Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Comparison of the Properties of Rare-Earth Zirconate Thermal Barrier Coatings for Hydrogen-Fueled Gas Turbines
- Gun-Woong Lee, Min-Soo Nam, Min-Ji Kim, HyunSuk Jung, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):472-480. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00423

- 661 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) for hydrogen-fueled gas turbines withstand higher combustion temperatures and increased steam concentrations compared to conventional natural-gas systems. These harsh operating conditions significantly accelerate the thermal degradation of widely used YSZ coatings, emphasizing the need for alternative top-coat materials with improved phase stability and reduced thermal conductivity. In this study, rare-earth zirconate ceramics, Gd2Zr2O7 (GdZO), Tm2Zr2O7 (TmZO), and a mixed composition (Gd0.5Tm0.5)2Zr2O7 (Gd/TmZO), are synthesized and investigated as potential next-generation TBC candidates. Each material was comparatively examined with a focus on crystal structure, thermophysical properties, and thermal conductivity. Furthermore, high-temperature steam exposure experiments were performed to simulate hydrogen combustion environments. Microstructural analyses, high-temperature degradation behavior, and phase stability evaluations were carried out to obtain fundamental experimental data. This study provides essential baseline information for the design and development of high-performance TBC materials suitable for the hydrogen-fueled gas turbine systems.
- [English]
- High-Temperature Steam Oxidation Behavior of Silicide- or Aluminide- Coated Mo and Nb Refractory Metals
- Woojin Lim, Je-Kyun Baek, JaeJoon Kim, Hyun Gil Kim, Ho Jin Ryu
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):546-555. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00381
- 1,405 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Refractory materials, such as molybdenum and niobium, are potential candidates for cladding material due to their high melting temperatures and desirable mechanical properties at higher temperatures than those of zirconium alloys. However, refractory materials have low resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures. Therefore, this study examined silicide or aluminide surface coatings as protection against rapid oxidation of refractory materials at elevated temperatures for a potential accident-tolerant fuel cladding. Silicide or aluminide layers were formed on refractory metal substrates by using the pack cementation method. The steam oxidation behavior of both coated and uncoated samples was compared by thermogravimetric analysis at 1200°C. The weight changes of the coated samples were greatly reduced than those of uncoated samples. Microstructural analyses demonstrated that the silicide and aluminide layers were oxidized to form a protective surface oxide that prevented rapid oxidation of the refractory substrate at elevated temperatures.
- [Korean]
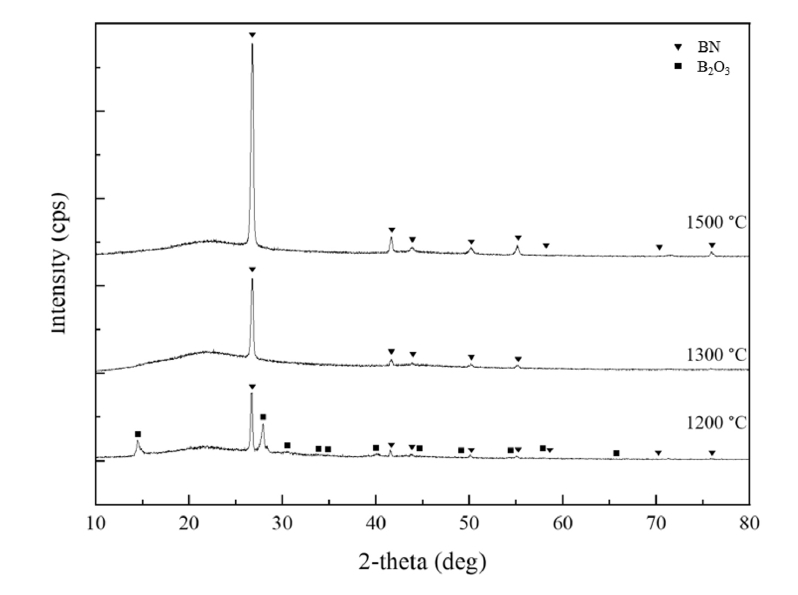
- Fabrication of SiCf/SiC Composites with a BN Interphase Prepared by the Wet Method
- Kyung Ho Kim, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):530-536. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00339
- 883 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study presents a cost-effective wet chemical coating process for fabricating a boron nitride (BN) interphase on silicon carbide (SiC) fibers, increasing the oxidation resistance and performance of SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composites. Using urea as a precursor, optimal nitriding conditions were determined by adjusting the composition, concentration, and immersion time. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed distinct BN phase formation at 1300°C and 1500°C, while a mixture of BN and B₂O₃ was observed at 1200°C. HF treatment improved coating uniformity by removing SiO₂ layers formed during the de-sizing process. Optimization of the boric acid-to-urea molar ratio resulted in a uniform, 130-nm-thick BN layer. This study demonstrates that the wet coating process offers a viable and economical alternative to chemical vapor deposition for fabricating high-performance BN interphases in SiCf/SiC composites that are suitable for high-temperature applications.
- [Korean]
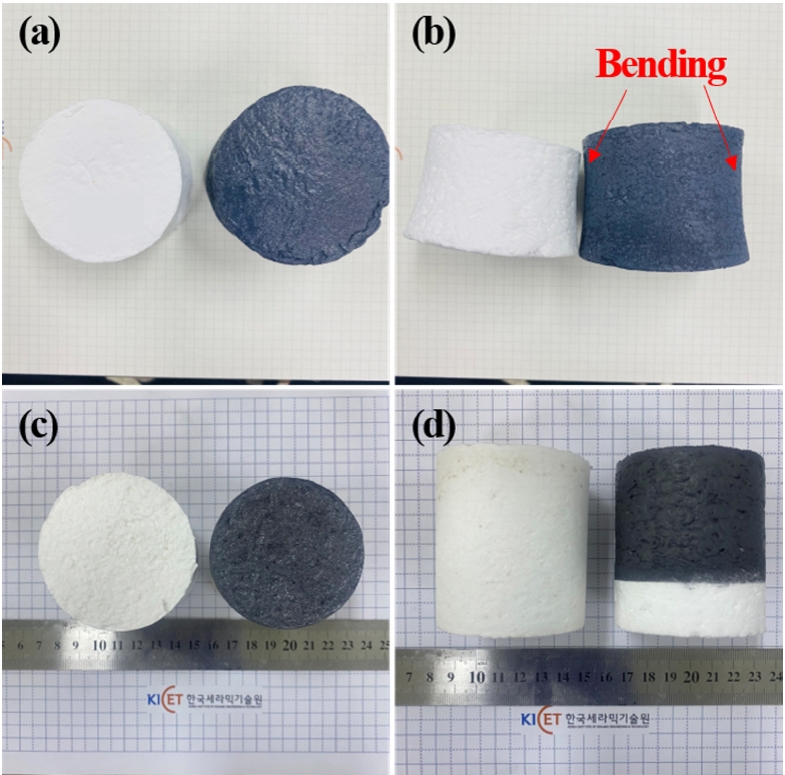
- Fabrication and High-Temperature Performance Evaluation of Light-Weight Insulation Materials and Coatings for Reusable Thermal Protection Systems
- Min-Soo Nam, Jong-Il Kim, Jaesung Shin, Hyeonjun Kim, Bum-Seok Oh, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):521-529. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00318
- 1,461 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Light-weight ceramic insulation materials and high-emissivity coatings were fabricated for reusable thermal protection systems (TPS). Alumina-silica fibers and boric acid were used to fabricate the insulation, which was heat treated at 1250 °C. High-emissivity coating of borosilicate glass modified with TaSi2, MoSi2, and SiB6 was applied via dip-and-spray coating methods and heat-treated at 1100°C. Testing in a high-velocity oxygen fuel environment at temperatures over 1100 °C for 120 seconds showed that the rigid structures withstood the flame robustly. The coating effectively infiltrated into the fibers, confirmed by scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction analyses. Although some oxidation of TaSi2 occurred, thereby increasing the Ta2O5 and SiO2 phases, no significant phase changes or performance degradation were observed. These results demonstrate the potential of these materials for reusable TPS applications in extreme thermal environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Durability Assessment of Tile-Type Reusable Thermal Protection Materials
Minjeong Kim, Seong Man Choi
Materials.2026; 19(2): 303. CrossRef
- Durability Assessment of Tile-Type Reusable Thermal Protection Materials
- [Korean]
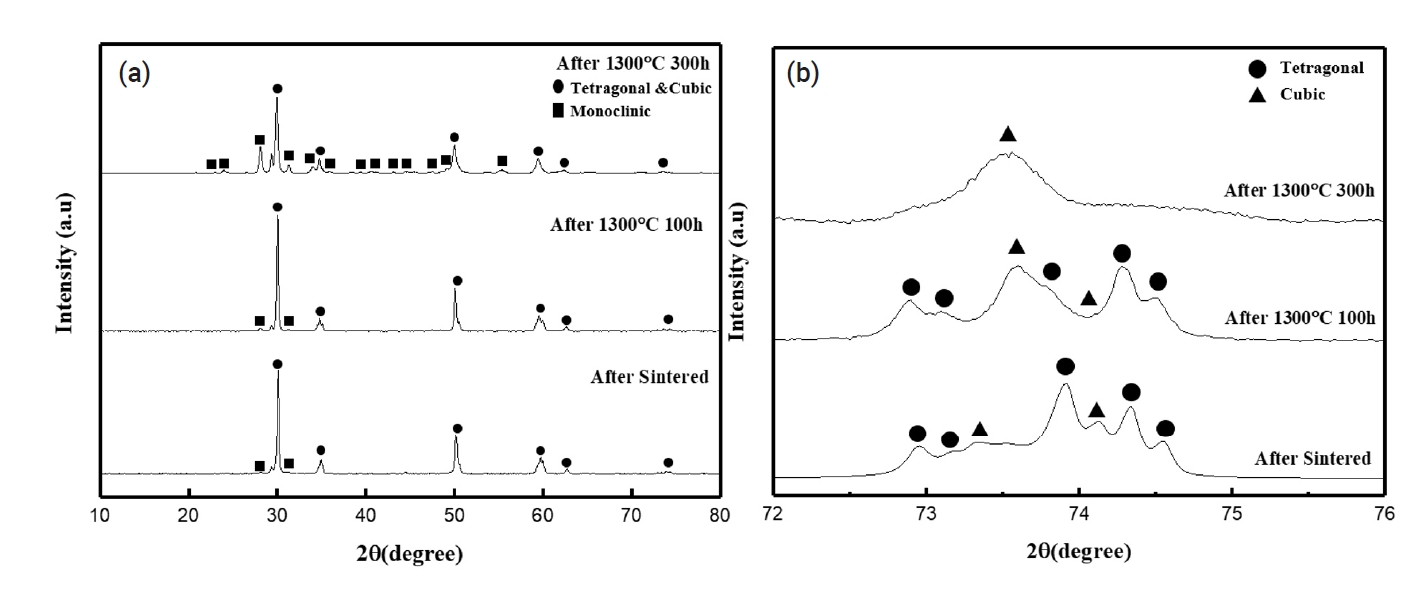
- Effect of TiO2 Content on High-Temperature Degradation Behavior of Nd2O3 and Yb2O3 Doped YSZ Composite Materials
- Gye-Won Lee, Seonung Choi, Tae-jun Park, Jong-il Kim, In-hwan Lee, Yoon-seok Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):431-436. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00269
- 608 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hot section components of gas turbines are exposed to a high operating temperature environment. To protect these components, thermal barrier coatings (TBC) are applied to their surfaces. Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), which is widely used as a TBC material, faces limitations at temperatures above 1200℃. To mitigate these issues, research has focused on adding lanthanide rare earth oxides and tetravalent oxides to prevent the phase-transformation of the monoclinic phase in zirconia. This study investigated the effects of varying TiO2 content in Nd2O3 and Yb2O3 co-doped YSZ composites. Increasing TiO2 content effectively suppressed formation of the monoclinic phase and increased the thermal degradation resistance compared to YSZ in environments over 1200℃. These findings will aid in developing more thermally stable and efficient TBC materials for application in high-temperature environments.
- [Korean]
- Tribological Behavior Analysis of WC-Ni-Cr + Cr3C2 and WC-Ni-Cr + YSZ Coatings Sprayed by HVOF
- Tae-Jun Park, Gye-Won Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):415-423. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.415
- 947 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
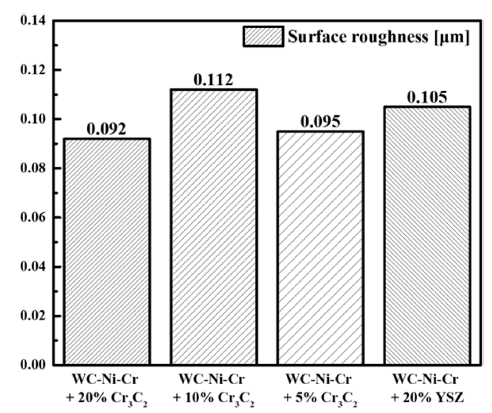
PDF With the increasing attention to environmental pollution caused by particulate matter globally, the automotive industry has also become increasingly interested in particulate matter, especially particulate matter generated by automobile brake systems. Here, we designed a coating composition and analyzed its mechanical properties to reduce particulate matter generated by brake systems during braking of vehicles. We designed a composition to check the mechanical properties change by adding Cr3C2 and YSZ to the WC-Ni-Cr composite composition. Based on the designed composition, coating samples were manufactured, and the coating properties were analyzed by Vickers hardness and ball-on-disk tests. As a result of the experiments, we found that the hardness and friction coefficient of the coating increased as the amount of Cr3C2 added decreased. Furthermore, we found that the hardness of the coating layer decreased when YSZ was added at 20vol%, but the friction coefficient was higher than the composition with Cr3C2 addition.
- [Korean]
- Comparison Study of Compact Titanium Oxide (c-TiO2) Powder Electron Transport Layer Fabrication for Carbon Electrode-based Perovskite Solar Cells
- Chae Young Woo, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):297-302. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.297
- 792 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
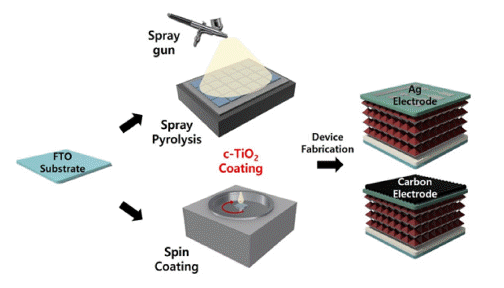
PDF This study compares the characteristics of a compact TiO2 (c-TiO2) powdery film, which is used as the electron transport layer (ETL) of perovskite solar cells, based on the manufacturing method. Additionally, its efficiency is measured by applying it to a carbon electrode solar cell. Spin-coating and spray methods are compared, and spraybased c-TiO2 exhibits superior optical properties. Furthermore, surface analysis by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) exhibits the excellent surface properties of spray-based TiO2. The photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) is 14.31% when applied to planar perovskite solar cells based on metal electrodes. Finally, carbon nanotube (CNT) film electrode-based solar cells exhibits a 76% PCE compared with that of metal electrodebased solar cells, providing the possibility of commercialization.
- [Korean]
- Improvement of the Mechanical Property and Corrosion Resistivity of the Ni-/Fe-based Hybrid Coating Layer using High-velocity Oxygen Fuel Spraying by Heat Treatment
- Jungjoon Kim, Yeonjoo Lee, Song-Yi Kim, Jong-Jae Lee, Jae-hun Kim, Seok-Jae Lee, Hyunkyu Lim, Min-Ha Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):240-246. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.240
- 875 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Novel Ni- and Fe-based alloys are developed to impart improved mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The designed alloys are manufactured as a powder and deposited on a steel substrate using a high-velocity oxygen-fuel process. The coating layer demonstrates good corrosion resistance, and the thus-formed passive film is beneficial because of the Cr contained in the alloy system. Furthermore, during low-temperature heat treatment, factors that deteriorate the properties and which may arise during high-temperature heat treatment, are avoided. For the heattreated coating layers, the hardness increases by up to 32% and the corrosion resistance improves. The influence of the heat treatment is investigated through various methods and is considered to enhance the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the coating layer.
- [Korean]
- A Study of Various SiO2 Coating Control on White TiO2 Pigment for Cosmetic Applications
- Minsol Park, Wooyoung Shim, YooJin Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):207-212. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.207
- 1,043 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
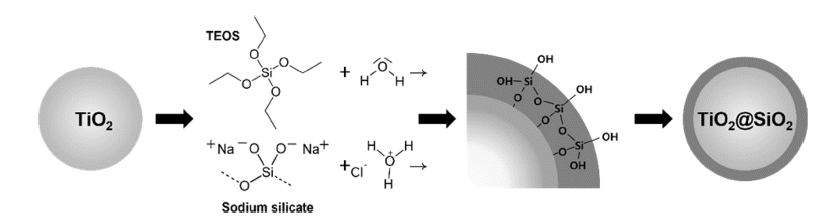
PDF Nanosized rutile titanium dioxide (TiO2) is used in inorganic pigments and cosmetics because of its high whiteness and duality. The high quality of the white pigments depends on their surface coating technique via the solgel process. SiO2 coatings are required to improve the dispersibility, UV-blocking, and whiteness of TiO2. Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) is an important coating precursor owing to its ability to control various thicknesses and densities. In addition, we use Na2SiO3 (sodium silicate) as a precursor because of its low cost. Compared to TEOS, which controls the pH using a basic catalyst, Na2SiO3 controls the pH using an acid catalyst, giving a uniform coating. The coating thickness of TiO2 is controlled using a surface modifier, cetrimonium bromide, which is used in various applications. The shape and thickness of the nanosized coating layer on TiO2 are analyzed using transmission electron microscopy, and the SiO2 nanoparticle behavior in terms of the before-and-after size distribution is measured using a particle size analyzer. The color measurements of the SiO2 pigment are performed using UV-visible spectroscopy.
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Roll Manufacturing Technology Applying Powder Flame Spray Coating Technology of Ni-Based Alloy Powder
- Ji Woong Park, Soon Kook Kim, Gye Bum Ban
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):123-131. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.123

- 1,027 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to improve the mechanical properties and develop manufacturing technology through self-soluble alloy powder flame spray coating on the surface of a run-out table roller for hot rolling. The roller surface of the run-out table should maintain high hardness at high temperatures and possess high wear, corrosion, and heat resistances. In addition, sufficient bonding strength between the thermal spray coating layer and base material, which would prevent the peel-off of the coating layer, is also an important factor. In this study, the most suitable powder and process for roll manufacturing technology are determined through the initial selection of commercial alloy powder for roll manufacturing, hardness, component analysis, and bond strength analysis of the powder and thermal spray coating layer according to the powder.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of rare earth oxides on microstructure and mechanical properties of nickel-based superalloys fabricated by high energy beam processing: A review
Lianjie Bi, Hua Yan, Peilei Zhang, Haichuan Shi, Zhiyuan Li, Ruidi Li
Journal of Rare Earths.2024; 42(9): 1629. CrossRef
- Influence of rare earth oxides on microstructure and mechanical properties of nickel-based superalloys fabricated by high energy beam processing: A review
- [Korean]
- Recent progress on Performance Improvements of Thermoelectric Materials using Atomic Layer Deposition
- Seunghyeok Lee, Tae Joo Park, Seong Keun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):56-62. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.56
- 1,495 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a promising technology for the uniform deposition of thin films. ALD is based on a self-limiting mechanism, which can effectively deposit thin films on the surfaces of powders of various sizes. Numerous studies are underway to improve the performance of thermoelectric materials by forming core-shell structures in which various materials are deposited on the powder surface using ALD. Thermoelectric materials are especially relevant as clean energy storage materials due to their ability to interconvert between thermal and electrical energy by the Seebeck and Peltier effects. Herein, we introduce a surface and interface modification strategy based on ALD to control the performance of thermoelectric materials. We also discuss the properties of the interface between various deposition materials and thermoelectric materials.
- [Korean]
- Development of Amorphous Iron Based Coating Layer using High-velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) Spraying
- Jungjoon Kim, Song-Yi Kim, Jong-Jae Lee, Seok-Jae Lee, Hyunkyu Lim, Min-Ha Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):483-490. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.483
- 681 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A new Fe-Cr-Mo-B-C amorphous alloy is designed, which offers high mechanical strength, corrosion resistance as well as high glass-forming ability and its gas-atomized amorphous powder is deposited on an ASTM A213-T91 steel substrate using the high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) process. The hybrid coating layer, consisting of nanocrystalline and amorphous phases, exhibits strong bonding features with the substrate, without revealing significant pore formation. By the coating process, it is possible to obtain a dense structure in which pores are hardly observed not only inside the coating layer but also at the interface between the coating layer and the substrate. The coating layer exhibits good adhesive strength as well as good wear resistance, making it suitable for coating layers for biomass applications.
- [Korean]
- Oxidation Behaviors and Degradation Properties of Aluminide Coated Stainless Steel at High Temperature
- Cheol Hong Hwang, Hyo Min Lee, Jeong Seok Oh, Dong Hyeon Hwang, Yu Seok Hwang, Jong Won Lee, Jeong Mook Choi, Joon Sik Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):396-402. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.396
- 722 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Stainless steel, a type of steel used for high-temperature parts, may cause damage when exposed to high temperatures, requiring additional coatings. In particular, the Cr2O3 product layer is unstable at 1000°C and higher temperatures; therefore, it is necessary to improve the oxidation resistance. In this study, an aluminide (Fe2Al5 and FeAl3) coating layer was formed on the surface of STS 630 specimens through Al diffusion coatings from 500°C to 700°C for up to 25 h. Because the coating layers of Fe2Al5 and FeAl3 could not withstand temperatures above 1200°C, an Al2O3 coating layer is deposited on the surface through static oxidation treatment at 500°C for 10 h. To confirm the ablation resistance of the resulting coating layer, dynamic flame exposure tests were conducted at 1350°C for 5–15 min. Excellent oxidation resistance is observed in the coated base material beneath the aluminide layer. The conditions of the flame tests and coating are discussed in terms of microstructural variations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermal Stability and Degradation Properties of Aluminide Coated and Uncoated Ti-6Al-4V Alloys Exposed to High Temperature Flame
C. Hwang, J. Park, J. Oh, D. Han, S. Lee, K. Shin, J. Choi, K. P. Shinde, J. S. Park
Metals and Materials International.2023; 29(7): 1855. CrossRef
- Thermal Stability and Degradation Properties of Aluminide Coated and Uncoated Ti-6Al-4V Alloys Exposed to High Temperature Flame
- [Korean]
- Effect of Spray Angle the on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Y2O3 Coating Layer Manufactured by Atmospheric Plasma Spray Process
- Yu-Jin Hwang, Kyoung-Wook Kim, Ho-Young Lee, Sik-Chol Kwon, Kee Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(4):310-316. Published online August 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.4.310
- 1,439 View
- 35 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The effects of different spray angles (90°, 85°, 80°) on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a Y2O3 coating layer prepared using the atmospheric plasma spray (APS) process were studied. The powders employed in this study had a spherical shape and included a cubic Y2O3 phase. The APS coating layer exhibited the same phase as the powders. Thickness values of the coating layers were 90°: 203.7 ± 8.5 μm, 85°: 196.4 ± 9.6 μm, and 80°: 208.8 ± 10.2 μm, and it was confirmed that the effect of the spray angle on the thickness was insignificant. The porosities were measured as 90°: 3.9 ± 0.85%, 85°: 11.4 ± 2.3%, and 80°: 12.7 ± 0.5%, and the surface roughness values were 90°: 5.9 ± 0.3 μm, 85°: 8.5 ± 1.1 μm, and 80°: 8.5 ± 0.4 μm. As the spray angle decreased, the porosity increased, but the surface roughness did not show a significant difference. Vickers hardness measurements revealed values of 90°: 369.2 ± 22.3, 85°: 315.8 ± 31.4, and 80°: 267.1 ± 45.1 HV. It was found that under the condition of a 90° angle with the lowest porosity exhibited the best hardness value. Based on the aforementioned results, an improved method for the APS Y2O3 coating layer was also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of In Situ Laser-Assisted Plasma Spraying on the Plasma Etching Resistance of Yttrium Oxide Coating
Xutao Zhao, Tian Xie, Panpan Zhang, Zhehe Yao, Qunli Zhang, Jiake Deng, Yongfeng Sui, Jianhua Yao
Coatings.2024; 14(11): 1427. CrossRef - Investigation of contamination particles generation and surface chemical reactions on Al2O3, Y2O3, and YF3 coatings in F-based plasma
Jongho So, Minjoong Kim, Hyuksung Kwon, Seonjeong Maeng, Eunmi Choi, Chin-Wook Chung, Ju-Young Yun
Applied Surface Science.2023; 629: 157367. CrossRef - Cleaning Effect of Atmospheric-Plasma-Sprayed Y2O3 Coating Using Piranha Solution Based on Contamination Particle Measurement
Hyuksung Kwon, Minjoong Kim, Jongho So, Seonjeong Maeng, Jae-Soo Shin, Ju-Young Yun
Coatings.2023; 13(3): 653. CrossRef - The effect of powder particle size on the corrosion behavior of atmospheric plasma spray-Y2O3 coating: Unraveling the corrosion mechanism by fluorine-based plasma
Minjoong Kim, Eunmi Choi, Dongjin Lee, Jungpil Seo, Tae-Sun Back, Jongho So, Ju-Young Yun, Song-Moon Suh
Applied Surface Science.2022; 606: 154958. CrossRef - The Effect of Powder Particle Size on the Corrosion Behavior of Atmospheric Plasma Spray-Y2o3 Coating: Unraveling the Corrosion Mechanism by Fluorine-Based Plasma
Minjoong Kim, Eunmi Choi, Dongjin Lee, Jungpil Seo, Tae Sun Back, Jongho So, Ju-Young Yun, Song-Moon Suh
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Effect of In Situ Laser-Assisted Plasma Spraying on the Plasma Etching Resistance of Yttrium Oxide Coating
- [Korean]
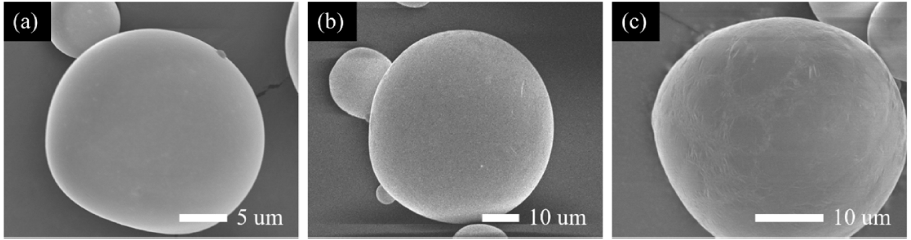
- Development of Hybrid Insulating Coating for Fe-based Soft Magnetic Powder
- Jungjoon Kim, Sungyeom Kim, Youngkyun Kim, Taesuk Jang, Hwi-jun Kim, Youngjin Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):233-238. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.233
- 595 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Iron-based amorphous powder attracts increasing attention because of its excellent soft magnetic properties and low iron loss at high frequencies. The development of an insulating layer on the surface of the amorphous soft magnetic powder is important for minimizing the eddy current loss and enhancing the energy efficiency of highfrequency devices by further increasing the electrical resistivity of the cores. In this study, a hybrid insulating coating layer is investigated to compensate for the limitations of monolithic organic or inorganic coating layers. Fe2O3 nanoparticles are added to the flexible silicon-based epoxy layer to prevent magnetic dilution; in addition TiO2 nanoparticles are added to enhance the mechanical durability of the coating layer. In the hybrid coating layer with optimal composition, the decrease in magnetic permeability and saturation magnetization is suppressed.
- [Korean]
- Effect of High Frequency Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Wear Properties of Ni based Self Fluxing Composite Coating Layer Manufactured by HVOF Spray Process
- Dong-Yeol Wi, Gi-Su Ham, Sun-Hong Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):421-431. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.421

- 774 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, the formation, microstructure, and wear properties of Colmonoy 88 (Ni-17W-15Cr-3B-4Si wt.%) + Stellite 1 (Co-32Cr-17W wt.%) coating layers fabricated by high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) spraying are investigated. Colmonoy 88 and Stellite 1 powders were mixed at a ratio of 1:0 and 5:5 vol.%. HVOF sprayed selffluxing composite coating layers were fabricated using the mixed powder feedstocks. The microstructures and wear properties of the composite coating layers are controlled via a high-frequency heat treatment. The two coating layers are composed of γ-Ni, Ni3B, W2B, and Cr23C6 phases. Co peaks are detected after the addition of Stellite 1 powder. Moreover, the WCrB2 hard phase is detected in all coating layers after the high-frequency heat treatment. Porosities were changed from 0.44% (Colmonoy 88) to 3.89% (Colmonoy 88 + ST#1) as the content of Stellite 1 powder increased. And porosity is denoted as 0.3% or less by inducing high-frequency heat treatment. The wear results confirm that the wear property significantly improves after the high-frequency heat treatment, because of the presence of wellcontrolled defects in the coating layers. The wear surfaces of the coated layers are observed and a wear mechanism for the Ni-based self-fluxing composite coating layers is proposed.
- [Korean]
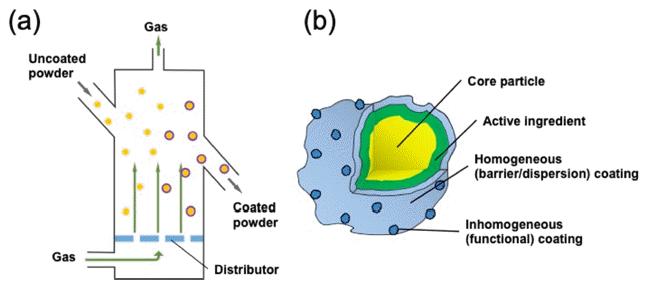
- Atomic Layer Deposition for Powder Coating
- Seok Choi, Jeong Hwan Han, Byung Joon Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):243-250. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.243
- 1,979 View
- 41 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is widely used as a tool for the formation of near-atomically flat and uniform thin films in the semiconductor and display industries because of its excellent uniformity. Nowadays, ALD is being extensively used in diverse fields, such as energy and biology. By controlling the reactivity of the surface, either homogeneous or inhomogeneous coating on the shell of nanostructured powder can be accomplished by the ALD process. However, the ALD process on the powder largely depends on the displacement of powder in the reactor. Therefore, the technology for the fluidization of the powder is very important to redistribute its position during the ALD process. Herein, an overview of the three types of ALD reactors to agitate or fluidize the powder to improve the conformality of coating is presented. The principle of fluidization its advantages, examples, and limitations are addressed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-performance of ZnO/TiO2 heterostructured thin-film photocatalyst fabricated via atomic layer deposition
Ji Young Park, Jeong Hwan Han, Byung Joon Choi
Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - TiO2 Thin Film Coating on an Nb-Si–Based Superalloy via Atomic Layer Deposition
Ji Young Park, Su Min Eun, Jongmin Byun, Byung Joon Choi
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(3): 255. CrossRef - Atomic layer deposition of ZnO layers on Bi2Te3 powders: Comparison of gas fluidization and rotary reactors
Myeong Jun Jung, Myeongjun Ji, Jeong Hwan Han, Young-In Lee, Sung-Tag Oh, Min Hwan Lee, Byung Joon Choi
Ceramics International.2022; 48(24): 36773. CrossRef
- High-performance of ZnO/TiO2 heterostructured thin-film photocatalyst fabricated via atomic layer deposition
- [English]
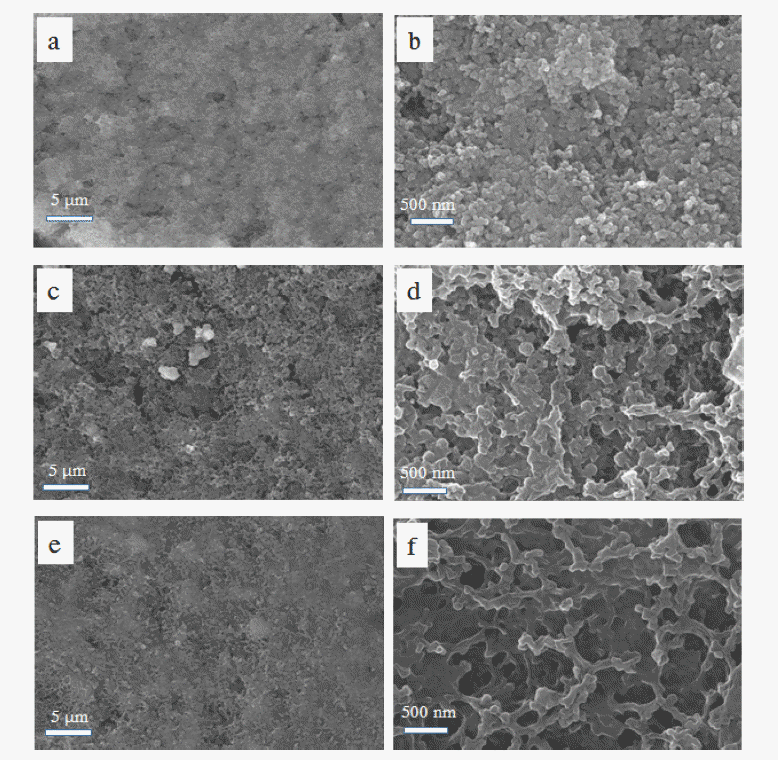
- A Separator with Activated Carbon Powder Layer to Enhance the Performance of Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
- Duc-Luong Vu, Jae-Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):466-474. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.466
- 1,054 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The high theoretical energy density (2600 Wh kg−1) of Lithium-sulfur batteries and the high theoretical capacity of elemental sulfur (1672 mAh g−1) attract significant research attention. However, the poor electrical conductivity of sulfur and the polysulfide shuttle effect are chronic problems resulting in low sulfur utilization and poor cycling stability. In this study, we address these problems by coating a polyethylene separator with a layer of activated carbon powder. A lithium-sulfur cell containing the activated carbon powder-coated separator exhibits an initial specific discharge capacity of 1400 mAh g−1 at 0.1 C, and retains 63% of the initial capacity after 100 cycles at 0.2 C, whereas the equivalent cell with a bare separator exhibits a 1200 mAh g−1 initial specific discharge capacity, and 50% capacity retention under the same conditions. The activated carbon powder-coated separator also enhances the rate capability. These results indicate that the microstructure of the activated carbon powder layer provides space for the sulfur redox reaction and facilitates fast electron transport. Concurrently, the activated carbon powder layer traps and reutilizes any polysulfides dissolved in the electrolyte. The approach presented here provides insights for overcoming the problems associated with lithium-sulfur batteries and promoting their practical use.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A one-step deposition method to prepare separators with carbon soot loading for lithium-sulfur battery
Yueting Zhu, Jingjing Wang, Yanshu Wang, Ying Zhu, Yixuan Li, Shicheng Zhao
Ionics.2022; 28(4): 1693. CrossRef - High thermal stability multilayered electrolyte complexes via layer-by-layer for long-life lithium-sulfur battery
Jing Wang, Yufan Li, Xianmei Deng, Lei Yan, Zhiqiang Shi
Ionics.2020; 26(11): 5481. CrossRef
- A one-step deposition method to prepare separators with carbon soot loading for lithium-sulfur battery
- [Korean]
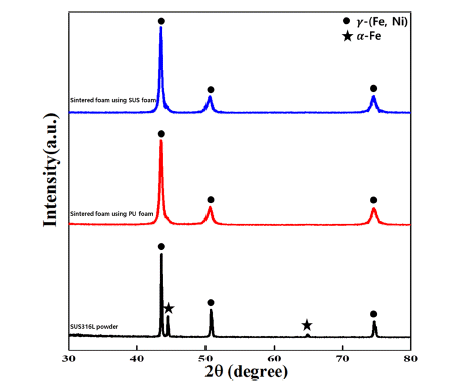
- A Study on Pore Properties of SUS316L Powder Porous Metal Fabricated by Electrostatic Powder Coating Process
- Min-Jeong Lee, Yu-Jeong Yi, Hyeon-Ju Kim, Manho Park, Byoung-Kee Kim, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):415-419. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.415
- 751 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Porous metals demonstrate not only excessively low densities, but also novel physical, thermal, mechanical, electrical, and acoustic properties. Thus, porous metals exhibit exceptional performance, which are useful for diesel particulate filters, heat exchangers, and noise absorbers. In this study, SUS316L foam with 90% porosity and 3,000 μm pore size is successfully manufactured using the electrostatic powder coating (ESPC) process. The mean size of SUS316L powders is approximately 12.33 μm. The pore properties are evaluated using SEM and Archimedes. As the quantity of powder coating increases, pore size decreases from 2,881 to 1,356 μm. Moreover, the strut thickness and apparent density increase from 423.7 to 898.3 μm and from 0.278 to 0.840 g/cm3, respectively. It demonstrates that pore properties of SUS316L powder porous metal are controllable by template type and quantity of powder coating.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
Minji Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Su-Jin Yun, Poong-Yeon Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Juyong Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 299. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
- [Korean]
- Study of Color Evolution by Silica Coating and Etching based Morphological Control of α-FeOOH
- NaRi Lee, Ri Yu, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):379-383. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.379
- 1,136 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
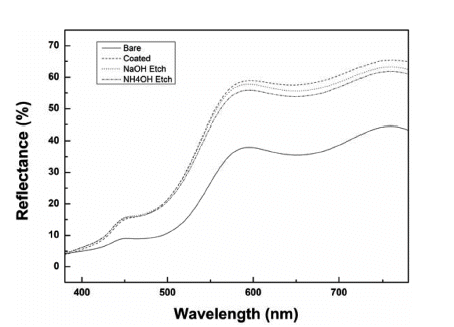
PDF Silica is used in shell materials to minimize oxidation and aggregation of nanoparticles. Particularly, porous silica has gained attention because of its performance in adsorption, catalysis, and medical applications. In this study, to investigate the effect of the density of the silica coating layer on the color of the pigment, we arbitrarily change the structure of a silica layer using an etchant. We use NaOH or NH4OH to etch the silica coating layer. First, we synthesize α-FeOOH for a length of 400 nm and coat it with TEOS to fabricate particles with a 50 nm coating layer. The coating thickness is then adjusted to 30–40 nm by etching the silica layer for 5 h. Four different shapes of α-FeOOH with different colors are measured using UV–vis light. From the color changes of the four different shapes of α-FeOOH features during coating or etching, the
L * value is observed to increase and brighten the overall color, and theb * value increases to impart a clear yellow color to the pigment. The brightest yellow color was that coated with silica; if the sample is etched with NaOH or NH4OH, theb * value can be controlled to study the yellow colors.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trend of Ceramic Nano Pigments
Ri Yu, YooJin Kim
Ceramist.2019; 22(3): 256. CrossRef
- Trend of Ceramic Nano Pigments
- [Korean]
- Formation of Uniform SnO2 Coating Layer on Carbon Nanofiber by Pretreatment in Atomic Layer Deposition
- Dong Ha Kim, Doh-Hyung Riu, Byung Joon Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):43-47. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.1.43
- 783 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Carbon nanofibers (CNF) are widely used as active agents for electrodes in Li-ion secondary battery cells, supercapacitors, and fuel cells. Nanoscale coatings on CNF electrodes can increase the output and lifespan of battery devices. Atomic layer deposition (ALD) can control the coating thickness at the nanoscale regardless of the shape, suitable for coating CNFs. However, because the CNF surface comprises stable C–C bonds, initiating homogeneous nuclear formation is difficult because of the lack of initial nucleation sites. This study introduces uniform nucleation site formation on CNF surfaces to promote a uniform SnO2 layer. We pretreat the CNF surface by introducing H2O or Al2O3 (trimethylaluminum + H2O) before the SnO2 ALD process to form active sites on the CNF surface. Transmission electron microscopy and energy-dispersive spectroscopy both identify the SnO2 layer morphology on the CNF. The Al2O3-pretreated sample shows a uniform SnO2 layer, while island-type SnOx layers grow sparsely on the H2Opretreated or untreated CNF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Atomic layer deposition of ZnO layers on Bi2Te3 powders: Comparison of gas fluidization and rotary reactors
Myeong Jun Jung, Myeongjun Ji, Jeong Hwan Han, Young-In Lee, Sung-Tag Oh, Min Hwan Lee, Byung Joon Choi
Ceramics International.2022; 48(24): 36773. CrossRef - Effects of SnO2 layer coated on carbon nanofiber for the methanol oxidation reaction
Dong Ha Kim, Dong-Yo Shin, Young-Geun Lee, Geon-Hyoung An, Jeong Hwan Han, Hyo-Jin Ahn, Byung Joon Choi
Ceramics International.2018; 44(16): 19554. CrossRef
- Atomic layer deposition of ZnO layers on Bi2Te3 powders: Comparison of gas fluidization and rotary reactors
- [Korean]
- Effect of Deposition Parameter and Mixing Process of Raw Materials on the Phase and Structure of Ytterbium Silicate Environmental Barrier Coatings by Suspension Plasma Spray Method
- Ho-lim Ryu, Seon-A Choi, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Soo Han, Kyun Choi, Sahn Nahm, Yoon-Suk Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):437-443. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.437

- 790 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF SiC-based composite materials with light weight, high durability, and high-temperature stability have been actively studied for use in aerospace and defense applications. Moreover, environmental barrier coating (EBC) technologies using oxide-based ceramic materials have been studied to prevent chemical deterioration at a high temperature of 1300°C or higher. In this study, an ytterbium silicate material, which has recently been actively studied as an environmental barrier coating because of its high-temperature chemical stability, is fabricated on a sintered SiC substrate. Yb2O3 and SiO2 are used as the raw starting materials to form ytterbium disilicate (Yb2Si2O7). Suspension plasma spraying is applied as the coating method. The effect of the mixing method on the particle size and distribution, which affect the coating formation behavior, is investigated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), an energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. It is found that the originally designed compounds are not effectively formed because of the refinement and vaporization of the raw material particles, i.e., SiO2, and the formation of a porous coating structure. By changing the coating parameters such as the deposition distance, it is found that a denser coating structure can be formed at a closer deposition distance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
Seong-June Youn, Young-Kyun Kim, Jae-Sung Park, Joo-Hyun Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(4): 333. CrossRef
- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
- [English]
- Lithium-silicate coating on Lithium Nickel Manganese Oxide (LiNi0.7Mn0.3O2) with a Layered Structure
- Dong-jin Kim, Da-ye Yoon, Woo-byoung Kim, Jae-won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):87-95. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.87
- 1,242 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Lithium silicate, a lithium-ion conducting ceramic, is coated on a layer-structured lithium nickel manganese oxide (LiNi0.7Mn0.3O2). Residual lithium compounds (Li2CO3 and LiOH) on the surface of the cathode material and SiO2 derived from tetraethylorthosilicate are used as lithium and silicon sources, respectively. Powder X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive spectroscopy analyses show that lithium silicate is coated uniformly on the cathode particles. Charge and discharge tests of the samples show that the coating can enhance the rate capability and cycle life performance. The improvements are attributed to the reduced interfacial resistance originating from suppression of solid-electrolyte interface (SEI) formation and dissolution of Ni and Mn due to the coating. An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of the cycled electrodes shows that nickel oxide and manganese oxide particles are formed on the surface of the electrode and that greater decomposition of the electrolyte occurs for the bare sample, which confirms the assumption that SEI formation and Ni and Mn dissolution can be reduced using the coating process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Artificial cathode-electrolyte interphases on nickel-rich cathode materials modified by silyl functional group
Hye Ji Song, Seol Heui Jang, Juhyeon Ahn, Si Hyoung Oh, Taeeun Yim
Journal of Power Sources.2019; 416: 1. CrossRef
- Artificial cathode-electrolyte interphases on nickel-rich cathode materials modified by silyl functional group
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Polytetrafluoroethylene thin Film from Powder Dispersion-solution for Energy Nanogenerator Applications
- Il-Kyu Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):102-107. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.102
- 1,047 View
- 13 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
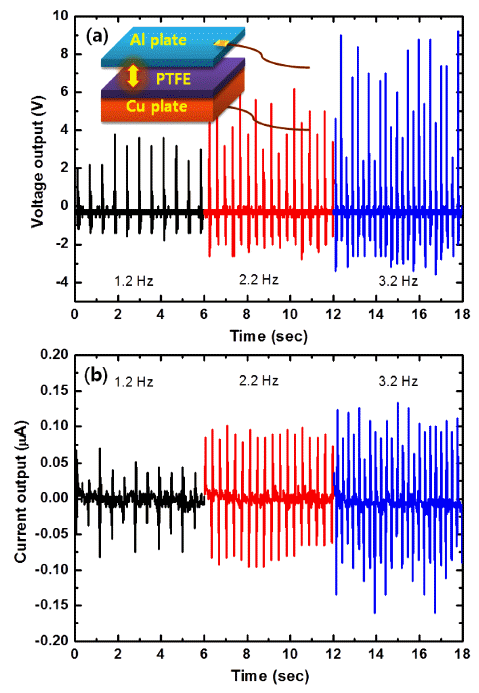
PDF Porous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) thin films are fabricated by spin-coating using a dispersion solution containing PTFE powders, and their crystalline properties are investigated after thermal annealing at various temperatures ranging from 300 to 500°C. Before thermal annealing, the film is densely packed and consists of many granular particles 200-300 nm in diameter. However, after thermal annealing, the film contains many voids and fibrous grains on the surface. In addition, the film thickness decreases after thermal annealing owing to evaporation of the surfactant, binder, and solvent composing the PTFE dispersion solution. The film thickness is systematically controlled from 2 to 6.5 μm by decreasing the spin speed from 1,500 to 500 rpm. A triboelectric nanogenerator is fabricated by spin-coating PTFE thin films onto polished Cu foils, where they act as an active layer to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy. A triboelectric nanogenerator consisting of a PTFE layer and Al metal foil pair shows typical output characteristics, exhibiting positive and negative peaks during applied strain and relief cycles due to charging and discharging of electrical charge carriers. Further, the voltage and current outputs increase with increasing strain cycle owing to accumulation of electrical charge carriers during charge-discharge.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent Development in Performance Enhancement of PVDF-Nanopowder Composite-based Energy Harvesting Devices
Geon-Ju Choi, Il-Kyu Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 247. CrossRef
- Recent Development in Performance Enhancement of PVDF-Nanopowder Composite-based Energy Harvesting Devices
- [Korean]
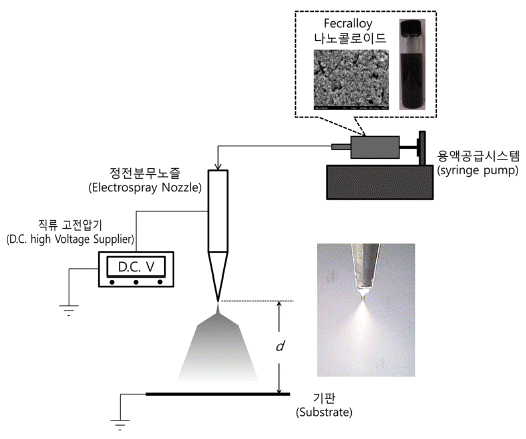
- Electrospray and Thermal Treatment Process for Enhancing Surface Roughness of Fecralloy Coating Layer on a Large Sized Substrate
- Hye Moon Lee, Hye Young Koo, Sangsun Yang, Dahee Park, Sooho Jung, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):46-52. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.46
- 360 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fecralloy coating layer with large surface area is suitable for use as a filter media for efficient removal of hot gaseous pollutants exhausted from combustion processes. For uniform preparation of a Fecralloy coating layer with large surface area and strong adhesion to substrate, electrospray coating and thermal treatment processes are experimentally optimized in this study. A nano-colloidal solution with 0.05 wt% Fecralloy nanoparticles is successfully prepared. Optimized electrospraying conditions are experimentally discovered to prepare a uniform coating layer of Fecralloy nanocolloidal solution on a substrate. Drying the electrospray coated Fecralloy nano-colloidal solution layer at 120°C and subsequent heating at 600°C are the best post-treatment for enhancing the adhesion force and surface roughness of the Fecralloy coating layer on a substrate. An electrospray coating system, consisting of several multi-groove nozzles, is also experimentally confirmed as a reasonable device for uniform coating of Fecralloy nano-colloid on a large area substrate.
- [Korean]
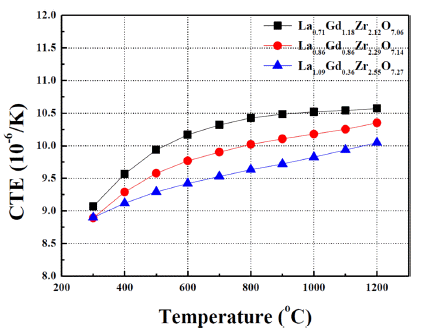
- Phase Formation and Thermo-physical Properties of Lanthanum/Gadolinium Zirconate with Reduced Rare-earth Contents for Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Sujin Lee, Chang-Sup Kwon, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):420-425. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.420
- 1,059 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare-earth zirconates, such as lanthanum zirconates and gadolinium zirconates, have been intensively investigated due to their excellent properties of low thermal conductivity as well as chemical stability at high temperature, which can make these materials ones of the most promising candidates for next-generation thermal barrier coating applications. In this study, three compositions, lanthanum/gadolinium zirconates with reduced rare-earth contents from stoichiometric RE2Zr2O7 compositions, are fabricated via solid state reaction as well as sintering at 1600°C for 4 hrs. The phase formation, microstructure, and thermo-physical properties of three oxide ceramics are examined. In particular, each oxide ceramics exhibits composite structures between pyrochlore and fluorite phases. The potential of lanthanum/ gadolinium zirconate ceramics for TBC applications is also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rare earth zirconate nanostructures: Recent development on preparation and photocatalytic applications
Sahar Zinatloo-Ajabshir, Masoud Salavati-Niasari, Azam Sobhani, Zahra Zinatloo-Ajabshir
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2018; 767: 1164. CrossRef - A novel Co-ions complexation method to synthesize pyrochlore La 2 Zr 2 O 7
Chunhui Xu, Hongyun Jin, Qifeng Zhang, Can Huang, Daifeng Zou, Fujian He, Shuen Hou
Journal of the European Ceramic Society.2017; 37(8): 2871. CrossRef - Fabrication and Characteristics of Thermal Barrier Coatings in the La2O3-Gd2O3-ZrO2System by Using Suspension Plasma Spray with Different Suspension Preparations
Soyul Lee, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
Journal of the Korean institute of surface engineering.2016; 49(6): 595. CrossRef
- Rare earth zirconate nanostructures: Recent development on preparation and photocatalytic applications
- [Korean]
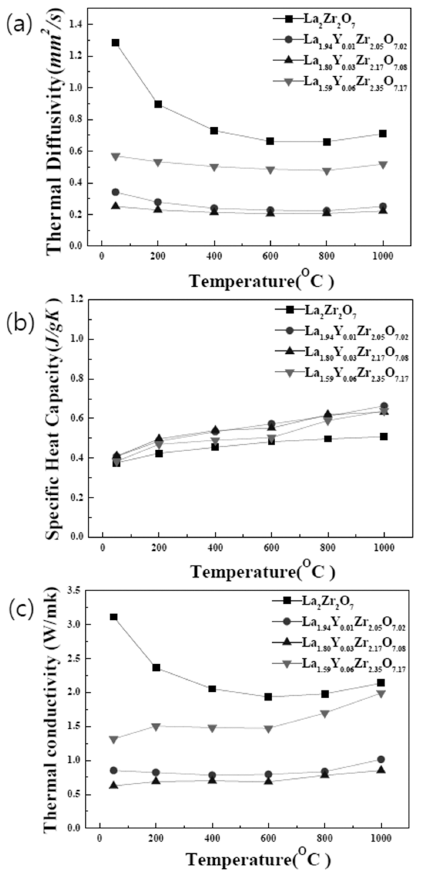
- Fabrication and Characterization of Ceramics and Thermal Barrier Coatings of Lanthanum Zirconate with Reduced Rare-earth Contents in the La2O3-ZrO2 System
- Chang-Sup Kwon, Sujin Lee, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Byung-Koog Jang, Seongwon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):413-419. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.413
- 788 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Lanthanum zirconate, La2Zr2O7, is one of the most promising candidates for next-generation thermal barrier coating (TBC) applications in high efficient gas turbines due to its low thermal conductivity and chemical stability at high temperature. In this study, bulk specimens and thermal barrier coatings are fabricated via a variety of sintering processes as well as suspension plasma spray in lanthanum zirconates with reduced rare-earth contents. The phase formation, microstructure, and thermo-physical properties of these oxide ceramics and coatings are examined. In particular, lanthanum zirconates with reduced rare-earth contents in a La2Zr2O7-4YSZ composite system exhibit a single phase of fluorite or pyrochlore after fabricated by suspension plasma spray or spark plasma sintering. The potential of lanthanum zirconate ceramics for TBC applications is also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phase Formation and Thermo-physical Properties of Lanthanum/Gadolinium Zirconate with Reduced Rare-earth Contents for Thermal Barrier Coatings
Sujin Lee, Chang-Sup Kwon, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(6): 420. CrossRef
- Phase Formation and Thermo-physical Properties of Lanthanum/Gadolinium Zirconate with Reduced Rare-earth Contents for Thermal Barrier Coatings
- [English]
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Cu Foam by Slurry Coating Process
- Dahee Park, Eun-Mi Jung, Sangsun Yang, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):87-92. Published online April 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.87

- 1,021 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metallic porous materials have many interesting combinations of physical and geometrical properties with very low specific weight or high gas permeability. In this study, highly porous Cu foam is successfully fabricated by a slurry coating process. The Cu foam is fabricated specifically by changing the coating amount and the type of polyurethane foam used as a template. The processing parameters and pore characteristics are observed to identify the key parameters of the slurry coating process and the optimized morphological properties of the Cu foam. The pore characteristics of Cu foam are investigated by scanning electron micrographs and micro-CT analyzer, and air permeability of the Cu foam is measured by capillary flow porometer. We confirmed that the characteristics of Cu foam can be easily controlled in the slurry coating process by changing the microstructure, porosity, pore size, strut thickness, and the cell size. It can be considered that the fabricated Cu foams show tremendous promise for industrial application.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation and comparative evolution of mechanical behavior of Fe and Fe2O3 foams and their polymer composites
Vemoori Raju, Roy Johnson, Asit Kumar Khanra
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2018; 750: 71. CrossRef
- Preparation and comparative evolution of mechanical behavior of Fe and Fe2O3 foams and their polymer composites
- [Korean]
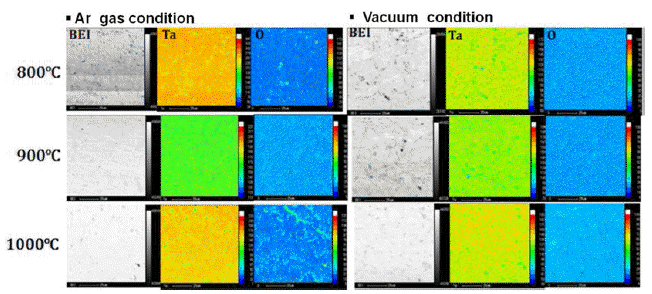
- Effect of Heat Treatment Environment on the Microstructure and Properties of Kinetic Sprayed Tantalum Coating Layer
- Ji-Hye Lee, Hyung-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):32-38. Published online February 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.32
- 652 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The effect of heat treatment environment on the microstructure and properties of tantalum coating layer manufactured by kinetic spraying was examined. Heat treatments are conducted for one hour at 800°C, 900°C, and 1000°C in two different environments of vacuum and Ar gas. Evaluation of microstructure and physical properties are conducted. High density α- tantalum single phase coating layer with a porosity of 0.04% and hardness of 550 Hv can be obtained. As heat treatment temperature increases, porosity identically decreases regardless of heat treatment environment (vacuum and Ar gas). Hardness of heat treated coating layer especially in Ar gas environment deceases from 550 Hv to 490 Hv with increasing heat treatment temperature. That in vacuum environment deceases from 550 Hv to 530 Hv. The boundary between particles became vague as heat treatment temperature increases. Oxygen distribution of tantalum coating layer is minute after heat treatment in vacuum environment than Ar gas environment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sintering Behavior and Microstructures of Tantalum and Tantalum-Tungsten Alloys Powders
Youngmoo Kim, Sung Ho Yang, Seong Lee, Sung Ho Lee, Joon-Woong Noh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 373. CrossRef
- Sintering Behavior and Microstructures of Tantalum and Tantalum-Tungsten Alloys Powders
- [Korean]
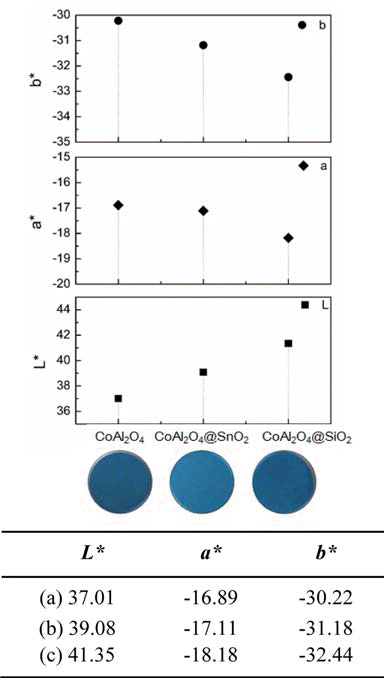
- Coloration and Chemical Stability of SiO2 and SnO2 Coated Blue CoAl2O4 Pigment
- JiYeon Yun, Ri Yu, Jae-Hwan Pee, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):377-381. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.377
- 635 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This work describes the coloration, chemical stability of SiO2 and SnO2-coated blue CoAl2O4 pigment. The CoAl2O4, raw materials, were synthesized by a co-precipitation method and coated with silica (SiO2) and tin oxide (SnO2) using sol-gel method, respectively. To study phase and coloration of CoAl2O4, we prepared nano sized CoAl2O4 pigments which were coated SiO2 and SnO2 using tetraethylorthosilicate, Na2SiO3 and Na2SnO3 as a coating material. To determine the stability of the coated samples and their colloidal solutions under acidic and basic conditions, colloidal nanoparticle solutions with various pH values were prepared and monitored over time. Blue CoAl2O4 solutions were tuned yellow color under all acidic/basic conditions. On the other hand, the chemical stability of SiO2 and SnO2-coated CoAl2O4 solution were improved when all samples pH values, respectively. Phase stability under acidic/basic condition of the core-shell type CoAl2O4 powders were characterized by transmission electron microscope, X-ray diffraction,
CIE L*a*b* color parameter measurements.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Characterization of SnO2-CoO/carbon-coated CoO Core/shell Nanowire Composites
- Yu-Jin Lee, Bon-Ryul Koo, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):360-365. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.360
- 692 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF SnO2-CoO/carbon-coated CoO core/shell nanowire composites were synthesized by using electrospinning and hydrothermal methods. In order to obtain SnO2-CoO/carbon-coated CoO core/shell nanowire composites, SnO2-Co3O4 nanowire composites and SnO2-Co3O4/polygonal Co3O4 core/shell nanowire composites are also synthesized. To demonstrate their structural, chemical bonding, and morphological properties, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy were carried out. These results indicated that the morphologies and structures of the samples were changed from SnO2-Co3O4 nanowires having cylindrical structures to SnO2-Co3O4/Co3O4 core/shell nanowires having polygonal structures after a hydrothermal process. At last, SnO2-CoO/carbon-coated CoO core/shell nanowire composites having irregular and high surface area are formed after carbon coating using a polypyrrole (PPy). Also, there occur phases transformation of cobalt phases from Co3O4 to CoO during carbon coating using a PPy under a argon atmosphere.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Co-Embedded Graphitic Porous Carbon Nanofibers for Pt-Free Counter Electrode in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
혜란 안, 혜린 강, 효정 선, 지호 한, 효진 안
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2015; 25(12): 672~677. CrossRef - Synthesis of Perforated Polygonal Cobalt Oxides usinga Carbon Nanofiber Template
Dong-Yo Sin, Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(5): 350. CrossRef
- Co-Embedded Graphitic Porous Carbon Nanofibers for Pt-Free Counter Electrode in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
- [Korean]
- The Effect of Fe and Fe2O3 Powder Mixing Ratios on the Pore Properties of Fe Foam Fabricated by a Slurry Coating Process
- Jin Ho Choi, Eun-Mi Jeong, Dahee Park, Sangsun Yang, Yoo-Dong Hahn, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):266-270. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.266

- 1,275 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal foams have a cellular structure consisting of a solid metal containing a large volume fraction of pores. In particular, open, penetrating pores are necessary for industrial applications such as in high temperature filters and as a support for catalysts. In this study, Fe foam with above 90% porosity and 2 millimeter pore size was successfully fabricated by a slurry coating process and the pore properties were characterized. The Fe and Fe2O3 powder mixing ratios were controlled to produce Fe foams with different pore size and porosity. First, the slurry was prepared by uniform mixing with powders, distilled water and polyvinyl alcohol(PVA). After slurry coating on the polyurethane( PU) foam, the sample was dried at 80°C. The PVA and PU foams were then removed by heating at 700°C for 3 hours. The debinded samples were subsequently sintered at 1250°C with a holding time of 3 hours under hydrogen atmosphere. The three dimensional geometries of the obtained Fe foams with an open cell structure were investigated using X-ray micro CT(computed tomography) as well as the pore morphology, size and phase. The coated amount of slurry on the PU foam were increased with Fe2O3 mixing powder ratio but the shrinkage and porosity of Fe foams were decreased with Fe2O3 mixing powder ratio.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of STS316L Porous Metal for Vacuum Injection Mold
Se Hoon Kim, Sang Min Kim, Sang Ho Noh, Jin Pyeong Kim, Jae Hyuck Shin, Si-Young Sung, Jin Kwang Jin, Taean Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(3): 197. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of STS316L Porous Metal for Vacuum Injection Mold
- [Korean]
- Manufacturing and Properties of CGI-based Composite Coating Layer Utilizing a Warm Spray Process and Cu-Ga and Cu-In Mixed Powders
- Min-Gwang Jeon, Myeong-Ju Lee, Hyeong-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):229-234. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.229

- 768 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study manufactured a CIG-based composite coating layer utilizing a new warm spray process, and a mixed powder of Cu-20at.%Ga and Cu-20at.%In. In order to obtain the mixed powder with desired composition, the Cu-20at.%Ga and Cu-20at.%In powders were mixed with a 7:1 ratio. The mixed powder had an average particle size of 35.4 μm. Through the utilization of a warm spray process, a CIG-based composite coating layer of 180 μm thickness could be manufactured on a pure Al matrix. To analyze the microstructure and phase, the warm sprayed coating layer underwent XRD, SEM/EDS and EMPA analyses. In addition, to improve the physical properties of the coating layer, an annealing heat treatment was conducted at temperatures of 200°C, 400°C and 600°C for 1 hour each. The microstructure analysis identified α-Cu, Cu4In and Cu3Ga phases in the early mixed powder, while Cu4In disappeared, and additional Cu9In4 and Cu9Ga4 phases were identified in the warm sprayed coating layer. Porosity after annealing heat treatment reduced from 0.75% (warm sprayed coating layer) to 0.6% (after 600°C/1 hr. heat treatment), and hardness reduced from 288 Hv to 190 Hv. No significant phase changes were found after annealing heat treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Microstructure/Properties of Bulk-typeTantalum Material by a Kinetic Spray Process
Ji-Hye Lee, Ji-Won Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(1): 8. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Treatment Environment on the Microstructure and Properties of Kinetic Sprayed Tantalum Coating Layer
Ji-Hye Lee, Hyung-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(1): 32. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Microstructure/Properties of Bulk-typeTantalum Material by a Kinetic Spray Process
- [English]
- Coating of Cobalt Over Tungsten Carbide Powder by Wet Chemical Reduction Method
- Hyun-Seon Hong, Jin-Ho Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):93-96. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.93
- 1,533 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Cobalt coated tungsten carbide-cobalt composite powder has been prepared through wet chemical reduction method. The cobalt sulfate solution was converted to the cobalt chloride then the cobalt hydroxide. The tungsten carbide powders were added in to the cobalt hydroxide, the cobalt hydroxide was reduced and coated over tungsten carbide powder using hypo-phosphorous acid. Both the cobalt and the tungsten carbide phase peaks were evident in the tungsten carbide-cobalt composite powder by X-ray diffraction. The average particle size measured via scanning electron microscope, particle size analysis was around 380 nm and the thickness of coated cobalt was determined to be 30~40 nm by transmission electron microscopy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Electroless Ni-P deposition on WC powders through direct PdCl2 activation and study on the underlying mechanisms
Peng Tang, Shuwen Jiang, Jiawei Yan, Xianquan Li
Next Materials.2025; 6: 100496. CrossRef - Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
Jae Jin Sim, Sang Hoon Choi, Ji Hwan Park, Il Kyu Park, Jae Hong Lim, Kyoung Tae Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 251. CrossRef - Spark plasma sintering of WC–Co tool materials prepared with emphasis on WC core–Co shell structure development
Sungkyu Lee, Hyun Seon Hong, Hyo-Seob Kim, Soon-Jik Hong, Jin-Ho Yoon
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2015; 53: 41. CrossRef
- Electroless Ni-P deposition on WC powders through direct PdCl2 activation and study on the underlying mechanisms
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


