Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Enhanced H2S Gas Sensing Using ZnO Porous Nanorod Synthesized via a Rotational Hydrothermal Method
- Jimyeong Park, Changyu Kim, Minseo Kim, Jiyeon Shin, Jae-Hyoung Lee, Myung Sik Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):406-415. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00262
- 363 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
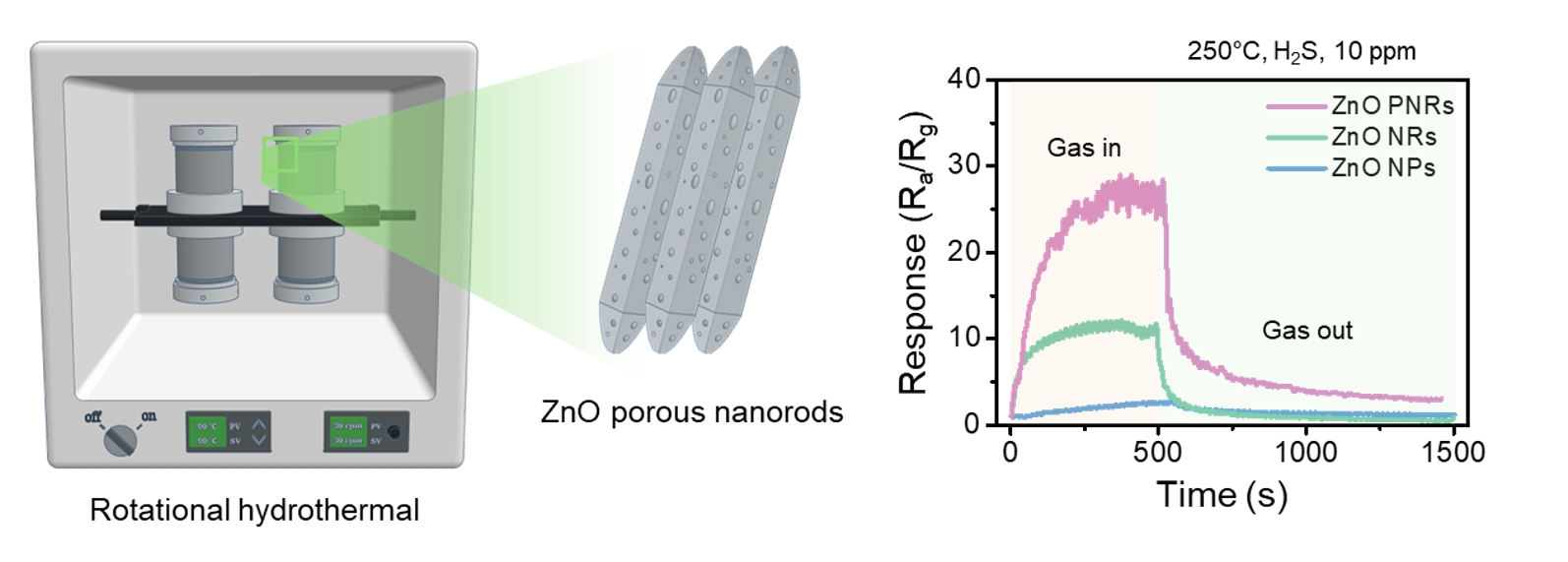
PDF - In this study, ZnO porous nanorods were synthesised using a rotational hydrothermal process, and their performance as hydrogen sulphide (H2S) gas sensors was analysed. Compared to commercial ZnO nanoparticles and conventionally hydrothermally synthesised ZnO nanorods, the ZnO porous nanorods exhibited a more uniform structure and improved crystal growth in the (002) plane, with surfaces rich in porosity and oxygen vacancies. These structural and chemical characteristics significantly improved the sensitivity toward H2S, showing high detection performance at 250°C across various concentrations of H2S gas. Additionally, the sensor demonstrated excellent selectivity against other gases such as C2H5OH, C6H6, C7H8, and NH3. This study indicated that the rotational hydrothermal process is an effective method for developing high-performance ZnO-based gas sensors and suggests its applicability to other metal oxide materials.
- [English]
- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
- Eunbi Park, Jongwon Bae, Sera Kang, Minsu Kang, Suseong Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):375-382. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00248
- 997 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
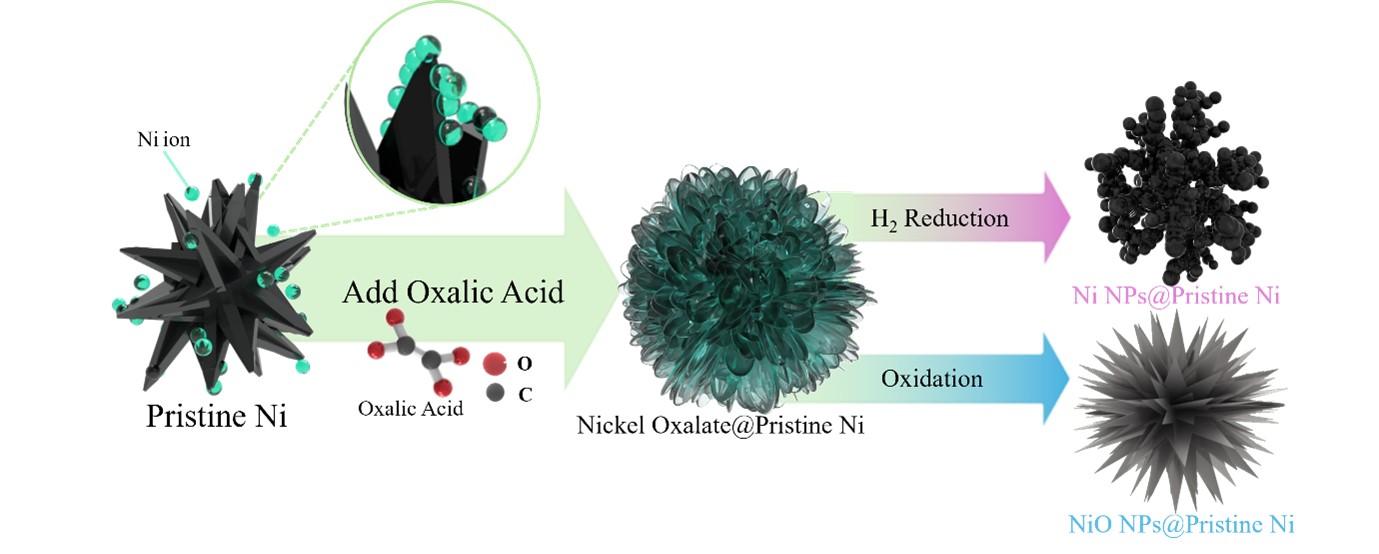
PDF - Nickel is widely used in industrial fields such as electrocatalysis and energy storage devices. Although micron-sized nickel particles exhibit excellent mechanical durability, their low specific surface area limits their reactivity. We modified the surface of micron-sized nickel particles with nanostructured nickel oxalate and investigated the effects of the solvent dielectric constant, surfactant, and thermal treatment atmosphere on the resulting particle morphology and phase transformation. Rietveld refinement analysis confirmed that changes in the solvent dielectric constant led to increased or diminished crystallinity of specific planes in nickel oxalate, resulting in diffraction patterns distinct from standard JCPDS data. These structural changes were also found to influence the morphology of the synthesized nickel oxalate. The results demonstrate that nickel oxalate serves as an effective precursor for producing Ni and NiO phases, and shape control of the final product can increase the surface reactivity of micron-sized nickel materials.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Morphology Control of Needle Type 513 MHSH and Mg(OH)2 from Dolomite
- Jiyeon Kim, HyunSeung Shim, Seong-Ju Hwang, YooJin Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):399-405. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00227
- 373 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
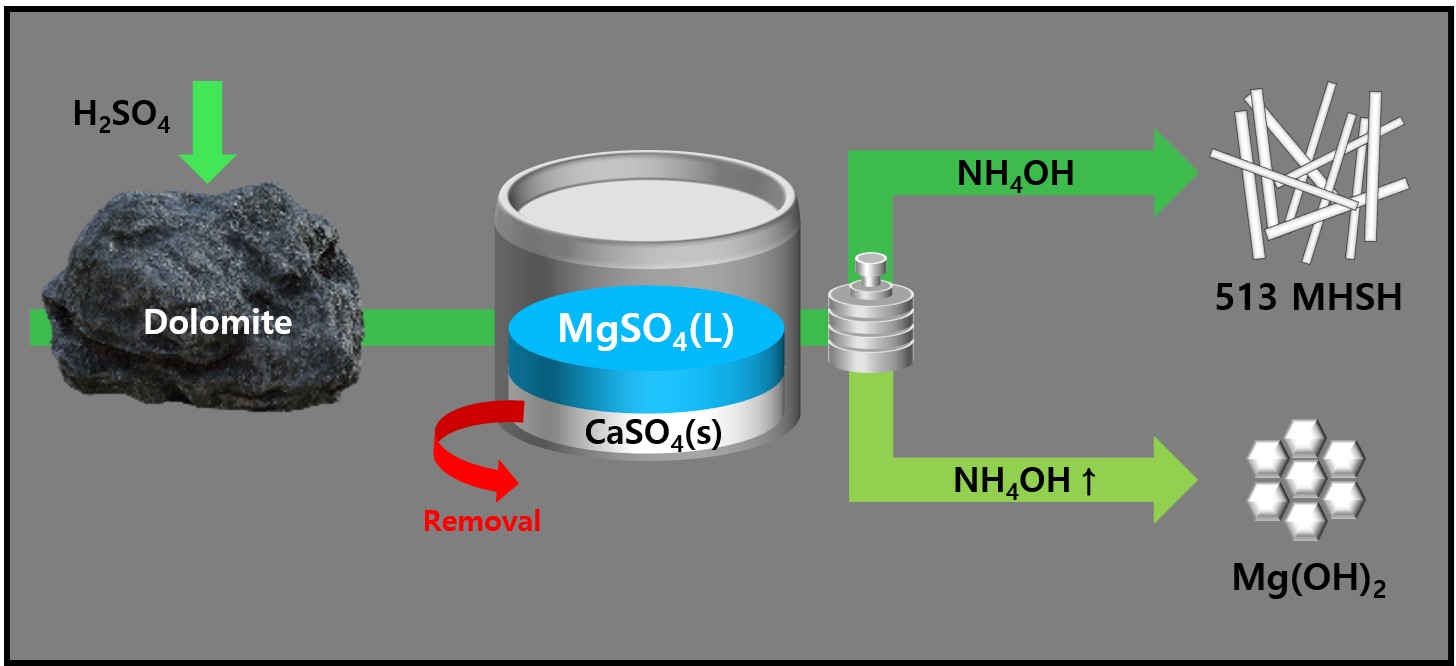
PDF - 513 magnesium hydroxide sulfate hydrate (MHSH) and Mg(OH)₂ were synthesized by controlling the pH and concentration using a domestic resource, dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2), as the raw material. The MgSO₄ was extracted by treating dolomite with sulfuric acid under various conditions. Hexagonal plate-shaped Mg(OH)₂ and needle-like 513 MHSH were synthesized under the hydrothermal condition. The morphology of the synthesized materials was controlled by adjusting the pH (SO42-/OH- ratio) and hydrothermal reaction time. As the pH of the solution increased, the formation of plate-like structures became dominant, whereas lower pH values (higher SO42- concentration) led to needle-like forms. The results of the 513 MHSH, which was synthesized using reagents and sea bittern, are consistent with the synthesis conditions, and we observed changes in the length and aspect ratio of the needle-shaped structure in response to adjusting the hydrothermal reaction time.
- [English]
- Comparative Study of Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogels and Films for Supercapacitor Electrodes
- Sunghee Choi, Seulgi Kim, Seojin Woo, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):23-29. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00472
- 1,627 View
- 32 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
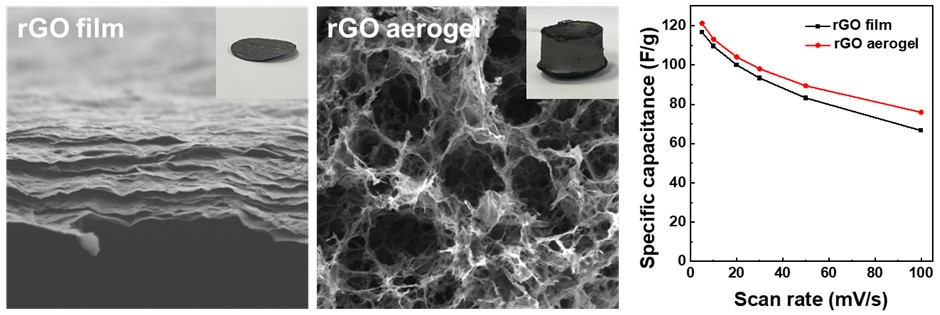
PDF - Supercapacitors, renowned for their high power density and rapid charge-discharge rates, are limited by their low energy density. This limitation has prompted the need for advanced electrode materials. The present study investigated reduced graphene oxide (rGO) in two distinct structures, as a film and as an aerogel, for use as supercapacitor electrodes. The rGO film, prepared by vacuum filtration and thermal reduction, exhibited a compact, lamellar structure, while the aerogel, synthesized through hydrothermal treatment, was a highly porous three-dimensional network. Electrochemical analyses demonstrated the aerogel’s superior performance, as shown by a specific capacitance of 121.2 F/g at 5 mV/s, with 94% capacitance retention after 10,000 cycles. These findings emphasize the importance of structural design in optimizing ion accessibility and charge transfer. They also demonstrate the potential of rGO aerogels for increasing the energy storage efficiency of advanced supercapacitor systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 492. CrossRef
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- [English]
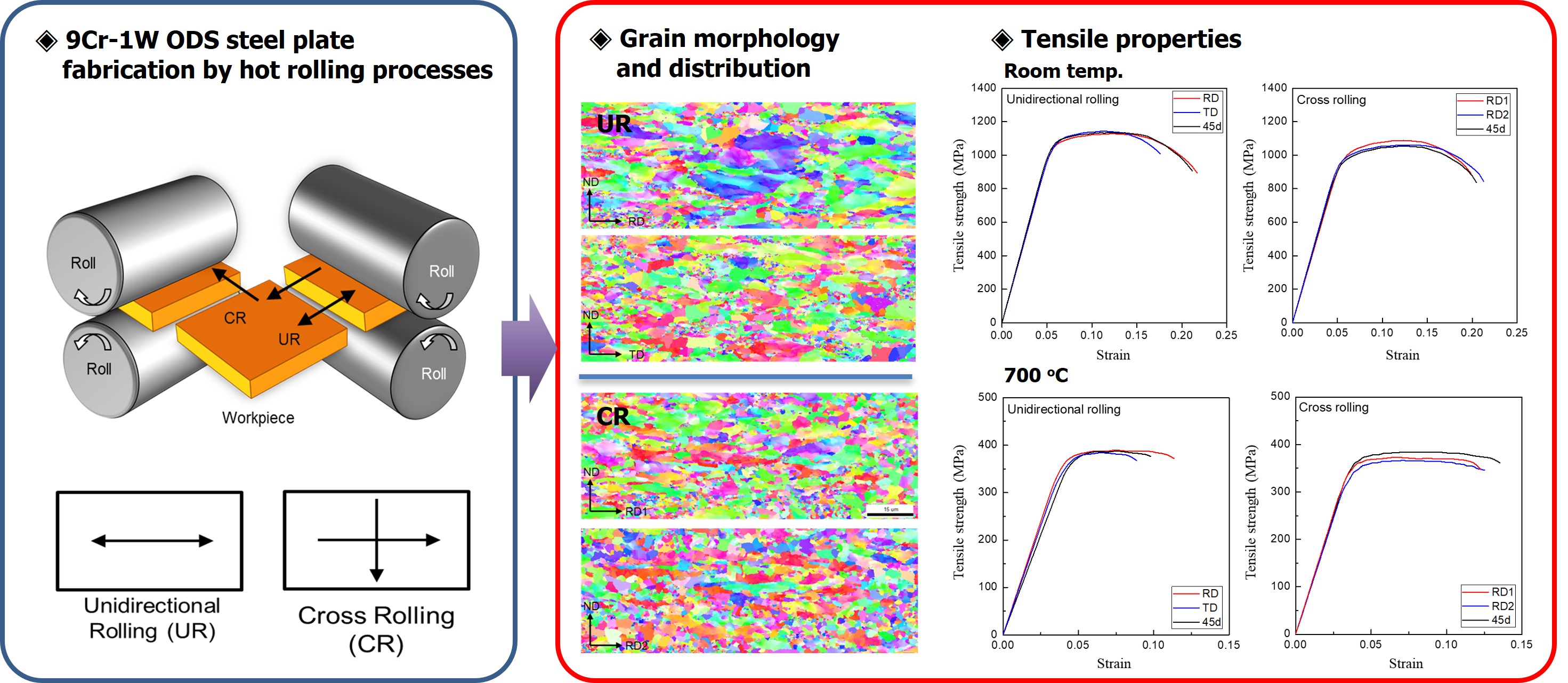
- Effect of the Cross-rolling Process on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of 9Cr-1W ODS Steel
- Bu-An Kim, Sanghoon Noh
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):37-42. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00332
- 951 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study employed a cross-rolling process to fabricate oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel plates and investigated their microstructures and mechanical properties. The 9Cr-1W ODS ferritic steel was fabricated using mechanical alloying and hot isostatic pressing. The hot cross-rolling process produced thick ODS ferritic steel plates with a well-extended rectangular shape. The working direction greatly affected the grain structure and crystal texture of the ODS ferritic steel. Cross-rolled plates showed fine micro-grains with random crystal orientation, while unidirectionally rolled plates exhibited a strong orientation with larger, elongated grains. Transmission electron microscopy revealed a uniform distribution of nano-oxide particles in both rolling methods, with no major differences. Tensile tests of the ODS ferritic steel plates showed that the unidirectional rolled plates had anisotropic elongation, while cross-rolled plates exhibited isotropic behavior with uniform elongation. Cross-rolling produced finer, more uniform grains, reducing anisotropy and improving mechanical properties, making it ideal for manufacturing wide ODS steel components.
- [Korean]
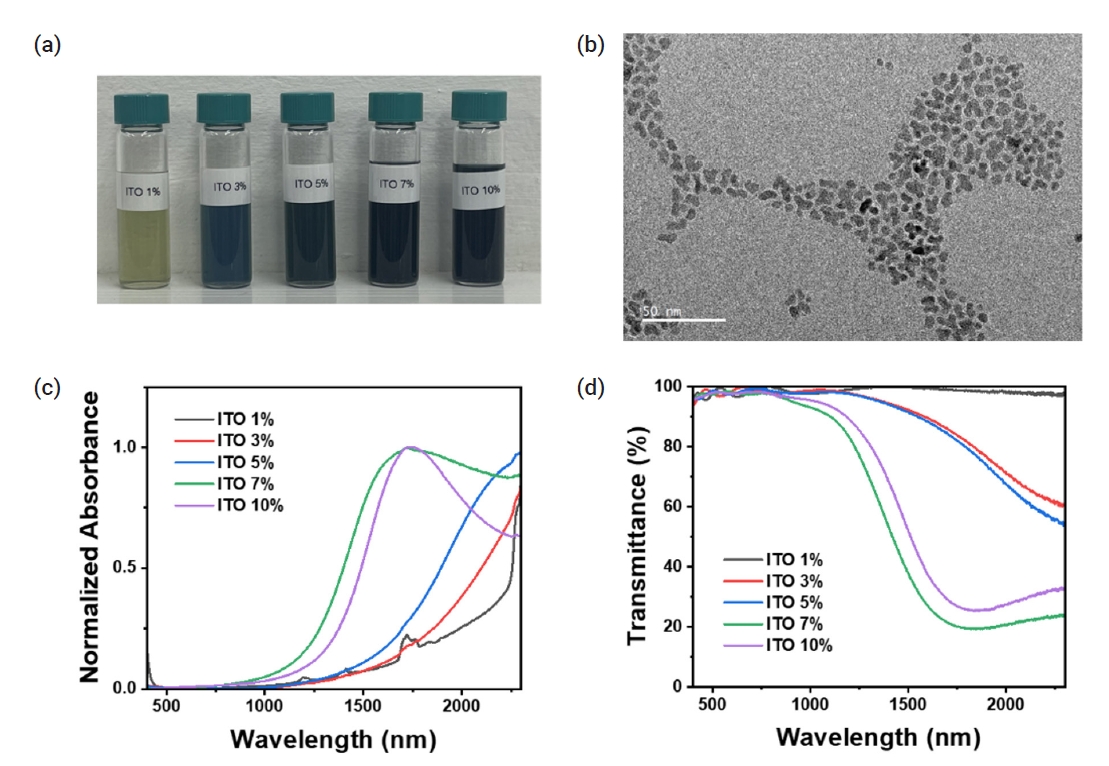
- Development of Highly Transparent and Thermo-Shielding Flexible Film via Colloidal ITO Nanocrystals
- Hyoin Bae, Hyeyeon Jung, Juna Lee, Dahye Shin, Sungyeon Heo
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):508-512. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00423
- 931 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Infrared radiation accounts for approximately 50% of the solar spectrum. Specifically, the near-infrared (NIR) spectrum, ranging from 760 nm to 2500 nm, is primarily responsible for solar heat gain, increasing indoor temperatures and reducing heating and cooling efficiency. To address this issue, we developed a highly transparent thermo-shielding flexible film that maintains a high transmittance of the visible region (T = 80%) while reducing the transmittance of the NIR region (T ≈ 0%). NIR-absorbing indium tin oxide (ITO) nanocrystals were coated onto polyethylene terephthalate (PET) films, and both films were sandwiched to improve the NIR absorption properties and protect the nanocrystal film layer. The fabricated films were applied to a model house and decreased the indoor temperature by approximately 8°C. Our study demonstrates that energy consumption can be reduced by ITO nanocrystal-coated flexible films, with potential implications for the smart window and mobility markets.
- [English]
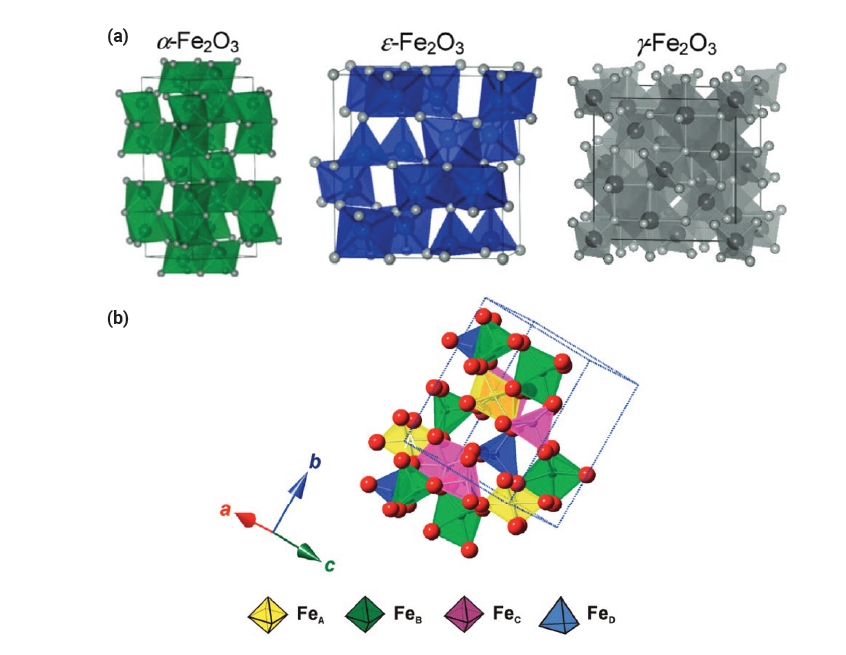
- Epsilon Iron Oxide (ε-Fe2O3) as an Electromagnetic Functional Material: Properties, Synthesis, and Applications
- Ji Hyeong Jeong, Hwan Hee Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):465-479. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00290
- 3,276 View
- 87 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Iron oxide (ε-Fe₂O₃) is emerging as a promising electromagnetic material due to its unique magnetic and electronic properties. This review focuses on the intrinsic properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, particularly its high coercivity, comparable to that of rare-earth magnets, which is attributed to its significant magnetic anisotropy. These properties render it highly suitable for applications in millimeter wave absorption and high-density magnetic storage media. Furthermore, its semiconducting behavior offers potential applications in photocatalytic hydrogen production. The review also explores various synthesis methods for fabricating ε-Fe₂O₃ as nanoparticles or thin films, emphasizing the optimization of purity and stability. By exploring and harnessing the properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, this study aims to contribute to the advancement of next-generation electromagnetic materials with potential applications in 6G wireless telecommunications, spintronics, high-density data storage, and energy technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
Babak Enami Alamdari, Yu Tang, Danilo Erricolo, Lesley H. Sneed
Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical Pressure Induced Strain Control of Magnetic Anisotropy in the Simple Perovskite ϵ-Fe2O3
Subir Roy, Gurleen K. Uppal, Alberto Acosta, Rachel Nickel, Charles A. Roberts, Johan van Lierop
Nano Letters.2026; 26(1): 34. CrossRef - Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling
Petr Kharitonskii, Andrei Krasilin, Nadezhda Belskaya, Svetlana Yanson, Nikita Bobrov, Andrey Ralin, Kamil Gareev, Nikita Zolotov, Dmitry Zaytsev, Elena Sergienko
Magnetochemistry.2025; 11(12): 103. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
- [English]
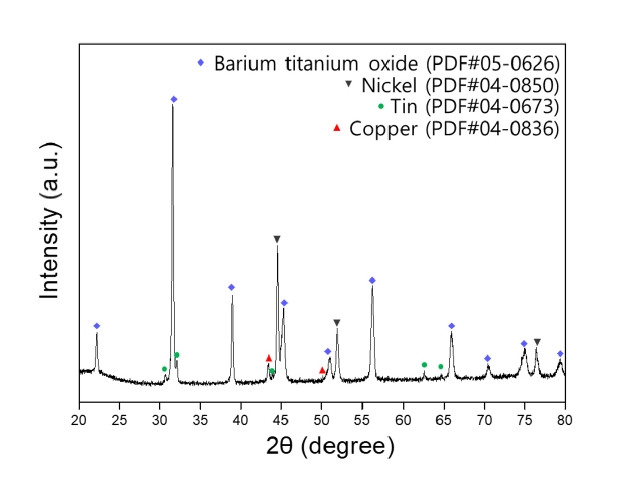
- Recovery of Barium, Nickel, and Titanium Powders from Waste MLCC
- Haein Shin, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):374-381. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00192
- 2,057 View
- 52 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of the electronics industry has led to an increased demand for the manufacture of MLCC (Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors), which in turn is expected to result in a rise in MLCC waste. The MLCC contains various metals, notably barium, titanium, and nickel, whose disposal is anticipated to increase correspondingly. Recently, recycling technologies for electronic waste have garnered attention as they address waste management and raw material supply challenges. This paper investigates the recovery of barium, nickel, and titanium from the MLCC by a hydrometallurgical process. Using citric acid, which is an organic acid, the metal inside the MLCC was leached. Additionally, metal materials were recovered through precipitation and complexing processes. As a result, barium and titanium were recovered from the leachate of the waste MLCC, and 93% of the nickel-based powder was recovered. Furthermore, the optimal recovery process conditions for recycling these metal elements were investigated.
- [Korean]
- Characterization of Compacted and Pressureless Sintered Parts for Molybdenum Oxide Powder according to Hydrogen Reduction Temperature
- Jong Hoon Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):336-341. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00241
- 1,165 View
- 16 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
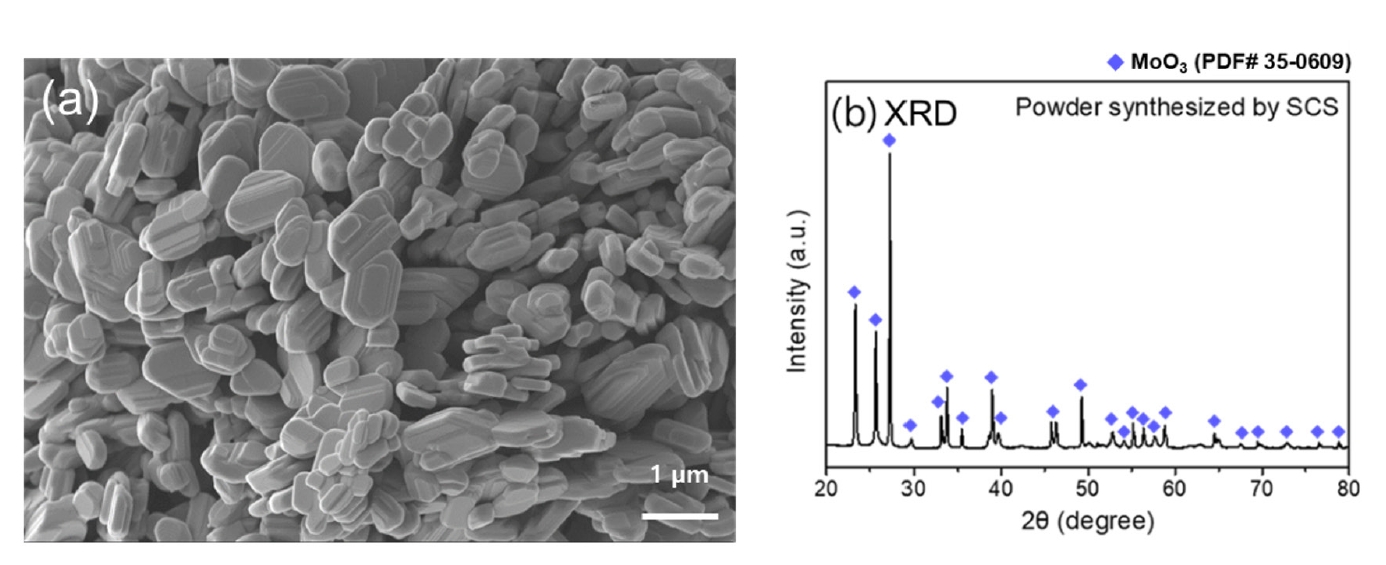
PDF - Molybdenum, valued for its high melting point and exceptional physical and chemical properties, is studied in diverse fields such as electronics, petrochemicals, and aviation. Among molybdenum oxides, molybdenum dioxide stands out for its higher electrical conductivity than other transition metal oxides due to its structural characteristics, exhibiting metallic properties. It is applied as pellets to gas sensors, semiconductors, and secondary batteries for its properties. Thus, research on molybdenum dioxide compaction and pressureless sintering is necessary, yet research on pressureless sintering is currently insufficient. This study synthesized MoO₃ powder via solution combustion synthesis and reduced it using the 3% hydrogen/argon gas mixture to investigate the effect of reduction temperature on the powder. Additionally, the reduced powder was compacted and subjected to pressureless sintering with temperature as a variable. The density and the microstructure of brown parts were analyzed and discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-sensitivity optical fiber hydrogen sensing with MoO3/PANI/Pd nanocomposite
Mohammed M. Alkhabet, Saad H. Girei, Ammar H. Farhan, Fatimah F. Hashim, Jaafar A. Jaafar, Husam K. Salih, Manar F. Abbood, Mohd H. Yaacob
Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing.2025; 200: 110021. CrossRef
- High-sensitivity optical fiber hydrogen sensing with MoO3/PANI/Pd nanocomposite
- [English]
- A Review of Inorganic Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries: Challenges and Progress
- Seul Ki Choi, Jaehun Han, Gi Jeong Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jaewon Choi, MinHo Yang
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):293-301. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00206
- 11,299 View
- 268 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
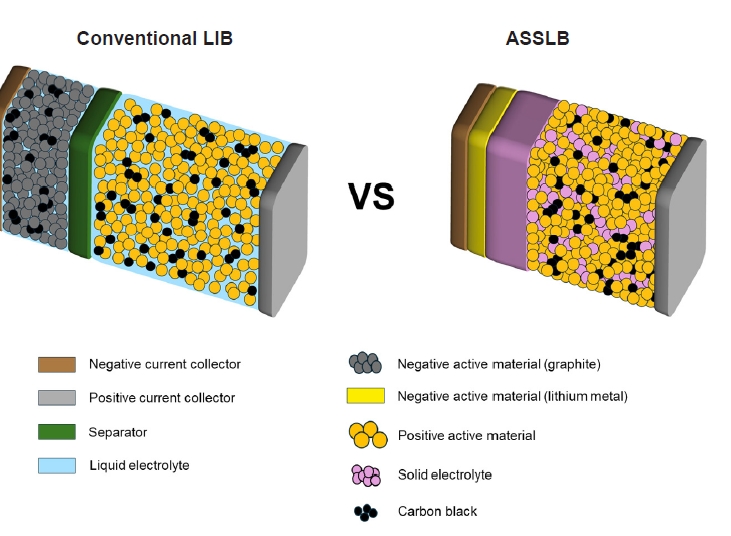
PDF - All-solid-state lithium batteries (ASSLBs) are receiving attention as a prospective next-generation secondary battery technology that can reduce the risk of commercial lithium-ion batteries by replacing flammable organic liquid electrolytes with non-flammable solid electrolytes. The practical application of ASSLBs requires developing robust solid electrolytes that possess ionic conductivity at room temperature on a par with that of organic liquids. These solid electrolytes must also be thermally and chemically stable, as well as compatible with electrode materials. Inorganic solid electrolytes, including oxide and sulfide-based compounds, are being studied as promising future candidates for ASSLBs due to their higher ionic conductivity and thermal stability than polymer electrolytes. Here, we present the challenges currently facing the development of oxide and sulfide-based solid electrolytes, as well as the research efforts underway aiming to resolve these challenges.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A facile synthesis of bulk LiPON in solution for solid-state electrolytes
Osma J. Gomez, Adam Antar, Alex T. Hall, Leopoldo Tapia-Aracayo, Joshua Seo, Nam Kim, Zihan Sun, Ryan Lim, Fu Chen, Yue Li, John Cumings, Gary Rubloff, Sang Bok Lee, David Stewart, Yang Wang
Journal of Materials Chemistry A.2025; 13(34): 28368. CrossRef - Uniform lithium deposition using Cu teepee structures for anode-free lithium metal batteries
Seo Yun Jung, Jaehun Han, Seul Ki Choi, Se Youn Cho, Jong Ho Won, Jaewon Choi, Minho Yang
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 522: 167302. CrossRef - Garnet-type LLZO electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: Interfaces, conductivity, in-situ processing, and industrial prospects
Kaleab Habtamu Ayalew, Nithyadharseni Palaniyandy, Mkhulu K. Mathe, Phumlani F. Msomi
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 524: 168098. CrossRef
- A facile synthesis of bulk LiPON in solution for solid-state electrolytes
- [Korean]
- TiO2 Thin Film Coating on an Nb-Si–Based Superalloy via Atomic Layer Deposition
- Ji Young Park, Su Min Eun, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):255-262. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00052
- 1,995 View
- 50 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
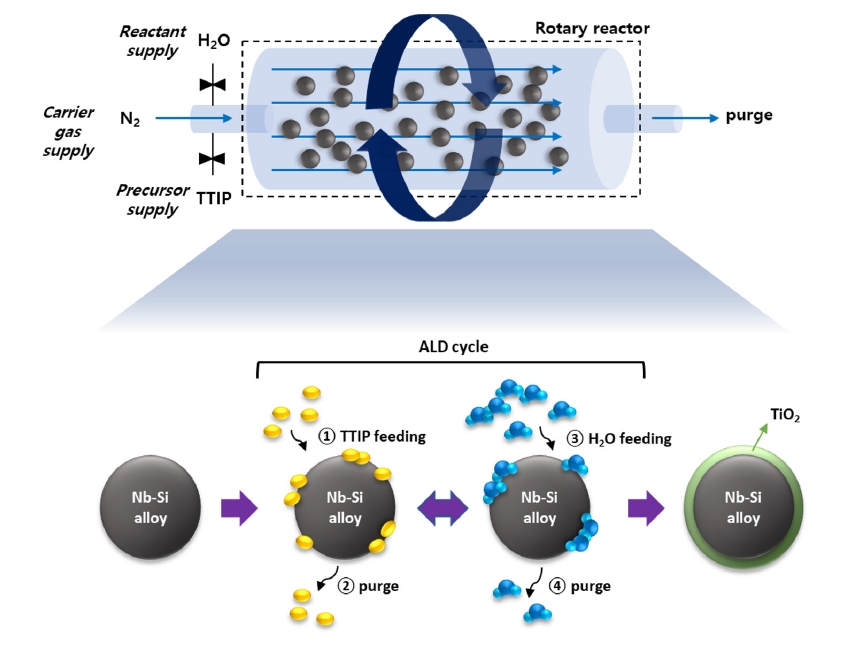
PDF - Nano-oxide dispersion–strengthened (ODS) superalloys have attracted attention because of their outstanding mechanical reinforcement mechanism. Dispersed oxides increase the material’s strength by preventing grain growth and recrystallization, as well as increasing creep resistance. In this research, atomic layer deposition (ALD) was applied to synthesize an ODS alloy. It is useful to coat conformal thin films even on complex matrix shapes, such as nanorods or powders. We coated an Nb-Si–based superalloy with TiO2 thin film by using rotary-reactor type thermal ALD. TiO2 was grown by controlling the deposition recipe, reactor temperature, N2 flow rate, and rotor speed. We could confirm the formation of uniform TiO2 film on the surface of the superalloy. This process was successfully applied to the synthesis of an ODS alloy, which could be a new field of ALD applications.
- [Korean]
- Hydrogen Reduction Behavior of NCM-based Lithium-ion Battery Cathode Materials
- So-Yeong Lee, So-Yeon Lee, Dae-Hyeon Lee, Ho-Sang Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):163-168. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00017
- 1,561 View
- 41 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
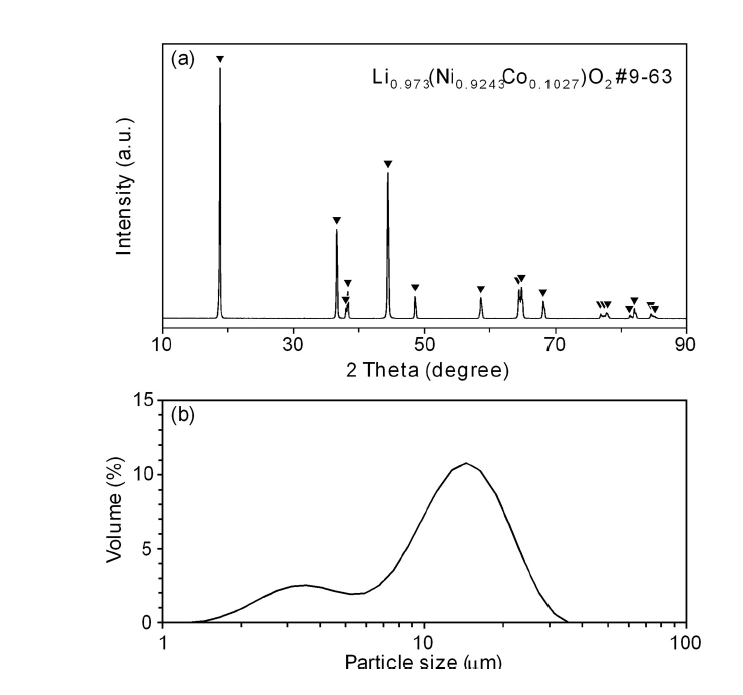
PDF - As the demand for lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles is increasing, it is important to recover valuable metals from waste lithium-ion batteries. In this study, the effects of gas flow rate and hydrogen partial pressure on hydrogen reduction of NCM-based lithium-ion battery cathode materials were investigated. As the gas flow rate and hydrogen partial pressure increased, the weight loss rate increased significantly from the beginning of the reaction due to the reduction of NiO and CoO by hydrogen. At 700 °C and hydrogen partial pressure above 0.5 atm, Ni and Li2O were produced by hydrogen reduction. From the reduction product and Li recovery rate, the hydrogen reduction of NCM-based cathode materials was significantly affected by hydrogen partial pressure. The Li compounds recovered from the solution after water leaching of the reduction products were LiOH, LiOH·H2O, and Li2CO3, with about 0.02 wt% Al as an impurity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reduction Roasting of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries Using CH4 Gas
Sang-Yeop Lee, Jae-Ho Hwang, Ho-Sang Sohn
Resources Recycling.2025; 34(5): 93. CrossRef
- Reduction Roasting of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries Using CH4 Gas
- [Korean]
- Inorganic Compound and Cycloserine Composite Particles for Improved Stability
- Dongwon Kim, Heeseo Kim, Hongjun Yoon, Hyuk Jun Cho, Sung Giu Jin
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):126-131. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00002
- 1,771 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
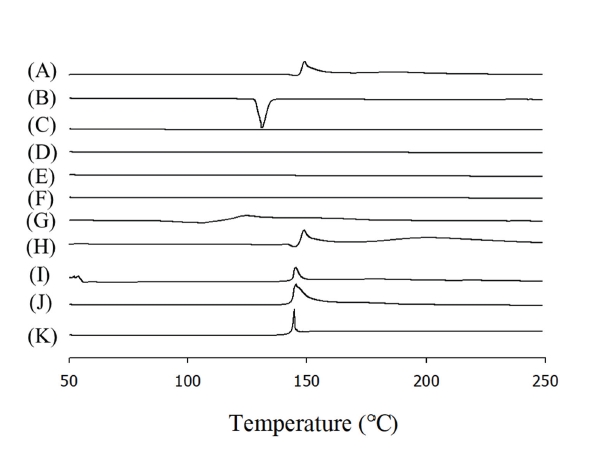
PDF - The aim of this study was to improve the chemical stability of cycloserine containing organic and inorganic compounds. Composite particles were manufactured with a 1:1 weight ratio of organic/inorganic compounds and cycloserine. The influence of organic/inorganic compounds on the stability of cycloserine was investigated under accelerated stress conditions at 60°C/75% RH for 24 hours. In addition, the properties of the composite particles were evaluated using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and the dissolution of the drug was assessed by preparing it as a hard capsule. Among the organic and inorganic compounds investigated, calcium hydroxide most improved the stability of cycloserine under accelerated stress conditions (53.3 ± 2.2% vs 1.7 ± 0.2%). DSC results confirmed the compatibility between calcium hydroxide and the cycloserine, and SEM results confirmed that it was evenly distributed around the cycloserine. Calcium hydroxide also showed more than 90% cycloserine dissolution within 15 minutes. Therefore, the calcium hydroxide and cycloserine composite particles may be candidates for cycloserine oral pharmaceuticals with enhanced drug stability.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Bi2Te2.5Se0.5 by Combining Oxide-reduction and Compressive-forming Process and Its Thermoelectric Properties
- Young Soo Lim, Gil-Geun Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):50-56. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.50
- 1,046 View
- 20 Download
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Nanowire by Electrospinning Process Using Nickel Oxide Particle Recovered from MLCC
- Haein Shin, Jongwon Bae, Minsu Kang, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):502-508. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.502
- 706 View
- 14 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF With the increasing demand for electronic products, the amount of multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC) waste has also increased. Recycling technology has recently gained attention because it can simultaneously address raw material supply and waste disposal issues. However, research on recovering valuable metals from MLCCs and converting the recovered metals into high-value-added materials remains insufficient. Herein, we describe an electrospinning (E-spinning) process to recover nickel from MLCCs and modulate the morphology of the recovered nickel oxide particles. The nickel oxalate powder was recovered using organic acid leaching and precipitation. Nickel oxide nanoparticles were prepared via heat treatment and ultrasonic milling. A mixture of nickel oxide particles and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) was used as the E-spinning solution. A PVP/NiO nanowire composite was fabricated via Espinning, and a nickel oxide nanowire with a network structure was manufactured through calcination. The nanowire diameters and morphologies are discussed based on the nickel oxide content in the E-spinning solution.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
Eunbi Park, Jongwon Bae, Sera Kang, Minsu Kang, Suseong Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(5): 375. CrossRef
- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
- [Korean]
- Evaluation of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ni-Y2O3 Sintered Alloys Based on the Powder Preparation Methods
- Gun-Woo Jung, Ji-Ho Cha, Min-Seo Jang, Minsuk Oh, Jeshin Park
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):484-492. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.484
- 1,056 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, Ni-Y2O3 powder was prepared by alloying recomposition oxidation sintering (AROS), solution combustion synthesis (SCS), and conventional mechanical alloying (MA). The microstructure and mechanical properties of the alloys were investigated by spark plasma sintering (SPS). Among the Ni-Y2O3 powders synthesized by the three methods, the AROS powder had approximately 5 nm of Y2O3 crystals uniformly distributed within the Ni particles, whereas the SCS powder contained a mixture of Ni and Y2O3 nanoparticles, and the MA powder formed small Y2O3 crystals on the surface of large Ni particles by milling the mixture of Ni and Y2O3. The average grain size of Y2O3 in the sintered alloys was approximately 15 nm, with the AROS sinter having the smallest, followed by the SCS sinter at 18 nm, and the MA sinter at 22 nm. The yield strength (YS) of the SCS- and MA-sintered alloys were 1511 and 1688 MPa, respectively, which are lower than the YS value of 1697 MPa for the AROS-sintered alloys. The AROS alloy exhibited improved strength compared to the alloys fabricated by SCS and conventional MA methods, primarily because of the increased strengthening from the finer Y2O3 particles and Ni grains.
- [Korean]
- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
- Jin-Kwon Kim, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Nahm Sahn, Sung-Soo Ryu, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):409-414. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.409
- 571 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
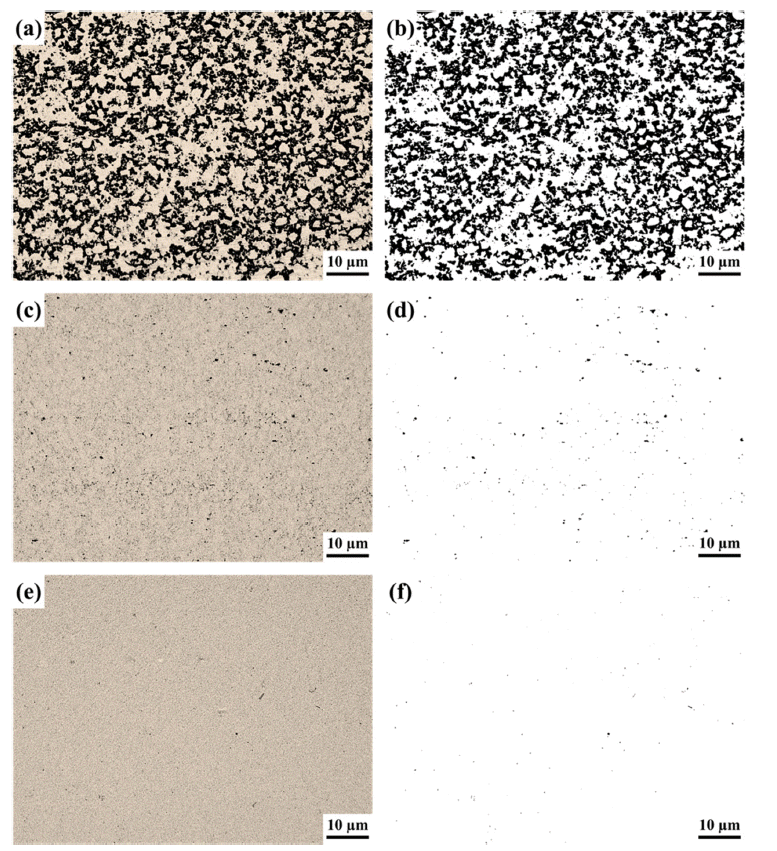
PDF YSZ (Y2O3-stabilized zirconia)-based ceramics have excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength and wear resistance. In the application, YSZ is utilized in the bead mill, a fine-grinding process. YSZ-based parts, such as the rotor and pin, can be easily damaged by continuous application with high rpm in the bead mill process. In that case, adding WC particles improves the tribological and mechanical properties. YSZ-30 vol.% WC composite ceramics are manufactured via hot pressing under different pressures (10/30/60 MPa). The hot-pressed composite ceramics measure the physical properties, such as porosity and bulk density values. In addition, the phase formation of these composite ceramics is analyzed and discussed with those of physical properties. For the increased applied pressure of hot pressing, the tetragonality of YSZ and the crystallinity of WC are enhanced. The mechanical properties indicate an improved tendency with the increase in the applied pressure of hot pressing.
- [Korean]
- Controlling Particle Size of Recycled Copper Oxide Powder for Copper Thermite Welding Characteristics
- Hansung Lee, Minsu Kim, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):332-338. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.332
- 853 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
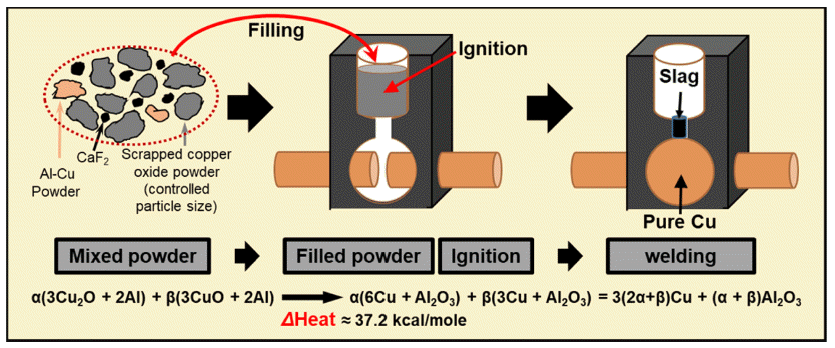
PDF Thermite welding is an exceptional process that does not require additional energy supplies, resulting in welded joints that exhibit mechanical properties and conductivity equivalent to those of the parent materials. The global adoption of thermite welding is growing across various industries. However, in Korea, limited research is being conducted on the core technology of thermite welding. Currently, domestic production of thermite powder in Korea involves recycling copper oxide (CuO). Unfortunately, controlling the particle size of waste CuO poses challenges, leading to the unwanted formation of pores and cracks during thermite welding. In this study, we investigate the influence of powder particle size on thermite welding in the production of Cu-thermite powder using waste CuO. We conduct the ball milling process for 0.5–24 h using recycled CuO. The evolution of the powder shape and size is analyzed using particle size analysis and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Furthermore, we examine the thermal reaction characteristics through differential scanning calorimetry. Additionally, the microstructures of the welded samples are observed using optical microscopy and SEM to evaluate the impact of powder particle size on weldability. Lastly, hardness measurements are performed to assess the strengths of the welded materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Friction Welding of Casted SCM440 and Sintered F-05-140 Dissimilar Steels and Their Joint Properties under Various Welding Conditions
Jisung Lee, Hansung Lee, Eunhyo Song, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 414. CrossRef
- Friction Welding of Casted SCM440 and Sintered F-05-140 Dissimilar Steels and Their Joint Properties under Various Welding Conditions
- [English]
- Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
- Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):318-323. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.318
- 1,686 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
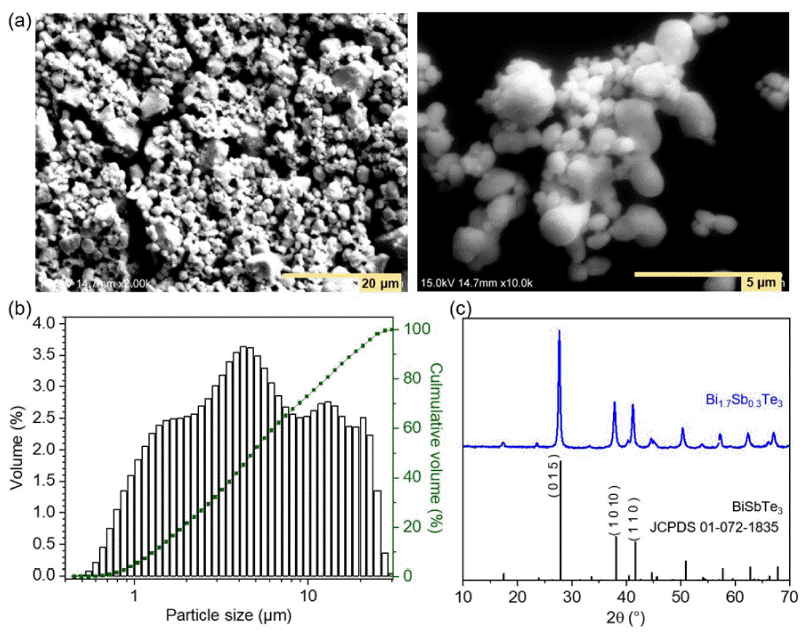
PDF The thermoelectric effect, which converts waste heat into electricity, holds promise as a renewable energy technology. Recently, bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3)-based alloys are being recognized as important materials for practical applications in the temperature range from room temperature to 500 K. However, conventional sintering processes impose limitations on shape-changeable and tailorable Bi2Te3 materials. To overcome these issues, three-dimensional (3D) printing (additive manufacturing) is being adopted. Although some research results have been reported, relatively few studies on 3D printed thermoelectric materials are being carried out. In this study, we utilize extrusion 3D printing to manufacture n-type Bi1.7Sb0.3Te3 (N-BST). The ink is produced without using organic binders, which could negatively influence its thermoelectric properties. Furthermore, we introduce graphene oxide (GO) at the crystal interface to enhance the electrical properties. The formed N-BST composites exhibit significantly improved electrical conductivity and a higher Seebeck coefficient as the GO content increases. Therefore, we propose that the combination of the extrusion 3D printing process (Direct Ink Writing, DIW) and the incorporation of GO into N-BST offers a convenient and effective approach for achieving higher thermoelectric efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef
- Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
- [Korean]
- Size Control of Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Nanoclusters according to Reaction Factors and Consequent Change in Their Magnetic Attraction
- Sanghoon Lee, Arim Byun, Jin-sil Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):297-304. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.297
- 992 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
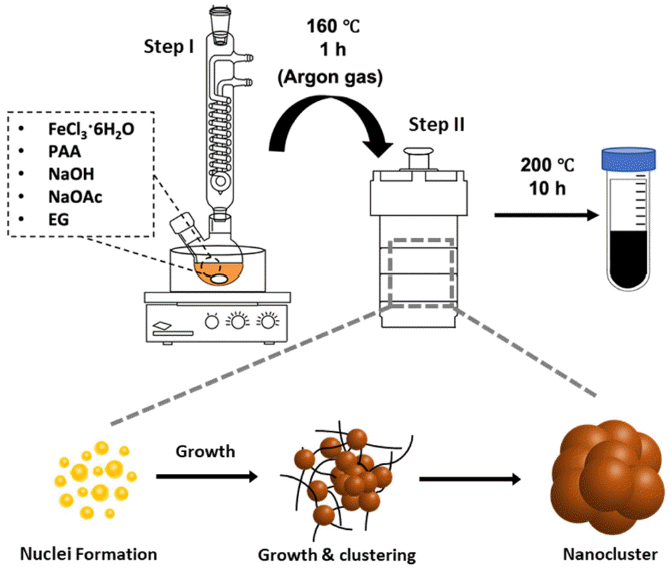
PDF Iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoclusters exhibit significant potential in the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields due to their strong magnetic properties, stability in solutions, and compatibility with living systems. They excel in magnetic separation processes, displaying high responsiveness to external magnetic fields. In contrast to conventional Fe2O3 nanoparticles that can aggregate in aqueous solutions due to their ferrimagnetic properties, these nanoclusters, composed of multiple nanoparticles, maintain their magnetic traits even when scaled to hundreds of nanometers. In this study, we develop a simple method using solvothermal synthesis to precisely control the size of nanoclusters. By adjusting precursor materials and reducing agents, we successfully control the particle sizes within the range of 90 to 420 nm. Our study not only enhances the understanding of nanocluster creation but also offers ways to improve their properties for applications such as magnetic separation. This is supported by our experimental results highlighting their size-dependent magnetic response in water. This study has the potential to advance both the knowledge and practical utilization of Fe2O3 nanoclusters in various applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enzymatic properties of iron oxide nanoclusters and their application as a colorimetric glucose detection probe
Dahyun Bae, Minhee Kim, Jin-sil Choi
RSC Advances.2025; 15(6): 4573. CrossRef
- Enzymatic properties of iron oxide nanoclusters and their application as a colorimetric glucose detection probe
- [Korean]
- Effect of Acid Leaching Conditions on the Properties of Cr Powder Produced by Self-propagating High-temperature Synthesis
- YongKwan Lee, YeongWoo Cho, ShinYoung Choi, SungGue Heo, Ju Won, KyoungTae Park, MiHye Lee, JaeJin Sim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):233-241. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.233
- 731 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
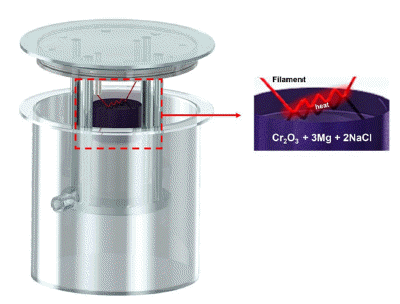
PDF In this study, we evaluated the effects of acid leaching on the properties of Cr powder synthesized using self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS). Cr powder was synthesized from a mixture of Cr2O3 and magnesium (Mg) powders using the SHS Process, and the byproducts after the reaction were removed using acid leaching. The properties of the recovered Cr powder were analyzed via X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), particle size analysis (PSA), and oxygen content analysis. The results show that perfect selective leaching of Cr is challenging because of various factors such as incomplete reaction, reaction kinetics, the presence of impurities, and incompatibility between the acid and metal mixture. Therefore, this study provides essential information on the properties under acidic conditions during the production of high-quality Cr powder using a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis method.
- [Korean]
- Thermal Atomic Layer Etching of the Thin Films: A Review
- Hyeonhui Jo, Seo Hyun Lee, Eun Seo Youn, Ji Eun Seo, Jin Woo Lee, Dong Hoon Han, Seo Ah Nam, Jeong Hwan Han
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):53-64. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.53
- 5,098 View
- 215 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
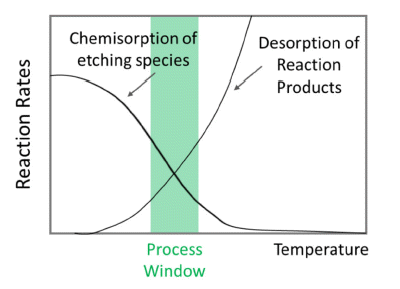
PDF Atomic layer etching (ALE) is a promising technique with atomic-level thickness controllability and high selectivity based on self-limiting surface reactions. ALE is performed by sequential exposure of the film surface to reactants, which results in surface modification and release of volatile species. Among the various ALE methods, thermal ALE involves a thermally activated reaction by employing gas species to release the modified surface without using energetic species, such as accelerated ions and neutral beams. In this study, the basic principle and surface reaction mechanisms of thermal ALE?processes, including “fluorination-ligand exchange reaction”, “conversion-etch reaction”, “conversion-fluorination reaction”, “oxidation-fluorination reaction”, “oxidation-ligand exchange reaction”, and “oxidation-conversion-fluorination reaction” are described. In addition, the reported thermal ALE processes for the removal of various oxides, metals, and nitrides are presented.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Self-Assembled Monolayers in Area-Selective Atomic Layer Deposition and Their Challenges
Si Eun Jung, Ji Woong Shin, Ye Jin Han, Byung Joon Choi
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 179. CrossRef
- Self-Assembled Monolayers in Area-Selective Atomic Layer Deposition and Their Challenges
- [Korean]
- The Synthesis of Lithium Lanthanum Titanium Oxide for Solid Electrolyte via Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis
- Jaeseok Roh, MinHo Yang, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):485-491. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.485

- 1,431 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Lithium lanthanum titanium oxide (LLTO) is a promising ceramic electrolyte because of its high ionic conductivity at room temperature, low electrical conductivity, and outstanding physical properties. Several routes for the synthesis of bulk LLTO are known, in particular, solid-state synthesis and sol-gel method. However, the extremely low ionic conductivity of LLTO at grain boundaries is one of the major problems for practical applications. To diminish the grain boundary effect, the structure of LLTO is tuned to nanoscale morphology with structures of different dimensionalities (0D spheres, and 1D tubes and wires); this strategy has great potential to enhance the ion conduction by intensifying Li diffusion and minimizing the grain boundary resistance. Therefore, in this work, 0D spherical LLTO is synthesized using ultrasonic spray pyrolysis (USP). The USP method primarily yields spherical particles from the droplets generated by ultrasonic waves passed through several heating zones. LLTO is synthesized using USP, and the effects of each precursor and their mechanisms as well as synthesis parameters are analyzed and discussed to optimize the synthesis. The phase structure of the obtained materials is analyzed using X-ray diffraction, and their morphology and particle size are analyzed using field-emission scanning electron microscopy.
- [English]
- Nitric Oxide Detection of Fe(DTC)3-hybrizided CdSe Quantum Dots Via Fluorescence Energy Transfer
- Chang-Yeoul Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):453-458. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.453
- 1,117 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
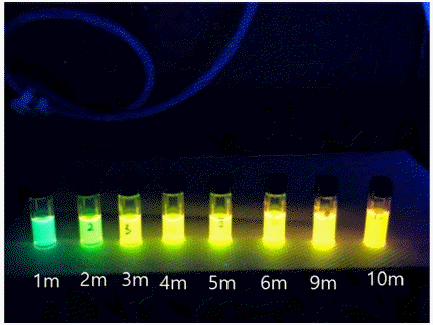
PDF We successfully synthesize water-dispersible CTAB-capped CdSe@ZnS quantum dots with the crystal size of the CdSe quantum dots controlled from green to orange colors. The quenching effect of Fe(DTC)3 is very efficient to turn off the emission light of quantum dots at four molar ratios of the CdSe quantum dots, that is, the effective covering the surface of quantum dots with Fe(DTC)3. However, the reaction with Fe(DTC)3 for more than 24 h is required to completely realize the quenching effect. The highly quenched quantum dots efficiently detect nitric oxide at nano-molar concentration of 110nM of NO with 34% of recovery of emission light intensity. We suggest that Fe(DTC)3-hybridized CdSe@ZnS quantum dots are an excellent fluorescence resonance energy transfer probe for the detection of nitric oxide in biological systems.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of NiCo2O4/Ni Foam Electrode for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Water Splitting
- Minsol Kwon, Jaeseong Go, Yesol Lee, Sungmin Lee, Jisu Yu, Hyowon Lee, Sung Ho Song, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):411-417. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.411
- 1,092 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
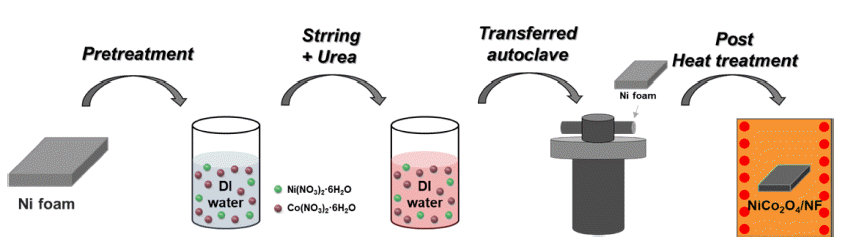
PDF Environmental issues such as global warming due to fossil fuel use are now major worldwide concerns, and interest in renewable and clean energy is growing. Of the various types of renewable energy, green hydrogen energy has recently attracted attention because of its eco-friendly and high-energy density. Electrochemical water splitting is considered a pollution-free means of producing clean hydrogen and oxygen and in large quantities. The development of non-noble electrocatalysts with low cost and high performance in water splitting has also attracted considerable attention. In this study, we successfully synthesized a NiCo2O4/NF electrode for an oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline water splitting using a hydrothermal method, which was followed by post-heat treatment. The effects of heat treatment on the electrochemical performance of the electrodes were evaluated under different heat-treatment conditions. The optimized NCO/NF-300 electrode showed an overpotential of 416 mV at a high current density of 50 mA/cm2 and a low Tafel slope (49.06 mV dec-1). It also showed excellent stability (due to the large surface area) and the lowest charge transfer resistance (12.59 Ω). The results suggested that our noble-metal free electrodes have great potential for use in developing alkaline electrolysis systems.
- [Korean]
- Comparison Study of Compact Titanium Oxide (c-TiO2) Powder Electron Transport Layer Fabrication for Carbon Electrode-based Perovskite Solar Cells
- Chae Young Woo, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):297-302. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.297
- 792 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
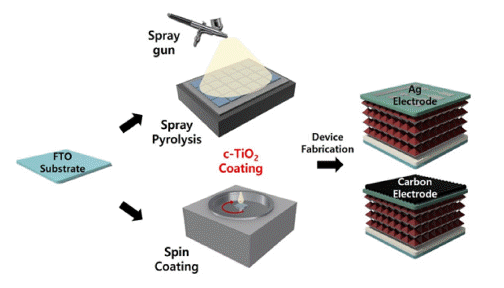
PDF This study compares the characteristics of a compact TiO2 (c-TiO2) powdery film, which is used as the electron transport layer (ETL) of perovskite solar cells, based on the manufacturing method. Additionally, its efficiency is measured by applying it to a carbon electrode solar cell. Spin-coating and spray methods are compared, and spraybased c-TiO2 exhibits superior optical properties. Furthermore, surface analysis by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) exhibits the excellent surface properties of spray-based TiO2. The photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) is 14.31% when applied to planar perovskite solar cells based on metal electrodes. Finally, carbon nanotube (CNT) film electrode-based solar cells exhibits a 76% PCE compared with that of metal electrodebased solar cells, providing the possibility of commercialization.
- [Korean]
- Controlling the Heat Generation Capability of Iron Oxide-Base Nanoparticles
- Jin-sil Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):518-526. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.518

- 662 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This review summarizes the recent progress in iron-oxide-based heat generators. Cancer treatment using magnetic nanoparticles as a heat generator, termed magnetic fluid hyperthermia, is a promising noninvasive approach that has gained significant interest. Most previous studies on improving the hyperthermia effect have focused on the construction of dopant-containing iron oxides. However, their applications in a clinical application can be limited due to extra dopants, and pure iron oxide is the only inorganic material approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Several factors that influence the heat generation capability of iron-oxide-based nanoparticles are summarized by reviewing recent studies on hyperthermia agents. Thus, our paper will provide the guideline for developing pure iron oxide-based heat generators with high heat dissipation capabilities.
- [Korean]
- Cobalt Recovery by Oxalic Acid and Hydroxide Precipitation from Waste Cemented Carbide Scrap Cobalt Leaching Solution
- Jaesung Lee, Mingoo Kim, Seulgi Kim, Dongju Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):497-501. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.497
- 1,272 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
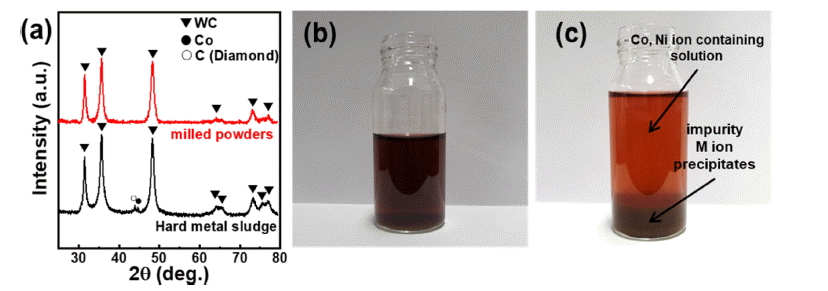
PDF Cobalt (Co) is mainly used to prepare cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) and binder metals for WC-Co hard metals. Developing an effective method for recovering Co from WC-Co waste sludge is of immense significance. In this study, Co is extracted from waste cemented carbide soft scrap via mechanochemical milling. The leaching ratio of Co reaches approximately 93%, and the leached solution, from which impurities except nickel are removed by pH titration, exhibits a purity of approximately 97%. The titrated aqueous Co salts are precipitated using oxalic acid and hydroxide precipitation, and the effects of the precipitating agent (oxalic acid and hydroxide) on the cobalt microstructure are investigated. It is confirmed that the type of Co compound and the crystal growth direction change according to the precipitation method, both of which affect the microstructure of the cobalt powders. This novel mechanochemical process is of significant importance for the recovery of Co from waste WC-Co hard metal. The recycled Co can be applied as a cemented carbide binder or a cathode material for lithium secondary batteries.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of the Multi-layered SnO Nanoparticles and Enhanced Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries by Heat treatment
- So Yi Lee, Yoon Myung, Kyu-Tae Lee, Jaewon Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):455-461. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.455

- 1,676 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, multilayered SnO nanoparticles are prepared using oleylamine as a surfactant at 165°C. The physical and chemical properties of the multilayered SnO nanoparticles are determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Interestingly, when the multilayered SnO nanoparticles are heated at 400°C under argon for 2 h, they become more efficient anode materials, maintaining their morphology. Heat treatment of the multilayered SnO nanoparticles results in enhanced discharge capacities of up to 584 mAh/g in 70 cycles and cycle stability. These materials exhibit better coulombic efficiencies. Therefore, we believe that the heat treatment of multilayered SnO nanoparticles is a suitable approach to enable their application as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and electrochemical properties of multi-layered SnO/rGO composite as anode materials for sodium ion batteries
So Yi Lee, Honggyu Seong, Geongil Kim, Youngho Jin, Joon Ha Moon, Wonbin Nam, Sung Kuk Kim, MinHo Yang, Jaewon Choi
Applied Surface Science.2023; 612: 155859. CrossRef
- Synthesis and electrochemical properties of multi-layered SnO/rGO composite as anode materials for sodium ion batteries
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and High Temperature Mechanical Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steels Manufactured by Combination Milling Process
- Jung-Uk Lee, Young-Kyun Kim, Jeoung Han Kim, Hwi-Jin Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):389-395. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.389
- 782 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
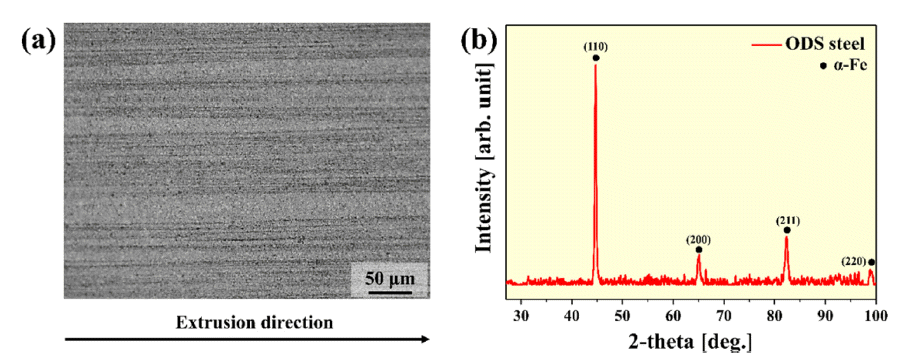
PDF Oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel has excellent high-temperature properties, corrosion resistance, and oxidation resistance, and is expected to be applicable in various fields. Recently, various studies on mechanical alloying (MA) have been conducted for the dispersion of oxide particles in ODS steel with a high number density. In this study, ODS steel is manufactured by introducing a complex milling process in which planetary ball milling, cryogenic ball milling, and drum ball milling are sequentially performed, and the microstructure and high-temperature mechanical properties of the ODS steel are investigated. The microstructure observation revealed that the structure is stretched in the extrusion direction, even after the heat treatment. In addition, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis confirmed the presence of oxide particles in the range of 5 to 10 nm. As a result of the room-temperature and high-temperature compression tests, the yield strengths were measured as 1430, 1388, 418, and 163 MPa at 25, 500, 700, and 900°C, respectively. Based on these results, the correlation between the microstructure and mechanical properties of ODS steel manufactured using the composite milling process is also discussed.
- [Korean]
- Evolution on Microstructures and Tensile Properties of 10Cr-1Mo ODS Steel with Different Lengths of Mechanical Alloying Process Times
- Sanghoon Noh, Tae Kyu Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):375-380. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.375

- 878 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we investigate the effect of the duration of mechanical alloying on the microstructures and mechanical properties of ODS ferritic/martensitic steel. The Fe(bal.)-10Cr-1Mo pre-alloyed powder and Y2O3 powder are mechanically alloyed for the different mechanical alloying duration (0 to 40 h) and then constantly fabricated using a uniaxial hot pressing process. Upon increasing the mechanical alloying time, the average powder diameter and crystallite size increased dramatically. In the initial stages within 5 h of mechanical alloying, inhomogeneous grain morphology is observed along with coarsened carbide and oxide distributions; thus, precipitate phases are temporarily observed between the two powders because of insufficient collision energy to get fragmented. After 40 h of the MA process, however, fine martensitic grains and uniformly distributed oxide particles are observed. This led to a favorable tensile strength and elongation at room temperature and 650°C.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of
Bangpungtongseong-san Extract-loaded Particles for Tablet Dosage Form - Jinwoo Park, Sung Giu Jin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):227-232. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.227

- 988 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to optimize the powder formulation and manufacturing conditions for the solidification of an extract of the herb
Bangpungtongseong-san (BPTS). To develop BPTS-loaded particles for the tablet dosage form, various BPTS-loaded particles composed of BPTS, dextrin, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), silicon dioxide, ethanol, and water are prepared using spray-drying and high shear granulation (high-speed mixing). Their physical properties are evaluated using scanning electron microscopy and measurements of the angle of repose, Hausner ratio, Carr’s index, hardness, and disintegration time. The optimal BPTS-loaded particles exhibit improved flowability and compressibility. In particular, the BPTS-loaded particles containing silicon dioxide show significantly improved flowability and compressibility (the angle of repose, Hausner ratio, and Carr’s index are 35.27 ± 0.58°, 1.18 ± 0.06, and 15.67 ± 1.68%, respectively), hardness (18.97 ± 1.00 KP), and disintegration time (17.60 ± 1.50 min) compared to those without silicon dioxide. Therefore, this study suggests that particles prepared by high-speed mixing can be used to greatly improve the flowability and compressibility of BPTS using MCC and silicon dioxide.
- [Korean]
- Effect of H2SO4 and Reaction Time on Synthesis of 5Mg(OH)2∙MgSO4∙3H2O Whiskers using Hydrothermal Reaction
- Areum Choi, Nuri Oh, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):401-405. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.401

- 1,005 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Magnesium hydroxide sulfate hydrate (MHSH) whiskers were synthesized via a hydrothermal reaction by using MgO as the reactant as well as the acid solution. The effects of the H2SO4 amount and reaction time at the same temperature were studied. In general, MHSH whiskers were prepared using MgSO4 in aqueous ammonia. In this work, to reduce the formation of impurities and increase the purity of MHSH, we employed a synthesis technique that did not require the addition of a basic solution. Furthermore, the pH value, which was controlled by the H2SO4 amount, acted as an important factor for the formation of high-purity MHSH. MgO was used as the raw material because it easily reacts in water and forms Mg+ and MgOH+ ions that bind with SO4 2- ions to produce MHSH. Their morphologies and structures were determined using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and Morphology Control of Needle Type 513 MHSH and Mg(OH)2 from Dolomite
Jiyeon Kim, HyunSeung Shim, Seong-Ju Hwang, YooJin Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(5): 399. CrossRef - Study of SiO2 coating and carboxylic surface-modification on Mg-based inorganic fiber by one-step reflux reaction
Minsol Park, Areum Choi, Seiki Kim, Wooyoung Shim, YooJin Kim
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2022; 59(6): 869. CrossRef - Effect of sulfate ion on synthesis of 5 Mg(OH)2·MgSO4·3H2O whiskers using non-hydrothermal method with acid catalyst
Areum Choi, Nuri Oh, YooJin Kim
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2022; 59(2): 224. CrossRef
- Synthesis and Morphology Control of Needle Type 513 MHSH and Mg(OH)2 from Dolomite
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Nucleation Behavior of MoO3 Nano Particles with Concentration of Precursors
- Seyoung Lee, Namhun Kwon, Jaeseok Roh, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):394-400. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.394

- 1,488 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) is used in various applications including sensors, photocatalysts, and batteries owing to its excellent ionic conductivity and thermal properties. It can also be used as a precursor in the hydrogen reduction process to obtain molybdenum metals. Control of the parameters governing the MoO3 synthesis process is extremely important because the size and shape of MoO3 in the reduction process affect the shape, size, and crystallization of Mo metal. In this study, we fabricated MoO3 nanoparticles using a solution combustion synthesis (SCS) method that utilizes an organic additive, thereby controlling their morphology. The nucleation behavior and particle morphology were confirmed using ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis) and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). The concentration of the precursor (ammonium heptamolybdate tetrahydrate) was adjusted to be 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 M. Depending on this concentration, different nucleation rates were obtained, thereby resulting in different particle morphologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterization of Compacted and Pressureless Sintered Parts for Molybdenum Oxide Powder according to Hydrogen Reduction Temperature
Jong Hoon Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(4): 336. CrossRef
- Characterization of Compacted and Pressureless Sintered Parts for Molybdenum Oxide Powder according to Hydrogen Reduction Temperature
- [Korean]
- Effect of Cobalt Contents on the Microstructure and Charpy Impact Properties of Ferritic/martensitic Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel
- Daehyun Kwon, Sanghoon Noh, Jung Gu Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):311-317. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.311
- 876 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
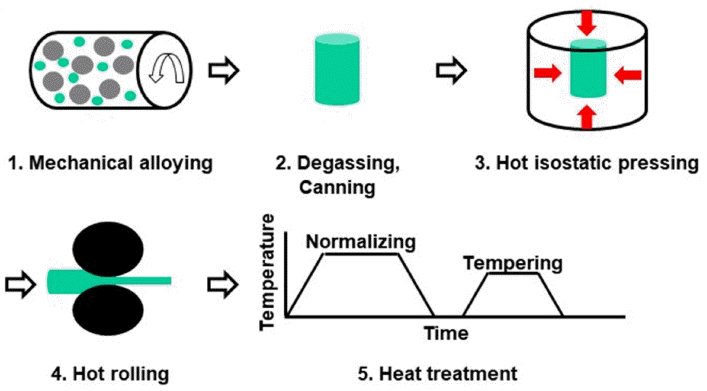
PDF In this study, the effects of Co content on the microstructure and Charpy impact properties of Fe-Cr-W ferritic/martensitic oxide dispersion strengthened (F/M ODS) steels are investigated. F/M ODS steels with 0–5 wt% Co are fabricated by mechanical alloying, followed by hot isostatic pressing, hot-rolling, and normalizing/tempering heat treatment. All the steels commonly exhibit two-phase microstructures consisting of ferrite and tempered martensite. The volume fraction of ferrite increases with the increase in the Co content, since the Co element considerably lowers the hardenability of the F/M ODS steel. Despite the lowest volume fraction of tempered martensite, the F/M ODS steel with 5 wt% Co shows the highest micro-Vickers hardness, owing to the solid solution-hardening effect of the alloyed Co. The high hardness of the steel improves the resistance to fracture initiation, thereby resulting in the enhanced fracture initiation energy in a Charpy impact test at – 40°C. Furthermore, the addition of Co suppresses the formation of coarse oxide inclusions in the F/M ODS steel, while simultaneously providing a high resistance to fracture propagation. Owing to these combined effects of Co, the Charpy impact energy of the F/M ODS steel increases gradually with the increase in the Co content.
- [Korean]
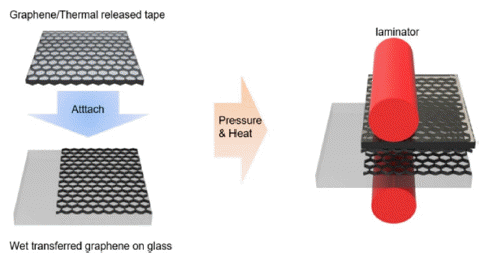
- Partially Dry-Transferred Graphene Electrode with Zinc Oxide Nanopowder and Its Application on Organic Solar Cells
- Yeongsu Jo, Chae Young Woo, Soon Kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):305-310. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.305
- 534 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, partially dry transfer is investigated to solve the problem of fully dry transfer. Partially dry transfer is a method in which multiple layers of graphene are dry-transferred over a wet-transferred graphene layer. At a wavelength of 550 nm, the transmittance of the partially dry-transferred graphene is seen to be about 3% higher for each layer than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene. Furthermore, the sheet resistance of the partially drytransferred graphene is relatively lower than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene, with the minimum sheet resistance being 179 Ω/sq. In addition, the fully dry-transferred graphene is easily damaged during the solution process, so that the performance of the organic photovoltaics (OPV) does not occur. In contrast, the best efficiency achievable for OPV using the partially dry-transferred graphene is 2.37% for 4 layers.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of
Gastrodia elata -loaded Particles for Increased Moisture Stability - Jae Hwan Jung, Sung Giu Jin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):241-246. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.241
- 809 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To develop
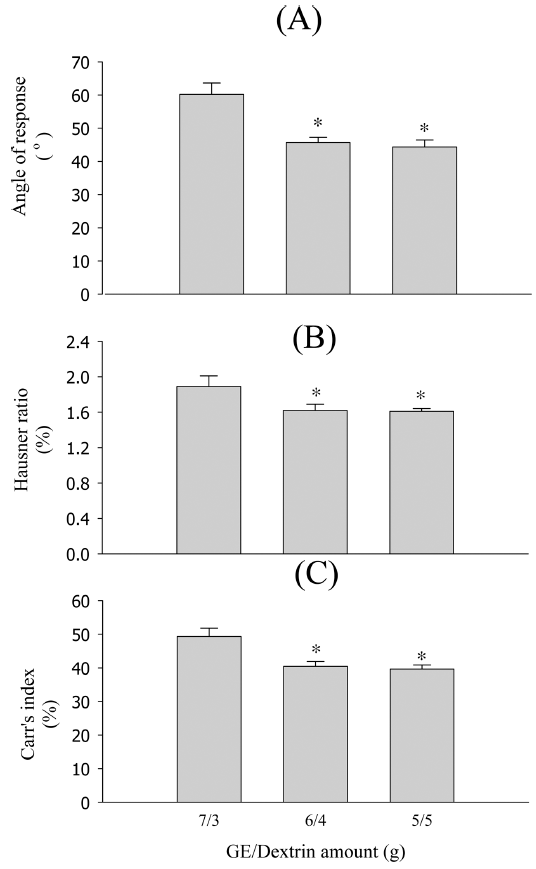
Gastrodia elata (GE)-loaded particles for herbal extract dosage forms, various GE-loaded particles containing dextrin, isomalt, maltodextrin, and silicon dioxide as solidifying carriers in the GE water extract are prepared using the spray drying method. Their physical properties are evaluated using the repose angle, Hausner ratio, Carr’s index, weight increase rate at 40°C/75% RH condition, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Particles made of dextrin improve the fluidity, compressibility, and water stability. In addition, 2% silicon dioxide increases the fluidity and moisture stability. The best flowability and compressibility of GE-loaded particles are observed with TP, dextrin, and silicon dioxide amounts in the ratio of 6/4/0.2 (34.29 ± 2.86°, 1.48 ± 0.03, and 38.29 ± 2.39%, repose angle, Hausner Ratio, and Carr’s index, respectively) and moisture stability with a 2% weight increase rate for 14 h at 40°C/75% RH condition. Therefore, our results suggest that the particles prepared by the spray drying method with dextrin and 2% silicon dioxide can be used as powerful particles to improve the flowability, compressibility, and moisture stability of GE.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Porous Cu-Co using Freeze Drying Process of Camphene Slurry with Oxide Composite Powders
- Gyuhwi Lee, Ju-Yeon Han, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):193-197. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.193
- 697 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
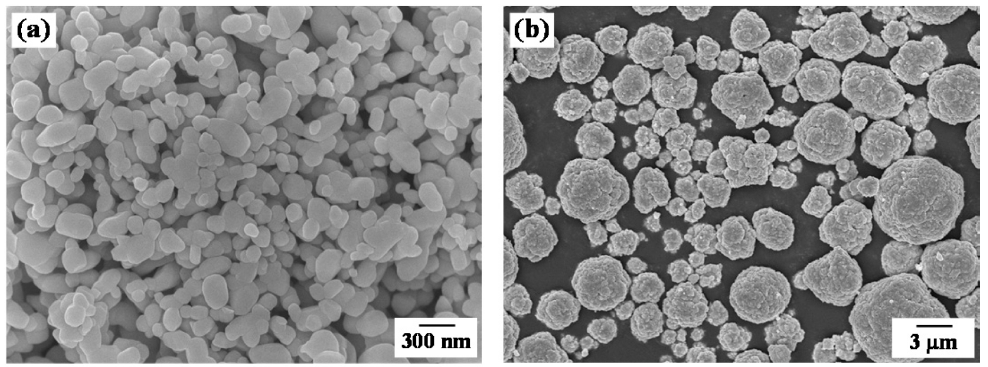
PDF Porous Cu-14 wt% Co with aligned pores is produced by a freeze drying and sintering process. Unidirectional freezing of camphene slurry with CuO-Co3O4 powders is conducted, and pores in the frozen specimens are generated by sublimation of the camphene crystals. The dried bodies are hydrogen-reduced at 500°C and sintered at 800°C for 1 h. The reduction behavior of the CuO-Co3O4 powder mixture is analyzed using a temperature-programmed reduction method in an Ar-10% H2 atmosphere. The sintered bodies show large and aligned parallel pores in the camphene growth direction. In addition, small pores are distributed around the internal walls of the large pores. The size and fraction of the pores decrease as the amount of solid powder added to the slurry increases. The change in pore characteristics according to the amount of the mixed powder is interpreted to be due to the rearrangement and accumulation behavior of the solid particles in the freezing process of the slurry.
- [English]
- Effects of Precipitates and Oxide Dispersion on the High-temperature Mechanical Properties of ODS Ni-Based Superalloys
- GooWon Noh, Young Do Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):8-13. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.8

- 1,765 View
- 35 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we investigated the effects of precipitates and oxide dispersoids on the high-temperature mechanical properties of oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) Ni-based super alloys. Two ODS Ni-based super alloy rods with different chemical compositions were fabricated by high-energy milling and hot extrusion process at 1150 °C to investigate the effects of precipitates on high-temperature mechanical properties. Further, the MA6000N alloy is an improvement over the commercial MA6000 alloy, and the KS6000 alloy has the same chemical composition as the MA6000 alloy. The phase and microstructure of Ni-based super alloys were investigated by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. It was found that MC carbide precipitates and oxide dispersoids in the ODS Ni-based super alloys developed in this study may effectively improve high-temperature hardness and creep resistance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanical Properties and Residual Stress Analysis of ODS Ni Superalloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
Dong Wan Lee, Su Gwan Lee, Cong Dhin Van, Cae Ryeong Kim, Jin Chun Kim, Hwi Jun Kim, Joong Gyeong Lim, Tae Sik Yoon
Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy.2025; 72(Supplement): S453. CrossRef - Additive manufacturing of oxide-dispersion strengthened alloys: Materials, synthesis and manufacturing
Markus B. Wilms, Silja-Katharina Rittinghaus, Mareen Goßling, Bilal Gökce
Progress in Materials Science.2023; 133: 101049. CrossRef
- Mechanical Properties and Residual Stress Analysis of ODS Ni Superalloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of C3S, C2S, C3A Powders using Ultra-fine Calcium Oxide Powder Synthesized from Eggshell and Effect of C3A Content on Hardened Mixed Aggregates
- Heon Kong, Ki-Beom Kwon, Sang-Jin Park, Whyo-Sub Noh, Sang-Jin Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):493-501. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.493
- 980 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
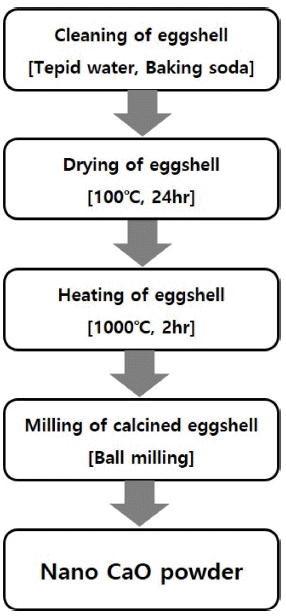
PDF In this work, ultra-fine calcium oxide (CaO) powder derived from eggshells is used as the starting material to synthesize mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA). The prepared CaO powder is confirmed to have an average particle size of 500 nm. MTAs are synthesized with three types of fine CaO-based powders, namely, tricalcium silicate (C3S), dicalcium silicate (C2S), and tricalcium aluminate (C3A). The synthesis behavior of C3S, C2S and C3A with ultra-fine CaO powder and the effects of C3A content and curing time on the properties of MTA are investigated. The characteristics of the synthesized MTA powders are examined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission-scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), and a universal testing machine (UTM). The microstructure and compressive strength characteristics of the synthesized MTA powders are strongly dependent on the C3A wt.% and curing time. Furthermore, MTA with 5 wt.% C3A is found to increase the compressive strength and shorten the curing time.
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Preparation and Growth Mechanism of Titanium Dioxide using Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Titanium Complex
- Yubin Kang, Jin-Ju Choi, Nam Hun Kwon, Dae-Guen Kim, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):487-492. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.487
- 1,110 View
- 15 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
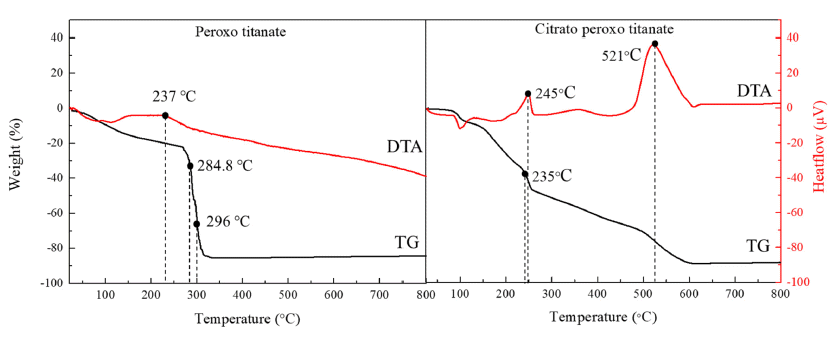
PDF Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is a typical inorganic material that has an excellent photocatalytic property and a high refractive index. It is used in water/air purifiers, solar cells, white pigments, refractory materials, semiconductors, etc.; its demand is continuously increasing. In this study, anatase and rutile phase titanium dioxide is prepared using hydroxyl and carboxyl; the titanium complex and its mechanism are investigated. As a result of analyzing the phase transition characteristics by a heat treatment temperature using a titanium complex having a hydroxyl group and a carboxyl group, it is confirmed that the material properties were different from each other and that the anatase and rutile phase contents can be controlled. The titanium complexes prepared in this study show different characteristics from the titania-formation temperatures of the known anatase and rutile phases. It is inferred that this is due to the change of electrostatic adsorption behavior due to the complexing function of the oxygen sharing point, which crystals of the TiO6 structure share.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
Minsu Kim, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 478. CrossRef
- Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
- [Korean]
- Magnetic Properties of Micron Sized Fe3O4 Crystals Synthesized by Hydrothermal Methods
- Ki-Bum Lee, Chunghee Nam
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):481-486. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.481
- 1,116 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
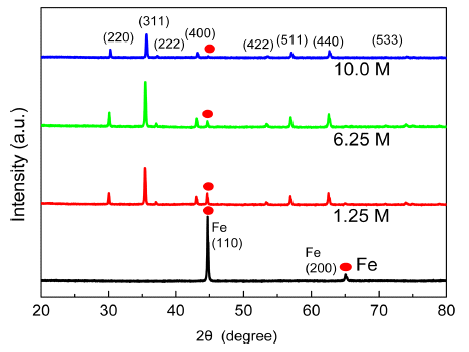
PDF Iron oxides currently attract considerable attention due to their potential applications in the fields of lithiumion batteries, bio-medical sensors, and hyperthermia therapy materials. Magnetite (Fe3O4) is a particularly interesting research target due to its low cost, good biocompatibility, outstanding stability in physiological conditions. Hydrothermal synthesis is one of several liquid-phase synthesis methods with water or an aqueous solution under high pressure and high temperature. This paper reports the growth of magnetic Fe3O4 particles from iron powder (spherical, <10 μm) through an alkaline hydrothermal process under the following conditions: (1) Different KOH molar concentrations and (2) different synthesis time for each KOH molar concentrations. The optimal condition for the synthesis of Fe3O4 using Fe powders is hydrothermal oxidation with 6.25 M KOH for 48 h, resulting in 89.2 emu/g of saturation magnetization at room temperature. The structure and morphologies of the synthesized particles are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD, 2θ = 20°–80°) with Cu-kα radiation and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), respectively. The magnetic properties of magnetite samples are investigated using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). The role of KOH in the formation of magnetite octahedron is observed.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Graphene Coated Aluminum Powders by Self-assemble Reaction
- Jin Uk Hwang, Woo Seong Tak, Sang Yong Nam, Woo Sik Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):383-388. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.383

- 905 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To improve the mechanical properties of aluminum, graphene has been used as a reinforcing material, yielding graphene-reinforced aluminum matrix composites (GRAMCs). Dispersion of graphene materials is an important factor that affects the properties of GRAMCs, which are mainly manufactured by mechanical mixing methods such as ball milling. However, the use of only mechanical mixing process is limited to achieve homogeneous dispersion of graphene. To overcome this problem, in this study, we have prepared composite materials by coating aluminum particles with graphene by a self-assembly reaction using poly vinylalcohol and ethylene diamine as coupling agents. The scanning electron microscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy results confirm the coating of graphene on the Al surface. Bulk density of the sintered composites by spark plasma sintering achieved a relative density of over 99% up to 0.5 wt.% graphene oxide content.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 492. CrossRef
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- [Korean]
- The Effects of Hexamethylenetetramine Concentration on the Structural and Electrochemical Performances of Ni(OH)2 Powder for Pseudocapacitor Applications
- Dong Yeon Kim, Young-Min Jeong, Seong-Ho Baek, Injoon Son
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):231-236. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.231
- 1,135 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
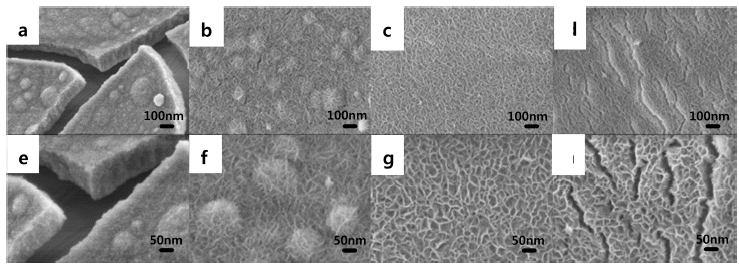
PDF Ni hydroxides (Ni(OH)2) are synthesized on Ni foam by varying the hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) concentration using an electrodeposition process for pseudocapacitor (PC) applications. In addition, the effects of HMT concentration on the Ni(OH)2 structure and the electrochemical properties of the PCs are investigated. HMT is the source of amine-based OH− in the solution; thus, the growth rate and morphological structure of Ni(OH)2 are influenced by HMT concentration. When Ni(OH)2 is electrodeposited at a constant voltage mode of -0.85 V vs. Ag/AgCl, the cathodic current and the number of nucleations are significantly reduced with increasing concentration of HMT from 0 to 10 mM. Therefore, Ni(OH)2 is sparsely formed on the Ni foam with increasing HMT concentration, showing a layered double-hydroxide structure. However, loosely packed Ni(OH)2 grains that are spread on Ni foam maintain a much greater surface area for reaction and result in the effective utilization of the electrode material due to the steric hindrance effect. It is suggested that the Ni(OH)2 electrodes with HMT concentration of 7.5 mM have the maximum specific capacitance (1023 F/g), which is attributed to the facile electrolyte penetration and fast proton exchange via optimized surface areas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of Domestic Research Trends on Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) Materials: Based on Research Articles in Korean Citation Index (KCI)
Seon Yong Lee, YoungJae Kim, Young Jae Lee
Economic and Environmental Geology.2023; 56(1): 23. CrossRef
- Review of Domestic Research Trends on Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) Materials: Based on Research Articles in Korean Citation Index (KCI)
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of
Taraxacum platycarpum Extract-loaded Particles for Tablet Dosage Form - Sung Giu Jin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):225-230. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.225
- 982 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To develop
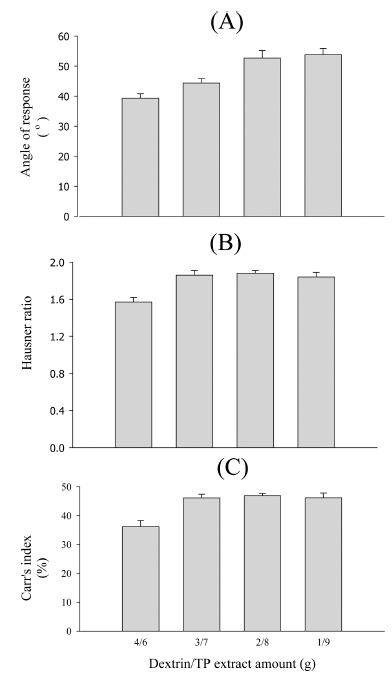
Taraxacum platycarpum extract (TP)-loaded particles for tablet dosage form, various TP-loaded particles composed of TP, dextrin, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), silicon dioxide, ethanol, and water are prepared using a spray-drying method and fluid-bed-drying method. Their physical properties are evaluated using angle of repose, Hausner ratio, Carr’s index, hardness, disintegrant time, and scanning electron microscopy. Optimal TP-loaded particles improve flowability and compressibility. Furthermore, 2% silicon dioxide gives increased flowability and compressibility. The formula of TP-loaded fluid-bed-drying particles at a TP/MCC/silicon-dioxide amount of 5/5/0.2 improves the angle of repose, Hausner ratio, Carr’s index, hardness, and disintegrant time as compared with the TP-loaded spray-drying particles. The TP-loaded fluid-bed-drying particles considerably improve flowability and compressibility (35.10° vs. 40.3°, 0.97 vs. 1.17, and 18.97% vs. 28.97% for the angle of repose, Hausner ratio, and Carr’s index, respectively), hardness (11.34 vs. 4.7 KP), and disintegrant time (7.4 vs. 10.4 min) as compared with the TP-loaded spray-drying particles. Thus, the results suggest that these fluid-bed-drying particles with MCC and silicon dioxide can be used as powerful particles to improve the flowability and compressibility of the TP.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Characterization of Gastrodia elata-loaded Particles for Increased Moisture Stability
Jae Hwan Jung, Sung Giu Jin
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 241. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Characterization of Gastrodia elata-loaded Particles for Increased Moisture Stability
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Highly Reactive Al/CuO Nano-composite using Graphene Oxide
- YeSeul Lim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):220-224. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.220

- 746 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The aluminum (Al)/copper oxide (CuO) complex is known as the most promising material for thermite reactions, releasing a high heat and pressure through ignition or thermal heating. To improve the reaction rate and wettability for handling safety, nanosized primary particles are applied on Al/CuO composite for energetic materials in explosives or propellants. Herein, graphene oxide (GO) is adopted for the Al/CuO composites as the functional supporting materials, preventing a phase-separation between solvent and composites, leading to a significantly enhanced reactivity. The characterizations of Al/CuO decorated on GO(Al/CuO/GO) are performed through scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy mapping analysis. Moreover, the functional bridging between Al/CuO and GO is suggested by identifying the chemical bonding with GO in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis. The reactivity of Al/CuO/GO composites is evaluated by comparing the maximum pressure and rate of the pressure increase of Al/CuO and Al/CuO/GO. The composites with a specific concentration of GO (10 wt%) demonstrate a well-dispersed mixture in hexane solution without phase separation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Controlling Particle Size of Recycled Copper Oxide Powder for Copper Thermite Welding Characteristics
Hansung Lee, Minsu Kim, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 332. CrossRef
- Controlling Particle Size of Recycled Copper Oxide Powder for Copper Thermite Welding Characteristics
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Molybdenum Alloys with Improved Fracture Toughness through the Dispersion of Lanthanum Oxide
- Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Jung Hyo Park, Young Do Kim, Jongmin Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):208-213. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.208
- 802 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
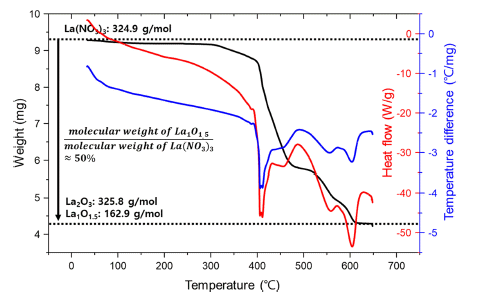
PDF In this study, lanthanum oxide (La2O3) dispersed molybdenum (Mo–La2O3) alloys are fabricated using lanthanum nitrate solution and nanosized Mo particles produced by hydrogen reduction of molybdenum oxide. The effect of La2O3 dispersion in a Mo matrix on the fracture toughness at room temperature is demonstrated through the formation behavior of La2O3 from the precursor and three-point bending test using a single-edge notched bend specimen. The relative density of the Mo–0.3La2O3 specimen sintered by pressureless sintering is approximately 99%, and La2O3 with a size of hundreds of nanometers is uniformly distributed in the Mo matrix. It is also confirmed that the fracture toughness is 19.46 MPa·m1/2, an improvement of approximately 40% over the fracture toughness of 13.50 MPa·m1/2 on a pure-Mo specimen without La2O3, and this difference in the fracture toughness occurs because of the changes in fracture mode of the Mo matrix caused by the dispersion of La2O3.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sintering property of micro/nano core-shell molybdenum powder synthesized by mechanochemical process
Chun Woong Park, Heeyeon Kim, Won Hee Lee, Wonjune Choi, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2024; 119: 106532. CrossRef - Novel design of Mo-Si-B + La2O3 powder with multi-shell structure for ideal microstructure and enhanced mechanical property
Wonjune Choi, Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim, Jongmin Byun
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2024; 120: 106611. CrossRef
- Sintering property of micro/nano core-shell molybdenum powder synthesized by mechanochemical process
- [Korean]
- Investigation on Size Distribution of Tungsten-based Alloy Particles with Solvent Viscosity During Ultrasonic Ball Milling Process
- KeunHyuk Ryu, HyeongSub So, JiSeok Yun, InHo Kim, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):201-207. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.201
- 1,091 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten heavy alloys (W–Ni–Fe) play an important role in various industries because of their excellent mechanical properties, such as the excellent hardness of tungsten, low thermal expansion, corrosion resistance of nickel, and ductility of iron. In tungsten heavy alloys, tungsten nanoparticles allow the relatively low-temperature molding of high-melting-point tungsten and can improve densification. In this study, to improve the densification of tungsten heavy alloy, nanoparticles are manufactured by ultrasonic milling of metal oxide. The physical properties of the metal oxide and the solvent viscosity are selected as the main parameters. When the density is low and the Mohs hardness is high, the particle size distribution is relatively high. When the density is high and the Mohs hardness is low, the particle size distribution is relatively low. Additionally, the average particle size tends to decrease with increasing viscosity. Metal oxides prepared by ultrasonic milling in high-viscosity solvent show an average particle size of less than 300 nm based on the dynamic light scattering and scanning electron microscopy analysis. The effects of the physical properties of the metal oxide and the solvent viscosity on the pulverization are analyzed experimentally.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
Eunbi Park, Jongwon Bae, Sera Kang, Minsu Kang, Suseong Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(5): 375. CrossRef - Manufacture of high sensitive Ag-Fe3O4-PDMS nanocomposite pressure sensor through morphology control of conductive filler
Keunhyuk Ryu, Namhun Kwon, Kun-Jae Lee
Advanced Powder Technology.2021; 32(7): 2441. CrossRef - Grinding behavior of WO3, NiO, Fe2O3 by ultrasonic milling parameters control and preparation of nanocomposite powder
Keunhyuk Ryu, Kun-Jae Lee
Advanced Powder Technology.2020; 31(9): 3867. CrossRef
- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Hexagonal Tungsten Oxide Nanopowders for High Performance Gas Sensing Application
- Jinsoo Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):28-33. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.28
- 812 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The gas sensor is essential to monitoring dangerous gases in our environment. Metal oxide (MO) gas sensors are primarily utilized for flammable, toxic and organic gases and O3 because of their high sensitivity, high response and high stability. Tungsten oxides (WO3) have versatile applications, particularly for gas sensor applications because of the wide bandgap and stability of WO3. Nanosize WO3 are synthesized using the hydrothermal method. Asprepared WO3 nanopowders are in the form of nanorods and nanorulers. The crystal structure is hexagonal tungsten bronze (MxWO3, x =< 0.33), characterized as a tunnel structure that accommodates alkali ions and the phase stabilizer. A gas detection test reveals that WO3 can detect acetone, butanol, ethanol, and gasoline. This is the first study to report this capability of WO3.
- [Korean]
- Recent Development in Fabrication and Control of Layered-Double Hydroxide Nanostructures
- Chan-Woo Jeon, Il-Kyu Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):514-522. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.514
- 1,759 View
- 24 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Layered-double hydroxide (LDH)-based nanostructures offer the two-fold advantage of being active catalysts with incredibly large specific surface areas. As such, they have been studied extensively over the last decade and applied in roles as diverse as light source, catalyst, energy storage mechanism, absorber, and anion exchanger. They exhibit a unique lamellar structure consisting of a wide variety of combinations of metal cations and various anions, which determine their physical and chemical performances, and make them a popular research topic. Many reviewed papers deal with these unique properties, synthetic methods, and applications. Most of them, however, are focused on the form-factor of nanopowder, as well as on the control of morphologies via one-step synthetic methods. LDH nanostructures need to be easy to control and fabricate on rigid substrates such as metals, semiconductors, oxides, and insulators, to facilitate more viable applications of these nanostructures to various solid-state devices. In this review, we explore ways to grow and control the various LDH nanostructures on rigid substrates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of Domestic Research Trends on Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) Materials: Based on Research Articles in Korean Citation Index (KCI)
Seon Yong Lee, YoungJae Kim, Young Jae Lee
Economic and Environmental Geology.2023; 56(1): 23. CrossRef
- Review of Domestic Research Trends on Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) Materials: Based on Research Articles in Korean Citation Index (KCI)
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


