Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Comparison Study of Compact Titanium Oxide (c-TiO2) Powder Electron Transport Layer Fabrication for Carbon Electrode-based Perovskite Solar Cells
- Chae Young Woo, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):297-302. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.297
- 820 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
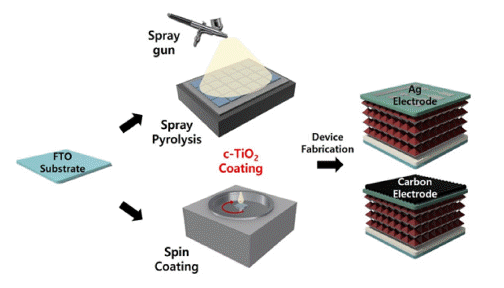
PDF This study compares the characteristics of a compact TiO2 (c-TiO2) powdery film, which is used as the electron transport layer (ETL) of perovskite solar cells, based on the manufacturing method. Additionally, its efficiency is measured by applying it to a carbon electrode solar cell. Spin-coating and spray methods are compared, and spraybased c-TiO2 exhibits superior optical properties. Furthermore, surface analysis by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) exhibits the excellent surface properties of spray-based TiO2. The photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) is 14.31% when applied to planar perovskite solar cells based on metal electrodes. Finally, carbon nanotube (CNT) film electrode-based solar cells exhibits a 76% PCE compared with that of metal electrodebased solar cells, providing the possibility of commercialization.
- [Korean]
- Partially Dry-Transferred Graphene Electrode with Zinc Oxide Nanopowder and Its Application on Organic Solar Cells
- Yeongsu Jo, Chae Young Woo, Soon Kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):305-310. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.305
- 557 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
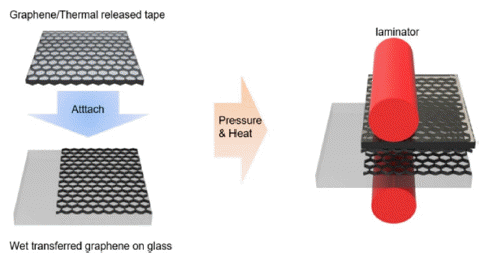
PDF In this study, partially dry transfer is investigated to solve the problem of fully dry transfer. Partially dry transfer is a method in which multiple layers of graphene are dry-transferred over a wet-transferred graphene layer. At a wavelength of 550 nm, the transmittance of the partially dry-transferred graphene is seen to be about 3% higher for each layer than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene. Furthermore, the sheet resistance of the partially drytransferred graphene is relatively lower than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene, with the minimum sheet resistance being 179 Ω/sq. In addition, the fully dry-transferred graphene is easily damaged during the solution process, so that the performance of the organic photovoltaics (OPV) does not occur. In contrast, the best efficiency achievable for OPV using the partially dry-transferred graphene is 2.37% for 4 layers.
- [Korean]
- Flexible Cu-In-Se Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells Based on Nanotube Electrodes
- Jae-Yup Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):45-48. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.45
- 556 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
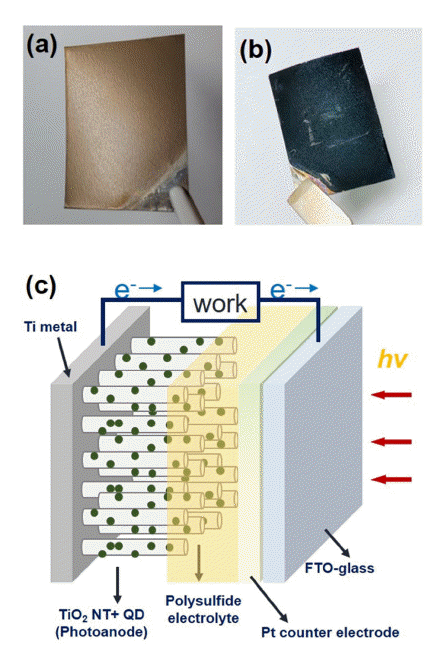
PDF Quantum dots (QDs) are an attractive material for application in solar energy conversion devices because of their unique properties including facile band-gap tuning, a high-absorption coefficient, low-cost processing, and the potential multiple exciton generation effect. Recently, highly efficient quantum dot-sensitized solar cells (QDSCs) have been developed based on CdSe, PbS, CdS, and Cu-In-Se QDs. However, for the commercialization and wide application of these QDSCs, replacing the conventional rigid glass substrates with flexible substrates is required. Here, we demonstrate flexible CISe QDSCs based on vertically aligned TiO2 nanotube (NT) electrodes. The highly uniform TiO2 NT electrodes are prepared by two-step anodic oxidation. Using these flexible photoanodes and semi-transparent Pt counter electrodes, we fabricate the QDSCs and examine their photovoltaic properties. In particular, photovoltaic performances are optimized by controlling the nanostructure of TiO2 NT electrodes.
- [Korean]
- Recent Developments in Synthesis of Colloidal Quantum Dots
- Jae-Yong Jung, Jong-Pal Hong, Young-Kuk Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):346-354. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.346
- 1,936 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
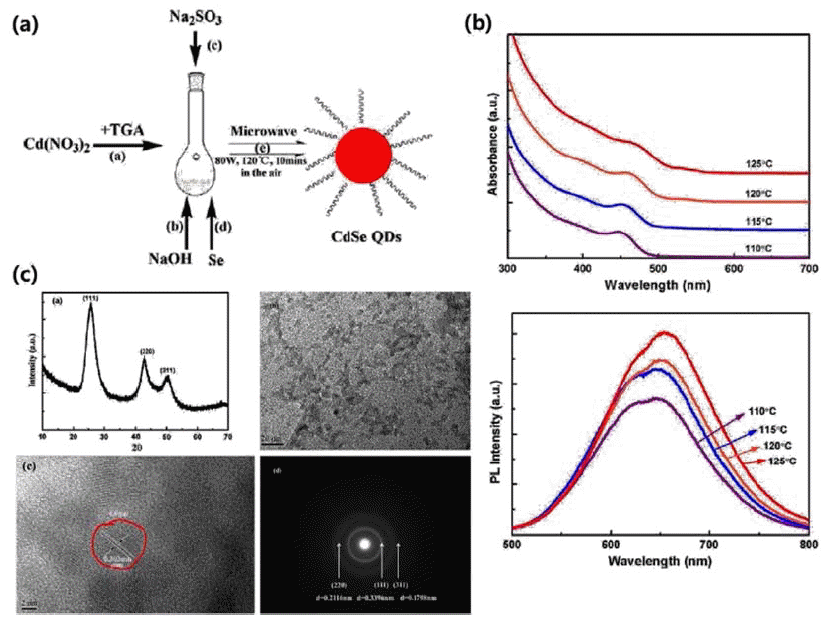
PDF Over the last decade, the study of the synthesis of semiconductor colloidal quantum dots has progressed at a tremendous rate. Colloidal quantum dots, which possess unique spectral-luminescent characteristics, are of great interest in the development of novel materials and devices, which are promising for use in various fields. Several studies have been carried out on hot injection synthesis methods. However, these methods have been found to be unsuitable for large-capacity synthesis. Therefore, this review paper introduces synthesis methods other than the hot injection synthesis method, to synthesize quantum dots with excellent optical properties, through continuous synthesis and large capacity synthesis. In addition, examples of the application of synthesized colloid quantum dots in displays, solar cells, and bio industries are provided.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Nanopowders by Hydrothermal Method and their Application to Dye-sentisized Solar Cell Materials
- JinYoung Lim, Jeongseok Ahn, Jung-Ho Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):309-315. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.309
- 688 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
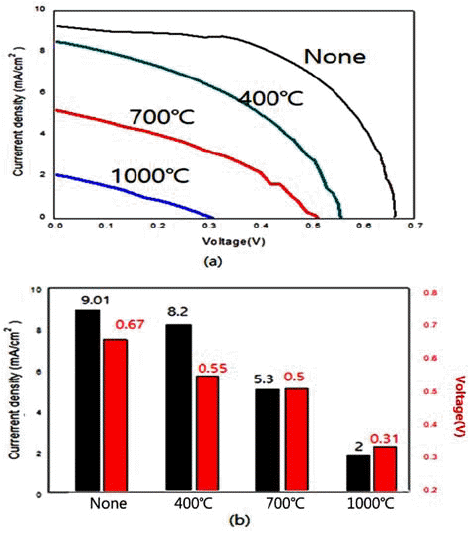
PDF In the present work, we synthesize nano-sized ZnO, SnO2, and TiO2 powders by hydrothermal reaction using metal chlorides. We also examine the energy-storage characteristics of the resulting materials to evaluate the potential application of these powders to dye-sensitized solar cells. The control of processing parameters such as pressure, temperature, and the concentration of aqueous solution results in the formation of a variety of powder morphologies with different sizes. Nano-rod, nano-flower, and spherical powders are easily formed with the present method. Heat treatment after the hydrothermal reaction usually increases the size of the powder. At temperatures above 1000°C, a complete collapse of the shape occurs. With regard to the capacity of DSSC materials, the hydrothermally synthesized TiO2 results in the highest current density of 9.1 mA/cm2 among the examined oxides. This is attributed to the fine particle size and morphology with large specific surface area.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Uniform TiO2 Blocking Layers for Prevention of Electron Recombination in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
- Ju-won Bae, Bon-Ryul Koo, Tae-Kuen Lee, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):1-6. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.1.1
- 756 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
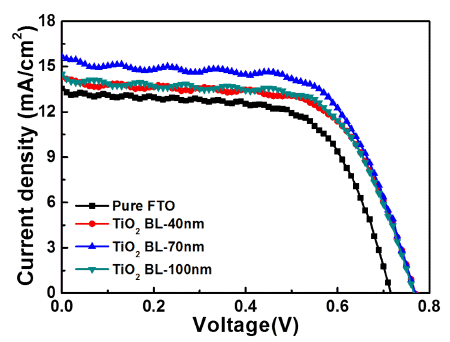
PDF Uniform TiO2 blocking layers (BLs) are fabricated using ultrasonic spray pyrolysis deposition (USPD) method. To improve the photovoltaic performance of dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs), the BL thickness is controlled by using USPD times of 0, 20, 60, and 100 min, creating TiO2 BLs of 0, 40, 70, and 100 nm, respectively, in average thickness on fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) glass. Compared to the other samples, the DSSC containing the uniform TiO2 BL of 70 nm in thickness shows a superior power conversion efficiency of 7.58±0.20% because of the suppression of electron recombination by the effect of the optimized thickness. The performance improvement is mainly attributed to the increased open-circuit voltage (0.77±0.02 V) achieved by the increased Fermi energy levels of the working electrodes and the improved short-circuit current density (15.67±0.43 mA/cm2) by efficient electron transfer pathways. Therefore, optimized TiO2 BLs fabricated by USPD may allow performance improvements in DSSCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Flexible Dye-sensitized Solar Cell Using Titanium Gel at Low Temperature
Seung Hwan Ji, Hyunsu Park, Doyeon Kim, Do Hyung Han, Hye Won Yun, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2019; 29(3): 183. CrossRef - Surface tailoring of zinc electrodes for energy storage devices with high-energy densities and long cycle life
Geon-Hyoung An, SeungNam Cha, Jung Inn Sohn
Applied Surface Science.2019; 467-468: 1157. CrossRef - Crystallinity Control Effects on Vanadium Oxide Films for Enhanced Electrochromic Performances
Kue-Ho Kim, Ju-Won Bae, Tae-Kuen Lee, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2019; 29(6): 385. CrossRef
- Flexible Dye-sensitized Solar Cell Using Titanium Gel at Low Temperature
- [Korean]
- Spindle-shaped Fe2O3 Nanoparticle Coated Carbon Nanofiber Composites for Low-cost Dye-sensitized Solar Cells
- Dong-Hyeun Oh, HyeLan An, Bon-Ryul Koo, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):95-101. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.95
- 1,044 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
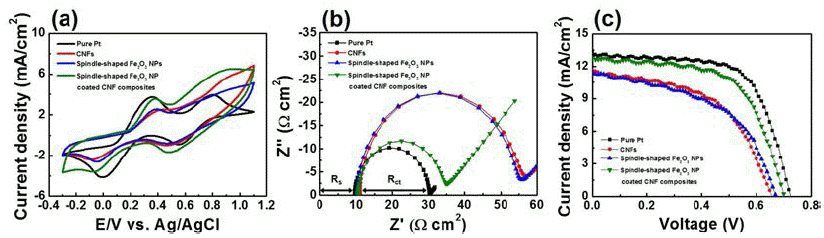
PDF Carbon nanofiber (CNF) composites coated with spindle-shaped Fe2O3 nanoparticles (NPs) are fabricated by a combination of an electrospinning method and a hydrothermal method, and their morphological, structural, and chemical properties are measured by field-emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, Xray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. For comparison, CNFs and spindle-shaped Fe2O3 NPs are prepared by either an electrospinning method or a hydrothermal method, respectively. Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) fabricated with the composites exhibit enhanced open circuit voltage (0.70 V), short-circuit current density (12.82 mA/cm2), fill factor (61.30%), and power conversion efficiency (5.52%) compared to those of the CNFs (0.66 V, 11.61 mA/cm2, 51.96%, and 3.97%) and spindle-shaped Fe2O3 NPs (0.67 V, 11.45 mA/cm2, 50.17%, and 3.86%). This performance improvement can be attributed to a synergistic effect of a superb catalytic reaction of spindle-shaped Fe2O3 NPs and efficient charge transfer relative to the one-dimensional nanostructure of the CNFs. Therefore, spindle-shaped Fe2O3-NPcoated CNF composites may be proposed as a potential alternative material for low-cost counter electrodes in DSSCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ni Nanoparticles-Graphitic Carbon Nanofiber Composites for Pt-Free Counter Electrode in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Dong-Hyeun Oh, Bon-Ryul Koo, Yu-Jin Lee, HyeLan An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2016; 26(11): 649. CrossRef
- Ni Nanoparticles-Graphitic Carbon Nanofiber Composites for Pt-Free Counter Electrode in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
- [Korean]
- Characterization of Films Sputtered with the Cu-Ga Target Prepared by the Cold Spray Process
- Youngji Cho, Jung Ho Yoo, Jun-Mo Yang, Dong-Yong Park, Jong-Kyun Kim, Gang-Bo Choi, Jiho Chang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):21-25. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.21
- 559 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
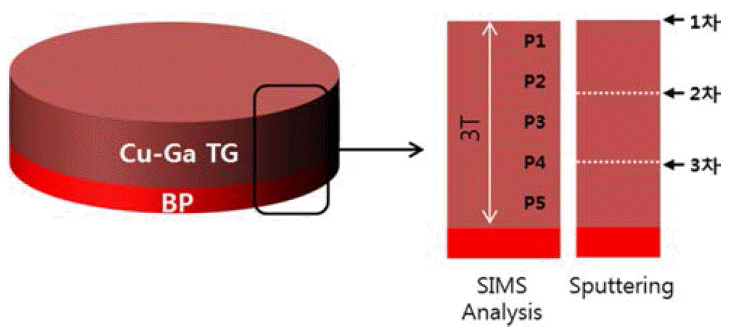
PDF The microstructural properties and electrical characteristics of sputtering films deposited with a Cu-Ga target are analyzed. The Cu-Ga target is prepared using the cold spray process and shows generally uniform composition distributions, as suggested by secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS) data. Characteristics of the sputtered Cu-Ga films are investigated at three positions (top, center and bottom) of the Cu-Ga target by X-ray diffraction (XRD), SIMS, 4-point probe and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis methods. The results show that the Cu-Ga films are composed of hexagonal and unknown phases, and they have similar distributions of composition and resistivity at the top, center, and bottom regions of the Cu-Ga target. It demonstrates that these films have uniform properties regardless of the position on the Cu-Ga target. In conclusion, the cold spray process is expected to be a useful method for preparing sputter targets.
- [Korean]
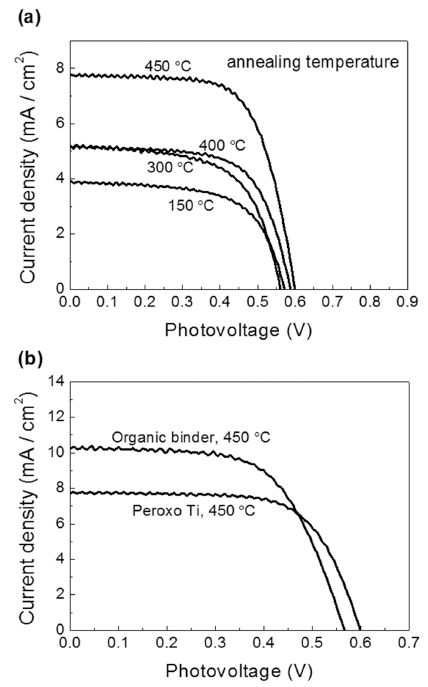
- The Preparation of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Paste Used the Peroxo Titanium Complex and Characteristics by Annealing Temperature
- Hyunsu Park, Soyeong Joo, Joon-Phil Choi, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):396-402. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.396
- 1,008 View
- 6 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The organic binder-free paste for dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC) has been investigated using peroxo titanium complex. The crystal structure of TiO2 nanoparticles, morphology of TiO2 film and electrical properties are analyzed by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Electrochemical Impedance Spectra (EIS), and solar simulator. The synthesized TiO2 nanopowders by the peroxo titanium complex at 150, 300, 400°C, and 450°C have anatase phase and average crystal sizes are calculated to be 4.2, 13.7, 16.9, and 20.9 nm, respectively. The DSSC prepared by the peroxo titanium complex binder have higher Voc and lower Jsc values than that of the organic binder. It can be attributed to improvement of sintering properties of TCO/TiO2 and TiO2/TiO2 interface and to formation of agglomerate by the nanoparticles. As a result, we have investigated the organic binder-free paste and 3.178% conversion efficiency of the DSSC at 450°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Eco-Friendly Ag Embedded Peroxo Titanium Complex Solution Based Thin Film and Electrical Behaviors of Resistive Random Access Memory
Won Jin Kim, Jinho Lee, Ryun Na Kim, Donghee Lee, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2024; 34(3): 152. CrossRef - Development of eco-friendly thin film manufacturing process using poeroxo titanium complex solution and potential for resistive random access memory
Jinho Lee, Ryun Na Kim, Kee-Ryung Park, Woo-Byoung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2021; 562: 150170. CrossRef - Preparation of ultra-thin TiO2 shell by peroxo titanium complex (PTC) solution-based green surface modification, and photocatalytic activity of homo-core/shell TiO2
Jinho Lee, Jiyong Hwang, Hyunsu Park, Tohru Sekino, Woo-Byoung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2021; 540: 148399. CrossRef - Effects of Annealing Temperature on the Crystal Structure, Morphology, and Optical Properties of Peroxo-Titanate Nanotubes Prepared by Peroxo-Titanium Complex Ion
Hyunsu Park, Tomoyo Goto, Sunghun Cho, Soo Wohn Lee, Masato Kakihana, Tohru Sekino
Nanomaterials.2020; 10(7): 1331. CrossRef - Study on thermal behavior of Ammonium Hexafluofide Titanate for Synthesis of TiO2 Powders
Duk-Hee Lee, Jae-Ryang Park, Chan-Gi Lee, Kyung-Soo Park, Hyeon-Mo Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(5): 353. CrossRef
- Development of Eco-Friendly Ag Embedded Peroxo Titanium Complex Solution Based Thin Film and Electrical Behaviors of Resistive Random Access Memory
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Highly Dispersible Metal Nanoparticles in P3HT:PCBM Layers and Their Effects on the Performance of Polymer Solar Cells
- Min-Ji Kim, Gyu-Chae Choi, Young-Kuk Kim, Yang-Do Kim, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):179-184. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.179

- 479 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, we prepare polymer solar cells incorporating organic ligand-modified Ag nanoparticles (OAgNPs) highly dispersed in the P3HT:PCBM layer. Ag nanoparticles decorated with water-dispersible ligands (WAgNPs) were also utilized as a control sample. The existence of the ligands on the Ag surface was confirmed by FTIR spectra. Metal nanoparticles with different surface chemistries exhibited different dispersion tendencies. O-AgNPs were highly dispersed even at high concentrations, whereas W-AgNPs exhibited significant aggregation in the polymer layer. Both dispersion and blending concentration of the Ag nanoparticles in P3HT:PCBM matrix had critical effects on the device performance as well as light absorption. The significant changes in short-circuit current density (JSC) of the solar cells seemed to be related to the change in the polymer morphology according to the concentration of AgNPs introduced. These findings suggested the importance of uniform dispersion of plasmonic metal nanoparticles and their blending concentration conditions in order to boost the solar cell performance.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


