 nanofibers with controlled microstructures, grain sizes, and crystallinities are successfully prepared by electrospinning followed by a precisely controlled heat treatment. The structural features, morphologies, and photo-absorption performances of the asprepared samples are systematically investigated and can be readily controlled by varying the calcination temperature. From the physicochemical analysis results of the synthesized nanofiber, it is found that the nanofiber calcines at a lower temperature, shows a smaller crystallite size, and lower crystallinity. The photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine-B (RhB) reveals that the photocatalytic activity of the BiVO4 nanofibers can be improved by a thermal treatment at a relatively low temperature because of the optimization of the conflicting characteristics, crystallinity, crystallite size, and microstructure. The photocatalytic activity of the nanofiber calcined at 350°C for the degradation of RhB under visible-light irradiation exhibits a greater photocatalytic activity than the nanofibers synthesized at 400°C and 450°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Design, synthesis, and characterization of a porous ceramic-supported CeO2 nanocatalyst for CO -free H2 evolution
Jimin Lee, Minseob Lim, Tae Sung Kim, Kee-Ryung Park, Jong-Sik Lee, Hong-Baek Cho, Joo Hyun Park, Yong-Ho Choa
Applied Surface Science.2021; 548: 149198. CrossRef
- Design, synthesis, and characterization of a porous ceramic-supported CeO2 nanocatalyst for CO -free H2 evolution
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2 Hollow Structures using One-pot Wet Chemical Process
- Duk-Hee Lee, Kyung-Soo Park, Jae-Ryang Park, Chan-Gi Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):132-138. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.132

- 533 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A facile one-pot wet chemical process to prepare pure anatase TiO2 hollow structures using ammonium hexafluorotitanate as a precursor is developed. By defining the formic acid ratio, we fabricate TiO2 hollow structures containing fluorine on the surface. The TiO2 hollow sphere is composed of an anatase phase containing fluorine by various analytical techniques. A possible formation mechanism for the obtained hollow samples by self-transformation and Ostwald ripening is proposed. The TiO2 hollow structures containing fluorine exhibits 1.2 - 2.7 times higher performance than their counterparts in photocatalytic activity. The enhanced photocatalytic activity of the TiO2 hollow structures is attributed to the combined effects of high crystallinity, specific surface area (62 m2g-1), and the advantage of surface fluorine ions (at 8%) having strong electron-withdrawing ability of the surface ≡ Ti-F groups reduces the recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Pyrolysis temperature on TiO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Salt-assisted Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
- Jae-Hyun Yoo, Myeong-Jun Ji, Woo-Young Park, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):237-242. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.237

- 824 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, ultrasonic spray pyrolysis combined with salt-assisted decomposition, a process that adds sodium nitrate (NaNO3) into a titanium precursor solution, is used to synthesize nanosized titanium dioxide (TiO2) particles. The added NaNO3 prevents the agglomeration of the primary nanoparticles in the pyrolysis process. The nanoparticles are obtained after a washing process, removing NaNO3 and NaF from the secondary particles, which consist of the salts and TiO2 nanoparticles. The effects of pyrolysis temperature on the size, crystallographic characteristics, and bandgap energy of the synthesized nanoparticles are systematically investigated. The synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles have a size of approximately 2–10 nm a bandgap energy of 3.1–3.25 eV, depending on the synthetic temperature. These differences in properties affect the photocatalytic activities of the synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructure and Sintering Behavior of Fine Tungsten Powders Synthesized by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
Hyeonhui Jo, Jeong Hyun Kim, Young-In Lee, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2021; 59(5): 289. CrossRef
- Microstructure and Sintering Behavior of Fine Tungsten Powders Synthesized by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
- [Korean]
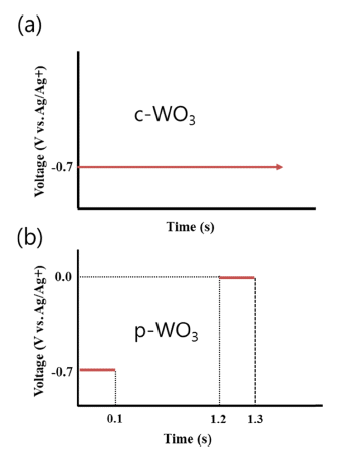
- Photocatalytic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Prepared by Electrodeposition Method
- Kwang-Mo Kang, Ji-Hye Jeong, Ga-In Lee, Jae-Min Im, Hyun-Jeong Cheon, Deok-Hyeon Kim, Yoon-Chae Nah
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):40-44. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.40
- 806 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten trioxide (WO3) is a promising candidate as a photocatalyst because of its outstanding electrical and optical properties. In this study, we prepare WO3 thin films by electrodeposition and characterize the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue using these films. Depending on the voltage conditions (static and pulse), compact and porous WO3 films are fabricated on a transparent ITO/glass substrate. The morphology and crystal structure of electrodeposited WO3 thin films are investigated by scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and X-ray diffraction. An application of static voltage during electrodeposition yields a compact layer of WO3, whereas a highly porous morphology with nanoflakes is produced by a pulse voltage process. Compared to the compact film, the porous WO3 thin film shows better photocatalytic activities. Furthermore, a much higher reaction rate of degradation of methylene blue can be achieved after post-annealing of WO3 thin films.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advanced IGZO Phototransistor Arrays: Enhancing Visible Light Detection Through Selectively Electrohydrodynamic Jet‐Printed Photocatalytic Layer Formation
Jong Bin An, Byung Ha Kang, Sujin Jung, Kunho Moon, Jusung Chung, Seok Min Hong, Kyungho Park, Jong Hyuk Ahn, Hyun Jae Kim
Advanced Functional Materials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advanced IGZO Phototransistor Arrays: Enhancing Visible Light Detection Through Selectively Electrohydrodynamic Jet‐Printed Photocatalytic Layer Formation
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Optical Property of TiO2 Nanoparticles Using a Salt-assisted Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
- Myeong-Jun Ji, Woo-Young Park, Jae-Hyun Yoo, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):34-39. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.34
- 824 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Current synthesis processes for titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles require expensive precursors or templates as well as complex steps and long reaction times. In addition, these processes produce highly agglomerated nanoparticles. In this study, we demonstrate a simple and continuous approach to synthesize TiO2 nanoparticles by a salt-assisted ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method. We also investigate the effect of salt content in a precursor solution on the morphology and size of synthesized products. The synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles are systematically characterized by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron micrograph, and UV-Vis spectroscopy. These nanoparticles appear to have a single anatase phase and a uniform particle-size distribution with an average particle size of approximately 10 nm. By extrapolating the plots of the transformed Kubelka-Munk function versus the absorbed light energy, we determine that the energy band gap of the synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles is 3.25 eV.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Pyrolysis temperature on TiO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Salt-assisted Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
Jae-Hyun Yoo, Myeong-Jun Ji, Woo-Young Park, Young-In Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(3): 237. CrossRef
- Effect of Pyrolysis temperature on TiO2 Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Salt-assisted Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
- [Korean]
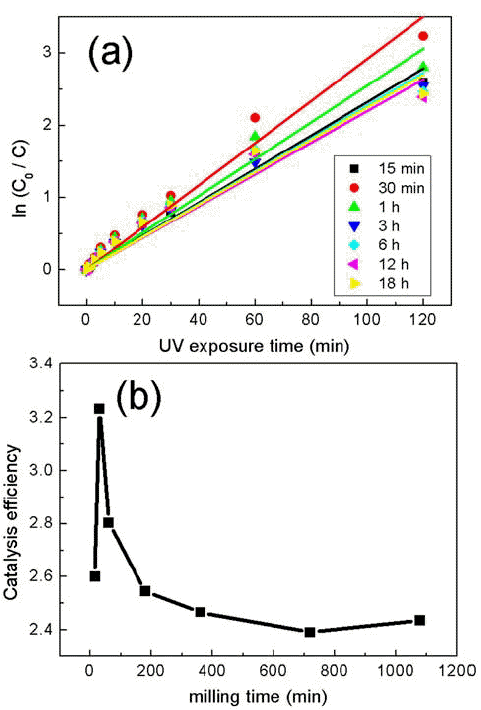
- Photocatalysis of TiO2/WO3 Composites Synthesized by Ball Milling
- Su-Yeol Yu, Chunghee Nam
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):316-321. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.316
- 779 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Composites of P25 TiO2 and hexagonal WO3 nanorods are synthesized through ball-milling in order to study photocatalytic properties. Various composites of TiO2/WO3 are prepared by controlling the weight percentages (wt%) of WO3, in the range of 1–30 wt%, and milling time to investigate the effects of the composition ratio on the photocatalytic properties. Scanning electron microscopy, x-ray diffraction, and transmission electron microscopy are performed to characterize the structure, shape and size of the synthesized composites of TiO2/WO3. Methylene blue is used as a test dye to analyze the photocatalytic properties of the synthesized composite material. The photocatalytic activity shows that the decomposition efficiency of the dye due to the photocatalytic effect is the highest in the TiO2/WO3 (3 wt%) composite, and the catalytic efficiency decreases sharply when the amount of WO3 is further increased. As the amount of WO3 added increases, dye-removal by adsorption occurs during centrifugation, instead of the decomposition of dyes by photocatalysts. Finally, TiO2/WO3 (3 wt%) composites are synthesized with various milling times. Experimental results show that the milling time has the best catalytic efficiency at 30 min, after which it gradually decreases. There is no significant change after 1 hour.
- [Korean]
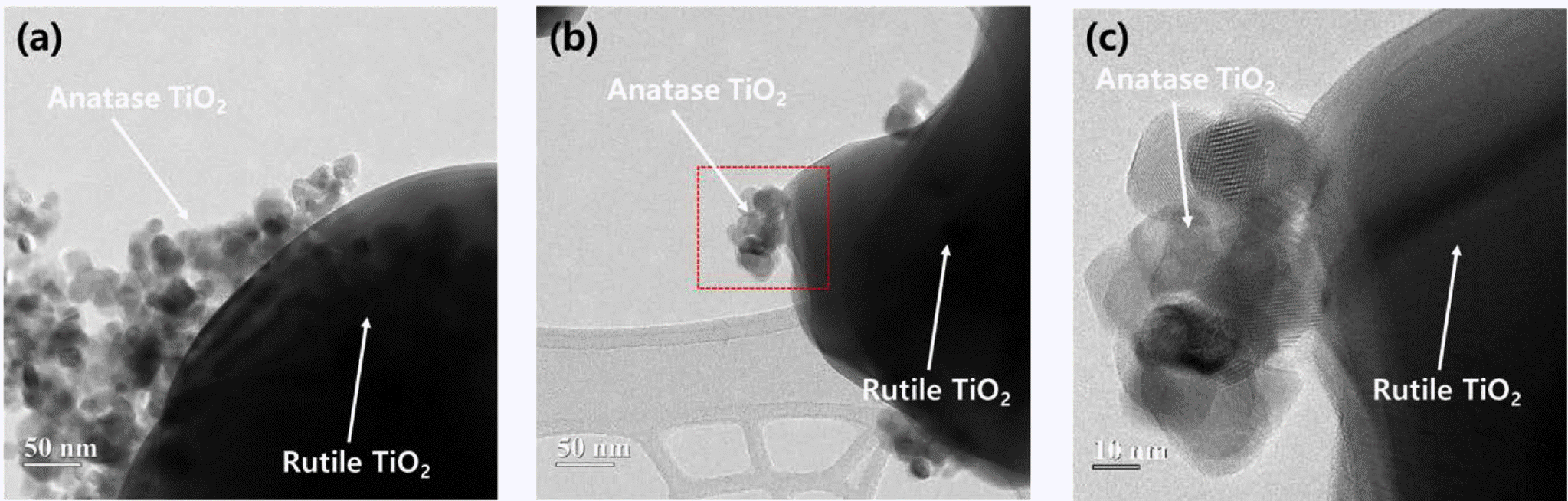
- Photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles using surfactant
- Jong Min Byun, Chun Woong Park, Young In Kim, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):257-262. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.257
- 1,136 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The coupling of two semiconducting materials is an efficient method to improve photocatalytic activity via the suppression of recombination of electron-hole pairs. In particular, the coupling between two different phases of TiO2, i.e., anatase and rutile, is particularly attractive for photocatalytic activity improvement of rutile TiO2 because these coupled TiO2 powders can retain the benefits of TiO2, one of the best photocatalysts. In this study, anatase TiO2 nanoparticles are synthesized and coupled on the surface of rutile TiO2 powders using a microemulsion method and heat treatment. Triton X-100, as a surfactant, is used to suppress the aggregation of anatase TiO2 nanoparticles and disperse anatase TiO2 nanoparticles uniformly on the surface of rutile TiO2 powders. Rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles are successfully prepared. Additionally, we compare the photocatalytic activity of these rutile-anatase coupled TiO2 powders under ultraviolet (UV) light and demonstrate that the reason for the improvement of photocatalytic activity is microstructural.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Refractory Metal Oxide–Doped Titanate Nanotubes: Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity under UV/Visible Light Range
Min-Sang Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi, Tohru Sekino, Young-Do Kim, Se-Hoon Kim
Catalysts.2021; 11(8): 987. CrossRef - Effect of Surfactant on the Dispersion Stability of Slurry for Semiconductor Silicon CMP
Hye Won Yun, Doyeon Kim, Do Hyung Han, Dong Wan Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(5): 395. CrossRef
- Refractory Metal Oxide–Doped Titanate Nanotubes: Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity under UV/Visible Light Range
- [Korean]
- Photocatalytic and Adsorption Properties of WO3 Nanorods Prepared by Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Su-Yeol Yu, Chunghee Nam
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):483-488. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.483
- 1,146 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
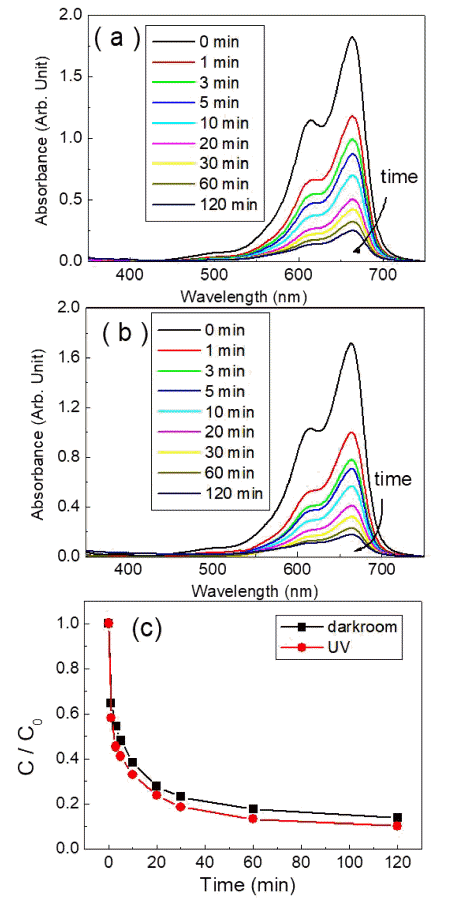
PDF Transition-metal oxide semiconductors have various band gaps. Therefore, many studies have been conducted in various application fields. Among these, methods for the adsorption of organic dyes and utilization of photocatalytic properties have been developed using various metal oxides. In this study, the adsorption and photocatalytic effects of WO3 nanomaterials prepared by hydrothermal synthesis are investigated, with citric acid added in the hydrothermal process as a structure-directing agent. The nanostructures of WO3 are studied using transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy images. The crystal structure is investigated using X-ray diffraction patterns, and the changes in the dye concentrations adsorbed on WO3 nanorods are measured with a UV-visible absorption spectrophotometer based on Beer-Lambert’s law. The methylene blue (MB) dye solution is subjected to acid or base conditions to monitor the change in the maximum adsorption amount in relation to the pH. The maximum adsorption capacity is observed at pH 3. In addition to the dye adsorption, UV irradiation is carried out to investigate the decomposition of the MB dye as a result of photocatalytic effects. Significant photocatalytic properties are observed and compared with the adsorption effects for dye removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Photocatalytic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Prepared by Electrodeposition Method
Kwang-Mo Kang, Ji-Hye Jeong, Ga-In Lee, Jae-Min Im, Hyun-Jeong Cheon, Deok-Hyeon Kim, Yoon-Chae Nah
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(1): 40. CrossRef - Photocatalysis of TiO<sub>2</sub>/WO<sub>3</sub> Composites Synthesized by Ball Milling
Su-Yeol Yu, Chunghee Nam
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(4): 316. CrossRef
- Photocatalytic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Prepared by Electrodeposition Method
- [English]
- The Synthesis and Photocatalytic activity of Carbon Nanotube-mixed TiO2 Nanotubes
- Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim, Tohru Sekino, Se Hoon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):279-284. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.279
- 1,517 View
- 11 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
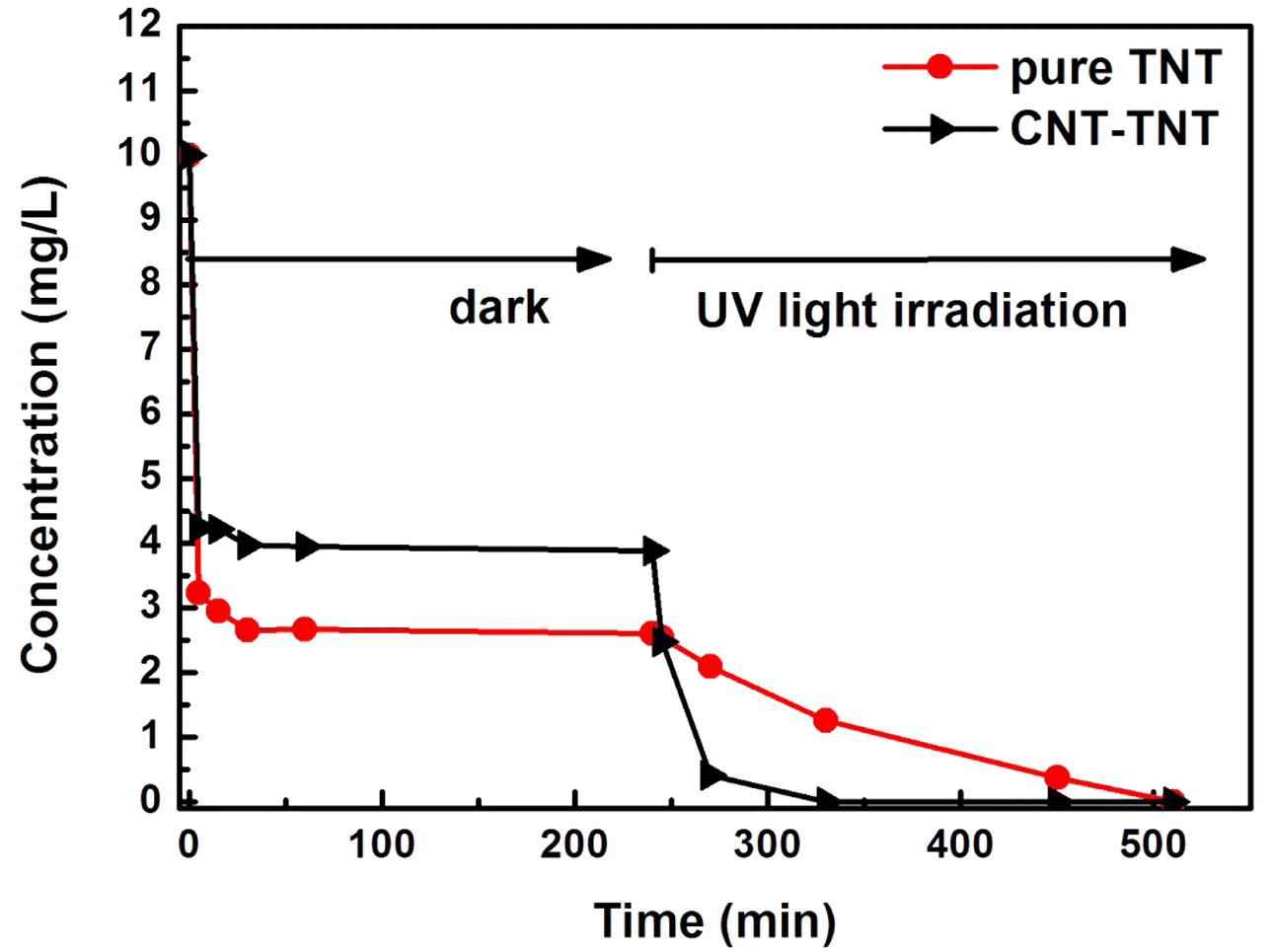
PDF The formation mechanism and photocatalytic properties of a multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)/TiO2- based nanotube (TNTs) composite are investigated. The CNT/TNT composite is synthesized via a solution chemical route. It is confirmed that this 1-D nanotube composite has a core-shell nanotubular structure, where the TNT surrounds the CNT core. The photocatalytic activity investigated based on the methylene blue degradation test is superior to that of with pure TNT. The CNTs play two important roles in enhancing the photocatalytic activity. One is to act as a template to form the core-shell structure while titanate nanosheets are converted into nanotubes. The other is to act as an electron reservoir that facilitates charge separation and electron transfer from the TNT, thus decreasing the electronhole recombination efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carbon-based photocatalysis in organic transformation
Md Razu Ahmed, Yuta Nishina
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Low-Dimensional Carbon and Titania Nanotube Composites via a Solution Chemical Process and Their Nanostructural and Electrical Properties for Electrochemical Devices
Sunghun Eom, Sung Hun Cho, Tomoyo Goto, Myoung Pyo Chun, Tohru Sekino
ACS Applied Nano Materials.2019; 2(10): 6230. CrossRef
- Carbon-based photocatalysis in organic transformation
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Optical Property of a TiOF2 Powder via an Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
- Young Hwangbo, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):307-310. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.307
- 672 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
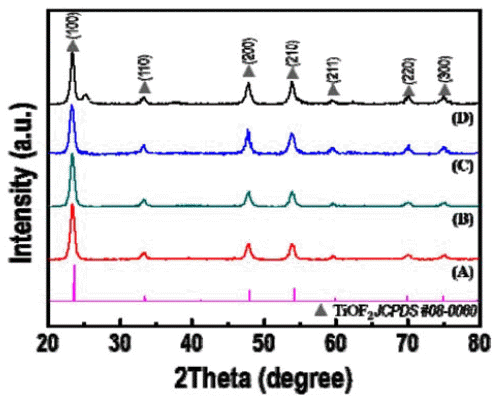
PDF TiOF2, which has remarkable electrochemical and optical properties, is used in various applications such as Li-ion batteries, electrochemical displays, and photocatalysts. In addition, it is possible to utilize the template which is allowed to synthesize fluorine doped TiO2 powders with hollow or faceted structures. However, common synthesis methods of TiOF2 powders have some disadvantages such as the use of expensive and harmful precursors and batchtype processes with a limited production scale. In this study, we report a synthetic route for preparing TiOF2 powders by using an inexpensive and harmless precursor and a continuous ultrasonic spray pyrolysis process under a controlled atmosphere to address the aforementioned problems. The synthesized powder has an average size of 1 μm, a spherical shape, a pure TiOF2 phase, and exhibits a band-gap energy of 3.2 eV.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles using surfactant
Jong Min Byun, Chun Woong Park, Young In Kim, Young Do Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 257. CrossRef
- Photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles using surfactant
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


