Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
- Eunbi Park, Jongwon Bae, Sera Kang, Minsu Kang, Suseong Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):375-382. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00248
- 992 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
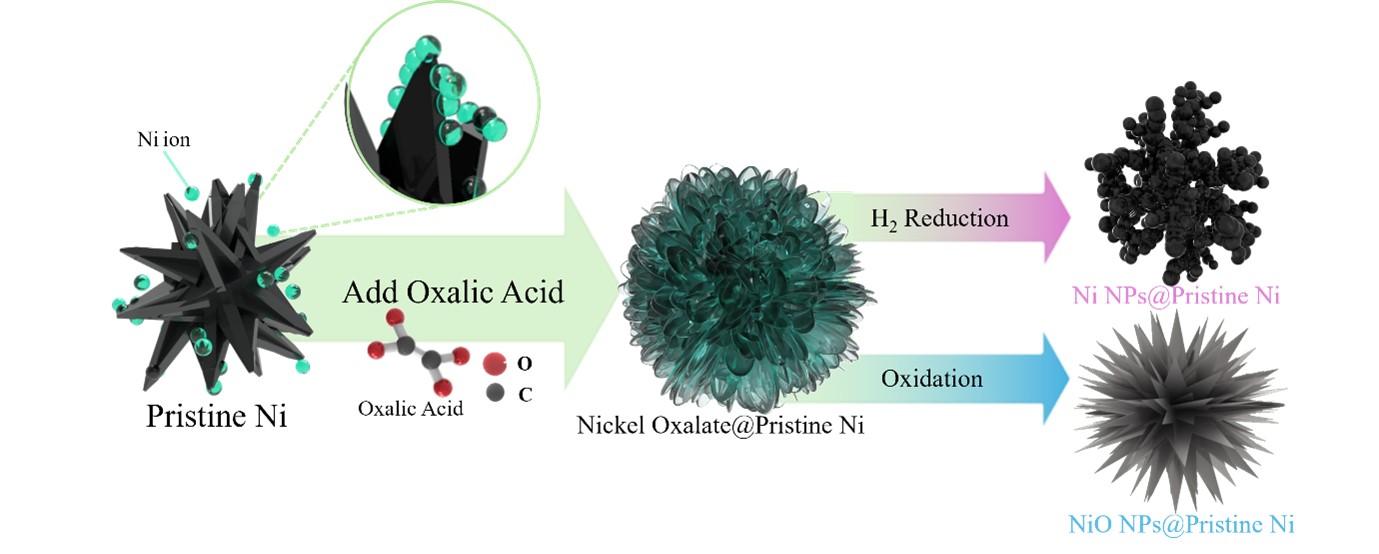
PDF - Nickel is widely used in industrial fields such as electrocatalysis and energy storage devices. Although micron-sized nickel particles exhibit excellent mechanical durability, their low specific surface area limits their reactivity. We modified the surface of micron-sized nickel particles with nanostructured nickel oxalate and investigated the effects of the solvent dielectric constant, surfactant, and thermal treatment atmosphere on the resulting particle morphology and phase transformation. Rietveld refinement analysis confirmed that changes in the solvent dielectric constant led to increased or diminished crystallinity of specific planes in nickel oxalate, resulting in diffraction patterns distinct from standard JCPDS data. These structural changes were also found to influence the morphology of the synthesized nickel oxalate. The results demonstrate that nickel oxalate serves as an effective precursor for producing Ni and NiO phases, and shape control of the final product can increase the surface reactivity of micron-sized nickel materials.
- [Korean]
- Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Pure Ni Coatings on a Type 316H Stainless Steel Substrate via High-Velocity Oxy-fuel and Directed Energy Deposition Processes
- Won Chan Lee, Seung Ju Nam, Ji-Hyun Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):309-314. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00185
- 801 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
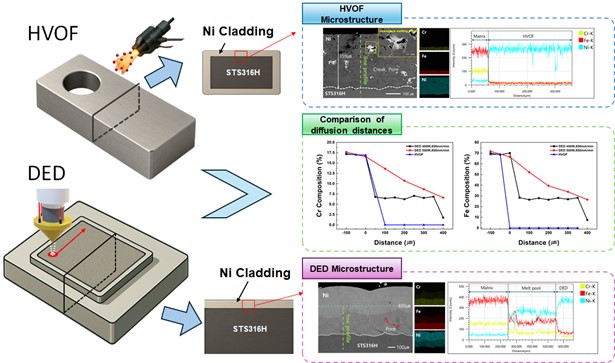
PDF - This study compares pure Ni coatings deposited on type 316H stainless steel using high-velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF) and directed energy deposition (DED) processes. Microstructural analysis showed that DED produced more uniform claddings with fewer pores, while HVOF resulted in incomplete melting and cracks. Elemental diffusion of Cr and Fe from the substrate into the cladding was evident in DED samples, especially at higher laser power, but minimal in HVOF due to low heat input. Vickers hardness testing revealed that DED claddings had higher hardness near the interface, which was attributed to solid solution strengthening and reduced porosity. Although HVOF better suppressed diffusion, it exhibited inferior mechanical properties due to internal defects. Overall, the DED process demonstrated superior coating quality and mechanical performance, suggesting its suitability for corrosion-resistant applications requiring both structural integrity and thermal stability, such as molten salt reactors.
- [English]
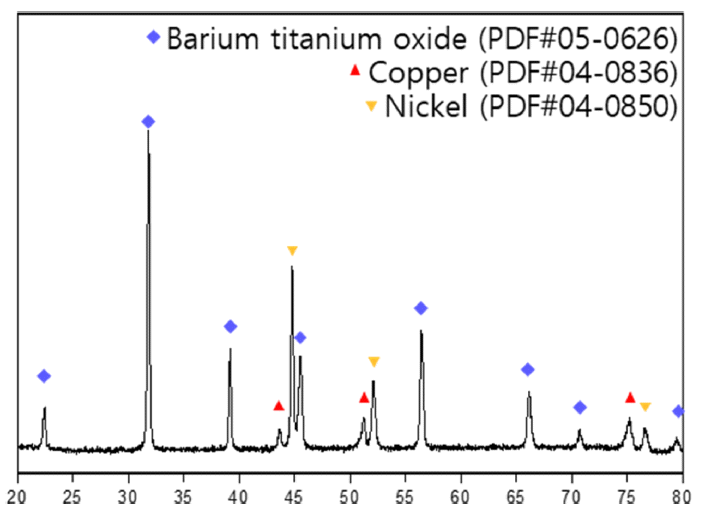
- Recovery of Barium, Nickel, and Titanium Powders from Waste MLCC
- Haein Shin, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):374-381. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00192
- 2,054 View
- 52 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
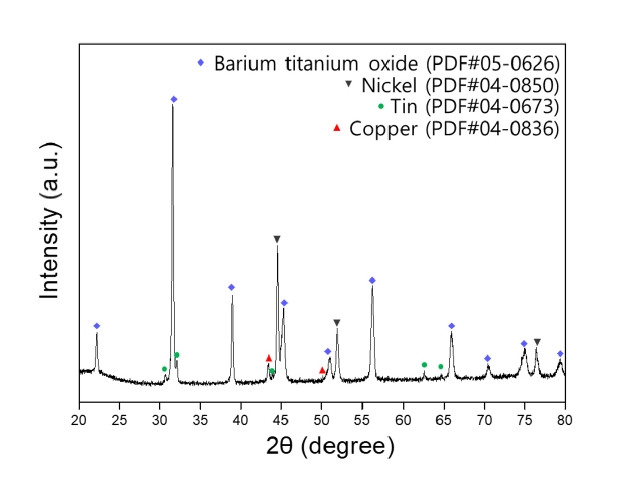
PDF - The development of the electronics industry has led to an increased demand for the manufacture of MLCC (Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors), which in turn is expected to result in a rise in MLCC waste. The MLCC contains various metals, notably barium, titanium, and nickel, whose disposal is anticipated to increase correspondingly. Recently, recycling technologies for electronic waste have garnered attention as they address waste management and raw material supply challenges. This paper investigates the recovery of barium, nickel, and titanium from the MLCC by a hydrometallurgical process. Using citric acid, which is an organic acid, the metal inside the MLCC was leached. Additionally, metal materials were recovered through precipitation and complexing processes. As a result, barium and titanium were recovered from the leachate of the waste MLCC, and 93% of the nickel-based powder was recovered. Furthermore, the optimal recovery process conditions for recycling these metal elements were investigated.
- [Korean]
- High-Hardness Cemented Carbide With Nickel-Tungsten Alloy Binder
- Hanjung Kwon
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):318-323. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00227
- 796 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
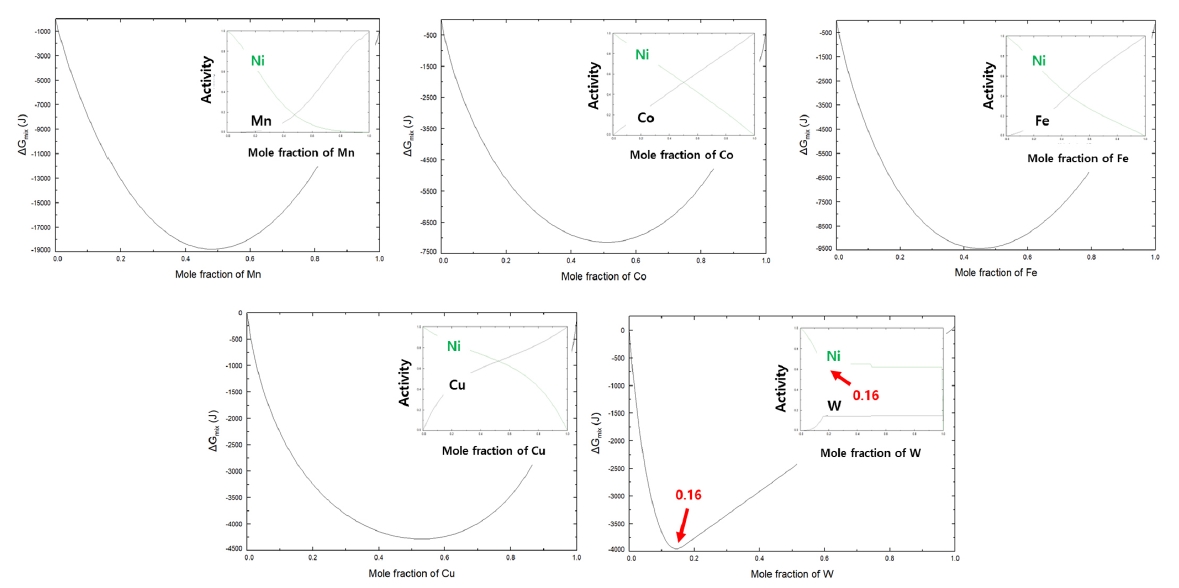
PDF - Cemented carbide for cutting tools, which is composed of carbide as a hard phase and metallic component as a metallic phase, mainly uses cobalt as the metallic phase due to the excellent mechanical properties of cobalt. However, as the demand for machining difficult-to-machine materials such as titanium and carbon fiber-reinforced plastics has recently increased, the development of high-hardness cemented carbide is necessary and the replacement of cobalt metal with a high-hardness alloy is required. In this study, we would like to introduce high-hardness cemented carbide fabricated using nickel-tungsten alloy as the metallic phase. First, nickel-tungsten alloy powder of the composition for formation of intermetallic compound confirmed through thermodynamic calculations was synthesized, and cemented carbide was prepared through the sintering process of tungsten carbide and the synthesized alloy powder. Through evaluating the mechanical properties of high-hardness cemented carbide with the nickel-tungsten alloy binder, the possibility of producing high-hardness cemented carbide by using the alloys with high-hardness was confirmed.
- [Korean]
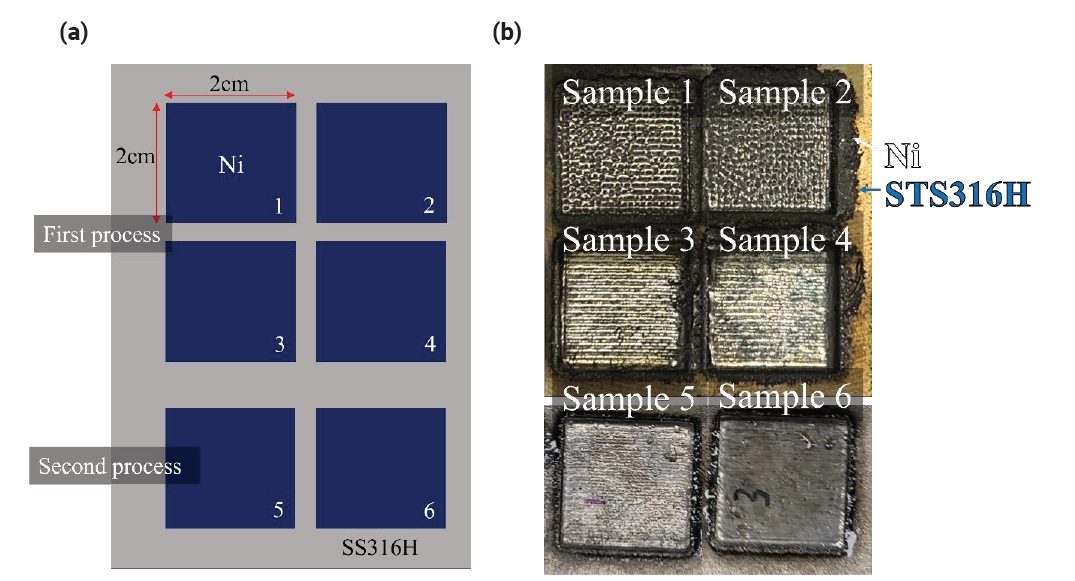
- Study on the Elemental Diffusion Distance of a Pure Nickel Layer Additively Manufactured on 316H Stainless Steel
- UiJun Ko, Won Chan Lee, Gi Seung Shin, Ji-Hyun Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):220-225. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00164
- 1,526 View
- 52 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Molten salt reactors represent a promising advancement in nuclear technology due to their potential for enhanced safety, higher efficiency, and reduced nuclear waste. However, the development of structural materials that can survive under severe corrosion environments is crucial. In the present work, pure Ni was deposited on the surface of 316H stainless steel using a directed energy deposition (DED) process. This study aimed to fabricate pure Ni alloy layers on an STS316H alloy substrate. It was observed that low laser power during the deposition of pure Ni on the STS316H substrate could induce stacking defects such as surface irregularities and internal voids, which were confirmed through photographic and SEM analyses. Additionally, the diffusion of Fe and Cr elements from the STS316H substrate into the Ni layers was observed to decrease with increasing Ni deposition height. Analysis of the composition of Cr and Fe components within the Ni deposition structures allows for the prediction of properties such as the corrosion resistance of Ni.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microstructural analysis and characterization of nickel deposition on 316H stainless steel via gas tungsten arc welding and powder laser cladding
Won Chan Lee, Jin Woong Park, Seung Ju Nam, Ji-Hyun Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 342. CrossRef - Effect of oxygen content in feedstock powders on microstructure and mechanical properties of ELI Ti-6Al-4V fabricated via laser powder bed fusion
Woo Hyeok Kim, Sang Woo Kim, Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, Jeoung Han Kim
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 307. CrossRef - Development of Aluminum Alloys for Additive Manufacturing Using Machine Learning
Sungbin An, Juyeon Han, Seoyeon Jeon, Dowon Kim, Jae Bok Seol, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 202. CrossRef - Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Pure Ni Coatings on a Type 316H Stainless Steel Substrate via High-Velocity Oxy-fuel and Directed Energy Deposition Processes
Won Chan Lee, Seung Ju Nam, Ji-Hyun Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 309. CrossRef
- Microstructural analysis and characterization of nickel deposition on 316H stainless steel via gas tungsten arc welding and powder laser cladding
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Nanowire by Electrospinning Process Using Nickel Oxide Particle Recovered from MLCC
- Haein Shin, Jongwon Bae, Minsu Kang, Kun-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):502-508. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.502
- 705 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF With the increasing demand for electronic products, the amount of multilayer ceramic capacitor (MLCC) waste has also increased. Recycling technology has recently gained attention because it can simultaneously address raw material supply and waste disposal issues. However, research on recovering valuable metals from MLCCs and converting the recovered metals into high-value-added materials remains insufficient. Herein, we describe an electrospinning (E-spinning) process to recover nickel from MLCCs and modulate the morphology of the recovered nickel oxide particles. The nickel oxalate powder was recovered using organic acid leaching and precipitation. Nickel oxide nanoparticles were prepared via heat treatment and ultrasonic milling. A mixture of nickel oxide particles and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) was used as the E-spinning solution. A PVP/NiO nanowire composite was fabricated via Espinning, and a nickel oxide nanowire with a network structure was manufactured through calcination. The nanowire diameters and morphologies are discussed based on the nickel oxide content in the E-spinning solution.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
Eunbi Park, Jongwon Bae, Sera Kang, Minsu Kang, Suseong Lee, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(5): 375. CrossRef
- Morphological Control and Surface Modification Characteristics of Nickel Oxalate Synthesized via Oxalic Acid Precipitation
- [Korean]
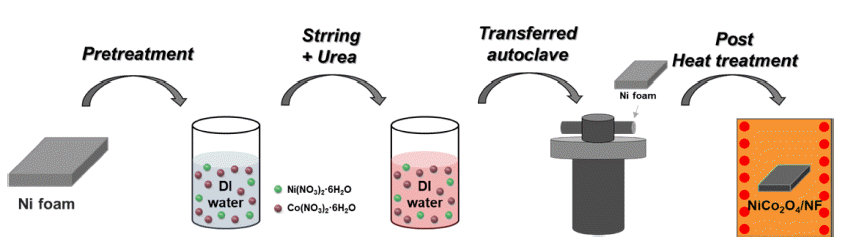
- Fabrication and Characterization of NiCo2O4/Ni Foam Electrode for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Water Splitting
- Minsol Kwon, Jaeseong Go, Yesol Lee, Sungmin Lee, Jisu Yu, Hyowon Lee, Sung Ho Song, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):411-417. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.411
- 1,089 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Environmental issues such as global warming due to fossil fuel use are now major worldwide concerns, and interest in renewable and clean energy is growing. Of the various types of renewable energy, green hydrogen energy has recently attracted attention because of its eco-friendly and high-energy density. Electrochemical water splitting is considered a pollution-free means of producing clean hydrogen and oxygen and in large quantities. The development of non-noble electrocatalysts with low cost and high performance in water splitting has also attracted considerable attention. In this study, we successfully synthesized a NiCo2O4/NF electrode for an oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline water splitting using a hydrothermal method, which was followed by post-heat treatment. The effects of heat treatment on the electrochemical performance of the electrodes were evaluated under different heat-treatment conditions. The optimized NCO/NF-300 electrode showed an overpotential of 416 mV at a high current density of 50 mA/cm2 and a low Tafel slope (49.06 mV dec-1). It also showed excellent stability (due to the large surface area) and the lowest charge transfer resistance (12.59 Ω). The results suggested that our noble-metal free electrodes have great potential for use in developing alkaline electrolysis systems.
- [English]
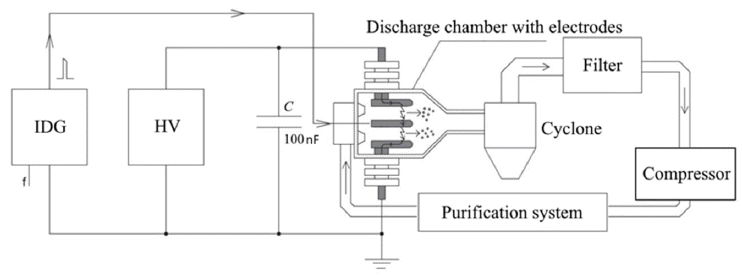
- Features of Nickel Nanoparticles Structure Synthesized by the Spark Discharge Method
- C. K. Rhee, A. D. Maksimov, I. V. Beketov, A. I. Medvedev, A. M. Murzakaev
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):464-467. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.464
- 1,272 View
- 11 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nickel nanopowders are obtained by the spark discharge method, which is based on the evaporation of the electrode surface under the action of the discharge current, followed by vapor condensation and the formation of nanoparticles. Nickel electrodes with a purity of 99.99% are used to synthesize the nickel nanoparticles in the setup. Nitrogen is used as the carrier gas with a purity of 99.998%. XRD, TEM, and EDX analyses of the nanopowders are performed. Moreover, HRTEM images with measured interplanar spacings are obtained. In the nickel nanopowder samples, a phase of approximately 90 wt% with an expanded crystal lattice of 6.5% on average is found. The results indicate an unusual process of nickel nanoparticle formation when the spark discharge method is employed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Study of Spots and Craters Formed during Spark Discharge in Air on Electrodes Made of Different Metals
A. D. Maksimov, E. I. Azarkevich, I. V. Beketov, D. S. Koleukh
Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics.2025; 89(10): 1941. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Craters Formed on Cathode and Anode Spots of a Spark Discharge in Air on Iron Electrodes
A. D. Maksimov, E. I. Azarkevich, I. V. Beketov, D. S. Koleukh
Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics.2023; 87(S2): S274. CrossRef
- Comparative Study of Spots and Craters Formed during Spark Discharge in Air on Electrodes Made of Different Metals
- [English]
- Spark Plasma Sintering of the Ni-graphite Composite Powder Prepared by Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid and Its Properties
- Minh Thuyet-Nguyena, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):14-24. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.14

- 923 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this work, the electrical explosion of wire in liquid and subsequent spark plasma sintering (SPS) was introduced for the fabrication of Ni-graphite nanocomposites. The fabricated composite exhibited good enhancements in mechanical properties, such as yield strength and hardness, but reduced the ductility in comparison with that of nickel. The as-synthesized Ni-graphite (5 vol.% graphite) nanocomposite exhibited a compressive yield strength of 275 MPa (about 1.6 times of SPS-processed monolithic nickel ~170 MPa) and elongation to failure ~22%. The hardness of Nigraphite composite had a value of 135.46 HV, which is about 1.3 times higher than that of pure SPS-processed Ni (105.675 HV). In terms of processing, this work demonstrated that this processing route is a novel, simple, and low-cost method for the synthesis of nickel-graphite composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Top-down strategies for achieving high-quality graphene: Recent advancements
Arpana Agrawal
Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry.2025; 142: 103. CrossRef - Electrodeposition of nickel-titanium dioxide coatings and powders from aqueous sulfate solutions
Tazhibayeva Aigerim Shotaevna, Bayeshova Azhar Kospanovna, Bayeshov Abduali, Osińska Małgorzata
Polyhedron.2025; 277: 117571. CrossRef
- Top-down strategies for achieving high-quality graphene: Recent advancements
- [English]
- Synthesis of Nanosized Nickel Particle from Spent Cathodic Material Containing Lithium
- Jei-Pil Wang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):340-344. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.340
- 840 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
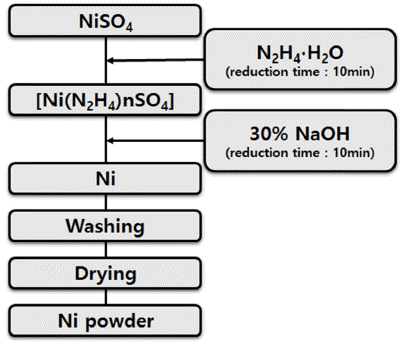
PDF Due to the rapid development of electricity, electronics, information communication, and biotechnology in recent years, studies are actively being conducted on nanopowders as it is required not only for high strengthening but also for high-function powder with electric, magnetic, and optical properties. Nonetheless, studies on nickel nanopowders are rare. In this study of the synthesis of nickel nanoparticles from LiNiO2 (LNO), which is a cathode active material, we have synthesized the nanosized nickel powder by the liquid reduction process of NiSO4 obtained through the leaching and purification of LNO. Moreover, we have studied the reduction reaction rate according to the temperature change of liquid phase reduction and the change of particle size as a function of NaOH addition amount using hydrazine monohydrate (N2H4·H2O) and NaOH.
- [Korean]
- The Effects of Hexamethylenetetramine Concentration on the Structural and Electrochemical Performances of Ni(OH)2 Powder for Pseudocapacitor Applications
- Dong Yeon Kim, Young-Min Jeong, Seong-Ho Baek, Injoon Son
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):231-236. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.231
- 1,135 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ni hydroxides (Ni(OH)2) are synthesized on Ni foam by varying the hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) concentration using an electrodeposition process for pseudocapacitor (PC) applications. In addition, the effects of HMT concentration on the Ni(OH)2 structure and the electrochemical properties of the PCs are investigated. HMT is the source of amine-based OH− in the solution; thus, the growth rate and morphological structure of Ni(OH)2 are influenced by HMT concentration. When Ni(OH)2 is electrodeposited at a constant voltage mode of -0.85 V vs. Ag/AgCl, the cathodic current and the number of nucleations are significantly reduced with increasing concentration of HMT from 0 to 10 mM. Therefore, Ni(OH)2 is sparsely formed on the Ni foam with increasing HMT concentration, showing a layered double-hydroxide structure. However, loosely packed Ni(OH)2 grains that are spread on Ni foam maintain a much greater surface area for reaction and result in the effective utilization of the electrode material due to the steric hindrance effect. It is suggested that the Ni(OH)2 electrodes with HMT concentration of 7.5 mM have the maximum specific capacitance (1023 F/g), which is attributed to the facile electrolyte penetration and fast proton exchange via optimized surface areas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of Domestic Research Trends on Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) Materials: Based on Research Articles in Korean Citation Index (KCI)
Seon Yong Lee, YoungJae Kim, Young Jae Lee
Economic and Environmental Geology.2023; 56(1): 23. CrossRef
- Review of Domestic Research Trends on Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) Materials: Based on Research Articles in Korean Citation Index (KCI)
- [English]
- Microwave Absorbance of Polymer Composites Containing SiC Fibers Coated with Ni-Fe Thin Films
- Tian Liu, Sung-Soo Kim, Woo-cheal Choi, Byungil Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):375-378. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.375

- 1,046 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Conductive and dielectric SiC are fabricated using electroless plating of Ni–Fe films on SiC chopped fibers to obtain lightweight and high-strength microwave absorbers. The electroless plating of Ni–Fe films is achieved using a two-step process of surface sensitizing and metal plating. The complex permeability and permittivity are measured for the composite specimens with the metalized SiC chopped fibers dispersed in a silicone rubber matrix. The original noncoated SiC fibers exhibit considerable dielectric losses. The complex permeability spectrum does not change significantly with the Ni–Fe coating. Moreover, dielectric constant is sensitively increased with Ni–Fe coating, owing to the increase of the space charge polarization. The improvements in absorption capability (lower reflection loss and small matching thickness) are evident with Ni–Fe coating on SiC fibers. For the composite SiC fibers coated with Ni–Fe thin films, a -35 dB reflection loss is predicted at 7.6 GHz with a matching thickness of 4 mm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Magnetic sputtering of FeNi/C bilayer film on SiC fibers for effective microwave absorption in the low-frequency region
Tong Guo, Ben Huang, Changgeng Li, Yumin Lou, Xiu-Zhi Tang, Xiaozhong Huang, Jianling Yue
Ceramics International.2021; 47(4): 5221. CrossRef
- Magnetic sputtering of FeNi/C bilayer film on SiC fibers for effective microwave absorption in the low-frequency region
- [Korean]
- Characterization of Classification of Synthesized Ni Nanopowders by Pulsed Wire Evaporation Method
- Joong-Hark Park, Geon-Hong Kim, Dong-Jin Lee, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):389-394. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.389
- 612 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
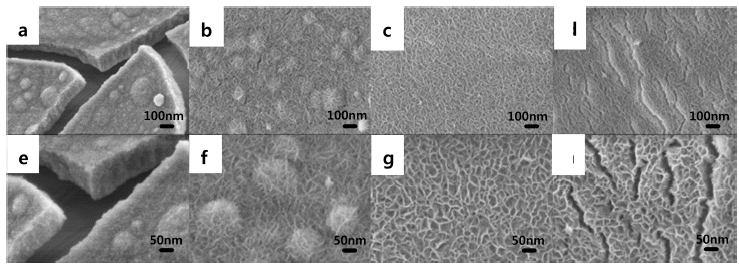
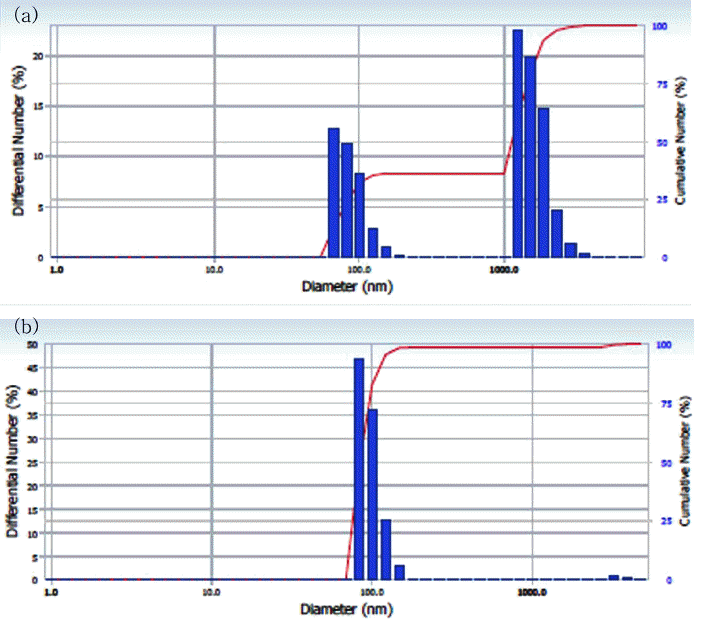
PDF Ni wires with a diameter and length of 0.4 and 100 mm, respectively, and a purity of 99.9% are electrically exploded at 25 cycles per minute. The Ni nanopowders are successfully synthesized by a pulsed wire evaporation (PWE) method, in which Ar gas is used as the ambient gas. The characterization of the nanopowders is carried out using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and a high-resolution transmission electronmicroscope (HRTEM). The Ni nanopowders are classified for a multilayer ceramic condenser (MLCC) application using a type two Air-Centrifugal classifier (model: CNI, MP-250). The characterization of the classified Ni nanopowders are carried out using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and particle size analysis (PSA) to observe the distribution and minimum classification point (minimum cutting point) of the nanopowders.
- [Korean]
- Preparation of Ni(OH)2 Hollow Spheres by Solvent Displacement Crystallization Using Micro-Injection Device
- Seiki Kim, Kyungsoo Park, Kwang-Il Jung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):311-316. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.311
- 998 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
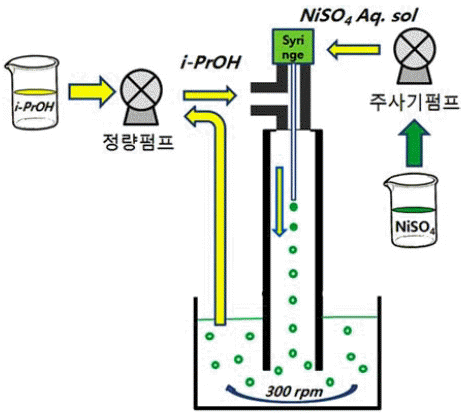
PDF Ni(OH)2 hollow spheres have been prepared by solvent displacement crystallization using a micro-injection device, and the effect of process parameters such as concentration and the relative ratio of the injection speed of the precursor solution, which is an aqueous solution of NiSO4·6H2O, to isopropyl alcohol of displacement solvent have been investigated. The crystal phases after NaOH treatment are in the β-phase for all process parameters. A higher concentration of NiSO4·6H2O aqueous solution is injected by a micro-injection device and bigger Ni(OH)2 hollow spheres with a narrower particle size distribution are formed. The crystallinity and hardness of the as-obtained powder are so poor that hydrothermal treatment of the as-obtained Ni(OH)2 at 120°C for 24 h in distilled water is performed in order to greatly improve the crystallinity. It is thought that a relative ratio of the injection speed of NiSO4·6H2O to that of isopropyl alcohol of at least more than 1 is preferable to synthesize Ni(OH)2 hollow spheres. It is confirmed that this solution- based process is very effective in synthesizing ceramic hollow spheres by simple adjustment of the process parameters such as the concentration and the injection speed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Hexamethylenetetramine Concentration on the Structural and Electrochemical Performances of Ni(OH)2 Powder for Pseudocapacitor Applications
Dong Yeon Kim, Young-Min Jeong, Seong-Ho Baek, Injoon Son
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(3): 231. CrossRef
- The Effects of Hexamethylenetetramine Concentration on the Structural and Electrochemical Performances of Ni(OH)2 Powder for Pseudocapacitor Applications
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Nickel Nanoparticle-adsorbed Aluminum Powders for Energetic Applications
- Dong Won Kim, Gu Hyun Kwon, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;24(3):242-247. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.242

- 1,187 View
- 8 Download
- 8 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, the electroless nickel plating method has been investigated for the coating of Ni nanoparticles onto fine Al powder as promising energetic materials. The adsorption of nickel nanoparticles onto the surface of Al powders has been studied by varying various process parameters, namely, the amounts of reducing agent, complexing agent, and pH-controller. The size of nickel nanoparticles synthesized in the process has been optimized to approximately 200 nm and they have been adsorbed on the Al powder. TGA results clearly show that the temperature at which oxidation of Al mainly occurs is lowered as the amount of Ni nanoparticles on the Al surface increases. Furthermore, the Ni-plated Al powders prepared for all conditions show improved exothermic reaction due to the selfpropagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) between Ni and Al. Therefore, Al powders fully coated by Ni nanoparticles show the highest exothermic reactivity: this demonstrates the efficiency of Ni coating in improving the energetic properties of Al powders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and oxidation behavior of Al@Ni-Fe core-shell energetic composite powders
Khawar Yaqoob, Asifa Kusar, Amena Mohsin, Onur Ertuğrul, Ahmet Çağrı Kılınç, Fahad Ali, Rub Nawaz Shahid, Naeem ul Haq Tariq, Hassan Wahab, Hasan Bin Awais
Energetic Materials Frontiers.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Study Progress in Improving the Energy Release Rate of Al Powders
永鹏 陈
Material Sciences.2024; 14(08): 1178. CrossRef - Study on the Combustion Characteristics of Ethanol Nanofuel
Kwanyoung Noh, Hyemin Kim, Siwook Nam, Soonho Song
Aerospace.2023; 10(10): 878. CrossRef - The Self-Reduction during the Thermal Decomposition of an Ammonium Molybdate
Kyoungkeun Yoo, Won Beom Koo, Hanggoo Kim, Sang-hun Lee
Minerals.2023; 13(2): 133. CrossRef - Increased exothermic reactivity of polytetrafluoroethylene-coated aluminum powders: Impact of powder size reduction
Soo-ho Jung, Kyung Tae Kim, Jinhee Bae, Yoon Jeong Choi, Jae Min Kim, Jeong-Yun Sun
Materials Letters.2023; 351: 135009. CrossRef - High energy Al@Ni preparation of core-shell particles by adjusting nickel layer thickness
Yongpeng Chen, Jianguo Zhang, Jiawei Zhu, Ning Xiang, Huichao Zhang, Zunning Zhou
Vacuum.2022; 205: 111344. CrossRef - Electroless deposition of Ni nanoparticles on micron-sized boron carbide particles: Physicochemical and oxidation properties
Prashant Ravasaheb Deshmukh, Hyung Soo Hyun, Youngku Sohn, Weon Gyu Shin
Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering.2020; 37(3): 546. CrossRef - Synthesis and exothermic reactions of ultra-fine snowman-shaped particles with directly bonded Ni/Al interfaces
Gu Hyun Kwon, Kyung Tae Kim, Dong Won Kim, Jungho Choe, Jung Yeul Yun, Jong-Man Kim
Applied Surface Science.2019; 476: 481. CrossRef
- Synthesis and oxidation behavior of Al@Ni-Fe core-shell energetic composite powders
- [Korean]
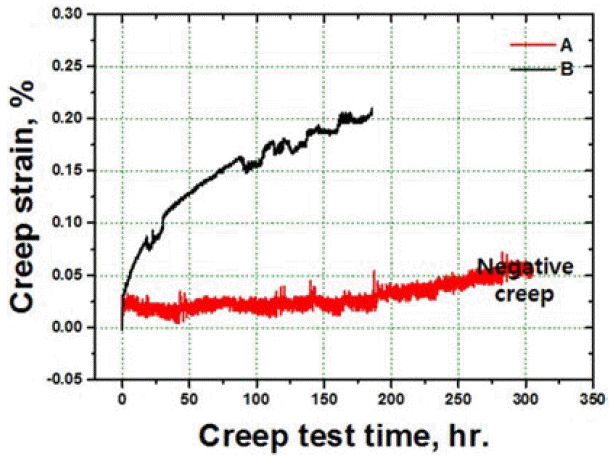
- Analyses of Creep Properties of Ni-base Superalloy Powders as Cooling Rate after Solid Solution Heat Treatment
- Chan Jun, Youngseon Lee, Byeong Beom Bae, Hong-Kyu Kim, Seong Suk Hong, Donghoon Kim, Jondo Yun, Eun Yoo Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):247-253. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.247
- 911 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, solid solution heat treatment of consolidated nickel-based superalloy powders is carried out by hot isotactic pressing. The effects of the cooling rate of salt quenching, and air cooling on the microstructures and the mechanical properties of the specimens are analyzed . The specimen that is air cooled shows the formation of serrated grain boundaries due to their obstruction by the carbide particles. Moreover, the specimen that is salt quenched shows higher strength than the one that is air cooled due to the presence of fine and close-packed tertiary gamma prime phase. The tensile elongation at high temperatures improves due to the presence of grain boundary serrations in the specimen that is air cooled. On the contrary, the specimen that is salt quenched and consists of unserrated grain boundaries shows better creep properties than the air cooled specimen with the serrated grain boundaries, due to the negative creep phenomenon.
- [Korean]
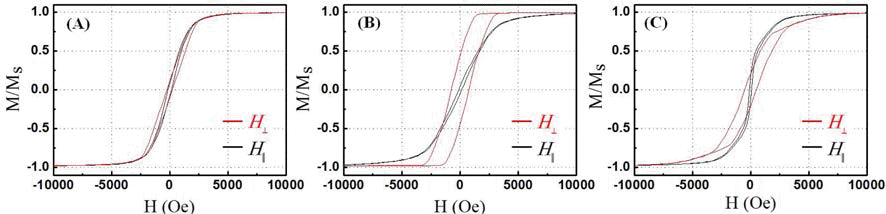
- Synthesis and Characterization of Nickel Nanowires by an Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template-Based Electrodeposition
- Hyo-Ryoung Lim, Yong-Ho Choa, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):216-220. Published online June 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.216
- 728 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Vertically oriented nickel nanowire arrays with a different diameter and length are synthesized in porous anodic aluminium oxide templates by an electrodeposition method. The pore diameters of the templates are adjusted by controlling the anodization conditions and then they are utilized as templates to grow nickel nanowire arrays. The nickel nanowires have the average diameters of approximately 25 and 260 nm and the crystal structure, morphology and microstructure of the nanowires are systematically investigated using XRD, FE-SEM and TEM analysis. The nickel nanowire arrays show a magnetic anisotropy with the easy axis parallel to the nanowires and the coercivity and remanence enhance with decreasing a wire diameter and increasing a wire length.
- [Korean]
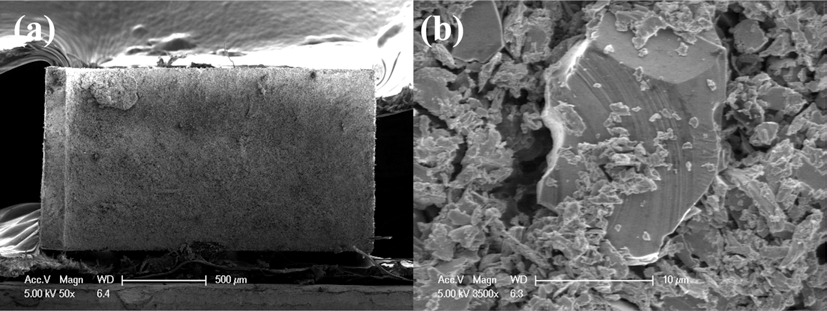
- Manufacturing and Evaluation of Properties of Nanocrystalline Ni bulk by Dynamic Compaction of Nano Ni powders using a Gas-gun System
- Wooyeol Kim, Dong-Hyun Ahn, Lee Ju Park, Jong-Il Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):44-49. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.44
- 621 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, nanocrystalline nickel powders were cold compacted by a dynamic compaction method using a single-stage gas gun system. A bending test was conducted to measure the bonding strengths of the compacted regions and microstructures of the specimen were analyzed using a scanning electron microscopy. The specimen was separated into two parts by a horizontal crack after compaction. Density test shows that the powder compaction occurred only in the upper part of the specimen. Brittle fracture was occurred during the bending test of the compact sample. Dispersion of shock energy due to spalling highly affected the bonding status of the nanocrystalline nickel powder.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


