Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
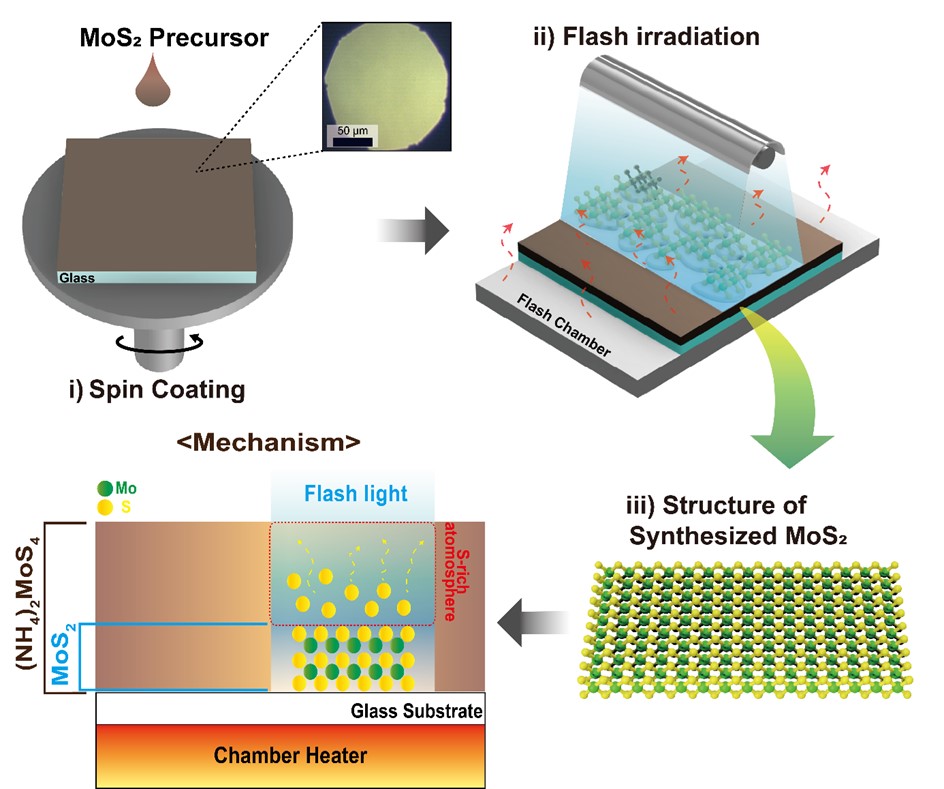
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
- Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):509-516. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00339
- 684 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study presents the synthesis of molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) using flashlamp annealing and provides a comprehensive investigation of its structural and physical properties. The proposed flash-induced approach enables rapid production of high-quality MoS₂, offering superior process efficiency compared to conventional synthesis techniques. The structural, electronic, and thermal characteristics of the synthesized MoS₂ were systematically examined using multiple analytical methods, with particular attention to how synthesis conditions influence layer structure, crystallinity, and defect density. The results indicate that MoS₂ produced through this method exhibits material properties suitable for high-performance electronic devices and energy storage applications. Moreover, this work demonstrates the potential of flash-induced synthesis for scalable and practical fabrication of MoS₂-based nanomaterials, thereby contributing to the broader advancement of transition metal dichalcogenide technologies across diverse nanotechnology applications.
- [Korean]
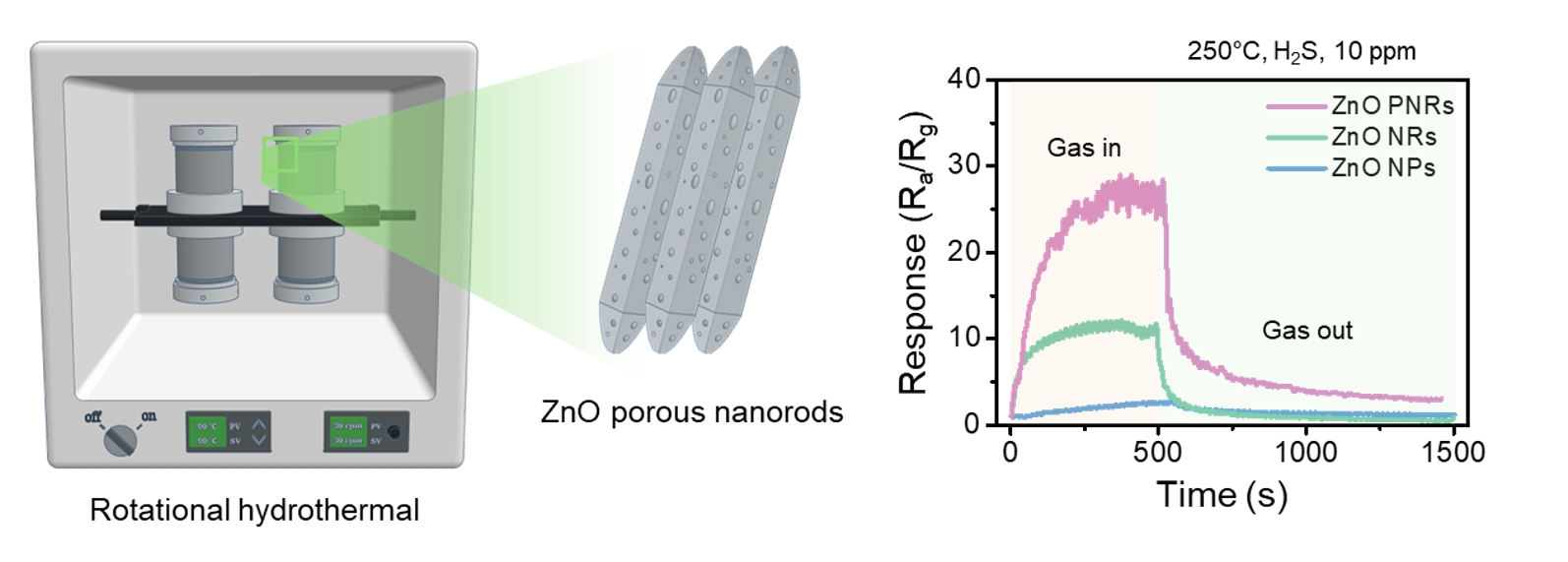
- Enhanced H2S Gas Sensing Using ZnO Porous Nanorod Synthesized via a Rotational Hydrothermal Method
- Jimyeong Park, Changyu Kim, Minseo Kim, Jiyeon Shin, Jae-Hyoung Lee, Myung Sik Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):406-415. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00262
- 431 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, ZnO porous nanorods were synthesised using a rotational hydrothermal process, and their performance as hydrogen sulphide (H2S) gas sensors was analysed. Compared to commercial ZnO nanoparticles and conventionally hydrothermally synthesised ZnO nanorods, the ZnO porous nanorods exhibited a more uniform structure and improved crystal growth in the (002) plane, with surfaces rich in porosity and oxygen vacancies. These structural and chemical characteristics significantly improved the sensitivity toward H2S, showing high detection performance at 250°C across various concentrations of H2S gas. Additionally, the sensor demonstrated excellent selectivity against other gases such as C2H5OH, C6H6, C7H8, and NH3. This study indicated that the rotational hydrothermal process is an effective method for developing high-performance ZnO-based gas sensors and suggests its applicability to other metal oxide materials.
- [English]
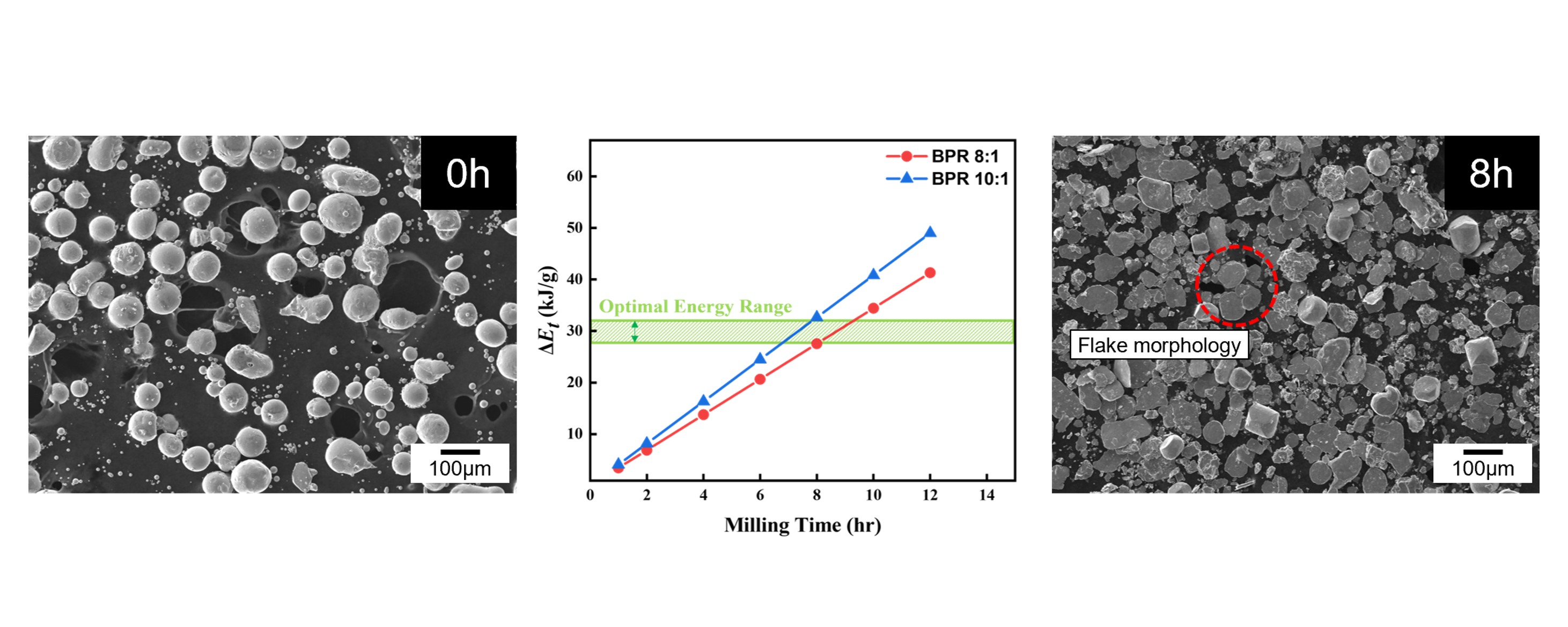
- Preparation of Flake-shape Cobalt Powders by High-Energy Ball Milling for rSOC Current Collectors
- Poong-Yeon Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Hyeon Ju Kim, Su-Jin Yun, Si Young Chang, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):383-389. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00241
- 442 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Reversible solid oxide cells (rSOCs), which enable two-way conversion between electricity and hydrogen, have gained attention with the rise of hydrogen energy. However, foam-type current collectors in rSOC stacks exhibit poor structural controllability and limited electrode contact area. To address these limitations, this study aimed to convert spherical cobalt powders into flake-type morphology via high-energy ball milling, as a preliminary step toward fabricating flake-based current collectors. Milling parameters—specifically, the ball-to-powder ratio (BPR), milling time, and process control agent (PCA) content—were varied. At an 8:1 BPR, over 90% of the powder became flake-shaped after 8 hours, while extended milling caused cold welding. In contrast, a 10:1 BPR resulted in dominant fragmentation. The Burgio–Rojac model quantified energy input and defined the optimal range for flake formation. Increasing the PCA to 4 wt% delayed flake formation to 16 hours and induced cold welding, as shown by bimodal particle size distributions. These results support the development of Co-based current collectors for use in rSOCs.
- [English]
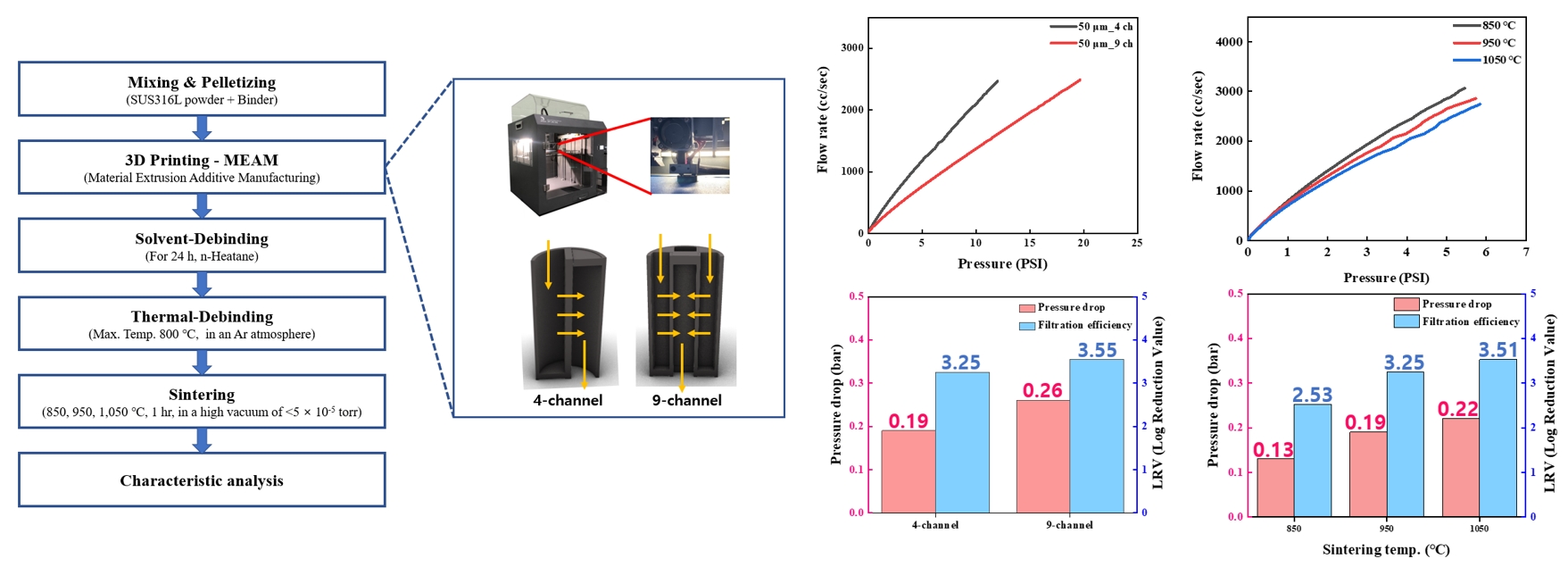
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
- Minji Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Su-Jin Yun, Poong-Yeon Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Juyong Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):299-308. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00234
- 963 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of high-performance metal filters is essential for maintaining ultra-clean environments in semiconductor manufacturing. In this study, cross-sealed honeycomb filters were fabricated using STS316L powder via material extrusion additive manufacturing (MEAM) for semiconductor gas filtration. The effects of filter geometry (4 or 9 channels) and sintering temperature (850°C, 950°C, or 1,050°C) on performance were examined. First, 4-channel and 9-channel filters sintered at the same temperature (950°C) exhibited similar porosities of 50.08% and 50.57%, but the 9-channel filter showed a higher pressure-drop (0.26 bar) and better filtration-efficiency (3.55 LRV) than the 4-channel filter (0.19 bar and 3.25 LRV, respectively). Second, for filters with the same geometry (4-channel) increasing the sintering temperature reduced porosity from 64.52% to 40.33%, while the pressure-drop increased from 0.13 bar to 0.22 bar and filtration-efficiency improved from 2.53 LRV to 3.51 LRV. These findings demonstrate that filter geometry and sintering temperature are key factors governing the trade-off between air permeability, pressure-drop, and filtration efficiency. This work provides insights and data for optimizing MEAM-based high-performance metal powder filter design.
- [English]
- SnF2-Induced LiF Interphase for Stable Lithium Metal Anodes with Suppressed Dendrite Growth
- Yeong Hoon Jeon, Seul Ki Choi, Yun Seung Nah, Wonil Shin, Yong-Ho Choa, Minho Yang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):212-221. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00164

- 1,764 View
- 53 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Lithium (Li) metal is a promising anode for next-generation batteries due to its high capacity, low redox potential, and low density. However, dendrite growth and interfacial instability limit its use. In this study, an artificial solid electrolyte interphase layer of LiF and Li-Sn (LiF@Li-Sn) was fabricated by spray-coating SnF2 onto Li. The LiF@Li-Sn anode exhibited improved air stability and electrochemical performance. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy indicated a charge transfer resistance of 25.2 Ω after the first cycle. In symmetric cells, it maintained a low overpotential of 27 mV after 250 cycles at 2 mA/cm2, outperforming bare Li. In situ microscopy confirmed dendrite suppression during plating. Full cells with NMC622 cathodes and LiF@Li-Sn anodes delivered 130.8 mAh/g with 79.4% retention after 300 cycles at 1 C and 98.8% coulombic efficiency. This coating effectively stabilized the interface and suppressed dendrites, with promising implications for practical lithium metal batteries.
- [English]
- The Effect of Aluminum Powder Size on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Foam
- Seunghyeok Choi, Sungjin Kim, Tae-Young Ahn, Yu-Song Choi, Jae-Gil Jung, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):232-243. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00157

- 1,378 View
- 54 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, we analyzed the structural and mechanical properties of aluminum foams fabricated using aluminum powders of varying sizes and mixtures. The effects of sintering and pore structure at each size on the integrity and mechanical properties of the foams were investigated. Structural characteristics were examined using scanning electron microscopy and micro–computed tomography, while mechanical properties were evaluated through compression testing. The experimental results demonstrated that smaller powder sizes improved foam integrity, reduced porosity and pore size, and resulted in thinner cell walls. In combination, these effects increased compressive strength as the powder size decreased. The findings of this study contribute to the understanding and improvement of the mechanical properties of aluminum foams and highlight their potential for use in a wide range of applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sustainable Manufacturing of Graphene–Aluminum Composites: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment
Xinwei Yang, Qian Peng, Changke Chen, Qingcui Liu, Yudai Huang
Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy.2026; 12(1): 727. CrossRef
- Sustainable Manufacturing of Graphene–Aluminum Composites: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
- Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):254-261. Published online June 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00059

- 666 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) incorporating low-melting-point elements (Mg and Al) and high-melting-point elements (Ti, Cr, and V) were fabricated via mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Sintering temperatures were varied to investigate phase behavior and microstructural evolution. X-ray diffraction was used to identify phase structures, scanning electron microscopy to analyze microstructures, X-ray fluorescence to determine elemental composition, and a gas pycnometer to measure density. Micro-Vickers hardness testing was conducted to evaluate mechanical properties. Mechanical-alloyed HEAs exhibited a body-centered cubic (BCC) phase and lamellar structures with element-enriched regions. Sintering introduced additional BCC and Laves phases, while higher temperatures promoted Mg liquid-phase sintering, increasing density and hardness. This study highlights the effects of sintering on HEAs containing elements with differing melting points to optimize their properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
Wooyoung Lee, Munsu Choi, Sungwook Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song, Taek-Soo Kim, Jungwan Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Soo-Hyun Joo
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 954: 149811. CrossRef
- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
- [English]
- Stretch-Flangeability of Laser Powder Bed Fusion-Processed 316L Stainless Steel
- Rae Eon Kim, Yeon Taek Choi, Sang Guk Jeong, Do Won Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):87-94. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00017

- 2,271 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Metal additive manufacturing (AM) facilitates the production of complex geometries with enhanced functionality. Among various AM techniques, laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is distinguished by its precision and exceptional mechanical properties achieved via laser fusion deposition. Recent advancements in AM have focused on combining LPBF with post-processing methods such as cold rolling, high-pressure torsion, and forming processes. Therefore, understanding the forming behavior of LPBF-processed materials is essential for industrial adoption. This study investigates the stretch-flangeability of LPBF-fabricated 316L stainless steel, emphasizing its anisotropic microstructure and mechanical properties. Hole expansion tests were employed to assess stretch-flangeability in comparison to wrought 316L stainless steel. The results demonstrate that LPBF-processed samples exhibit significant anisotropic behavior, demonstrating the influence of microstructural evolution on formability. These findings contribute valuable insights into optimizing LPBF materials for industrial forming applications.
- [English]
- A Review of Recent Developments in CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys Processed by Powder Metallurgy
- Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Sheetal Kumar Dewangan, Hansung Lee, Eunhyo Song, K. Raja Rao, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):145-164. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00430
- 4,526 View
- 118 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
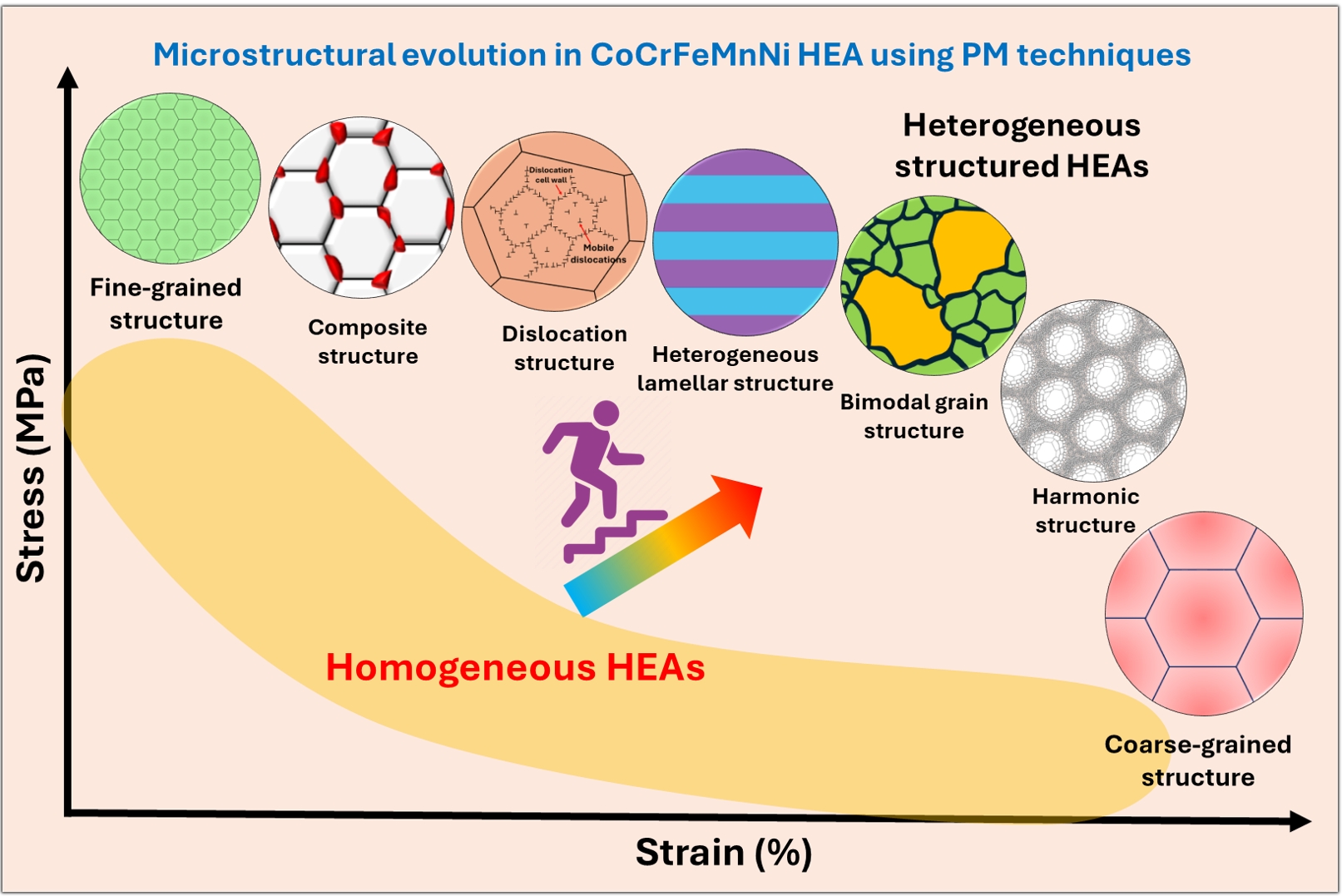
PDF - In recent years, high-entropy alloys (HEAs) have attracted considerable attention in materials engineering due to their unique phase stability and mechanical properties compared to conventional alloys. Since the inception of HEAs, CoCrFeMnNi alloys have been widely investigated due to their outstanding strength and fracture toughness at cryogenic temperatures. However, their lower yield strength at room temperature limits their structural applications. The mechanical properties of HEAs are greatly influenced by their processing methods and microstructural features. Unlike traditional melting techniques, powder metallurgy (PM) provides a unique opportunity to produce HEAs with nanocrystalline structures and uniform compositions. The current review explores recent advances in optimizing the microstructural characteristics in CoCrFeMnNi HEAs by using PM techniques to improve mechanical performance. The most promising strategies include grain refinement, dispersion strengthening, and the development of heterogeneous microstructures (e.g., harmonic, bimodal, and multi-metal lamellar structures). Thermomechanical treatments along with additive manufacturing techniques are also summarized. Additionally, the review addresses current challenges and suggests future research directions for designing advanced HEAs through PM techniques.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
Wooyoung Lee, Munsu Choi, Sungwook Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song, Taek-Soo Kim, Jungwan Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Soo-Hyun Joo
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 954: 149811. CrossRef - Structural and mechanical characteristics of high-entropy CoCrFeMnNi alloys manufactured by vacuum induction melting
V. K. Drobyshev, I. A. Panchenko, S. V. Konovalov, E. M. Zapolskaya
Russian Physics Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Sustainable powder metallurgy route to Densify oxide-derived CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy
Taehyeob Im, Minjong Kim, Gertrude Mugwe Mongella, Nelson Bayi, Caroline Sunyong Lee
Materials Today Sustainability.2026; 34: 101330. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef
- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
- [English]
- High-Temperature Steam Oxidation Behavior of Silicide- or Aluminide- Coated Mo and Nb Refractory Metals
- Woojin Lim, Je-Kyun Baek, JaeJoon Kim, Hyun Gil Kim, Ho Jin Ryu
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):546-555. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00381
- 1,484 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
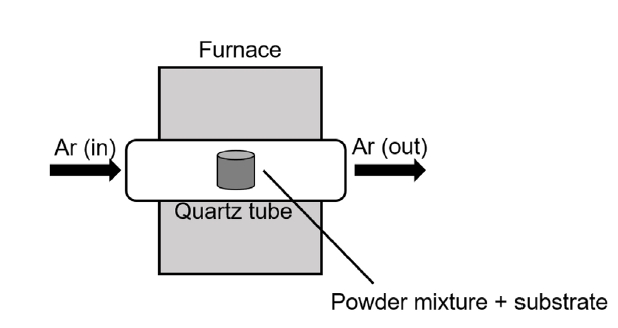
PDF - Refractory materials, such as molybdenum and niobium, are potential candidates for cladding material due to their high melting temperatures and desirable mechanical properties at higher temperatures than those of zirconium alloys. However, refractory materials have low resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures. Therefore, this study examined silicide or aluminide surface coatings as protection against rapid oxidation of refractory materials at elevated temperatures for a potential accident-tolerant fuel cladding. Silicide or aluminide layers were formed on refractory metal substrates by using the pack cementation method. The steam oxidation behavior of both coated and uncoated samples was compared by thermogravimetric analysis at 1200°C. The weight changes of the coated samples were greatly reduced than those of uncoated samples. Microstructural analyses demonstrated that the silicide and aluminide layers were oxidized to form a protective surface oxide that prevented rapid oxidation of the refractory substrate at elevated temperatures.
- [English]
- Advances in Powder Metallurgy for High-Entropy Alloys
- Sheetal Kumar Dewangan, Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Hansung Lee, K. Raja Rao, Man Mohan, Reliance Jain, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):480-492. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00297
- 5,026 View
- 169 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
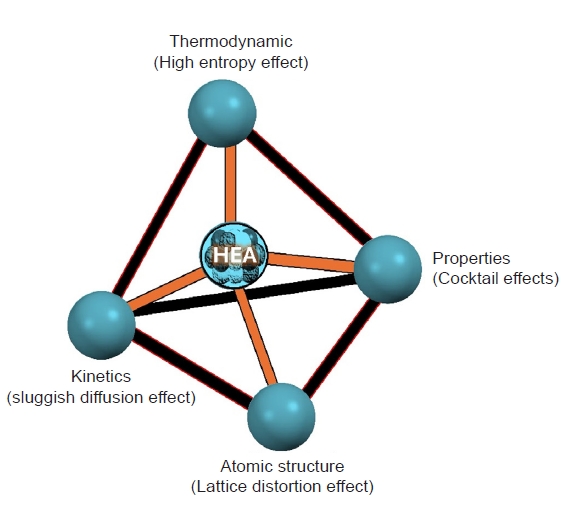
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) represent a revolutionary class of materials characterized by their multi-principal element compositions and exceptional mechanical properties. Powder metallurgy, a versatile and cost-effective manufacturing process, offers significant advantages for the development of HEAs, including precise control over their composition, microstructure, and mechanical properties. This review explores innovative approaches integrating powder metallurgy techniques in the synthesis and optimization of HEAs. Key advances in powder production, sintering methods, and additive manufacturing are examined, highlighting their roles in improving the performance, advancement, and applicability of HEAs. The review also discusses the mechanical properties, potential industrial applications, and future trends in the field, providing a comprehensive overview of the current state and future prospects of HEA development using powder metallurgy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Pressure and Temperature on the Microstructure and Vickers Microhardness of the CoCrFeMnNiAl1.5 Alloy During Conventional Sintering and High-Frequency Induction Sintering
Leonardo Baylón García, José Manuel Mendoza Duarte, Ivanovich Estrada Guel, Audel Santos Beltrán, Hansel Manuel Medrano Prieto, Gustavo Rodríguez Cabriales, Enrique Rocha Rangel, José Luis Hernández Rivera, Roberto Martínez Sánchez, Alfredo Martínez Garcí
Coatings.2026; 16(3): 275. CrossRef - Sustainable powder metallurgy route to Densify oxide-derived CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy
Taehyeob Im, Minjong Kim, Gertrude Mugwe Mongella, Nelson Bayi, Caroline Sunyong Lee
Materials Today Sustainability.2026; 34: 101330. CrossRef - Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Latest Advancements and Mechanistic Insights into High-Entropy Alloys: Design, Properties and Applications
Anthoula Poulia, Alexander E. Karantzalis
Materials.2025; 18(24): 5616. CrossRef
- Effect of Pressure and Temperature on the Microstructure and Vickers Microhardness of the CoCrFeMnNiAl1.5 Alloy During Conventional Sintering and High-Frequency Induction Sintering
- [English]
- Effect of Calcium Addition on the High-Temperature Recovery of Nd and Dy from Nd-Fe-B Scrap Using Mg-Based Extractants
- Hyoseop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):493-499. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00283
- 1,694 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
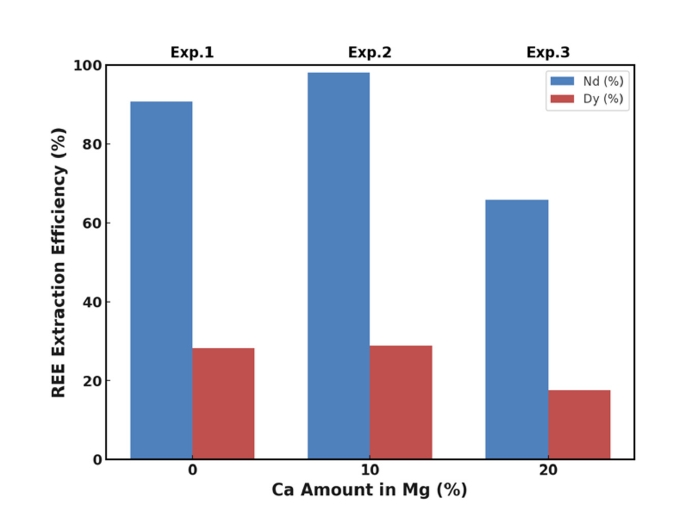
PDF - This study investigated whether calcium (Ca) addition improved the recovery of neodymium (Nd) and dysprosium (Dy) from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap using magnesium (Mg)-based liquid metal extraction (LME). Traditional LME processes are limited to temperatures up to 850 °C due to oxidation issues, reducing the efficiency of rare earth element (REE) recovery, especially for Dy. By adding 10 wt.% Ca to Mg and increasing the processing temperature to 1,000 °C, we achieved nearly 100% Nd and approximately 38% Dy recovery, compared to 91% and 28%, respectively, with pure Mg at 850 °C. However, excessive Ca addition (20 wt.%) decreased the recovery efficiency due to the formation of stable intermetallic compounds. These results highlight the critical role of Ca in optimizing REE recycling from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap.
- [Korean]
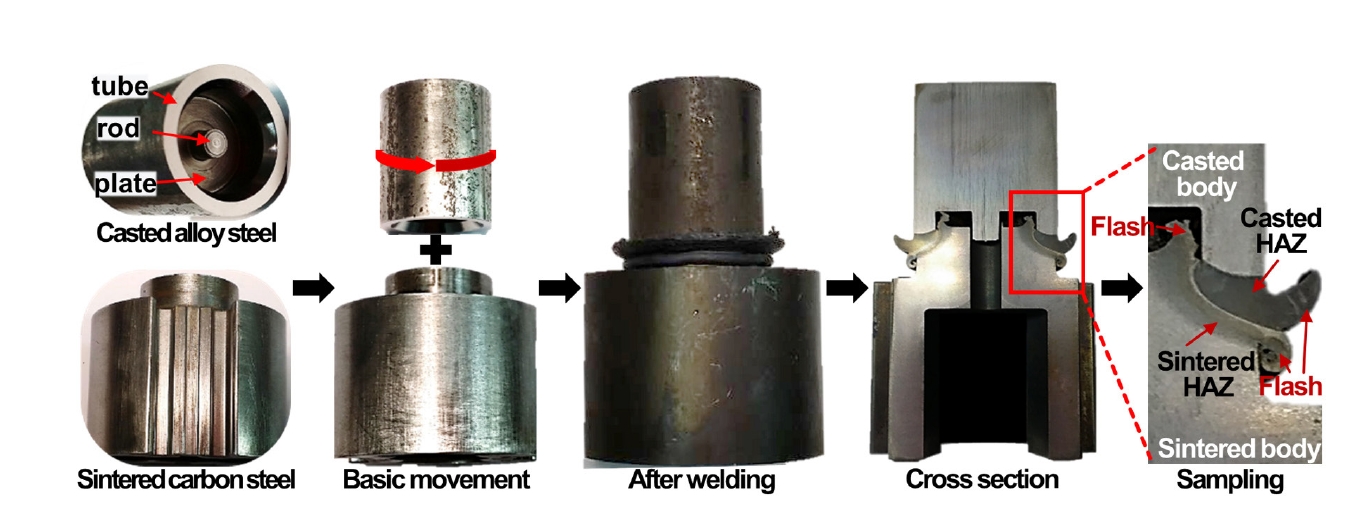
- Friction Welding of Casted SCM440 and Sintered F-05-140 Dissimilar Steels and Their Joint Properties under Various Welding Conditions
- Jisung Lee, Hansung Lee, Eunhyo Song, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):414-421. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00311
- 923 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Friction welding, which uses heat and plastic flow to join metals, is expanding across industries due to its ability to weld heterogeneous alloys and simple process. However, process research is essential for materials with complex geometries, and limited research has been conducted on friction welding between cast and sintered metals. This study analyzed the mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of the joint by controlling the rotational speed and friction pressure, which affect the removal of the heat-affected zone in friction welding of casted SCM440 and sintered F-05-140. Hardness mapping and microstructure observations with material transition were performed to investigate the correlation between phase behavior and welding conditions. These results are anticipated to reduce costs and improve the mechanical properties of key mobility components.
- [English]
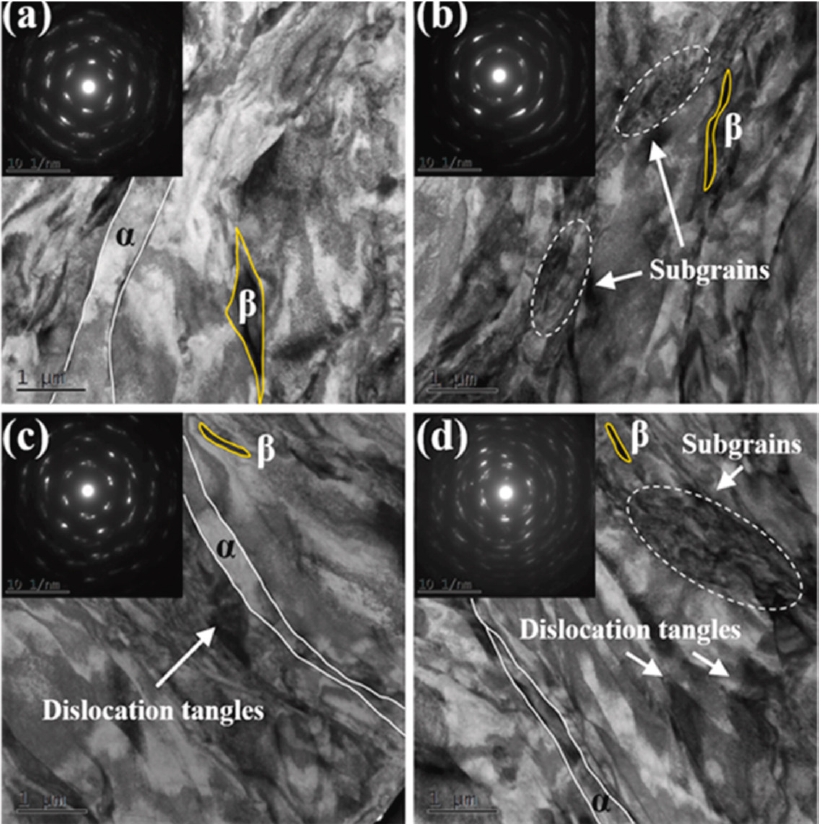
- Comparative Review of the Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated via Wrought and Powder Metallurgy Processes
- Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, An Seong Min, Hyunseok Lee, Jeoung Han Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):365-373. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00213
- 2,836 View
- 66 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This review examines the microstructural and mechanical properties of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by wrought processing and powder metallurgy (PM), specifically laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) and hot isostatic pressing. Wrought methods, such as forging and rolling, create equiaxed alpha (α) and beta (β) grain structures with balanced properties, which are ideal for fatigue resistance. In contrast, PM methods, particularly LPBF, often yield a martensitic α′ structure with high microhardness, enabling complex geometries but requiring post-processing to improve its properties and reduce stress. The study evaluated the effects of processing parameters on grain size, phase distribution, and material characteristics, guiding the choice of fabrication techniques for optimizing Ti-6Al-4V performance in aerospace, biomedical, and automotive applications. The analysis emphasizes tailored processing to meet advanced engineering demands.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants from Titanium Turning Scrap via Alkali and Acid Two-Step Cleaning
Seong Min An, Raj Narayan Hajra, Chan Hee Park, Jin-Ho Yoon, Jinsung Rho, Chang-Min Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(7): 855. CrossRef - Effect of oxygen content in feedstock powders on microstructure and mechanical properties of ELI Ti-6Al-4V fabricated via laser powder bed fusion
Woo Hyeok Kim, Sang Woo Kim, Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, Jeoung Han Kim
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 307. CrossRef
- Removal of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants from Titanium Turning Scrap via Alkali and Acid Two-Step Cleaning
- [Korean]
- Effect of Sintering Conditions on the Microstructure of an FeCrMnNiCo High-Entropy Alloy
- Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Junho Lee, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):406-413. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00185

- 1,292 View
- 40 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We investigated the microstructure of an FeCrMnNiCo alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering under different sintering temperatures (1000–1100°C) and times (1–600 s). All sintered alloys consisted of a single face-centered cubic phase. As the sintering time or temperature increased, the grains of the sintered alloys became partially coarse. The formation of Cr7C3 carbide occurred on the surface of the sintered alloys due to carbon diffusion from the graphite crucible. The depth of the layer containing Cr7C3 carbides increased to ~110 μm under severe sintering conditions (1100°C, 60 s). A molten zone was observed on the surface of the alloys sintered at higher temperatures (>1060°C) due to severe carbon diffusion that reduced the melting point of the alloy. The porosity of the sintered alloys decreased with increasing time at 1000°C, but increased at higher temperatures above 1060°C due to melting-induced porosity formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef - Microstructure and mechanical properties of oxide-dispersion-strengthened CrMnFeCoNiC0.2O0.2 high-entropy alloy fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering
Sang-Hwa Lee, Seonghyun Park, Ka Ram Lim, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 947: 149284. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
- [Korean]
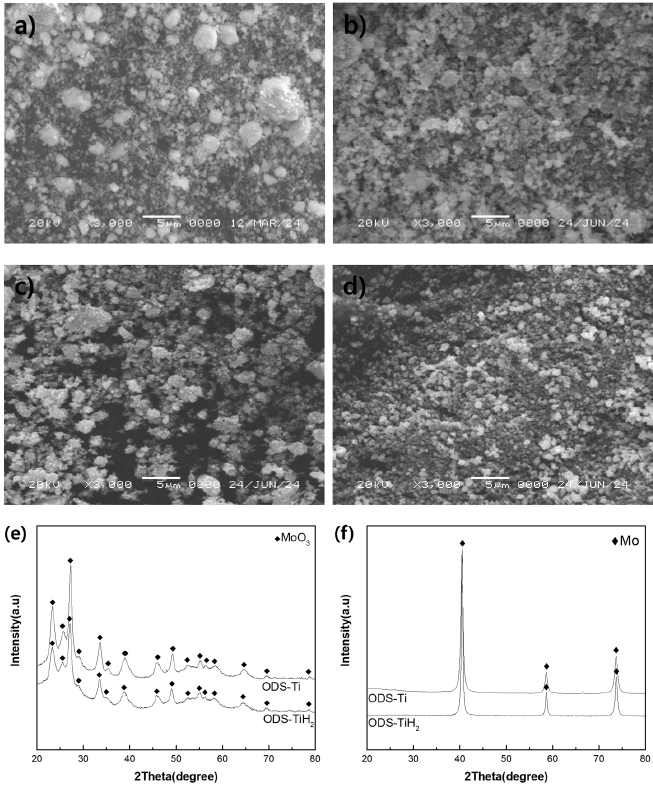
- The Use of TiH2 to Refine Y2Ti2O7 in a Nano Mo-ODS Alloy
- Yuncheol Ha, Chun Woong Park, Won Hee Lee, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):399-405. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00178
- 835 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mo-ODS alloys have excellent mechanical properties, including an improved recrystallization temperature, greater strength due to dispersed oxides, and the ability to suppress grain growth at high temperatures. In ODS alloys, the dispersed Y2O3 and added Ti form Y-Ti-O complex oxides, producing finer particles than those in the initial Y2O3. The complex oxides increase high-temperature stability and improve the mechanical properties of the alloy. In particular, the use of TiH2 powder, which is more brittle than conventional Ti, can enable the distribution of finer oxides than is possible with conventional Ti powder during milling. Moreover, dehydrogenation leads to a more refined powder size in the reduction process. This study investigated the refinement of Y2Ti2O7 in a nano Mo-ODS alloy using TiH2. The alloy compositions were determined to be Mo-0.5Ti-0.5Y2O3 and Mo-1.0Ti-0.5Y2O3. The nano Mo-ODS alloys were fabricated using Ti and TiH2 to explore the effects of adding different forms of Ti. The sintered specimens were analyzed through X-ray diffraction for phase analysis, and the microstructure of the alloys was analyzed using scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Vickers hardness tests were conducted to determine the effect of the form of Ti added on the mechanical properties, and it was found that using TiH2 effectively improved the mechanical properties.
- [English]
- Trends in Materials Modeling and Computation for Metal Additive Manufacturing
- Seoyeon Jeon, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):213-219. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00150

- 2,684 View
- 74 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Additive Manufacturing (AM) is a process that fabricates products by manufacturing materials according to a three-dimensional model. It has recently gained attention due to its environmental advantages, including reduced energy consumption and high material utilization rates. However, controlling defects such as melting issues and residual stress, which can occur during metal additive manufacturing, poses a challenge. The trial-and-error verification of these defects is both time-consuming and costly. Consequently, efforts have been made to develop phenomenological models that understand the influence of process variables on defects, and mechanical/electrical/thermal properties of geometrically complex products. This paper introduces modeling techniques that can simulate the powder additive manufacturing process. The focus is on representative metal additive manufacturing processes such as Powder Bed Fusion (PBF), Direct Energy Deposition (DED), and Binder Jetting (BJ) method. To calculate thermal-stress history and the resulting deformations, modeling techniques based on Finite Element Method (FEM) are generally utilized. For simulating the movements and packing behavior of powders during powder classification, modeling techniques based on Discrete Element Method (DEM) are employed. Additionally, to simulate sintering and microstructural changes, techniques such as Monte Carlo (MC), Molecular Dynamics (MD), and Phase Field Modeling (PFM) are predominantly used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
- [English]
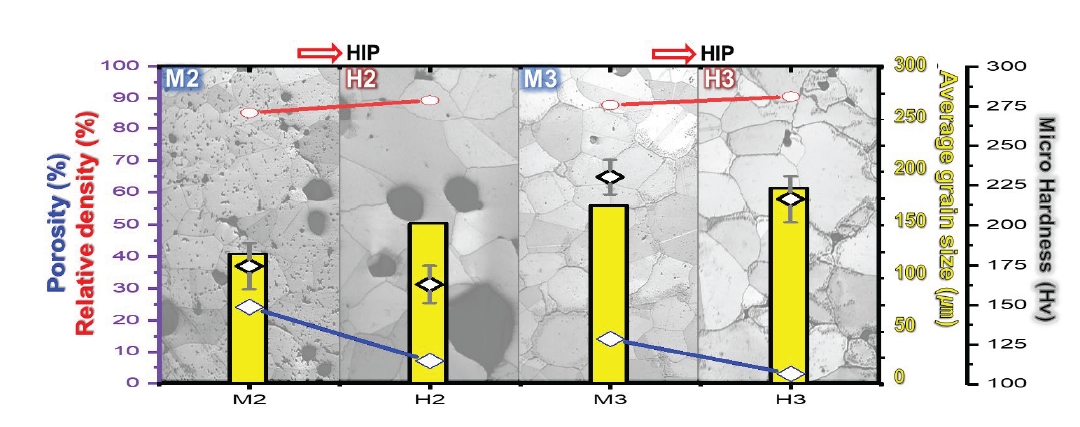
- Characterization of the Manufacturing Process and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys via Metal Injection Molding and Hot Isostatic Pressing
- Eun Seong Kim, Jae Man Park, Do Won Lee, Hyojeong Ha, Jungho Choe, Jaemin Wang, Seong Jin Park, Byeong-Joo Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):243-254. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00059
- 2,235 View
- 56 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) have been reported to have better properties than conventional materials; however, they are more expensive due to the high cost of their main components. Therefore, research is needed to reduce manufacturing costs. In this study, CoCrFeMnNi HEAs were prepared using metal injection molding (MIM), which is a powder metallurgy process that involves less material waste than machining process. Although the MIM-processed samples were in the face-centered cubic (FCC) phase, porosity remained after sintering at 1200°C, 1250°C, and 1275°C. In this study, the hot isostatic pressing (HIP) process, which considers both temperature (1150°C) and pressure (150 MPa), was adopted to improve the quality of the MIM samples. Although the hardness of the HIP-treated samples decreased slightly and the Mn composition was significantly reduced, the process effectively eliminated many pores that remained after the 1275°C MIM process. The HIP process can improve the quality of the alloy.
- [English]
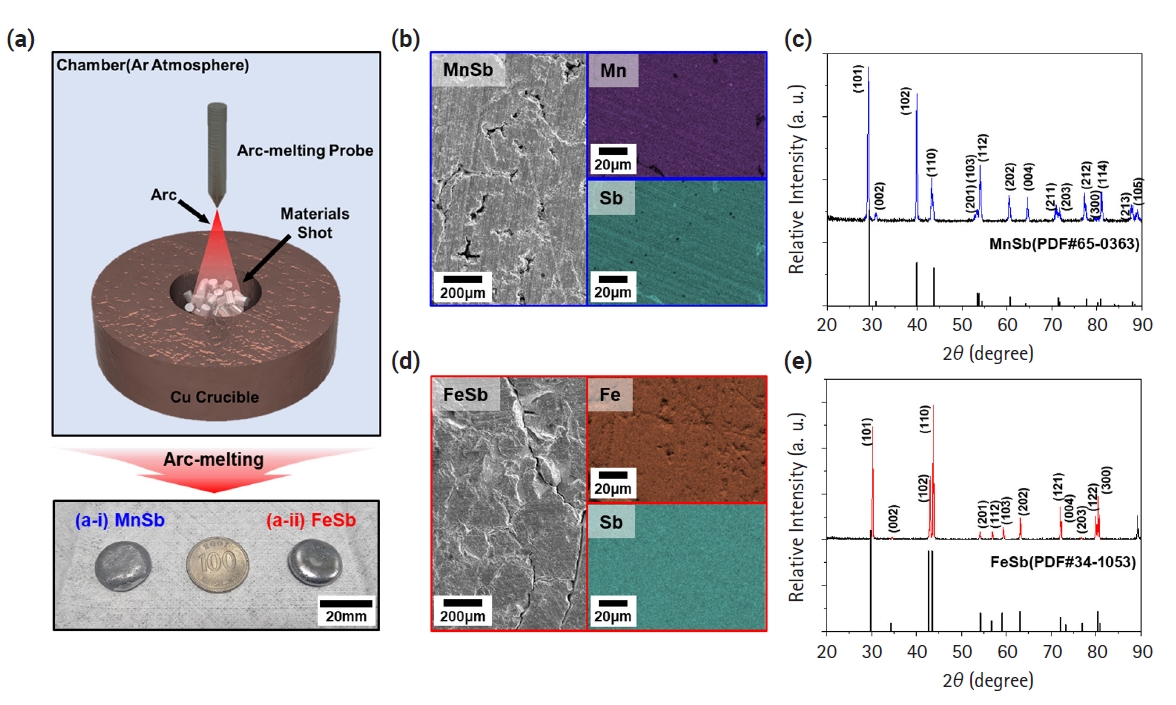
- Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
- Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):236-242. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00031
- 1,781 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of thermoelectric (TE) materials to replace Bi2Te3 alloys is emerging as a hot issue with the potential for wider practical applications. In particular, layered Zintl-phase materials, which can appropriately control carrier and phonon transport behaviors, are being considered as promising candidates. However, limited data have been reported on the thermoelectric properties of metal-Sb materials that can be transformed into layered materials through the insertion of cations. In this study, we synthesized FeSb and MnSb, which are used as base materials for advanced thermoelectric materials. They were confirmed as single-phase materials by analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns. Based on electrical conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity of both materials characterized as a function of temperature, the zT values of MnSb and FeSb were calculated to be 0.00119 and 0.00026, respectively. These properties provide a fundamental data for developing layered Zintl-phase materials with alkali/alkaline earth metal insertions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Jihun Yu, Kyung Tae Kim
Materials Letters.2025; 381: 137796. CrossRef - Highly deformable and hierarchical 3D composite sponge for versatile thermoelectric energy conversion
Jong Min Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Kwi-Il Park
Applied Surface Science.2025; 692: 162730. CrossRef
- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
- [English]
- Research Trends in Electromagnetic Shielding using MXene-based Composite Materials
- Siyeon Kim, Jongmin Byun
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):57-76. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.57
- 8,303 View
- 163 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Recent advancements in electronic devices and wireless communication technologies, particularly the rise of 5G, have raised concerns about the escalating electromagnetic pollution and its potential adverse impacts on human health and electronics. As a result, the demand for effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials has grown significantly. Traditional materials face limitations in providing optimal solutions owing to inadequacy and low performance due to small thickness. MXene-based composite materials have emerged as promising candidates in this context owing to their exceptional electrical properties, high conductivity, and superior EMI shielding efficiency across a broad frequency range. This review examines the recent developments and advantages of MXene-based composite materials in EMI shielding applications, emphasizing their potential to address the challenges posed by electromagnetic pollution and to foster advancements in modern electronics systems and vital technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
Pramod D. Mhase, Varsha C. Pujari, Santosh S. Jadhav, Abdullah G. Al-Sehemi, Sarah Alsobaie, Sunil M. Patange
Composites Communications.2025; 54: 102284. CrossRef - Microstructure tailoring of Nb-based MAX phase by low temperature synthesis with layer-structured Nb2C powder and molten salt method
Chaehyun Lim, Wonjune Choi, Jongmin Byun
Materials Characterization.2025; 225: 115106. CrossRef - Fabrication of MOF@MXene composites via surface modification of MXene under acidic conditions
Ji-Haeng Jeong, Woong-Ryeol Yu
Functional Composites and Structures.2025; 7(2): 025006. CrossRef - V2CTx MXene@ZIF-8 composite as an efficient adsorbent for Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution
Sarina Khojasteh Fard, Golshan Mazloom, Manoochehr Sobhani, Mohsen Tamtaji
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2025; 13(6): 120099. CrossRef
- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
- [Korean]
- Evaluation of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ni-Y2O3 Sintered Alloys Based on the Powder Preparation Methods
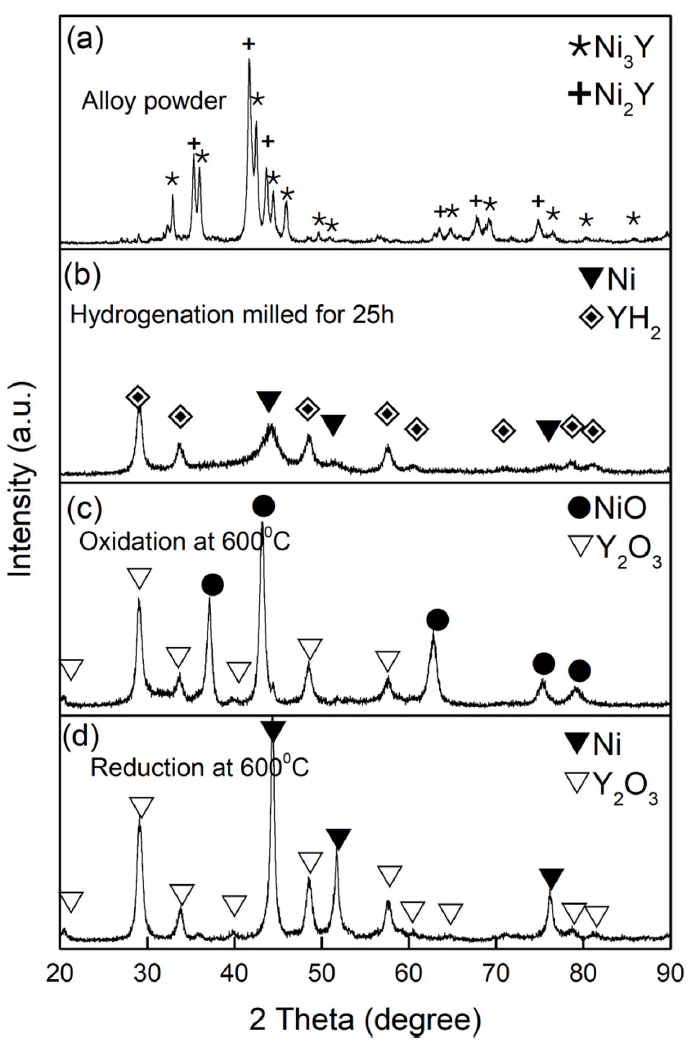
- Gun-Woo Jung, Ji-Ho Cha, Min-Seo Jang, Minsuk Oh, Jeshin Park
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):484-492. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.484
- 1,097 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, Ni-Y2O3 powder was prepared by alloying recomposition oxidation sintering (AROS), solution combustion synthesis (SCS), and conventional mechanical alloying (MA). The microstructure and mechanical properties of the alloys were investigated by spark plasma sintering (SPS). Among the Ni-Y2O3 powders synthesized by the three methods, the AROS powder had approximately 5 nm of Y2O3 crystals uniformly distributed within the Ni particles, whereas the SCS powder contained a mixture of Ni and Y2O3 nanoparticles, and the MA powder formed small Y2O3 crystals on the surface of large Ni particles by milling the mixture of Ni and Y2O3. The average grain size of Y2O3 in the sintered alloys was approximately 15 nm, with the AROS sinter having the smallest, followed by the SCS sinter at 18 nm, and the MA sinter at 22 nm. The yield strength (YS) of the SCS- and MA-sintered alloys were 1511 and 1688 MPa, respectively, which are lower than the YS value of 1697 MPa for the AROS-sintered alloys. The AROS alloy exhibited improved strength compared to the alloys fabricated by SCS and conventional MA methods, primarily because of the increased strengthening from the finer Y2O3 particles and Ni grains.
- [Korean]
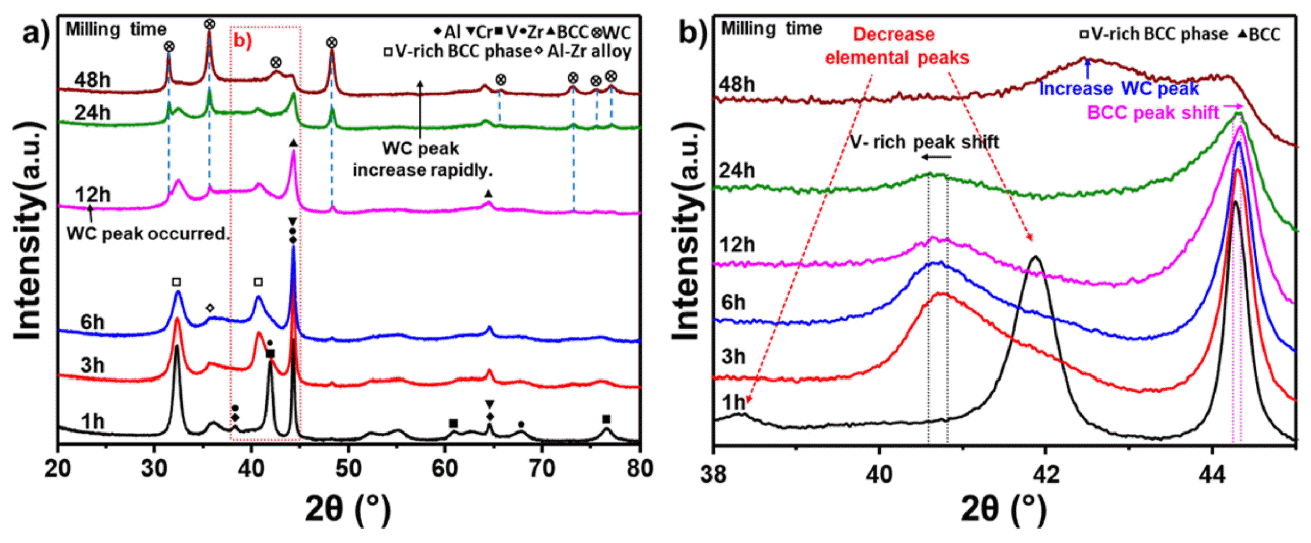
- Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
- Minsu Kim, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):478-483. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.478
- 1,224 View
- 15 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are characterized by having five or more main elements and forming simple solids without forming intermetallic compounds, owing to the high entropy effect. HEAs with these characteristics are being researched as structural materials for extreme environments. Conventional refractory alloys have excellent hightemperature strength and stability; however, problems occur when they are used extensively in a high-temperature environment, leading to reduced fatigue properties due to oxidation or a limited service life. In contrast, refractory entropy alloys, which provide refractory properties to entropy alloys, can address these issues and improve the hightemperature stability of the alloy through phase control when designed based on existing refractory alloy elements. Refractory high-entropy alloys require sufficient milling time while in the process of mechanical alloying because of the brittleness of the added elements. Consequently, the high-energy milling process must be optimized because of the possibility of contamination of the alloyed powder during prolonged milling. In this study, we investigated the hightemperature oxidation behavior of refractory high-entropy alloys while optimizing the milling time.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tailored high-temperature oxidation behavior and nanomechanical properties of Al0.75VCrZrNb lightweight refractory high-entropy alloys
Hansung Lee, Hwi Geun Yu, Reliance Jain, Man Mohan, Younggeon Lee, Sheetal Kumar Dewangan, Byungmin Ahn
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2026; 135: 107507. CrossRef - Simultaneous enhancement of strength and ductility of Al matrix composites enabled by submicron-sized high-entropy alloy phases
Chahee Jung, Seungin Nam, Hansol Son, Juyeon Han, Jaewon Jeong, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Seok Su Sohn, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2024; 33: 1470. CrossRef
- Tailored high-temperature oxidation behavior and nanomechanical properties of Al0.75VCrZrNb lightweight refractory high-entropy alloys
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Carbon Coated Nickel Cobalt Sulfide Yolk-shell Microsphere and Their Application as Anode Materials for Sodium Ion Batteries
- Hyo Yeong Seo, Gi Dae Park
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):387-393. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.387
- 789 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
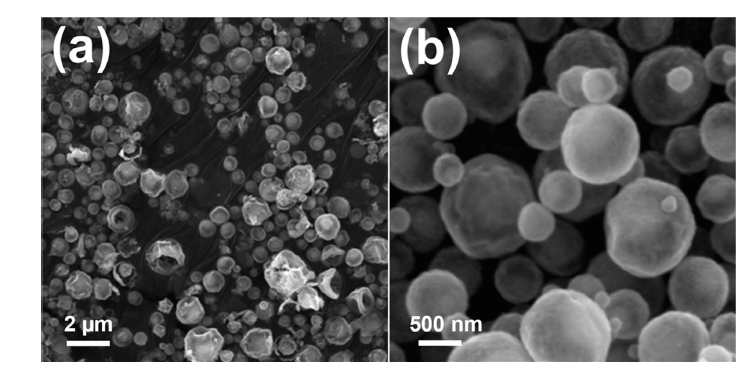
PDF Transition metal chalcogenides are promising cathode materials for next-generation battery systems, particularly sodium-ion batteries. Ni3Co6S8-pitch-derived carbon composite microspheres with a yolk-shell structure (Ni3Co6S8@C-YS) were synthesized through a three-step process: spray pyrolysis, pitch coating, and post-heat treatment process. Ni3Co6S8@C-YS exhibited an impressive reversible capacity of 525.2 mA h g-1 at a current density of 0.5 A g-1 over 50 cycles when employed as an anode material for sodium-ion batteries. However, Ni3Co6S8 yolk shell nanopowder (Ni3Co6S8-YS) without pitch-derived carbon demonstrated a continuous decrease in capacity during charging and discharging. The superior sodium-ion storage properties of Ni3Co6S8@C-YS were attributed to the pitchderived carbon, which effectively adjusted the size and distribution of nanocrystals. The carbon-coated yolk-shell microspheres proposed here hold potential for various metal chalcogenide compounds and can be applied to various fields, including the energy storage field.
- [Korean]
- Alloy Design and Powder Manufacturing of Al-Cu-Si alloy for Low-Temperature Aluminum Brazing
- Heeyeon Kim, Chun Woong Park, Won Hee Lee, Young Do Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):339-345. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.339
- 1,530 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
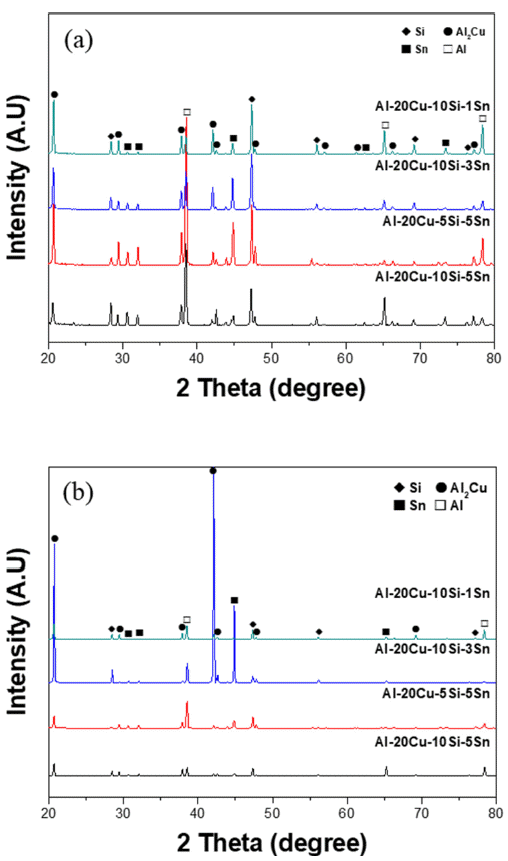
PDF This study investigates the melting point and brazing properties of the aluminum (Al)-copper (Cu)-silicon (Si)-tin (Sn) alloy fabricated for low-temperature brazing based on the alloy design. Specifically, the Al-20Cu-10Si-Sn alloy is examined and confirmed to possess a melting point of approximately 520°C. Analysis of the melting point of the alloy based on composition reveals that the melting temperature tends to decrease with increasing Cu and Si content, along with a corresponding decrease as the Sn content rises. This study verifies that the Al-20Cu-10Si-5Sn alloy exhibits high liquidity and favorable mechanical properties for brazing through the joint gap filling test and Vickers hardness measurements. Additionally, a powder fabricated using the Al-20Cu-10Si-5Sn alloy demonstrates a melting point of around 515°C following melting point analysis. Consequently, it is deemed highly suitable for use as a low-temperature Al brazing material.
- [Korean]
- Recent Studies on Area Selective Atomic Layer Deposition of Elemental Metals
- Min Gyoo Cho, Jae Hee Go, Byung Joon Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):156-168. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.156
- 3,107 View
- 81 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
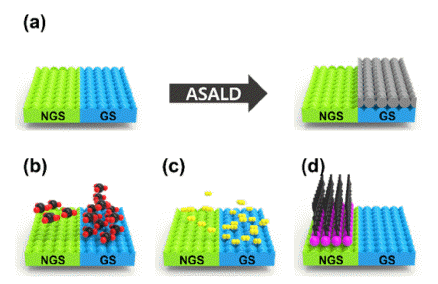
PDF The semiconductor industry faces physical limitations due to its top-down manufacturing processes. High cost of EUV equipment, time loss during tens or hundreds of photolithography steps, overlay, etch process errors, and contamination issues owing to photolithography still exist and may become more serious with the miniaturization of semiconductor devices. Therefore, a bottom-up approach is required to overcome these issues. The key technology that enables bottom-up semiconductor manufacturing is area-selective atomic layer deposition (ASALD). Here, various ASALD processes for elemental metals, such as Co, Cu, Ir, Ni, Pt, and Ru, are reviewed. Surface treatments using chemical species, such as self-assembled monolayers and small-molecule inhibitors, to control the hydrophilicity of the surface have been introduced. Finally, we discuss the future applications of metal ASALD processes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 509. CrossRef - Selective Atomic Layer Deposition of Co Thin Films Using Co(EtCp)2 Precursor
Sujeong Kim, Yong Tae Kim, Jaeyeong Heo
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2024; 34(3): 163. CrossRef
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
- [English]
- Study on Reaction Behavior of Mg-FeB Phase for Rare Earth Elements Recovery from End-of-life Magnet
- Sangmin Park, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Rongyu Liu, Jaeyun Jeong, Taek-Soo Kim, Myungsuk Song
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):101-106. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.101
- 1,476 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
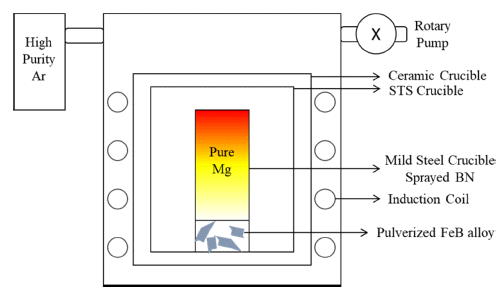
PDF Liquid metal extraction (LME), a pyrometallurgical recycling method, is popular owing to its negligible environmental impact. LME mainly targets rare-earth permanent magnets having several rare-earth elements. Mg is used as a solvent metal for LME because of its selective and eminent reactivity with rare-earth elements in magnets. Several studies concerning the formation of Dy-Fe intermetallic compounds and their effects on LME using Mg exist. However, methods for reducing these compounds are unavailable. Fe reacts more strongly with B than with Dy; B addition can be a reducing method for Dy-Fe intermetallic compounds owing to the formation of Fe2B, which takes Fe from Dy-Fe intermetallic compounds. The FeB alloy is an adequate additive for the decomposition of Fe2B. To accomplish the former process, Mg must convey B to a permanent magnet during the decomposition of the FeB alloy. Here, the effect of Mg on the transfer of B from FeB to permanent magnet is observed through microstructural and phase analyses. Through microstructural and phase analysis, it is confirmed that FeB is converted to Fe2B upon B transfer, owing to Mg. Finally, the transfer effect of Mg is confirmed, and the possibility of reducing Dy-Fe intermetallic compounds during LME is suggested.
- [Korean]
- Thermal Atomic Layer Etching of the Thin Films: A Review
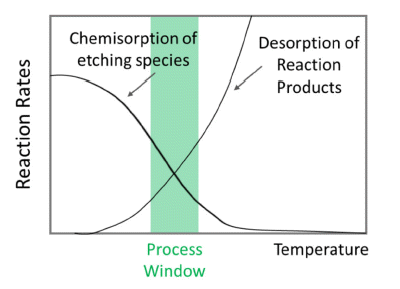
- Hyeonhui Jo, Seo Hyun Lee, Eun Seo Youn, Ji Eun Seo, Jin Woo Lee, Dong Hoon Han, Seo Ah Nam, Jeong Hwan Han
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):53-64. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.53
- 5,261 View
- 222 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Atomic layer etching (ALE) is a promising technique with atomic-level thickness controllability and high selectivity based on self-limiting surface reactions. ALE is performed by sequential exposure of the film surface to reactants, which results in surface modification and release of volatile species. Among the various ALE methods, thermal ALE involves a thermally activated reaction by employing gas species to release the modified surface without using energetic species, such as accelerated ions and neutral beams. In this study, the basic principle and surface reaction mechanisms of thermal ALE?processes, including “fluorination-ligand exchange reaction”, “conversion-etch reaction”, “conversion-fluorination reaction”, “oxidation-fluorination reaction”, “oxidation-ligand exchange reaction”, and “oxidation-conversion-fluorination reaction” are described. In addition, the reported thermal ALE processes for the removal of various oxides, metals, and nitrides are presented.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-Assembled Monolayers in Area-Selective Atomic Layer Deposition and Their Challenges
Si Eun Jung, Ji Woong Shin, Ye Jin Han, Byung Joon Choi
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 179. CrossRef
- Self-Assembled Monolayers in Area-Selective Atomic Layer Deposition and Their Challenges
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Al-Ni-Co-Y Bulk Metallic Glass fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
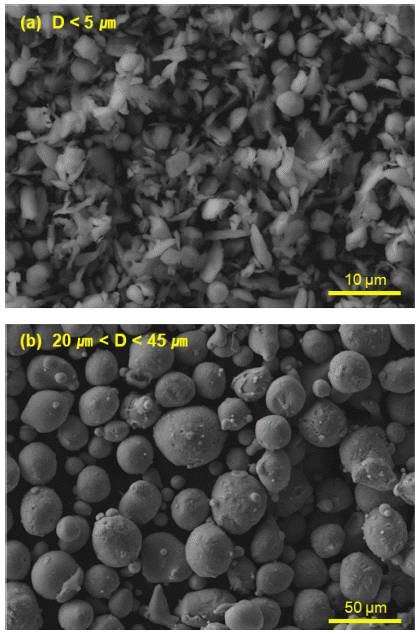
- Jeong Pyo Lee, Jin Kyu Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):41-46. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.41
- 925 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, an Al82Ni7Co3Y8 (at%) bulk metallic glass is fabricated using gas-atomized Al82Ni7Co3Y8 metallic glass powder and subsequent spark plasma sintering (SPS). The effect of powder size on the consolidation of bulk metallic glass is considered by dividing it into 5 μm or less and 20–45 μm. The sintered Al82Ni7Co3Y8 bulk metallic glasses exhibit crystallization behavior and crystallization enthalpy similar to those of the Al82Ni7Co3Y8 powder with 5 μm or less and it is confirmed that no crystallization occurred during the sintering process. From these results, we conclude that the Z-position-controlled spark plasma sintering process, using superplastic deformation by viscous flow in the supercooled liquid-phase region of amorphous powder, is an effective process for manufacturing bulk metallic glass.
- [English]
- Fabrication of Equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy by Metal Injection Molding Process Using Coarse-Sized Powders
- Eun Seong Kim, Jae Man Park, Ji Sun Lee, Jungho Choe, Soung Yeoul Ahn, Sang Guk Jeong, Do Won Lee, Seong Jin Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):1-6. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.1
- 1,794 View
- 33 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are attracting attention because of their excellent properties and functions; however, they are relatively expensive compared with commercial alloys. Therefore, various efforts have been made to reduce the cost of raw materials. In this study, MIM is attempted using coarse equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi HEA powders. The mixing ratio (powder:binder) for HEA feedstock preparation is explored using torque rheometer. The block-shaped green parts are fabricated through a metal injection molding process using feedstock. The thermal debinding conditions are explored by thermogravimetric analysis, and solvent and thermal debinding are performed. It is densified under various sintering conditions considering the melting point of the HEA. The final product, which contains a small amount of non-FCC phase, is manufactured at a sintering temperature of 1250°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of 3D interconnected nanoporous TiZrHfNbTaNi high-entropy alloy via liquid metal dealloying and subsequent synthesis of (TiZrHfNbTaNi)O high-entropy oxide
Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Vin Ha, Jihye Seong, Akira Takeuchi, Ruirui Song, Hidemi Kato, Soo-Hyun Joo
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 35: 5204. CrossRef - Development of 3D interconnected heterogeneous high-entropy alloy composites with enhanced multifunctionality via liquid metal dealloying
Munsu Choi, Gang Hee Gu, Jongun Moon, Jae Wung Bae, Hidemi Kato, Seung Zeon Han, Hyoung Seop Kim, Yongseok Choi, Soo-Hyun Joo
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 37: 5672. CrossRef - Characterization of the Manufacturing Process and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys via Metal Injection Molding and Hot Isostatic Pressing
Eun Seong Kim, Jae Man Park, Do Won Lee, Hyojeong Ha, Jungho Choe, Jaemin Wang, Seong Jin Park, Byeong-Joo Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(3): 243. CrossRef
- Development of 3D interconnected nanoporous TiZrHfNbTaNi high-entropy alloy via liquid metal dealloying and subsequent synthesis of (TiZrHfNbTaNi)O high-entropy oxide
- [Korean]
- A Study on Rinsing Effects of Sn Sensitization and Pd Activation Processes for Uniform Electroless Plating
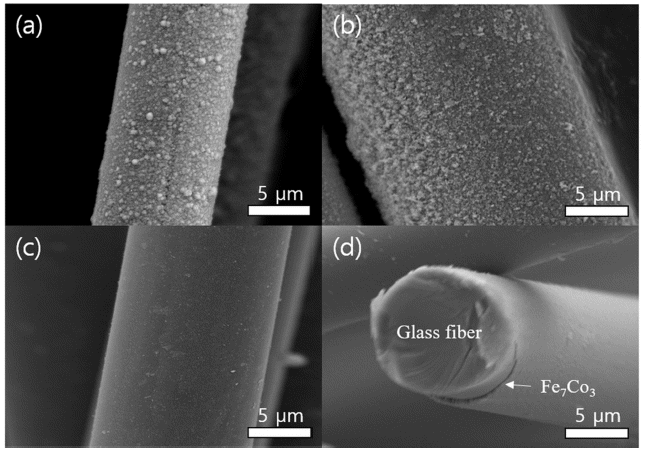
- Seong-Jae Jeong, Mi-Se Chang, Jae-Won Jeong, Sang-Sun Yang, Young-Tae Kwon
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):511-516. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.511
- 1,750 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Electroless plating is widely utilized in engineering for the metallization of insulator substrates, including polymers, glass, and ceramics, without the need for the application of external potential. Homogeneous nucleation of metals requires the presence of Sn-Pd catalysts, which significantly reduce the activation energy of deposition. Therefore, rinsing conducted during Sn sensitization and Pd activation is a key variable for the formation of a uniform seed layer without the lack or excess of catalysts. Herein, we report the optimized rinsing process for the functionalization of Sn-Pd catalysts, which enables the uniform FeCo metallization of the glass fibers. Rinsing enables good deposition of the FeCo alloy because of the removal of excess catalysts from the glass fiber. Concurrently, excessive rinsing results in a complete removal of the Sn–Pd nucleus. Collectively, the comprehensive study of the proposed nanomaterial preparation and surface science show that the metallization of insulators is a promising technology for electronics, solar cells, catalysts, and mechanical parts.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Iron Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Mo-Fe P/M Alloys
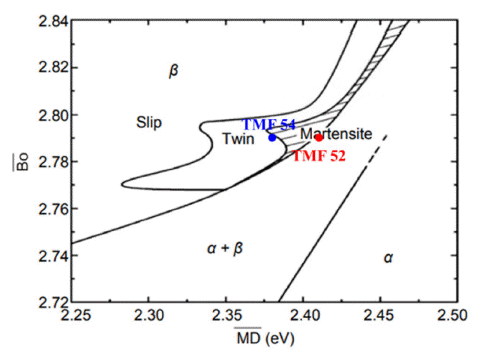
- HyoWoon Hwang, YongJae Lee, JiHwan Park, Dong-Geun Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):325-331. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.325
- 1,189 View
- 6 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Beta-titanium alloys are used in many industries due to their increased elongation resulting from their BCC structure and low modulus of elasticity. However, there are many limitations to their use due to the high cost of betastabilizer elements. In this study, biocompatible Ti-Mo-Fe beta titanium alloys are designed by replacing costly betastabilizer elements (e.g., Nb, Zr, or Ta) with inexpensive Mo and Fe elements. Additionally, Ti-Mo-Fe alloys designed with different Fe contents are fabricated using powder metallurgy. Fe is a strong, biocompatible beta-stabilizer element and a low-cost alloying element. The mechanical properties of the Ti-Mo-Fe metastable beta titanium alloys are analyzed in relation to the microstructural changes. When the Fe content increases, the tensile strength and elongation decrease due to brittle fracture despite a decreasing pore fraction. It is confirmed that the hardness and tensile strength of Ti-5Mo-2Fe P/M improve to more than 360 Hv and 900 MPa, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 288. CrossRef - Fabrication of Ti-Mo Core-shell Powder and Sintering Properties for Application as a Sputtering Target
Won Hee Lee, Chun Woong Park, Heeyeon Kim, Yuncheol Ha, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 43. CrossRef - Effect of Strain Rate on Deformation Behaviors of Ti-12.1Mo -1Fe Metastable Beta Alloy
In Kyeong Jin, Dong-Geun Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(10): 741. CrossRef
- Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
- [Korean]
- Extractive Metallurgy and Recycling of Cobalt
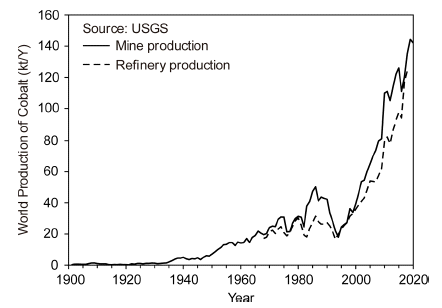
- Ho-Sang Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):252-261. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.252
- 1,221 View
- 16 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Cobalt is a vital metal in the modern society because of its applications in lithium-ion batteries, super alloys, hard metals, and catalysts. Further, cobalt is a representative rare metal and is the 30th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust. This study reviews the current status of cobalt extraction and recycling processes, along with the trends in its production amount and use. Although cobalt occurs in a wide range of minerals, such as oxides and sulfides of copper and nickel ores, the amounts of cobalt in the minerals are too low to be extracted economically. The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) leads cobalt mining, and accounts for 68.9 % of the global cobalt reserves (142,000 tons in 2020). Cobalt is mainly extracted from copper–cobalt and nickel–cobalt concentrates and is occasionally extracted directly from the ore itself by hydro-, pyro-, and electro-metallurgical processes. These smelting methods are essential for developing new recycling processes to extract cobalt from secondary resources. Cobalt is mainly recycled from lithium-ion batteries, spent catalysts, and cobalt alloys. The recycling methods for cobalt also depend on the type of secondary cobalt resource. Major recycling methods from secondary resources are applied in pyro- and hydrometallurgical processes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reduction Behavior of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries by CO Gas
Sang-Yeop Lee, Jae-Ho Hwang, So-Yeong Lee, Ho-Sang Sohn
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2025; 63(10): 820. CrossRef - Recovering cobalt from cobalt oxide ore using suspension roasting and magnetic separation technique
Xinlei Wei, Yongsheng Sun, Yanjun Li, Peng Gao
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2023; 27: 3005. CrossRef
- Reduction Behavior of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries by CO Gas
- [Korean]
- Interfacial Reaction between Spark Plasma Sintered High-entropy Alloys and Cast Aluminum
- Min-Sang Kim, Hansol Son, Cha Hee Jung, Juyeon Han, Jung Joon Kim, Young-Do Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Se Hoon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):213-218. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.213

- 889 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the interfacial reaction between powder-metallurgy high-entropy alloys (HEAs) and cast aluminum. HEA pellets are produced by the spark plasma sintering of Al0.5CoCrCu0.5FeNi HEA powder. These sintered pellets are then placed in molten Al, and the phases formed at the interface between the HEA pellets and cast Al are analyzed. First, Kirkendall voids are observed due to the difference in the diffusion rates between the liquid Al and solid HEA phases. In addition, although Co, Fe, and Ni atoms, which have low mixing enthalpies with Al, diffuse toward Al, Cu atoms, which have a high mixing enthalpy with Al, tend to form Al–Cu intermetallic compounds. These results provide guidelines for designing Al matrix composites containing high-entropy phases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Simultaneous enhancement of strength and ductility of Al matrix composites enabled by submicron-sized high-entropy alloy phases
Chahee Jung, Seungin Nam, Hansol Son, Juyeon Han, Jaewon Jeong, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Seok Su Sohn, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2024; 33: 1470. CrossRef
- Simultaneous enhancement of strength and ductility of Al matrix composites enabled by submicron-sized high-entropy alloy phases
- [Korean]
- Characterization and Classification of Pores in Metal 3D Printing Materials with X-ray Tomography and Machine Learning
- Eun-Ah Kim, Se-Hun Kwon, Dong-Yeol Yang, Ji-Hun Yu, Kwon-Ill Kim, Hak-Sung Lee
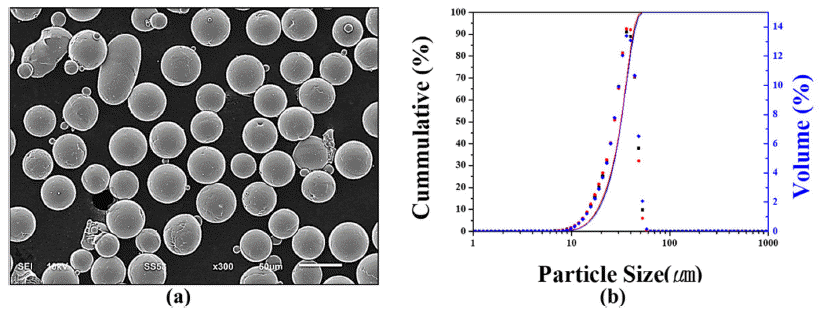
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):208-215. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.208
- 934 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal three-dimensional (3D) printing is an important emerging processing method in powder metallurgy. There are many successful applications of additive manufacturing. However, processing parameters such as laser power and scan speed must be manually optimized despite the development of artificial intelligence. Automatic calibration using information in an additive manufacturing database is desirable. In this study, 15 commercial pure titanium samples are processed under different conditions, and the 3D pore structures are characterized by X-ray tomography. These samples are easily classified into three categories, unmelted, well melted, or overmelted, depending on the laser energy density. Using more than 10,000 projected images for each category, convolutional neural networks are applied, and almost perfect classification of these samples is obtained. This result demonstrates that machine learning methods based on X-ray tomography can be helpful to automatically identify more suitable processing parameters.
- [English]
- Effect of Oxidation Behavior of (Nd,Dy)-Fe-B Magnet on Heavy Rare Earth Extraction Process
- Sangmin Park, Sun-Woo Nam, Sang-Hoon Lee, Myung-Suk Song, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):91-96. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.91

- 1,790 View
- 21 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare earth magnets with excellent magnetic properties are indispensable in the electric device, wind turbine, and e-mobility industries. The demand for the development of eco-friendly recycling techniques has increased to realize sustainable green technology, and the supply of rare earth resources, which are critical for the production of permanent magnets, are limited. Liquid metal extraction (LME), which is a type of pyrometallurgical recycling, is known to selectively extract the metal forms of rare earth elements. Although several studies have been carried out on the formation of intermetallic compounds and oxides, the effect of oxide formation on the extraction efficiency in the LME process remains unknown. In this study, microstructural and phase analyses are conducted to confirm the oxidation behavior of magnets pulverized by a jaw crusher. The LME process is performed with pulverized scrap, and extraction percentages are calculated to confirm the effect of the oxide phases on the extraction of Dy during the reaction. During the LME p rocess, Nd i s completely e xtracted a fter 6 h, w hile D y remains as D y2Fe17 and Dy-oxide. Because the decomposition rate of Dy2Fe17 is faster than the reduction rate of Dy-oxide, the importance of controlling Dy-oxide on Dy extraction is confirmed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Manipulation of reactivity based on metallic adsorption in magnesium alloy scraps for rare-earth recycling by liquid metal extraction
Sangmin Park, Yoonhyung Keum, Jaeyun Jeong, Seunghun Cha, Ju-Young Cho, Hyunchul Kim, Jiseong Lee, Taek-Soo Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1022: 178711. CrossRef - A Review of the Current Progress in High-Temperature Recycling Strategies for Recovery of Rare-Earth Elements from Magnet Waste
Ali Zakeri, Leili Tafaghodi
Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy.2025; 11(1): 88. CrossRef - Selective growth of Nb–Fe–B intermetallic compounds for the direct separation of rare earths based on manipulating liquation
Sangmin Park, Jaeyun Jeong, Seunghun Cha, Yoonhyung Keum, Ju-Young Cho, Hyungbeen Park, Taek-Soo Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song
Materials Today Sustainability.2024; 28: 101042. CrossRef - Separation and recovery Nd and Dy from Mg-REEs alloy by vacuum distillation
Sangmin Park, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Jaeyun Jeong, Jae Hong Shin, Yujin Kang, Rongyu Liu, Taek-Soo Kim, Myungsuk Song
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2023; 967: 171775. CrossRef - The Supported Boro-Additive Effect for the Selective Recovery of Dy Elements from Rare-Earth-Elements-Based Magnets
Sangmin Park, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Javid Hussain, Myungsuk Song, Taek-Soo Kim
Materials.2022; 15(9): 3032. CrossRef - Influence of Dysprosium Compounds on the Extraction Behavior of Dy from Nd-Dy-Fe-B Magnet Using Liquid Magnesium
Sun-Woo Nam, Sang-Min Park, Mohammad Zarar Rasheed, Myung-Suk Song, Do-Hyang Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
Metals.2021; 11(9): 1345. CrossRef
- Manipulation of reactivity based on metallic adsorption in magnesium alloy scraps for rare-earth recycling by liquid metal extraction
- [Korean]
- Current Status of Titanium Smelting Technology for Powder Metallurgy
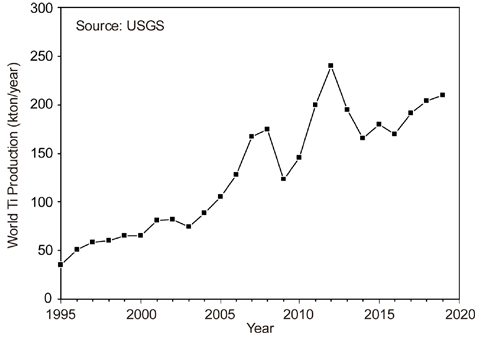
- Ho-Sang Sohn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):164-172. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.164
- 823 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Titanium is the ninth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust and is the fourth most abundant structural metal after aluminum, iron, and magnesium. It exhibits a higher specific strength than steel along with an excellent corrosion resistance, highlighting the promising potential of titanium as a structural metal. However, titanium is difficult to extract from its ore and is classified as a rare metal, despite its abundance. Therefore, the production of titanium is exceedingly low compared to that of common metals. Titanium is conventionally produced as a sponge by the Kroll process. For powder metallurgy (PM), hydrogenation-dehydrogenation (HDH) of the titanium sponge or gas atomization of the titanium bulk is required. Therefore, numerous studies have been conducted on smelting, which replaces the Kroll process and produces powder that can be used directly for PM. In this review, the Kroll process and new smelting technologies of titanium for PM, such as metallothermic, electrolytic, and hydrogen reduction of TiCl4 and TiO2 are discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing corrosion resistance of Ti-based amorphous alloy powders via misch metal addition
Yeon Joo Lee, Hyokyung Sung, Jae Bok Seol, Kisub Cho, Hwi Jun Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(3): 230. CrossRef
- Enhancing corrosion resistance of Ti-based amorphous alloy powders via misch metal addition
- [Korean]
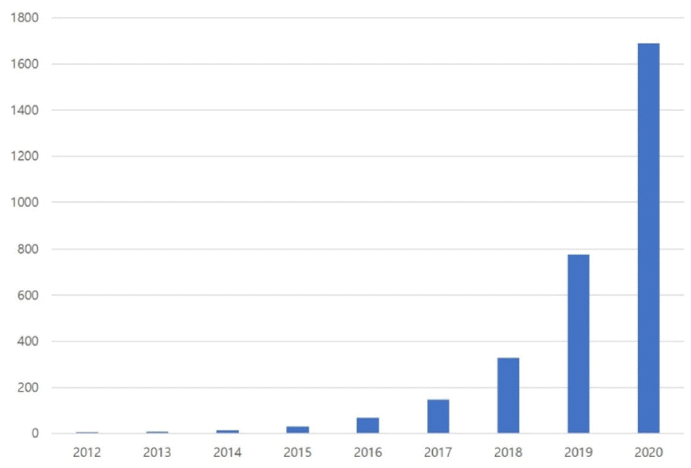
- Research trends of MXenes as the Next-generation Two-dimensional Materials
- Hojun Lee, Yejun Yun, Jinkwang Jang, Jongmin Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):150-163. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.150
- 3,521 View
- 106 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Interest in eco-friendly materials with high efficiencies is increasing significantly as science and technology undergo a paradigm shift toward environment-friendly and sustainable development. MXenes, a class of two-dimensional inorganic compounds, are generally defined as transition metal carbides or nitrides composed of few-atoms-thick layers with functional groups. Recently MXenes, because of their desirable electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties that emerge from conductive layered structures with tunable surface terminations, have garnered significant attention as promising candidates for energy storage applications (e.g., supercapacitors and electrode materials for Li-ion batteries), water purification, and gas sensors. In this review, we introduce MXenes and describe their properties and research trends by classifying them into two main categories: transition metal carbides and nitrides, including Ti-based MXenes, Mo-based MXenes, and Nb-based MXenes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Next-generation brackish water treatment: Exploring dual-ion capacitive deionization
Yize Li, Jing He, He Liu, Chao Yan
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2025; 13(2): 116037. CrossRef - Microstructure tailoring of Nb-based MAX phase by low temperature synthesis with layer-structured Nb2C powder and molten salt method
Chaehyun Lim, Wonjune Choi, Jongmin Byun
Materials Characterization.2025; 225: 115106. CrossRef - Review on 2D MXene and graphene electrodes in capacitive deionization
Hammad Younes, Ding Lou, Md. Mahfuzur Rahman, Daniel Choi, Haiping Hong, Linda Zou
Environmental Technology & Innovation.2022; 28: 102858. CrossRef
- Next-generation brackish water treatment: Exploring dual-ion capacitive deionization
- [Korean]
- Analysis of Wafer Cleaning Solution Characteristics and Metal Dissolution Behavior according to the Addition of Chelating Agent
- Myungsuk Kim, Keunhyuk Ryu, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):25-30. Published online February 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.25

- 1,016 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The surface of silicon dummy wafers is contaminated with metallic impurities owing to the reaction with and adhesion of chemicals during the oxidation process. These metallic impurities negatively affect the device performance, reliability, and yield. To solve this problem, a wafer-cleaning process that removes metallic impurities is essential. RCA (Radio Corporation of America) cleaning is commonly used, but there are problems such as increased surface roughness and formation of metal hydroxides. Herein, we attempt to use a chelating agent (EDTA) to reduce the surface roughness, improve the stability of cleaning solutions, and prevent the re-adsorption of impurities. The bonding between the cleaning solution and metal powder is analyzed by referring to the Pourbaix diagram. The changes in the ionic conductivity, H2O2 decomposition behavior, and degree of dissolution are checked with a conductivity meter, and the changes in the absorbance and particle size before and after the reaction are confirmed by ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) analyses. Thus, the addition of a chelating agent prevents the decomposition of H2O2 and improves the life of the silicon wafer cleaning solution, allowing it to react smoothly with metallic impurities.
- [Korean]
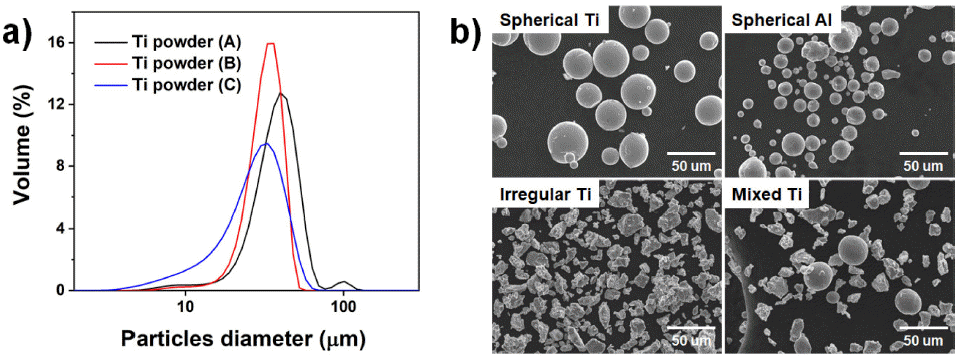
- Review on Characterization Method and Recent Research Trend about Metal Powder for Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) Process
- Bin Lee, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Young Il Kim, Do Hoon Kim, Yong Son, Kyoung-Tae Park, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):509-519. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.509
- 1,527 View
- 15 Download
- 9 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A well-established characterization method is required in powder bed fusion (PBF) metal additive manufacturing, where metal powder is used. The characterization methods from the traditional powder metallurgy process are still being used. However, it is necessary to develop advanced methods of property evaluation with the advances in additive manufacturing technology. In this article, the characterization methods of powders for metal PBF are reviewed, and the recent research trends are introduced. Standardization status and specifications for metal powder for the PBF process which published by the ISO, ASTM, and MPIF are also covered. The establishment of powder characterization methods are expected to contribute to the metal powder industry and the advancement of additive manufacturing technology through the creation of related databases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent advances in manufacture and application of Mg/Mg alloy powder: A comprehensive review
Yu Cao, Xiaohui Dong, Yulong Zhu, Tao Huang, Bin Jiang, Chenghang Zhang
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2026; 263: 140. CrossRef -
Enhanced flow properties of SiO
2
nanoparticles coated low-cost hydrogenation-dehydrogenation Ti-6Al-4V powder for powder bed fusion process
Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Tae hu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(2): 95. CrossRef -
SiO
2
nanoparticle-coated Ti-6Al-4V spherical powder for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process
Jongik Lee, Taehoo Kang, Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Sanghee Jung, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 333. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 288. CrossRef - A Study on Fabrication of PCD Endmill Holder using PBF Additive Manufacturing Technology
Min-Woo Sa, Ho-Min Son, Kyung-Hwan Park, Sang-Geun Lee, Dae-Ho Shin, Dong-Gyu Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2024; 23(6): 124. CrossRef - Rheological Characteristic Analysis Methods and Tests of Metal Powders for PBF Additive Manufacturing
Wan-Sik Woo, Ho-Jin Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2023; 22(10): 1. CrossRef - Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
SangCheol Park, InYeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee, Bin Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(7): 534. CrossRef - Enhancing spreadability of hydrogenation-dehydrogenation titanium powder and novel method to characterize powder spreadability for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing
Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, InYeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Dongju Lee, Bin Lee
Materials & Design.2022; 223: 111247. CrossRef
- Recent advances in manufacture and application of Mg/Mg alloy powder: A comprehensive review
- [Korean]
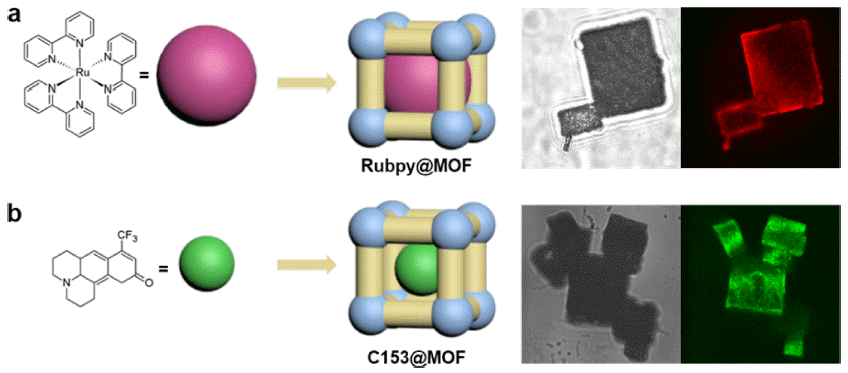
- Photophysical Properties of Guest Molecules Confined in Nanopores
- Suhyeon Park, Juyeong Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):477-483. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.477
- 560 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are of significant interest because of their high porosity, which facilitates their utilization in gas storage and catalysis. To enhance their current properties in these applications, it is necessary to elucidate the interactions between molecules in a confined environment that differ from those in bulk conditions. Herein, we study the confined molecular interaction by investigating the solvent-dependent photophysical properties of two different-sized molecules inside MOF-5. Ruthenium
tris -bipyridine (Rubpy) and coumarin 153 (C153) are encapsulated in MOF-5. Rubpy with MOF-5 (Rubpy@MOF) is prepared by building MOF-5 around it, resulting in limited space for solvent molecules in the pores. The smaller C153 is encapsulated in the preformed MOF-5 (C153@MOF) by simply soaking the MOF in a concentrated C153 solution. C153@MOF permits more space for solvent molecules in the pore. Their characteristic absorption and emission spectra are examined to elucidate the confined molecular interactions. Rubpy@MOF and C153@MOF exhibit different spectral shifts compared to the guest molecules under bulk conditions. This discrepancy is attributed to the different micro-environments inside the pores, derived from confined host-guest interactions in the interplay of solvent molecules.
- [English]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Immiscible Fe-Cu Alloys using Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid
- Chu Dac Phuc, Nguyen Minh Thuyet, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):449-457. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.449

- 1,587 View
- 12 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Iron and copper are practically immiscible in the equilibrium state, even though their atomic radii are similar. As non-equilibrium solid solutions, the metastable Fe-Cu alloys can be synthesized using special methods, such as rapid quenching, vapor deposition, sputtering, ion-beam mixing, and mechanical alloying. The complexity of these methods (multiple steps, low productivity, high cost, and non-eco-friendliness) is a hinderance for their industrial applications. Electrical explosion of wire (EEW) is a well-known and effective method for the synthesis of metallic and alloy nanoparticles, and fabrication using the EEW is a simple and economic process. Therefore, it can be potentially employed to circumvent this problem. In this work, we propose the synthesis of Fe-Cu nanoparticles using EEW in a suitable solution. The powder shape, size distribution, and alloying state are analyzed and discussed according to the conditions of the EEW.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Scaling up plasma-derived metallic nanoalloys: A comprehensive review of production bottlenecks, manufacturing readiness, and AI-driven pathways to viability
Hugues Nkomba Museba, BongJu Lee
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2026; 1054: 185926. CrossRef - Identification of the reconstruction induced high-entropy spinel oxide nanosheets for boosting alkaline water oxygen evolution
Xuexue Wang, Runqing Lu, Shanhe Gong, Shaokang Yang, Wenbo Wang, Zhongti Sun, Xiaozhen Zhang, Jun Liu, Xiaomeng Lv
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 503: 158488. CrossRef - Trends in bimetallic nanomaterials and methods for the removal of p-nitrophenol and its derivatives from wastewater
M. S. Qatan, F. Arshad, M. Miskam, G. A. Naikoo
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology.2024; 21(5): 5247. CrossRef - Control of cluster coalescence during formation of bimetallic nanoparticles and nanoalloys obtained via electric explosion of two wires
K.V. Suliz, A.Yu. Kolosov, V.S. Myasnichenko, N.I. Nepsha, N.Yu. Sdobnyakov, A.V. Pervikov
Advanced Powder Technology.2022; 33(3): 103518. CrossRef
- Scaling up plasma-derived metallic nanoalloys: A comprehensive review of production bottlenecks, manufacturing readiness, and AI-driven pathways to viability
- [Korean]
- Development of Fe-Mn-based Hybrid Materials Containing Nano-scale Oxides by a Powder Metallurgical Route
- Jonggyu Jeon, Jungjoon Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):203-209. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.203

- 893 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The automotive industry has focused on the development of metallic materials with high specific strength, which can meet both fuel economy and safety goals. Here, a new class of ultrafine-grained high-Mn steels containing nano-scale oxides is developed using powder metallurgy. First, high-energy mechanical milling is performed to dissolve alloying elements in Fe and reduce the grain size to the nanometer regime. Second, the ball-milled powder is consolidated using spark plasma sintering. During spark plasma sintering, nanoscale manganese oxides are generated in Fe-15Mn steels, while other nanoscale oxides (e.g., aluminum, silicon, titanium) are produced in Fe-15Mn-3Al-3Si and Fe-15Mn-3Ti steels. Finally, the phases and resulting hardness of a variety of high-Mn steels are compared. As a result, the sintered pallets exhibit superior hardness when elements with higher oxygen affinity are added; these elements attract oxygen from Mn and form nanoscale oxides that can greatly improve the strength of high-Mn steels.
- [Korean]
- Recent Trends and Application Status of the Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs)
- Hyo-Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):164-173. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.164
- 1,409 View
- 38 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal matrix composites (MMCs), which are a combination of two or more constituents with different physical or chemical properties, are today receiving great attention in various areas, as they have high specific strength, corrosion resistance, fatigue strength, and good tribological properties. This paper presents a research review on the combination of matrix and reinforced materials, fabrication processes, and application status of metal matrix composites. In this paper, we aim to discuss and review the importance of metal composite materials as advanced materials that can be used in various applications such as transportation, defense, sports, and extreme environments. In addition, the applicability and technology development trends in new process technology fields such as additive manufacturing of metal composites will be described.
- [Korean]
- Photoluminescence Enhancement of Y2O3:Eu3+ Red Phosphor Prepared by Spray Pyrolysis using Aliovalent Cation Substitution and Organic Additives
- Byeong Ho Min, Kyeong Youl Jung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):146-153. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.146
- 704 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The co-doping effect of aliovalent metal ions such as Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, and Zn2+ on the photoluminescence of the Y2O3:Eu3+ red phosphor, prepared by spray pyrolysis, is analyzed. Mg2+ metal doping is found to be helpful for enhancing the luminescence of Y2O3:Eu3+. When comparing the luminescence intensity at the optimum doping level of each Mg2+ ion, the emission enhancement shows the order of Zn2+ ≈ Ba2+ > Ca2+ > Sr3+> Mg2+. The highest emission occurs when doping approximately 1.3% Zn2+, which is approximately 127% of the luminescence intensity of pure Y2O3:Eu3+. The highest emission was about 127% of the luminescence intensity of pure Y2O3:Eu3+ when doping about 1.3% Zn2+. It is determined that the reason (Y, M)2O3:Eu3+ has improved luminescence compared to that of Y2O3:Eu3+ is because the crystallinity of the matrix is improved and the non-luminous defects are reduced, even though local lattice strain is formed by the doping of aliovalent metal. Further improvement of the luminescence is achieved while reducing the particle size by using Li2CO3 as a flux with organic additives.
- [Korean]
- Recent Research Progress on the Atomic Layer Deposition of Noble Metal Catalysts for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell
- Jeong Hwan Han
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):63-71. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.63
- 618 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF It is necessary to fabricate uniformly dispersed nanoscale catalyst materials with high activity and long-term stability for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells with excellent electrochemical characteristics of the oxygen reduction reaction and hydrogen oxidation reaction. Platinum is known as the best noble metal catalyst for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells because of its excellent catalytic activity. However, given that Pt is expensive, considerable efforts have been made to reduce the amount of Pt loading for both anode and cathode catalysts. Meanwhile, the atomic layer deposition (ALD) method shows excellent uniformity and precise particle size controllability over the three-dimensional structure. The research progress on noble metal ALD, such as Pt, Ru, Pd, and various metal alloys, is presented in this review. ALD technology enables the development of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells with excellent reactivity and durability.
- [Korean]
- Structural Characteristics, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-Cr-Al Metallic Foam Fabricated by Powder Alloying Process
- Kyu-Sik Kim, Byeong-Hoon Kang, Man-Ho Park, Jung-Yeul Yun, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):37-43. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.37
- 651 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The Fe-22wt.%Cr-6wt.%Al foams were fabricated via the powder alloying process in this study. The structural characteristics, microstructure, and mechanical properties of Fe-Cr-Al foams with different average pore sizes were investigated. Result of the structural analysis shows that the average pore sizes were measured as 474 μm (450 foam) and 1220 μm (1200 foam). Regardless of the pore size, Fe-Cr-Al foams had a Weaire-Phelan bubble structure, and α-ferrite was the major constituent phase. Tensile and compressive tests were conducted with an initial strain rate of 10−3 /s. Tensile yield strengths were 3.4 MPa (450 foam) and 1.4 MPa (1200 foam). Note that the total elongation of 1200 foam was higher than that of 450 foam. Furthermore, their compressive yield strengths were 2.5 MPa (450 foam) and 1.1 MPa (1200 foam), respectively. Different compressive deformation behaviors according to the pore sizes of the Fe-Cr-Al foams were characterized: strain hardening for the 450 foam and constant flow stress after a slight stress drop for the 1200 foam. The effect of structural characteristics on the mechanical properties was also discussed.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Phosphorus Addition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Low Alloy Steel
- Yoo-Young Kim, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):31-36. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.31

- 808 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Phosphorus is an element that plays many important roles in powder metallurgy as an alloy element. The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence of phosphorus addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of sintered low-alloy steel. The sintered low-alloy steels Fe-0.6%C-3.89%Ni-1.95%Cu-1.40%Mo-xP (x=0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20%) were manufactured by compacting at 700 MPa, sintering in H2-N2 at 1260 °C, rapid cooling, and low-temperature tempering in Ar at 160 °C. The microstructure, pore, density, hardness, and transverse rupture strength (TRS) of the sintered low-alloy steels were evaluated. The hardness increased as the phosphorus content increased, whereas the density and TRS showed maximum values when the content of P was 0.05%. Based on microstructure observation, the phase of the microstructure changed from bainite to martensite as the content of phosphorus is increased. Hence, the most appropriate addition of phosphorus in this study was 0.05%.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A new strategy for metal additive manufacturing using an economical water-atomized iron powder for laser powder bed fusion
Taehyeob Im, Kopila Gurung, Sebastian Meyers, Antonio Cutolo, Huengseok Oh, Jai-Sung Lee, Brecht Van Hooreweder, Caroline Sunyong Lee
Journal of Materials Processing Technology.2022; 308: 117705. CrossRef
- A new strategy for metal additive manufacturing using an economical water-atomized iron powder for laser powder bed fusion
- [Korean]
- Russian Mineral Market Flow and Economic Direction for Securing Stable Resources
- Nu Si A Eom, Su Noh, Muhammad Aneeq Haq, Bin Lee, Kyoung Mook Lim, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):345-349. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.345
- 857 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF With increasing demand for resources worldwide, Korea has been negotiating with resource-holding countries to achieve conservation of energy resources. Among them, Russia is the third largest resource-producing and exporting nation in the world and has several resource materials such as nickel, platinum group metals, gold, and other reserves. As a result, there is growing interest in cooperation between Korea and Russia. The aim of this article is to summarize the current status of market flow of Russian energy resources as well as Russia’s economic cooperation with Korea. Notably, South Korea needs to focus on investing in overseas mines for a stable supply of rare metals. Nevertheless, securing rare metals is a major task by understanding the flow and policy direction of Russian material mines.
- [Korean]
- Study on the Optimization of Reduction Conditions for Samarium-Cobalt Nanofiber Preparation
- Jimin Lee, Jongryoul Kim, Yong-Ho Choa
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):334-339. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.334

- 558 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To meet the current demand in the fields of permanent magnets for achieving a high energy density, it is imperative to prepare nano-to-microscale rare-earth-based magnets with well-defined microstructures, controlled homogeneity, and magnetic characteristics via a bottom-up approach. Here, on the basis of a microstructural study and qualitative magnetic measurements, optimized reduction conditions for the preparation of nanostructured Sm-Co magnets are proposed, and the elucidation of the reduction-diffusion behavior in the binary phase system is clearly manifested. In addition, we have investigated the microstructural, crystallographic, and magnetic properties of the Sm-Co magnets prepared under different reduction conditions, that is, H2 gas, calcium, and calcium hydride. This work provides a potential approach to prepare high-quality Sm-Co-based nanofibers, and moreover, it can be extended to the experimental design of other magnetic alloys.
- [Korean]
- Study on the Optimization of Reduction Conditions for Samarium-Cobalt Nanofiber Preparation
- Jimin Lee, Jongryoul Kim, Yong-Ho Choa
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):334-339. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.334

- 513 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To meet the current demand in the fields of permanent magnets for achieving a high energy density, it is imperative to prepare nano-to-microscale rare-earth-based magnets with well-defined microstructures, controlled homogeneity, and magnetic characteristics via a bottom-up approach. Here, on the basis of a microstructural study and qualitative magnetic measurements, optimized reduction conditions for the preparation of nanostructured Sm-Co magnets are proposed, and the elucidation of the reduction-diffusion behavior in the binary phase system is clearly manifested. In addition, we have investigated the microstructural, crystallographic, and magnetic properties of the Sm-Co magnets prepared under different reduction conditions, that is, H2 gas, calcium, and calcium hydride. This work provides a potential approach to prepare high-quality Sm-Co-based nanofibers, and moreover, it can be extended to the experimental design of other magnetic alloys.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


