Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- A Review of Inorganic Solid Electrolytes for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries: Challenges and Progress
- Seul Ki Choi, Jaehun Han, Gi Jeong Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jaewon Choi, MinHo Yang
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):293-301. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00206
- 11,757 View
- 284 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
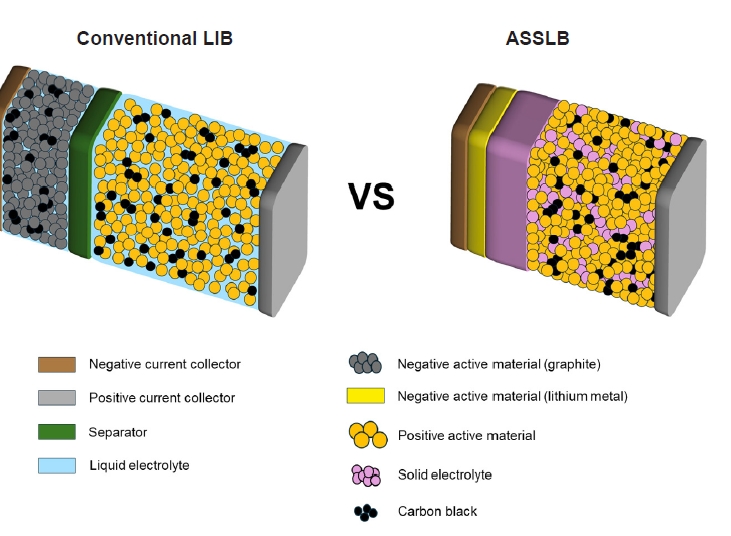
PDF - All-solid-state lithium batteries (ASSLBs) are receiving attention as a prospective next-generation secondary battery technology that can reduce the risk of commercial lithium-ion batteries by replacing flammable organic liquid electrolytes with non-flammable solid electrolytes. The practical application of ASSLBs requires developing robust solid electrolytes that possess ionic conductivity at room temperature on a par with that of organic liquids. These solid electrolytes must also be thermally and chemically stable, as well as compatible with electrode materials. Inorganic solid electrolytes, including oxide and sulfide-based compounds, are being studied as promising future candidates for ASSLBs due to their higher ionic conductivity and thermal stability than polymer electrolytes. Here, we present the challenges currently facing the development of oxide and sulfide-based solid electrolytes, as well as the research efforts underway aiming to resolve these challenges.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A facile synthesis of bulk LiPON in solution for solid-state electrolytes
Osma J. Gomez, Adam Antar, Alex T. Hall, Leopoldo Tapia-Aracayo, Joshua Seo, Nam Kim, Zihan Sun, Ryan Lim, Fu Chen, Yue Li, John Cumings, Gary Rubloff, Sang Bok Lee, David Stewart, Yang Wang
Journal of Materials Chemistry A.2025; 13(34): 28368. CrossRef - Uniform lithium deposition using Cu teepee structures for anode-free lithium metal batteries
Seo Yun Jung, Jaehun Han, Seul Ki Choi, Se Youn Cho, Jong Ho Won, Jaewon Choi, Minho Yang
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 522: 167302. CrossRef - Garnet-type LLZO electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries: Interfaces, conductivity, in-situ processing, and industrial prospects
Kaleab Habtamu Ayalew, Nithyadharseni Palaniyandy, Mkhulu K. Mathe, Phumlani F. Msomi
Chemical Engineering Journal.2025; 524: 168098. CrossRef
- A facile synthesis of bulk LiPON in solution for solid-state electrolytes
- [English]
- Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
- Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):236-242. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00031
- 1,781 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
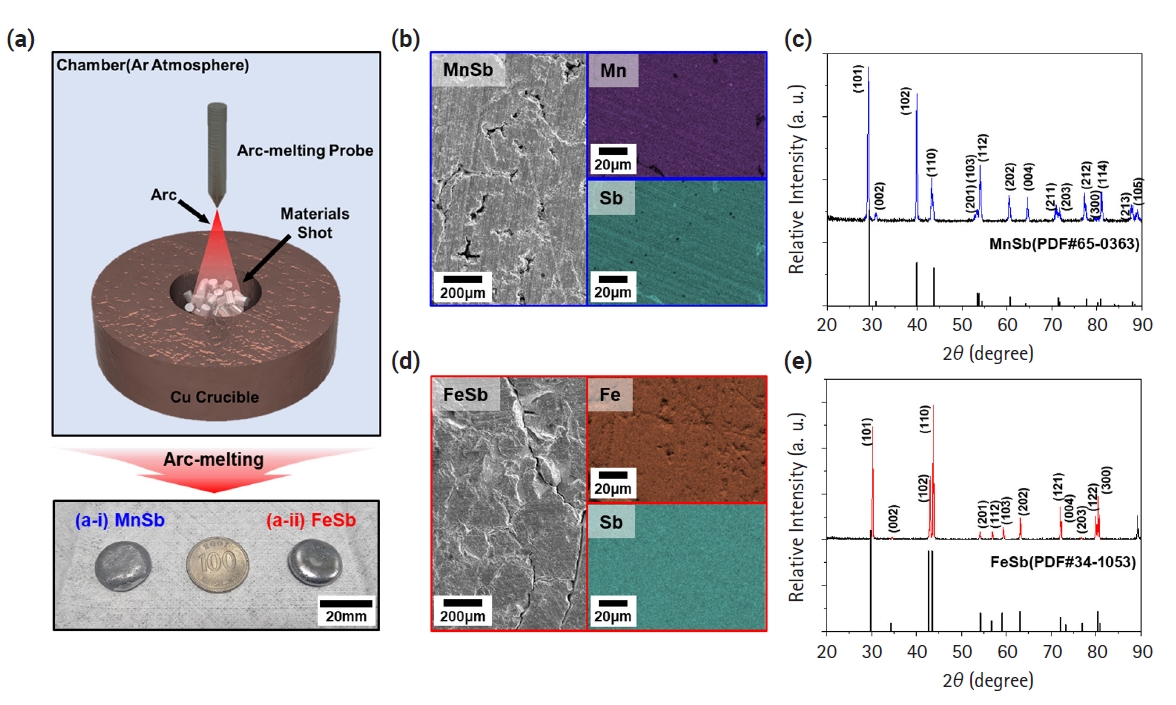
PDF - The development of thermoelectric (TE) materials to replace Bi2Te3 alloys is emerging as a hot issue with the potential for wider practical applications. In particular, layered Zintl-phase materials, which can appropriately control carrier and phonon transport behaviors, are being considered as promising candidates. However, limited data have been reported on the thermoelectric properties of metal-Sb materials that can be transformed into layered materials through the insertion of cations. In this study, we synthesized FeSb and MnSb, which are used as base materials for advanced thermoelectric materials. They were confirmed as single-phase materials by analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns. Based on electrical conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity of both materials characterized as a function of temperature, the zT values of MnSb and FeSb were calculated to be 0.00119 and 0.00026, respectively. These properties provide a fundamental data for developing layered Zintl-phase materials with alkali/alkaline earth metal insertions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Jihun Yu, Kyung Tae Kim
Materials Letters.2025; 381: 137796. CrossRef - Highly deformable and hierarchical 3D composite sponge for versatile thermoelectric energy conversion
Jong Min Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Kwi-Il Park
Applied Surface Science.2025; 692: 162730. CrossRef
- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
- [Korean]
- Effect of Abnormal Grain Growth on Ionic Conductivity in LATP
- Hyungik Choi, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):23-29. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.23
- 2,964 View
- 66 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temperature-dependent microstructural evolution in a compositionally complex solid electrolyte: The role of a grain boundary transition
Shu-Ting Ko, Chaojie Du, Huiming Guo, Hasti Vahidi, Jenna L. Wardini, Tom Lee, Yi Liu, Jingjing Yang, Francisco Guzman, Timothy J. Rupert, William J. Bowman, Shen J. Dillon, Xiaoqing Pan, Jian Luo
Journal of Advanced Ceramics.2025; 14(3): 9221047. CrossRef - Effect of bimodal particle size distribution on Li1.5Al0.5Ti1.5(PO4)3 solid electrolytes: Microstructures and electrochemical properties
Gi Jeong Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Seul Ki Choi, Jong Won Bae, Kun-Jae Lee, Minho Yang
Powder Technology.2025; 466: 121407. CrossRef
- Temperature-dependent microstructural evolution in a compositionally complex solid electrolyte: The role of a grain boundary transition
- [Korean]
- Enhancement of Thermoelectric Performance in Spark Plasma Sintered p-Type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3.0 Compound via Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) Induced Reduction of Lattice Thermal Conductivity
- Soo-Ho Jung, Ye Jin Woo, Kyung Tae Kim, Seungki Jo
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):123-129. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.123
- 1,613 View
- 9 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
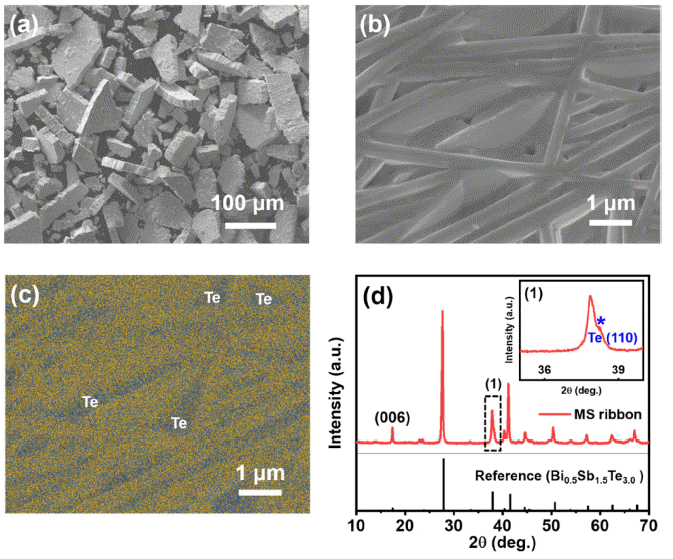
PDF High-temperature and high-pressure post-processing applied to sintered thermoelectric materials can create nanoscale defects, thereby enhancing their thermoelectric performance. Here, we investigate the effect of hot isostatic pressing (HIP) as a post-processing treatment on the thermoelectric properties of
p -type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3.0 compounds sintered via spark plasma sintering. The sample post-processed via HIP maintains its electronic transport properties despite the reduced microstructural texturing. Moreover, lattice thermal conductivity is significantly reduced owing to activated phonon scattering, which can be attributed to the nanoscale defects created during HIP, resulting in an ~18% increase in peakzT value, which reaches ~1.43 at 100°C. This study validates that HIP enhances the thermoelectric performance by controlling the thermal transport without having any detrimental effects on the electronic transport properties of thermoelectric materials.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced Electrical Properties of 3D Printed Bi2Te3-Based Thermoelectric Materials via Hot Isostatic Pressing
Seungki Jo
Ceramist.2025; 28(1): 126. CrossRef - Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef - Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(3): 236. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef
- Enhanced Electrical Properties of 3D Printed Bi2Te3-Based Thermoelectric Materials via Hot Isostatic Pressing
- [Korean]
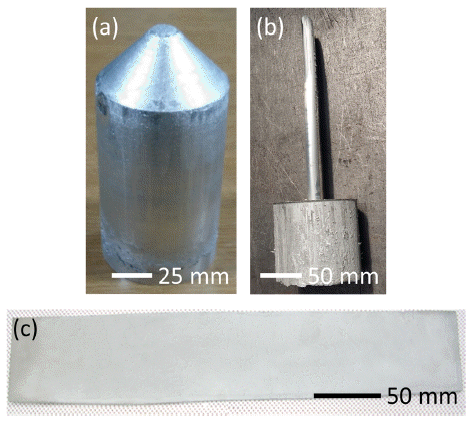
- Development of Aluminum Matrix Composites Containing Nano-carbon Materials
- Jungjoon Kim, Daeyoung Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):253-258. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.253
- 860 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF There is increasing demand for the development of a new material with high strength, high stiffness, and good electrical conductivity that can be used for high-voltage direct current cables. In this study, we develop aluminumbased composites containing C60 fullerenes, carbon nanotubes, or graphene using a powder metallurgical route and evaluate their strength, stiffness, coefficient of thermal expansion, and electrical conductivity. By optimizing the process conditions, a material with a tensile strength of 800 MPa, an elastic modulus of 90 GPa, and an electrical conductivity of 40% IACS is obtained, which may replace iron-core cables. Furthermore, by designing the type and volume fraction of the reinforcement, a material with a tensile strength of 380 MPa, elastic modulus of 80 GPa, and electrical conductivity of 54% IACS is obtained, which may compete with AA 6201 aluminum alloys for use in all-aluminum conductor cables.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synergistic strengthening of aluminum with SiC by grain refinement and dispersion hardening
Kanhu C. Nayak, Juyeon Han, Suwon Park, Miran Joo, Kon‐Bae Lee, Donghyun Bae, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2023; 106(12): 7340. CrossRef - Synergetic effect of milling speed and duration on particle morphology and mechanical properties of nanocrystalline Al matrix containing SiC
K.C. Nayak, J.Y. Han, C.H. Jung, M.R. Joo, K.B. Lee, D.H. Bae, H.J. Choi
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 519. CrossRef
- Synergistic strengthening of aluminum with SiC by grain refinement and dispersion hardening
- [Korean]
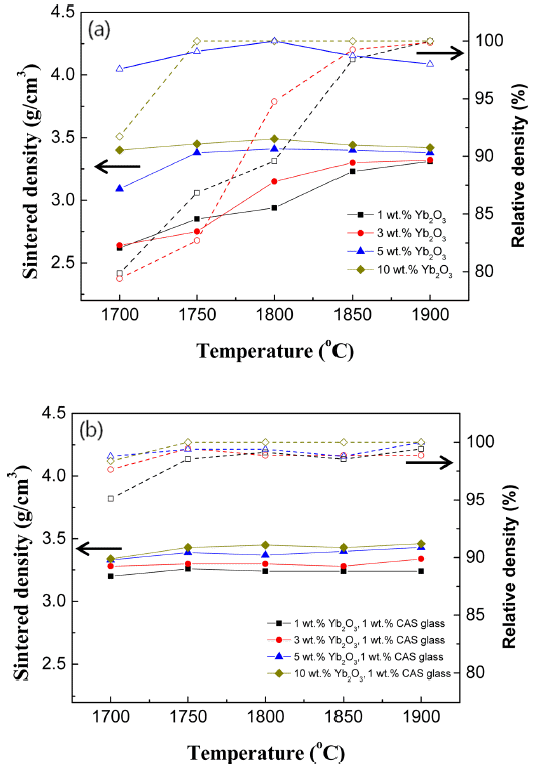
- Effect of Morphological Control of Secondary Phase using Yb2O3 and Ca-Al-Si-O-based Glass on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of AlN
- Dong Kyu Choi, Shi Yeon Kim, Dong Hun Yeo, Hyo Soon Shin, Dae Yong Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):498-502. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.498
- 853 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We investigate the effects of Yb2O3 and calcium aluminosilicate (CAS) glass as sintering additives on the sintering behavior of AlN. The AlN specimens are sintered at temperatures between 1700°C and 1900°C for 2 h in a nitrogen atmosphere. When the Yb2O3 content is low (within 3 wt.%), an isolated shape of secondary phase is observed at the AlN grain boundary. In contrast, when 3 wt.% Yb2O3 and 1 wt.% CAS glass are added, a continuous secondary phase is formed at the AlN grain boundary. The thermal conductivity decreases when the CAS glass is added, but the sintering density does not decrease. In particular, when 10 wt.% Yb2O3 and 1 wt.% CAS glass are added to AlN, the flexural strength is the highest, at 463 MPa. These results are considered to be influenced by changes in the microstructure of the secondary phase of AlN.
- [Korean]
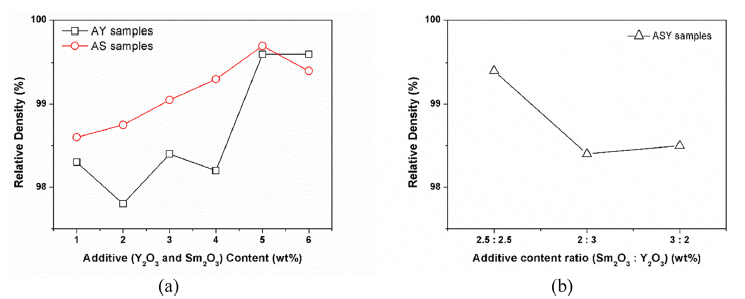
- Effects of Sintering Additives on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of AlN by Pressureless Sintering
- Jin Uk Hwang, So Youn Mun, Sang Yong Nam, Hwan Soo Dow
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):395-404. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.395
- 2,277 View
- 53 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Aluminum nitride (AlN) has excellent electrical insulation property, high thermal conductivity, and a low thermal expansion coefficient; therefore, it is widely used as a heat sink, heat-conductive filler, and heat dissipation substrate. However, it is well known that the AlN-based materials have disadvantages such as low sinterability and poor mechanical properties. In this study, the effects of addition of various amounts (1-6 wt.%) of sintering additives Y2O3 and Sm2O3 on the thermal and mechanical properties of AlN samples pressureless sintered at 1850°C in an N2 atmosphere for a holding time of 2 h are examined. All AlN samples exhibit relative densities of more than 97%. It showed that the higher thermal conductivity as the Y2O3 content increased than the Sm2O3 additive, whereas all AlN samples exhibited higher mechanical properties as Sm2O3 content increased. The formation of secondary phases by reaction of Y2O3, Sm2O3 with oxygen from AlN lattice influenced the thermal and mechanical properties of AlN samples due to the reaction of the oxygen contents in AlN lattice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of YH2 addition on pressureless sintered AlN ceramics
Liang Wang, Wei-Ming Guo, Peng-Fei Sheng, Li-Fu Lin, Xiao Zong, Shang-Hua Wu
Journal of the European Ceramic Society.2023; 43(3): 862. CrossRef
- Effects of YH2 addition on pressureless sintered AlN ceramics
- [Korean]
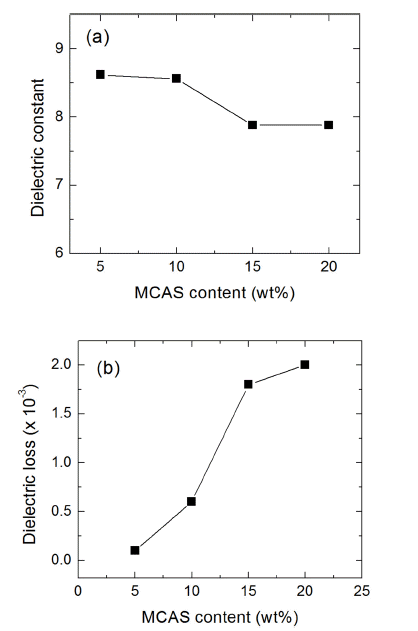
- Effect of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 Glass Additive Content on Properties of Aluminum Nitride Ceramics
- Kyung Min Kim, Su-Hyun Baik, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):494-500. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.494
- 1,464 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, the effect of the content of MgO-CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 (MCAS) glass additives on the properties of AlN ceramics is investigated. Dilatometric analysis and isothermal sintering for AlN compacts with MCAS contents varying between 5 and 20 wt% are carried out at temperatures ranging up to 1600°C. The results showed that the shrinkage of the AlN specimens increases with increasing MCAS content, and that full densification can be obtained irrespective of the MCAS content. Moreover, properties of the AlN-MCAS specimens such as microhardness, thermal conductivity, dielectric constant, and dielectric loss are analyzed. Microhardness and thermal conductivity decrease with increasing MCAS content. An acceptable candidate for AlN application is obtained: an AlN-MCAS composite with a thermal conductivity over 70 W/m·K and a dielectric loss tangent (tan δ) below 0.6 × 10−3, with up to 10 wt% MCAS content.
- [Korean]
- Effects of Morphologies of Carbon Nanomaterials on Conductivity of Composites Containing Copper/Carbon Nanomaterial Hybrid Fillers
- Yeonjoo Lee, Sung-uk Hong, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):435-440. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.435
- 555 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
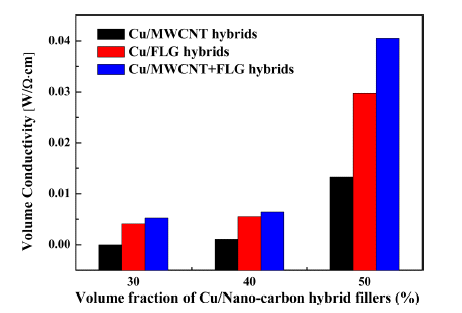
PDF In the present study, we develop a conductive copper/carbon nanomaterial additive and investigate the effects of the morphologies of the carbon nanomaterials on the conductivities of composites containing the additive. The conductive additive is prepared by mechanically milling copper powder with carbon nanomaterials, namely, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and/or few-layer graphene (FLG). During the milling process, the carbon nanomaterials are partially embedded in the surfaces of the copper powder, such that electrically conductive pathways are formed when the powder is used in an epoxy-based composite. The conductivities of the composites increase with the volume of the carbon nanomaterial. For a constant volume of carbon nanomaterial, the FLG is observed to provide more conducting pathways than the MWCNTs, although the optimum conductivity is obtained when a mixture of FLG and MWCNTs is used.
- [Korean]
- Thermoelectric Properties of PbTe Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering of Nano Powders
- Eun-Young Jun, Ho-Young Kim, Cham Kim, Kyung-Sik Oh, Tai-Joo Chung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):384-389. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.384
- 1,169 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
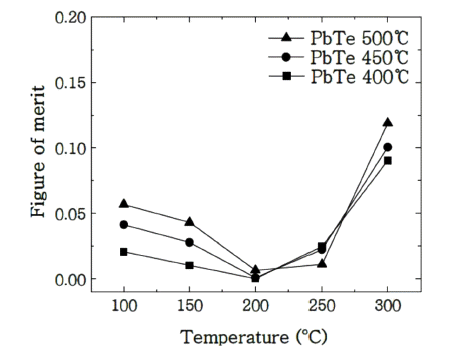
PDF Nanoparticles of PbTe are prepared via chemical reaction of the equimolar aqueous solutions of Pb(CH3COO)2 and Te at 120°C. The size of the obtained particles is 100 nm after calcination in a hydrogen atmosphere. Dense specimens for the thermoelectric characterization are produced by spark plasma sintering of prepared powders at 400°C to 500°C under 80 MPa for 5 min. The relative densities of the prepared specimens reach approximately 97% and are identified as cubic based on X-ray diffraction analyses. The thermoelectric properties are evaluated between 100°C and 300°C via electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity. Compared with PbTe ingot, the reduction of the thermal conductivities by more than 30% is verified via phonon scattering at the grain boundaries, which thus contributes to the increase in the figure of merit.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improved Thermoelectric Performance of Cu3Sb1−x−ySnxInySe4 Permingeatites Double-Doped with Sn and In
Ho-Jeong Kim, Il-Ho Kim
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(6): 422. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef
- Improved Thermoelectric Performance of Cu3Sb1−x−ySnxInySe4 Permingeatites Double-Doped with Sn and In
- [English]
- Development of Carbon Nanotube-copper Hybrid Powder as Conductive Additive
- Minjae Lee, Seoungjun Haa, Yeonjoo Lee, Haneul Jang, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):291-295. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.291

- 1,366 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A conductive additive is prepared by dispersing multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) on Cu powder by mechanical milling and is distributed in epoxy to enhance its electrical conductivity. During milling, the MWCNTs are dispersed and partially embedded on the surface of the Cu powder to provide electrically conductive pathways within the epoxy-based composite. The degree of dispersion of the MWCNTs is controlled by varying the milling medium and the milling time. The MWCNTs are found to be more homogeneously dispersed when solvents (particularly, non-polar solvent, i.e., NMP) are used. MWCNTs gradually disperse on the surface of Cu powder because of the plastic deformation of the ductile Cu powder. However, long-time milling is found to destroy the molecular structure of MWCNTs, instead of effectively dispersing the MWCNTs more uniformly. Thus, the epoxy composite film fabricated in this study exhibits a higher electrical conductivity than 1.1 S/cm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Morphologies of Carbon Nanomaterials on Conductivity of Composites Containing Copper/Carbon Nanomaterial Hybrid Fillers
Yeonjoo Lee, Sung-uk Hong, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(5): 435. CrossRef
- Effects of Morphologies of Carbon Nanomaterials on Conductivity of Composites Containing Copper/Carbon Nanomaterial Hybrid Fillers
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of CNT dispersed Cu matrix composites by wet mixing and spark plasma sintering process
- Seungchan Cho, Ilguk Jo, Sang-Bok Lee, Sang-Kwan Lee, Moonhee Choi, Jehong Park, Hansang Kwon, Yangdo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):158-164. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.158

- 967 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)–copper (Cu) composites are successfully fabricated by a combination of a binder-free wet mixing and spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. The SPS is performed under various conditions to investigate optimized processing conditions for minimizing the structural defects of CNTs and densifying the MWCNT–Cu composites. The electrical conductivities of MWCNT–Cu composites are slightly increased for compositions containing up to 1 vol.% CNT and remain above the value for sintered Cu up to 2 vol.% CNT. Uniformly dispersed CNTs in the Cu matrix with clean interfaces between the treated MWCNT and Cu leading to effective electrical transfer from the treated MWCNT to the Cu is believed to be the origin of the improved electrical conductivity of the treated MWCNT–Cu composites. The results indicate the possibility of exploiting CNTs as a contributing reinforcement phase for improving the electrical conductivity and mechanical properties in the Cu matrix composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Proposing Machine Learning Models Suitable for Predicting Open Data Utilization
Junyoung Jeong, Keuntae Cho
Sustainability.2024; 16(14): 5880. CrossRef
- Proposing Machine Learning Models Suitable for Predicting Open Data Utilization
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Electric Contact Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered Ta-Cu Composite
- Won Ju, Young Do Kim, Jae Jin Sim, Sang-Hoon Choi, Soong Keun Hyun, Kyoung Mook Lim, Kyoung-Tae Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):377-383. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.377
- 1,198 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
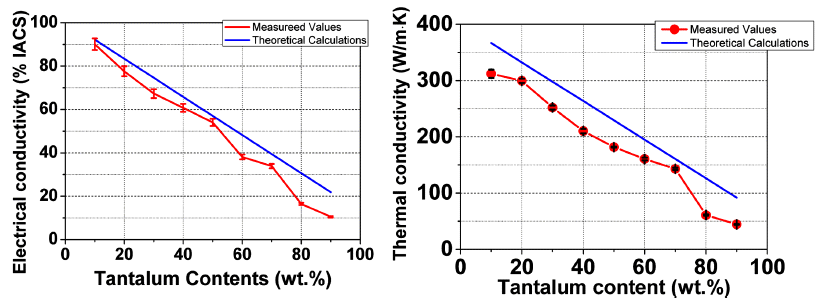
PDF Microstructure, electric, and thermal properties of the Ta-Cu composite is evaluated for the application in electric contact materials. This material has the potential to be used in a medium for a high current range of current conditions, replacing Ag-MO, W, and WC containing materials. The optimized SPS process conditions are a temperature of 900°C for a 5 min holding time under a 30 MPa mechanical pressure. Comparative research is carried out for the calculated and actual values of the thermal and electric properties. The range of actual thermal and electric properties of the Ta-Cu composite are 50~300W/mk and 10~90 %IACS, respectively, according to the compositional change of the 90 to 10 wt% Ta-Cu system. The results related to the electric contact properties, suggest that less than 50 wt% of Ta compositions are possible in applications of electric contact materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Formation mechanism, microstructural features and dry-sliding behaviour of “Bronze/WC carbide” composite synthesised by atmospheric pulsed-plasma deposition
V.G. Efremenko, Yu.G. Chabak, V.I. Fedun, K. Shimizu, T.V. Pastukhova, I. Petryshynets, A.M. Zusin, E.V. Kudinova, B.V. Efremenko
Vacuum.2021; 185: 110031. CrossRef
- Formation mechanism, microstructural features and dry-sliding behaviour of “Bronze/WC carbide” composite synthesised by atmospheric pulsed-plasma deposition
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Nanocrystals and Their Application to Thermally Conductive Composites
- Jae-Yong Jung, Yang-Do Kim, Pyung-Woo Shin, Young-Kuk Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(6):414-419. Published online December 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.6.414

- 1,503 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Much attention has been paid to thermally conductive materials for efficient heat dissipation of electronic devices to maintain their functionality and to support lifetime span. Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), which has a high thermal conductivity, is one of the most suitable materials for thermally conductive composites. In this study, we synthesize h-BN nanocrystals by pyrolysis of cost-effective precursors, boric acid, and melamine. Through pyrolysis at 900°C and subsequent annealing at 1500°C, h-BN nanoparticles with diameters of ~80 nm are synthesized. We demonstrate that the addition of small amounts of Eu-containing salts during the preparation of melamine borate precursors significantly enhanced the crystallinity of h-BN. In particular, addition of Eu assists the growth of h-BN nanoplatelets with diameters up to ~200 nm. Polymer composites containing both spherical Al2O3 (70 vol%) and Eu-doped h-BN nanoparticles (4 vol%) show an enhanced thermal conductivity (λ ~ 1.72W/mK), which is larger than the thermal conductivity of polymer composites containing spherical Al2O3 (70 vol%) as the sole fillers (λ ~ 1.48W/mK).
- [Korean]
- Investigation on the Thermoelectric Properties of Bismuth Telluride Matrix Composites by Addition of Graphene Oxide Powders
- Kyung Tae Kim, Taesik Min, Dong Won Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):263-269. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.263
- 787 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
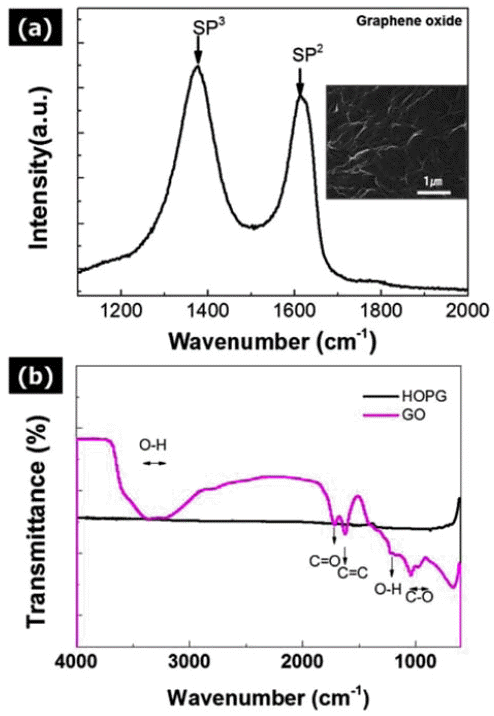
PDF Graphene oxide (GO) powder processed by Hummer's method is mixed with p-type Bi2Te3 based thermoelectric materials by a high-energy ball milling process. The synthesized GO-dispersed p-type Bi2Te3 composite powder has a composition of Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 (BSbT), and the powder is consolidated into composites with different contents of GO powder by using the spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. It is found that the addition of GO powder significantly decreases the thermal conductivity of the pure BSbT material through active phonon scattering at the newly formed interfaces. In addition, the electrical properties of the GO/BSbT composites are degraded by the addition of GO powder except in the case of the 0.1 wt% GO/BSbT composite. It is found that defects on the surface of GO powder hinder the electrical transport properties. As a result, the maximum thermoelectric performance (ZT value of 0.91) is achieved from the 0.1% GO/BSbT composite at 398 K. These results indicate that introducing GO powder into thermoelectric materials is a promising method to achieve enhanced thermoelectric performance due to the reduction in thermal conductivity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nanocomposite Strategy toward Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance in Bismuth Telluride
Hua‐Lu Zhuang, Jincheng Yu, Jing‐Feng Li
Small Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef - Advancement of thermoelectric performances through the dispersion of expanded graphene on p-type BiSbTe alloys
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Babu Madavali, Peyala Dharmaiah, Min-Woo Shin, Sung Ho Song, Soon-Jik Hong
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 722. CrossRef - The role of edge-oxidized graphene to improve the thermopower of p-type bismuth telluride-based thick films
Young Min Cho, Kyung Tae Kim, Gi Seung Lee, Soo Hyung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2019; 476: 533. CrossRef - The Preparation and Growth Mechanism of the Recovered Bi2Te3 Particles with Respect to Surfactants
Hyeongsub So, Eunpil Song, Yong-Ho Choa, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 141. CrossRef
- Nanocomposite Strategy toward Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance in Bismuth Telluride
- [Korean]
- Spark Plasma Sintering Behavior and Heat Dissipation Characteristics of the Aluminum Matrix Composite Materials with the Contents of Graphite
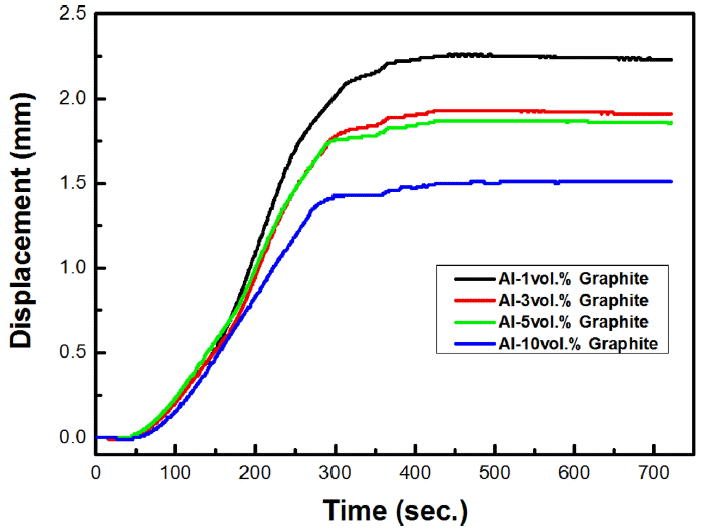
- Hansang Kwon, Jehong Park, Sungwook Joo, Sanghwui Hong, Jihoon Mun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):195-201. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.195
- 1,026 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Composite materials consisting of pure aluminum matrix reinforced with different amounts of graphite particles are successfully fabricated by mechanical ball milling and spark plasma sintering (SPS) processes. The shrinkage rates of the composite powders vary with the amount of graphite particles and the lowest shrinkage value is observed for the composite with the highest amount of graphite particles. The current slopes of time increase with increase in the amount of graphite particles whereas the current slopes of temperature show the opposite trend. The highest thermal conductivity is achieved for the composite with the least amount of graphite particles. Therefore, the thermal properties of the composite materials can be controlled by controlling the amount of the graphite particles during the SPS process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sintering Behavior and Thermal Properties of Cu-Graphite Materials by a Spark Plasma Sintering Method
Min-hyeok Yang, Bum-soon Park, Hyoung-seok Moon, Jae-cheol Park, Hyun-kuk Park
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2024; 62(6): 411. CrossRef - Effect of processing parameters on the microstructural and mechanical properties of aluminum–carbon nanotube composites produced by spark plasma sintering
B. Sadeghi, M. Shamanian, P. Cavaliere, F. Ashrafizadeh
International Journal of Materials Research.2018; 109(10): 900. CrossRef
- Sintering Behavior and Thermal Properties of Cu-Graphite Materials by a Spark Plasma Sintering Method
- [Korean]
- Thermal Properties of Diamond Aligned Electroless Ni Plating Layer/Oxygen Free Cu Substrates
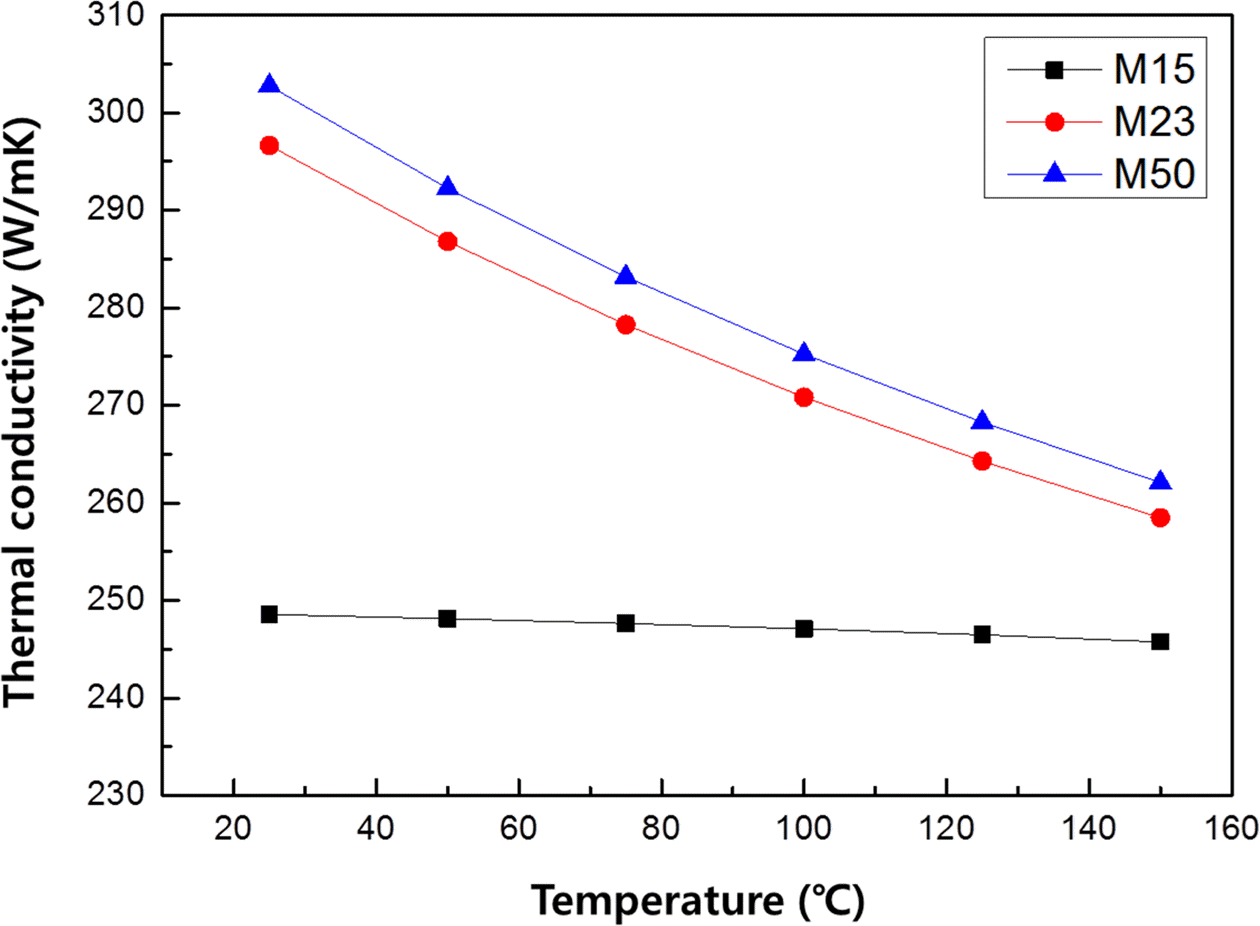
- Da-Woon Jeong, Song-Yi Kim, Kyoung-Tae Park, Seok-Jun Seo, Taek Soo Kim, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):134-137. Published online April 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.134
- 1,020 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The monolayer engineering diamond particles are aligned on the oxygen free Cu plates with electroless Ni plating layer. The mean diamond particle sizes of 15, 23 and 50 μm are used as thermal conductivity pathway for fabricating metal/carbon multi-layer composite material systems. Interconnected void structure of irregular shaped diamond particles allow dense electroless Ni plating layer on Cu plate and fixing them with 37-43% Ni thickness of their mean diameter. The thermal conductivity decrease with increasing measurement temperature up to 150°C in all diamond size conditions. When the diamond particle size is increased from 15 μm to 50 μm (Max. 304 W/mK at room temperature) tended to increase thermal conductivity, because the volume fraction of diamond is increased inside plating layer.
- [Korean]
- Controlling Structural and Electrical Properties of Pt Nanopowder-Dispersed SiO2 Film
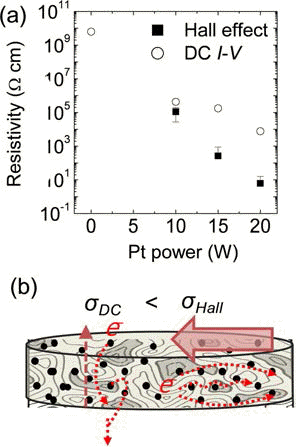
- Jae Ho Lee, In Joo Shin, Sung Woo Lee, Hyeong Cheol Kim, Byung Joon Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):355-359. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.355
- 622 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Pt nanopowder-dispersed SiO2 (SOP) films were prepared by RF co-sputtering method using Pt and SiO2 targets in Ar atmosphere. The growth rate and Pt content in the film were controlled by means of manipulating the RF power of Pt target while that of SiO2 was fixed. The roughness of the film was increased with increasing the power of Pt target, which was mainly due to the increment of the size and planar density of Pt nanopowder. It was revealed that SOP film formed at 10, 15, 20 W of Pt power contained 2.3, 2.7, and 3.0 nm of spherical Pt nanopowder, respectively. Electrical conductivity of SOP films was exponentially increased with increasing Pt power as one can expect. Interestingly, conductivity of SOP films from Hall effect measurement was greater than that from DC
I-V measurement, which was explained by the significant increase of electron density.
- [Korean]
- Micro-EDM Feasibility and Material Properties of Hybrid Ti2AlC Ceramic Bulk Materials
- Guk-Hyun Jeong, Kwang-Ho Kim, Myung-Chang Kang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):301-306. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.301
- 647 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Titanium alloys are extensively used in high-temperature applications due to their excellent high strength and corrosion resistance properties. However, titanium alloys are problematic because they tend to be extremely difficult-tocut material. In this paper, the powder synthesis, spark plasma sintering (SPS), bulk material characteristics and machinability test of hybrid Ti2AlC ceramic bulk materials were systematically examined. The bulk samples mainly consisted of Ti2AlC materials with density close to theoretical value were synthesized by a SPS method. Random orientation and good crystallization of the Ti2AlC was observed at 1100°C for 10 min under SPS sintering conditions. Scanning electron microscopy results indicated a homogeneous distribution and nano-laminated structure of Ti2AlC MAX phase. The hardness and electrical conductivity of Ti2AlC were higher than that of Ti 6242 alloy at sintering temperature of 1000°C~1100°C. Consequently, the machinability of the hybrid Ti2AlC bulk materials is better than that of the Ti 6242 alloy for micro-EDM process of micro-hole shape workpiece.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Material Characteristics with Sintering Temperature in Ti2AlC MAX Phase Material using Spark Plasma Sintering Method
Chang-Hun Lee, Gyung Rae Baek, Hee Sang Jung, Young-Keun Jeong, Myung Chang Kang
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(3): 175. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Material Characteristics with Sintering Temperature in Ti2AlC MAX Phase Material using Spark Plasma Sintering Method
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


