Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Electrochemical Properties of Ball-milled Tin-Graphite Composite Anode Materials for Lithium-Ion Battery
- Tae-Hui Lee, Hyeon-A Hong, Kwon-Koo Cho, Yoo-Young Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):462-469. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.462

- 1,204 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tin/graphite composites are prepared as anode materials for Li-ion batteries using a dry ball-milling process. The main experimental variables in this work are the ball milling time (0–8 h) and composition ratio (tin:graphite=5:95, 15:85, and 30:70 w/w) of graphite and tin powder. For comparison, a tin/graphite composite is prepared using wet ball milling. The morphology and structure of the different tin/graphite composites are investigated using X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and scanning and transmission electron microscopy. The electrochemical properties of the samples are also examined. The optimal dry ball milling time for the uniform mixing of graphite and tin is 6 h in a graphite-30wt.%Sn sample. The electrode prepared from the composite that is dry-ballmilled for 6 h exhibits the best cycle performance (discharge capacity after 50th cycle: 308 mAh/g and capacity retention: 46%). The discharge capacity after the 50th cycle is approximately 112 mAh/g, higher than that when the electrode is composed of only graphite (196 mAh/g after 50th cycle). This result indicates that it is possible to manufacture a tin/graphite composite anode material that can effectively buffer the volume change that occurs during cycling, even using a simple dry ball-milling process.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Phosphorus Addition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Low Alloy Steel
- Yoo-Young Kim, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):31-36. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.31

- 809 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Phosphorus is an element that plays many important roles in powder metallurgy as an alloy element. The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence of phosphorus addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of sintered low-alloy steel. The sintered low-alloy steels Fe-0.6%C-3.89%Ni-1.95%Cu-1.40%Mo-xP (x=0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20%) were manufactured by compacting at 700 MPa, sintering in H2-N2 at 1260 °C, rapid cooling, and low-temperature tempering in Ar at 160 °C. The microstructure, pore, density, hardness, and transverse rupture strength (TRS) of the sintered low-alloy steels were evaluated. The hardness increased as the phosphorus content increased, whereas the density and TRS showed maximum values when the content of P was 0.05%. Based on microstructure observation, the phase of the microstructure changed from bainite to martensite as the content of phosphorus is increased. Hence, the most appropriate addition of phosphorus in this study was 0.05%.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A new strategy for metal additive manufacturing using an economical water-atomized iron powder for laser powder bed fusion
Taehyeob Im, Kopila Gurung, Sebastian Meyers, Antonio Cutolo, Huengseok Oh, Jai-Sung Lee, Brecht Van Hooreweder, Caroline Sunyong Lee
Journal of Materials Processing Technology.2022; 308: 117705. CrossRef
- A new strategy for metal additive manufacturing using an economical water-atomized iron powder for laser powder bed fusion
- [Korean]
- Effect of Single and Dual Doping of Rare Earth Metal Ce and Nd Elements on Electrochemical Properties of LiNi0.83 Co0.11Mn0.06O2 Cathode Lithium-ion Battery Material
- Yoo-Young Kim, Jong-Keun Ha, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):49-57. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.49
- 2,009 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
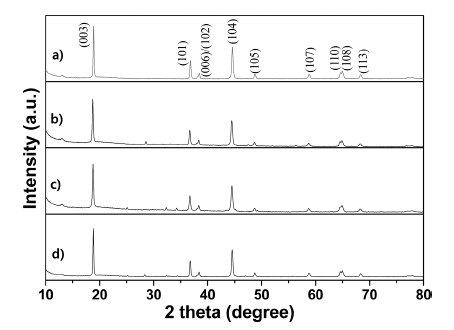
PDF Layered LiNi0.83Co0.11Mn0.06O2 cathode materials single- and dual-doped by the rare-earth elements Ce and Nd are successfully fabricated by using a coprecipitation-assisted solid-phase method. For comparison purposes, nondoping pristine LiNi0.83Co0.11Mn0.06O2 cathode material is also prepared using the same method. The crystal structure, morphology, and electrochemical performances are characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) mapping, and electrochemical techniques. The XRD data demonstrates that all prepared samples maintain a typical α-NaFeO2-layered structure with the
R-3m -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Numerical approach for lithium-ion battery performance considering various cathode active material composition for electric vehicles using 1D simulation
Heewon Choi, Nam-gyu Lim, Seong Jun Lee, Jungsoo Park
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology.2021; 35(6): 2697. CrossRef - Synthesis of CeVO4-V2O5 nanowires by cation-exchange method for high-performance lithium-ion battery electrode
Xueliu Xu, Shiying Chang, Taofang Zeng, Yidan Luo, Dong Fang, Ming Xie, Jianhong Yi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2021; 887: 161237. CrossRef
- Numerical approach for lithium-ion battery performance considering various cathode active material composition for electric vehicles using 1D simulation
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of TiO2 Nanowires by Thermal Oxidation of Titanium Alloy Powder
- Yoo-Young Kim, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):48-53. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.1.48

- 742 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF One-dimensional rutile TiO2 is an important inorganic compound with applicability in sensors, solar cells, and Li-based batteries. However, conventional synthesis methods for TiO2 nanowires are complicated and entail risks of environmental contamination. In this work, we report the growth of TiO2 nanowires on a Ti alloy powder (Ti-6wt%Al-4wt%V, Ti64) using simple thermal oxidation under a limited supply of O2. The optimum condition for TiO2 nanowire synthesis is studied for variables including temperature, time, and pressure. TiO2 nanowires of ~5 μm in length and 100 nm in thickness are richly synthesized under the optimum condition with single-crystalline rutile phases. The formation of TiO2 nanowires is greatly influenced by synthesis temperature and pressure. The synthesized TiO2 nanowires are characterized using field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM).
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Fe3O4/Fe/Graphene nanocomposite powder by Electrical Wire Explosion in Liquid Media and its Electrochemical Properties
- Yoo-Young Kim, Ji-Seub Choi, Hoi-Jin Lee, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):308-314. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.308
- 1,022 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
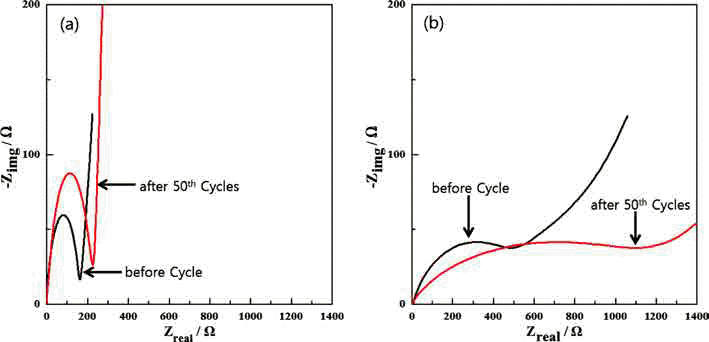
PDF Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is synthesized by electrical wire explosion of Fe wire and dispersed graphene in deionized water at room temperature. The structural and electrochemical characteristics of the powder are characterized by the field-emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, field-emission transmission electron microscopy, cyclic voltammetry, and galvanometric discharge-charge method. For comparison, Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposites are fabricated under the same conditions. The Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite particles, around 15-30 nm in size, are highly encapsulated in a graphene matrix. The Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder exhibits a high initial charge specific capacity of 878 mA/g and a high capacity retention of 91% (798 mA/g) after 50 cycles. The good electrochemical performance of the Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is clearly established by comparison of the results with those obtained for Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite powder and is attributed to alleviation of volume change, good distribution of electrode active materials, and improved electrical conductivity upon the addition of graphene.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
Kyunbae Lee, Joonsik Lee, Byung Mun Jung, Byeongjin Park, Taehoon Kim, Sang Bok Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 478: 733. CrossRef
- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Carbon-coated Tin Nano-powders by Electrical Wire Explosion in Liquid Media and its Electrochemical Properties
- Yoo-Young Kim, Ju-Suck Song, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):317-324. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.317
- 999 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
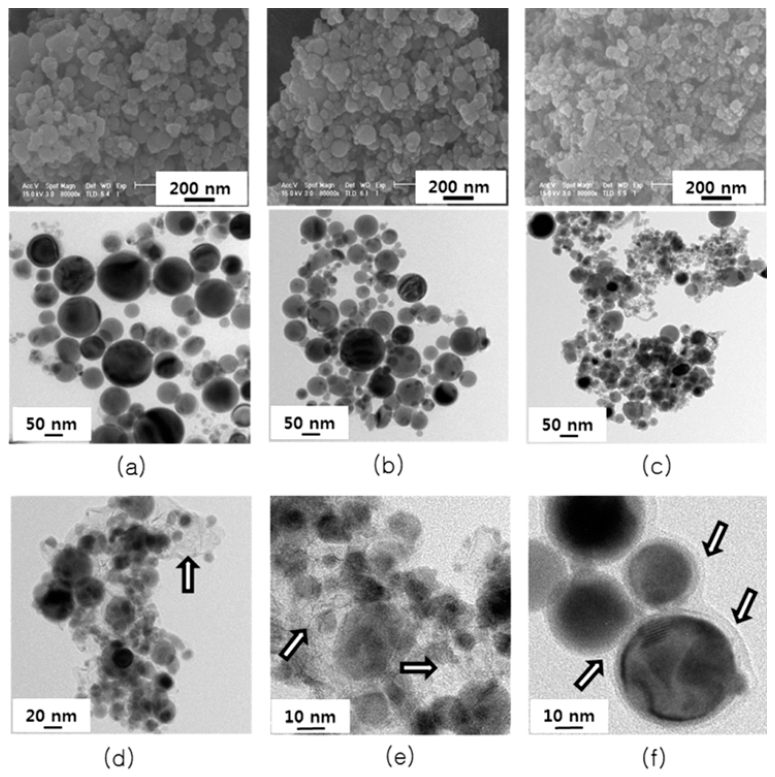
PDF Tin is one of the most promising anode materials for next-generation lithium-ion batteries with a high energy density. However, the commercialization of tin-based anodes is still hindered due to the large volume change (over 260%) upon lithiation/delithiation cycling. To solve the problem, many efforts have been focused on enhancing structural stability of tin particles in electrodes. In this work, we synthesize tin nano-powders with an amorphous carbon layer on the surface and surroundings of the powder by electrical wire explosion in alcohol-based liquid media at room temperature. The morphology and microstructures of the powders are characterized by scanning electron microscopy, Xray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The electrochemical properties of the powder for use as an anode material for lithium-ion battery are evaluated by cyclic voltammetry and a galvanometric dischargecharge method. It is shown that the carbon-coated tin nano-powders prepared in hexanol media exhibit a high initial charge specific capacity of 902 mAh/g and a high capacity retention of 89% after 50 cycles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimization of carbon coating thickness to prevent crack generation in Sn nanoparticles during charge/discharge process and their electrochemical properties
Ji-Seub Choi, Yeon-Ju Lee, Hoi-Jin Lee, Gyu-Bong Cho, Jai-Won Byeon, Hyo-Jun Ahn, Ki-Won Kim, Jou-Hyeon Ahn, Kwon-Koo Cho
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2020; 843: 155892. CrossRef - Fabrication of multilayer graphene-encapsulated Sn/SnO2 nanocomposite as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries and its electrochemical properties
Ju-Seok Song, Gyu-Bong Cho, Ki-Won Kim, Hyo-Jun Ahn, Hye-Sung Kim, Jou-Hyeon Ahn, Kwon-Koo Cho
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 736. CrossRef
- Optimization of carbon coating thickness to prevent crack generation in Sn nanoparticles during charge/discharge process and their electrochemical properties
- [Korean]
- Shape Control of Anodic Aluminum Oxide and Effect as Support of Silicon Powder Electrode
- Ju-Seok Song, Jong-Keun Ha, Yoo-Young Kim, Dong-Kyu Park, In-Shup Ahn, Jou-Hyeon Ahn, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):240-246. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.240

- 752 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) has been widely used for the development and fabrication of nano-powder with various morphologies such as particle, wire, rod, and tube. So far, many researchers have reported about shape control and fabrication of AAO films. However, they have reported on the shape control with different diameter and length of anodic aluminum oxide mainly. We present a combined mild-hard (or hard-mild) anodization to prepare shape-controlled AAO films. Two main parameters which are combination mild-hard (or hard-mild) anodization and run-time of voltage control are applied in this work. The voltages of mild and hard anodization are respectively 40 and 80 V. Anodization was conducted on the aluminum sheet in 0.3 mole oxalic acid at 4°C. AAO films with morphologies of varying interpore distance, branch-shaped pore, diameter-modulated pore and long funnel-shaped pore were fabricated. Those shapes will be able to apply to fabricate novel nano-materials with potential application which is especially a support to prevent volume expansion of inserted active materials, such as metal silicon or tin powder, in lithium ion battery. The silicon powder electrode using an AAO as a support shows outstanding cycle performance as 1003 mAh/g up to 200 cycles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nano silicon encapsulated in modified copper as an anode for high performance lithium ion battery
Jong-Keun Ha, Anupriya K. Haridas, Gyu-Bong Cho, Hyo-Jun Ahn, Jou-Hyeon Ahn, Kwon-Koo Cho
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 307. CrossRef
- Nano silicon encapsulated in modified copper as an anode for high performance lithium ion battery
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of LiNiO2 using NiSO4 Recovered from NCM (Li[Ni,Co,Mn]O2) Secondary Battery Scraps and Its Electrochemical Properties
- Yong-Gyu Kwag, Mi-So Kim, Yoo-Young Kim, Im-Sic Choi, Dong-Kyu Park, In-Sup Ahn, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):286-293. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.286

- 912 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The electrochemical properties of cells assembled with the LiNiO2 (LNO) recycled from cathode materials of waste lithium secondary batteries (Li[Ni,Co,Mn]O2), were evaluated in this study. The leaching, neutralization and solvent extraction process were applied to produce high-purity NiSO4 solution from waste lithium secondary batteries. High-purity NiO powder was then fabricated by the heat-treatment and mixing of the NiSO4 solution and H2C2O4. Finally, LiNiO2 as a cathode material for lithium ion secondary batteries was synthesized by heat treatment and mixing of the NiO and Li2CO3 powders. We assembled the cells using the LiNiO2 powders and evaluated the electrochemical properties. Subsequently, we evaluated the recycling possibility of the cathode materials for waste lithium secondary battery using the processes applied in this work.
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Sintering Behavior of T42 High Speed Steel by Powder Injection Molding (PIM) Process
- Dong-Wook Park, Hye-Seong Kim, Young-Sam Kwon, Kwon-Koo Cho, Su-Gun Lim, In-Shup Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(2):117-121.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.2.117

- 840 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tool steels serve a large range of applications including hot and cold workings of metals and injection mouldings of plastics or light alloys. The high speed steels (HSS) are specifically used as cutting tools and wear parts because it has high strength, wear resistance and hardness along with appreciable toughness and fatigue resistance. From the view of HSS microstructure, it can be described as metallic matrix composites formed by a ferrous with a dispersion of hard and wear resistant carbides. The experimental specimens were manufactured using the PIM with T42 powders (50~80 vol.%) and polymer (20~50 vol.%). The green parts were debinded in n-hexane solution at 60°C for 8 hours and thermal debinded at an N_2-H_2 mixed gas atmosphere for 8 hours. Specimens were sintered in high vacuum (10-5 Torr) and various temperatures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects Of Process Parameters On Cu Powder Synthesis Yield And Particle Size In A Wet-Chemical Process
Y.M. Shin, J.-H. Lee
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2015; 60(2): 1247. CrossRef
- Effects Of Process Parameters On Cu Powder Synthesis Yield And Particle Size In A Wet-Chemical Process
- [Korean]
- The Characteristic Changes of Sintered WC-10Co Fabricated by PIM Method with Different Carbon Content
- Sang-Dae Kang, Dong-Wook Park, Young-Sam Kwon, Kwon-Koo Cho, In-Shup Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(3):262-268.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.3.262

- 450 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to investigate the microstructure and mechanical properties of WC-10 wt% Co insert tool alloy fabricated by PIM (Powder Injection Molding) process, the feedstock of WC-10 wt% and wax used as a kind of binder were mixed together by two blade mixer. After injection molding, the debinding process was carried out by two-steps. First, solvent extraction, in which the binder was eliminated by putting the specimen into normal hexane for 24 hrs at 60°C, and subsequently thermal debinding which was conducted at 260°C and 480°C for 6 hrs in the mixed gas of H_2/N_2, respectively. Meantime, in order to compensate the decarburization due to hydrogen, 1.2~1.8% of carbon was added to ensure the integrity of the phase. Finally, the specimens were sintered in vacuum under different temperatures, and the relative density of 99.8% and hardness of 2100 Hv can be achieved when sintered at 1380°C, even the TRS is lower than the conventional sintering process.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Growth Behavior of TiO2 Nanotube Arrays by Anodic Oxidation Method
- Seon-Min Kim, Ki-Won Kim, Kwang-Sun Ryu, Yoo-Young Kim, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(1):56-63.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.1.056

- 549 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Recently, TiO_2 nanotubes have considerably researched because of their novel application about photocatalysis, dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs), lithium ion battery, etc. In this work, self-standing TiO_2 nanotube arrays were fabricated by anodic oxidation method using pure Ti foil as a working electrode in ethylene glycole with 0.3M NH_4F + 2%H_2O. Growth behavior of TiO_2 nanotube arrays was compared according to temperature, voltage and time. The morphology, structure and crystalline of anodized TiO_2 nanotube arrays were observed by FE-SEM (field emission scanning electron microscope) and XRD (X-ray diffraction).
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Growth of Ni Nanowires by using Anodic Aluminum Oxide(AAO) Template via Electrochemical Deposition
- Seong-Ju Sim, Kwon-Koo Cho, Yoo-Young Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(1):49-55.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.1.049

- 944 View
- 7 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ni nanowires were fabricated using anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) membrane as a template by electrochemical deposition. The nanowires were formed within the walls of AAO template with 200 nm in pore diameter. After researching proper voltage and temperature for electrochemical deposition, the length of Ni nanowires was controlled by deposition time and the supply of electrolyte. The morphology and microstructure of Ni nanowires were investigated by field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SE), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscope (TEM).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Electrocrystallization of Metals in Channels of Porous Films of Anodic Aluminum Oxide: The Real Template Structure and the Quantitative Model of Electrodeposition
A. A. Noyan, I. V. Kolesnik, A. P. Leont’ev, K. S. Napol’skii
Russian Journal of Electrochemistry.2023; 59(7): 489. CrossRef - Electrocrystallization of Metals in Channels of Porous Films of Anodic Aluminum Oxide: The Real Template Structure and the Quantitative Model of Electrodeposition
A. A. Noyan, I. V. Kolesnik, A. P. Leont’ev, K. S. Napol’skii
Электрохимия.2023; 59(7): 378. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of Nickel Nanowires by an Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template-Based Electrodeposition
Hyo-Ryoung Lim, Yong-Ho Choa, Young-In Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(3): 216. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of Cu Nanowires Using Anodic Alumina Template Based Electrochemical Deposition Method
Young-In Lee, Yong-Ho Choa
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(5): 367. CrossRef
- Electrocrystallization of Metals in Channels of Porous Films of Anodic Aluminum Oxide: The Real Template Structure and the Quantitative Model of Electrodeposition
- [Korean]
- The Microstructural Properties Change Owing to the Sintering Condition of T42 High Speed Steel Produced by Powder Injection Molding Process
- Kyoung-Rok Do, Sung-Hyun Choi, Young-Sam Kwon, Kwon-Koo Cho, In-Shup Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(4):312-318.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.4.312

- 498 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High speed steels (HSS) were used as cutting tools and wear parts, because of high strength, wear resistance, and hardness together with an appreciable toughness and fatigue resistance. Conventional manufacturing process for production of components with HSS was used by casting. The powder metallurgy techniques were currently developed due to second phase segregation of conventional process. The powder injection molding method (PIM) was received attention owing to shape without additional processes. The experimental specimens were manufactured with T42 HSS powders (59 vol%) and polymer (41 vol%). The metal powders were prealloyed water-atomised T42 HSS. The green parts were solvent debinded in normal n-Hexane at 60°C for 24 hours and thermal debinded at N_2-H_2 mixed gas atmosphere for 14 hours. Specimens were sintered in N_2, H_2 gas atmosphere and vacuum condition between 1200 and 1320°C. In result, polymer degradation temperatures about optimum conditions were found at 250°C and 480°C. After sintering at N_2 gas atmosphere, maximum hardness of 310Hv was observed at 1280°C. Fine and well dispersed carbide were observed at this condition. But relative density was under 90%. When sintering at H_2 gas atmosphere, relative density was observed to 94.5% at 1200°C. However, the low hardness was obtained due to decarbonization by hydrogen. In case of sintering at the vacuum of 10-5 torr at temperature of 1240°C, full density and 550Hv hardness were obtained without precipitation of MC and M_6C in grain boundary.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Iron-Molybdenum Alloyed Nanoparticle and Nanowire using Chemical Vapor Condensation(CVC)
- Jong-Keun Ha, Kwon-Koo Cho, Ki-Won Kim, Kwang-Sun Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(3):223-229.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.3.223

- 441 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Iron(Fe)-Molybdenum(Mo) alloyed nanoparticles and nanowires were produced by the chemical vapor condensation(CVC) process using the pyrolysis of iron pentacarbonyl(Fe(CO)_5) and Molybdenum hexacarbonyl(Mo(CO)_6). The influence of CVC parameter on the formation of nanoparticle, nanowire and size control was studied. The size of Fe-Mo alloyed nanoparticles can be controlled by quantity of gas flow. Also, Fe-Mo alloyed nanowires were produced by control of the work chamber pressure. Moreover, we investigated close correlation of size and morphology of Fe-Mo nanoparticles and nanowires with atomic quantity of inflow precursor into the electric furnace as the quantitative analysis. Obtained nanoparticles and nanowires were investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of TiO2 Nanotube Arrays by Anodic Oxidation Method and its Photoelectrochemical Properties
- Seon-Min Kim, Kwon-Koo Cho, Yeong-Jin Choe, Ki-Won Kim, Kwang-Sun Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(3):216-222.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.3.216

- 815 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Self-standing TiO_2 nanotube arrays were fabricated by potentiostatic anodic oxidation method using pure Ti foil as a working electrode and ethylene glycol solution as electrolytes with small addition of NH_4F and H_2O. The influences of anodization temperature and time on the morphology and formation of TiO_2 nanotube arrays were investigated. The fabricated TiO_2 nanotube arrays were applied as a photoelectrode to dye-sensitized solar cells. Regardless of anodizing temperature and time, the average diameter and wall thickness of TiO_2 nanotube show a similar value, whereas the thickness show a different trend with reaction temperature. The thickness of TiO_2 nanotube arrays anodized at 20°C and 30°C was time-dependent, but on the other hand its at 10°C are independent of anodization time. The conversion efficiency is low, which is due to a morphology breaking of the TiO_2 nanotube arrays in manufacturing process of photoelectrode.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The growth and morphology of copper phthalocyanine on TiO2 nanotube arrays
Sung Ha Ju, Sanghyun Han, Jeong Soo Kim
Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry.2013; 19(1): 272. CrossRef - Characteristics of Porous Titanium Fabricated by Space-holder Method using NaCl
Byoung-Hwi Son, Jae-Geun Hong, Yong-Taek Hyun, Seung-Eon Kim, Seok-Choun Bae
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(6): 488. CrossRef - Investigation About Surface Microstructure of Aluminum with Change of Voltage, a Period of Treatment and Density of Electrolyte in Micro-Arc Oxidation Treatment
In-Chul Yeo, In-Cheol Kang
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(6): 575. CrossRef
- The growth and morphology of copper phthalocyanine on TiO2 nanotube arrays
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


