Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Comparison of the Properties of Rare-Earth Zirconate Thermal Barrier Coatings for Hydrogen-Fueled Gas Turbines
- Gun-Woong Lee, Min-Soo Nam, Min-Ji Kim, HyunSuk Jung, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):472-480. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00423

- 768 View
- 13 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) for hydrogen-fueled gas turbines withstand higher combustion temperatures and increased steam concentrations compared to conventional natural-gas systems. These harsh operating conditions significantly accelerate the thermal degradation of widely used YSZ coatings, emphasizing the need for alternative top-coat materials with improved phase stability and reduced thermal conductivity. In this study, rare-earth zirconate ceramics, Gd2Zr2O7 (GdZO), Tm2Zr2O7 (TmZO), and a mixed composition (Gd0.5Tm0.5)2Zr2O7 (Gd/TmZO), are synthesized and investigated as potential next-generation TBC candidates. Each material was comparatively examined with a focus on crystal structure, thermophysical properties, and thermal conductivity. Furthermore, high-temperature steam exposure experiments were performed to simulate hydrogen combustion environments. Microstructural analyses, high-temperature degradation behavior, and phase stability evaluations were carried out to obtain fundamental experimental data. This study provides essential baseline information for the design and development of high-performance TBC materials suitable for the hydrogen-fueled gas turbine systems.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AA3003 Tube for Heat Exchanger Processed by Floating Plug Drawing
- Hyeon-Jun Heo, Sung Jun Oh, Seong-Hee Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):459-465. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00346

- 710 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An AA3003 tube was severely deformed by cold floating plug drawing, and then annealed at temperatures from 210 to 460℃. The as drawn Al tube exhibited a typical deformation structure in which the grains were greatly elongated along the drawing direction. The hardness increased with increasing the reduction of cross-sectional area (RA), became 68Hv after RA= 99%. Up to 310℃, the Al tube still mainly exhibited a deformed structure. While complete recrystallization occurred at temperatures above 360℃. The hardness decreased with increasing the annealing temperature, and it became 33Hv after annealing at 410℃. Both the tensile and yield strengths also decreased with increasing the annealing temperature, but the decrease was larger in yield strength than in tensile strength. The elongation increased with increasing the annealing temperature. The changes in the strength and the elongation with the annealing temperature were the largest at 360℃, in which the complete recrystallization occurred.
- [English]
- Cost-effective Fabrication of Near β-Ti Alloy via L-PBF: Process Optimization of In-situ Alloying Ti-3Fe
- Sehun Kim, Ukju Gim, Taehu Kang, Jongik Lee, Sanghee Jeong, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):288-298. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00213

- 1,173 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study presents a cost-effective approach to fabricating near β-Ti alloys via in-situ alloying during laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF). A blend of non-spherical pure Ti, 3 wt.% Fe, and 0.1 wt.% SiO2 nanoparticles was used to induce β-phase stabilization and improve flowability. Twenty-five process conditions were evaluated across a volumetric energy density range of 31.75-214.30 J/mm3, achieving a maximum relative density of 99.21% at 89.29 J/mm3. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that the β-Ti phase was partially retained at room temperature, accompanied by lattice contraction in the α’-Ti structure, indicating successful Fe incorporation. Elemental mapping confirmed that the Fe distribution was homogeneous, without significant segregation. Compared to pure Ti, the Ti-3Fe sample exhibited a 49.2% increase in Vickers hardness and notable improvements in yield and ultimate tensile strengths. These results demonstrate the feasibility of in-situ alloying with low-cost elemental powders to produce high-performance near β-Ti alloys using L-PBF.
- [English]
- The Effect of Aluminum Powder Size on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Foam
- Seunghyeok Choi, Sungjin Kim, Tae-Young Ahn, Yu-Song Choi, Jae-Gil Jung, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):232-243. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00157

- 1,378 View
- 54 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, we analyzed the structural and mechanical properties of aluminum foams fabricated using aluminum powders of varying sizes and mixtures. The effects of sintering and pore structure at each size on the integrity and mechanical properties of the foams were investigated. Structural characteristics were examined using scanning electron microscopy and micro–computed tomography, while mechanical properties were evaluated through compression testing. The experimental results demonstrated that smaller powder sizes improved foam integrity, reduced porosity and pore size, and resulted in thinner cell walls. In combination, these effects increased compressive strength as the powder size decreased. The findings of this study contribute to the understanding and improvement of the mechanical properties of aluminum foams and highlight their potential for use in a wide range of applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sustainable Manufacturing of Graphene–Aluminum Composites: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment
Xinwei Yang, Qian Peng, Changke Chen, Qingcui Liu, Yudai Huang
Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy.2026; 12(1): 727. CrossRef
- Sustainable Manufacturing of Graphene–Aluminum Composites: A Comparative Life Cycle Assessment
- [Korean]
- Effect of Building Orientation on Tensile Properties of Hastelloy X alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seong-June Youn, GooWon Noh, Seok Su Sohn, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):131-137. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00080
- 1,139 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
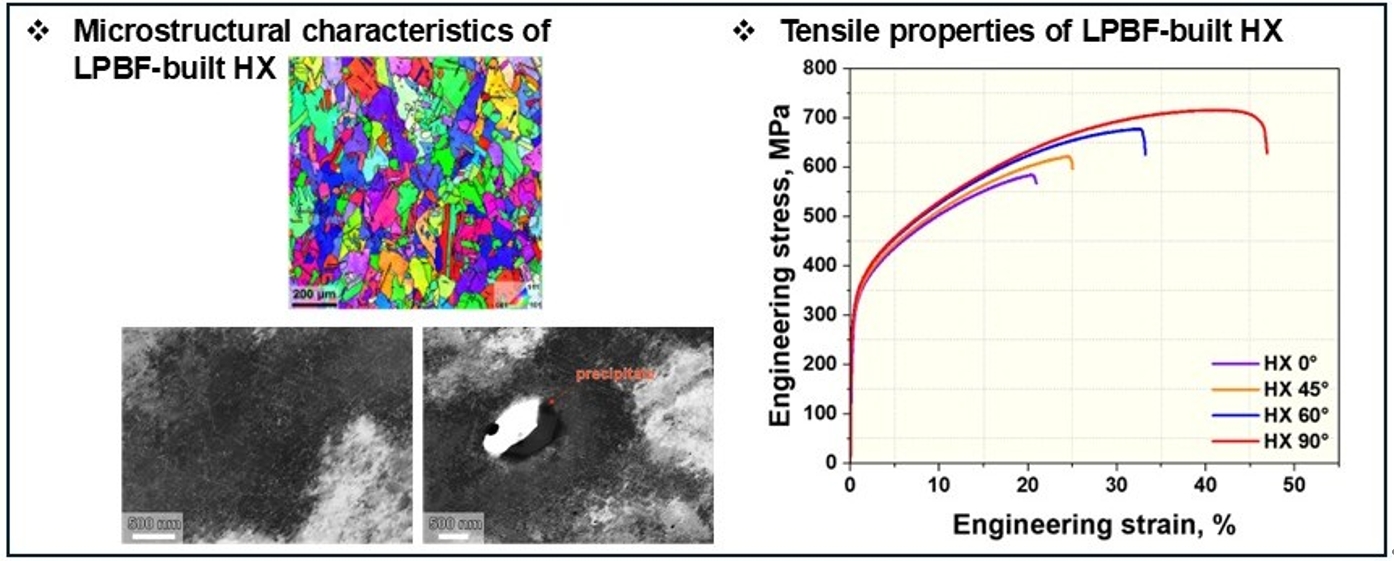
PDF - In this study, the effect of build orientation on the mechanical properties of Hastelloy X fabricated by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) process was investigated. Initial microstructural analysis revealed an equiaxed grain structure with random crystallographic orientation and annealing twins. Intragranular precipitates identified as Cr-rich M23C6 and Mo-rich M6C carbides were observed, along with a dense dislocation network and localized dislocation accumulation around the carbides. Mechanical testing showed negligible variation in yield strength with respect to build orientation; however, both ultimate tensile strength and elongation exhibited a clear increasing trend with higher build angles. Notably, the specimen built at 90° exhibited approximately 22% higher tensile strength and more than twice the elongation compared to the 0° specimen.
- [English]
- Ultra-Low-Temperature (4.2 K) Tensile Properties and Deformation Mechanism of Stainless Steel 304L Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seung-Min Jeon, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):95-103. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00066

- 1,927 View
- 57 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the ultra-low-temperature (4.2 K) tensile properties and deformation mechanisms of stainless steel 304L manufactured via laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). The tensile properties of LPBF 304L were compared to those of conventional 304L to assess its suitability for cryogenic applications. The results revealed that LPBF 304L exhibited a significantly higher yield strength but lower ultimate tensile strength and elongation than conventional 304L at 4.2 K. The temperature dependence of the yield strength also favored LPBF 304L. Microstructural analysis demonstrated that LPBF 304L features a high density of dislocation cells and nano-inclusions, contributing to its greater strength. Furthermore, strain-induced martensitic transformation was observed as a key deformation mechanism at cryogenic temperatures, where austenite transformed into both hexagonal-closed packed (HCP) and body-centered cubic (BCC) martensite. Notably, BCC martensite nucleation occurred within a single HCP band. These findings provide critical insights into the mechanical behavior of LPBF 304L at cryogenic temperatures and its potential for applications in extreme environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extremely low-temperature tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Heechan Jung, Min Young Sung, Young-Kyun Kim, Jaimyun Jung, Yoona Lee, Namhyun Kang, Kyung Tae Kim, Young-Sang Na, Seok Su Sohn, Jeong Min Park
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 950: 149460. CrossRef - Twinning- and transformation-induced high cryogenic strength and ductility of the CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy: Experiment and MD simulation
Yuze Wu, Zhide Li, Charlie Kong, M.W. Fu, Hailiang Yu
International Journal of Plasticity.2026; 196: 104553. CrossRef - Understanding the unique appearance behavior of shear bands during tensile deformation of α-brass at 4.2 K
Seon-Keun Oh, Sang-Hun Shim, Young-Kyun Kim, Young-Sang Na
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 945: 148989. CrossRef
- Extremely low-temperature tensile behavior of 316L stainless steel additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
- [English]
- A Review of Recent Developments in CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys Processed by Powder Metallurgy
- Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Sheetal Kumar Dewangan, Hansung Lee, Eunhyo Song, K. Raja Rao, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):145-164. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00430
- 4,526 View
- 118 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
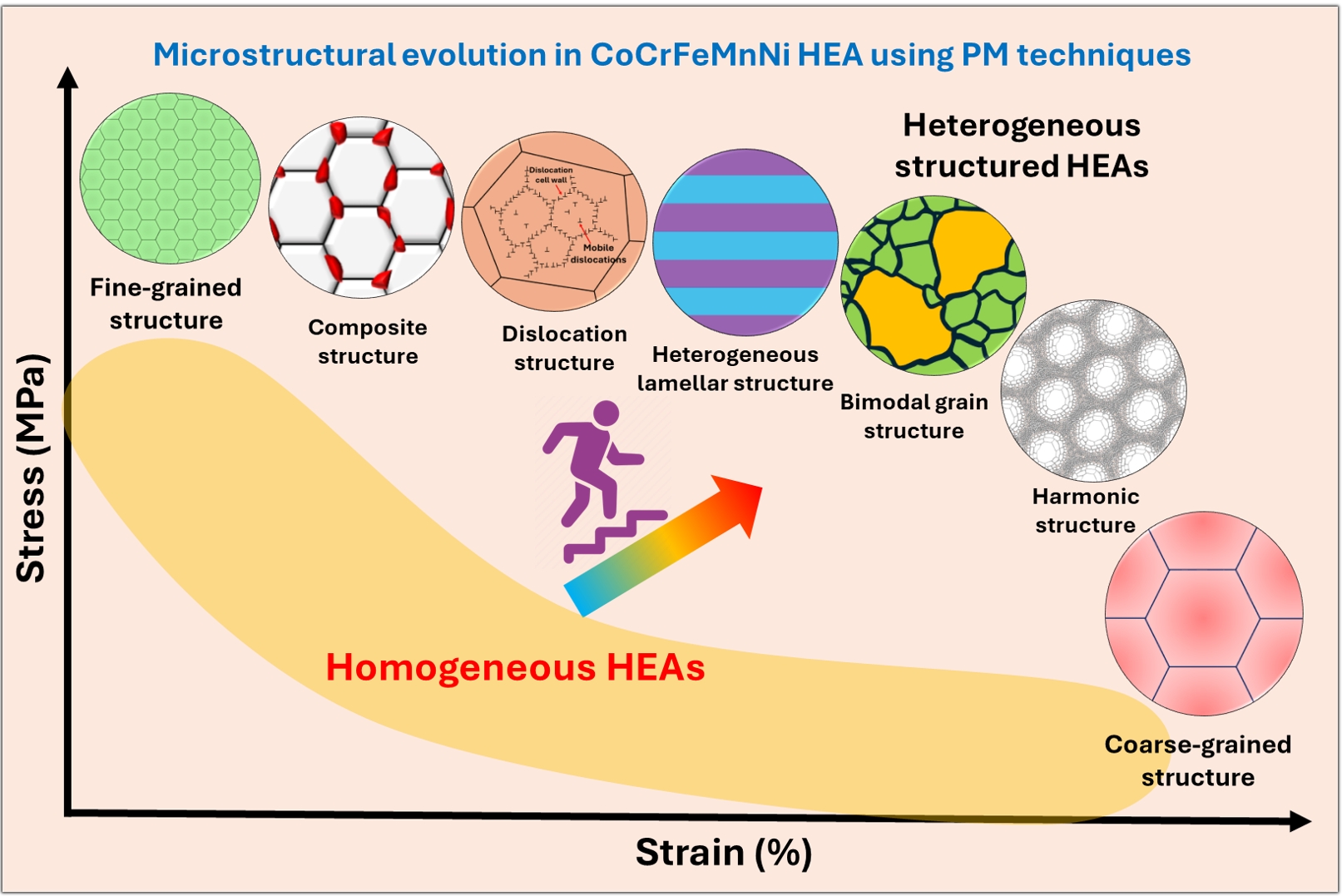
PDF - In recent years, high-entropy alloys (HEAs) have attracted considerable attention in materials engineering due to their unique phase stability and mechanical properties compared to conventional alloys. Since the inception of HEAs, CoCrFeMnNi alloys have been widely investigated due to their outstanding strength and fracture toughness at cryogenic temperatures. However, their lower yield strength at room temperature limits their structural applications. The mechanical properties of HEAs are greatly influenced by their processing methods and microstructural features. Unlike traditional melting techniques, powder metallurgy (PM) provides a unique opportunity to produce HEAs with nanocrystalline structures and uniform compositions. The current review explores recent advances in optimizing the microstructural characteristics in CoCrFeMnNi HEAs by using PM techniques to improve mechanical performance. The most promising strategies include grain refinement, dispersion strengthening, and the development of heterogeneous microstructures (e.g., harmonic, bimodal, and multi-metal lamellar structures). Thermomechanical treatments along with additive manufacturing techniques are also summarized. Additionally, the review addresses current challenges and suggests future research directions for designing advanced HEAs through PM techniques.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
Wooyoung Lee, Munsu Choi, Sungwook Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song, Taek-Soo Kim, Jungwan Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Soo-Hyun Joo
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 954: 149811. CrossRef - Structural and mechanical characteristics of high-entropy CoCrFeMnNi alloys manufactured by vacuum induction melting
V. K. Drobyshev, I. A. Panchenko, S. V. Konovalov, E. M. Zapolskaya
Russian Physics Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Sustainable powder metallurgy route to Densify oxide-derived CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy
Taehyeob Im, Minjong Kim, Gertrude Mugwe Mongella, Nelson Bayi, Caroline Sunyong Lee
Materials Today Sustainability.2026; 34: 101330. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef
- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
- [English]
- Comparative Review of the Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated via Wrought and Powder Metallurgy Processes
- Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, An Seong Min, Hyunseok Lee, Jeoung Han Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):365-373. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00213
- 2,836 View
- 66 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
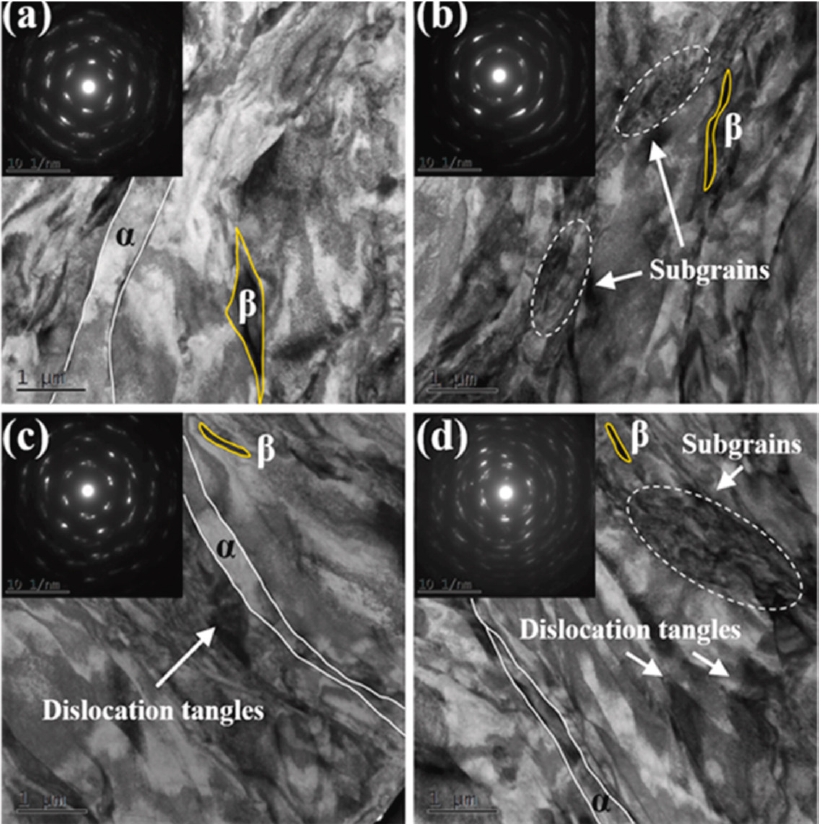
PDF - This review examines the microstructural and mechanical properties of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by wrought processing and powder metallurgy (PM), specifically laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) and hot isostatic pressing. Wrought methods, such as forging and rolling, create equiaxed alpha (α) and beta (β) grain structures with balanced properties, which are ideal for fatigue resistance. In contrast, PM methods, particularly LPBF, often yield a martensitic α′ structure with high microhardness, enabling complex geometries but requiring post-processing to improve its properties and reduce stress. The study evaluated the effects of processing parameters on grain size, phase distribution, and material characteristics, guiding the choice of fabrication techniques for optimizing Ti-6Al-4V performance in aerospace, biomedical, and automotive applications. The analysis emphasizes tailored processing to meet advanced engineering demands.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants from Titanium Turning Scrap via Alkali and Acid Two-Step Cleaning
Seong Min An, Raj Narayan Hajra, Chan Hee Park, Jin-Ho Yoon, Jinsung Rho, Chang-Min Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(7): 855. CrossRef - Effect of oxygen content in feedstock powders on microstructure and mechanical properties of ELI Ti-6Al-4V fabricated via laser powder bed fusion
Woo Hyeok Kim, Sang Woo Kim, Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, Jeoung Han Kim
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 307. CrossRef
- Removal of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants from Titanium Turning Scrap via Alkali and Acid Two-Step Cleaning
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of 3D Aligned h-BN based Polymer Composites with Enhanced Mechanical Properties for Battery Housing
- Kiho Song, Hyunseung Song, Sang In Lee, Changui Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):329-335. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00220
- 1,395 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
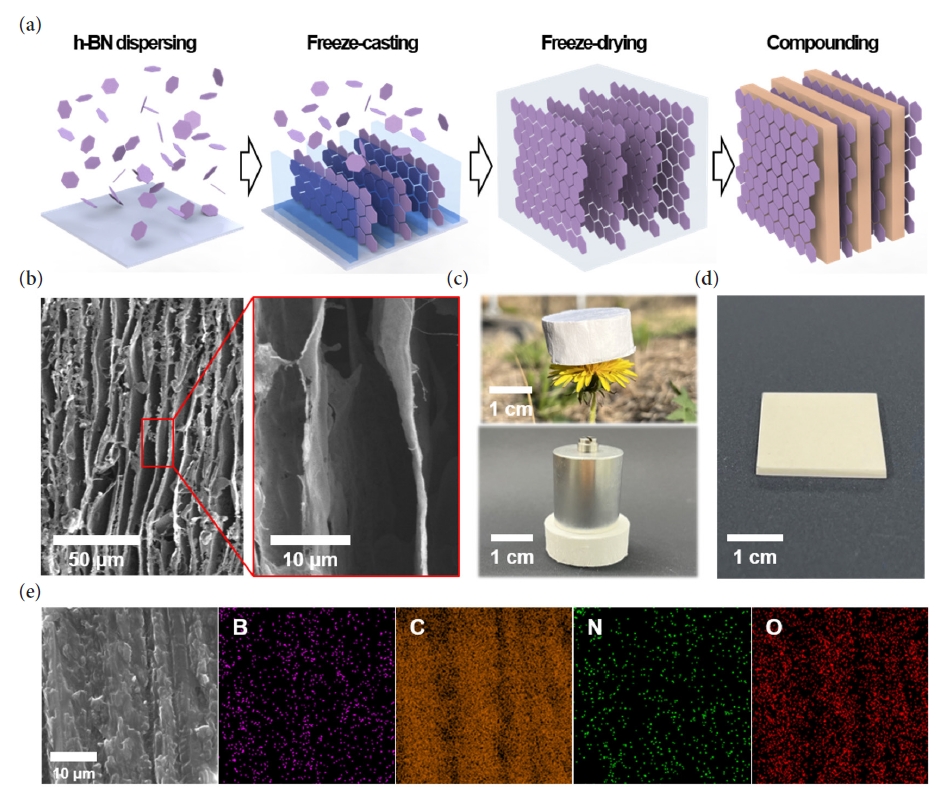
Supplementary Material - As the demand for electric vehicles increases, the stability of batteries has become one of the most significant issues. The battery housing, which protects the battery from external stimuli such as vibration, shock, and heat, is the crucial element in resolving safety problems. Conventional metal battery housings are being converted into polymer composites due to their lightweight and improved corrosion resistance to moisture. The transition to polymer composites requires high mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and thermal stability. In this paper, we proposes a high-strength nanocomposite made by infiltrating epoxy into a 3D aligned h-BN structure. The developed 3D aligned h-BN/epoxy composite not only exhibits a high compressive strength (108 MPa) but also demonstrates excellent electrical insulation and thermal stability, with a stable electrical resistivity at 200 °C and a low thermal expansion coefficient (11.46ⅹppm/℃), respectively.
- [English]
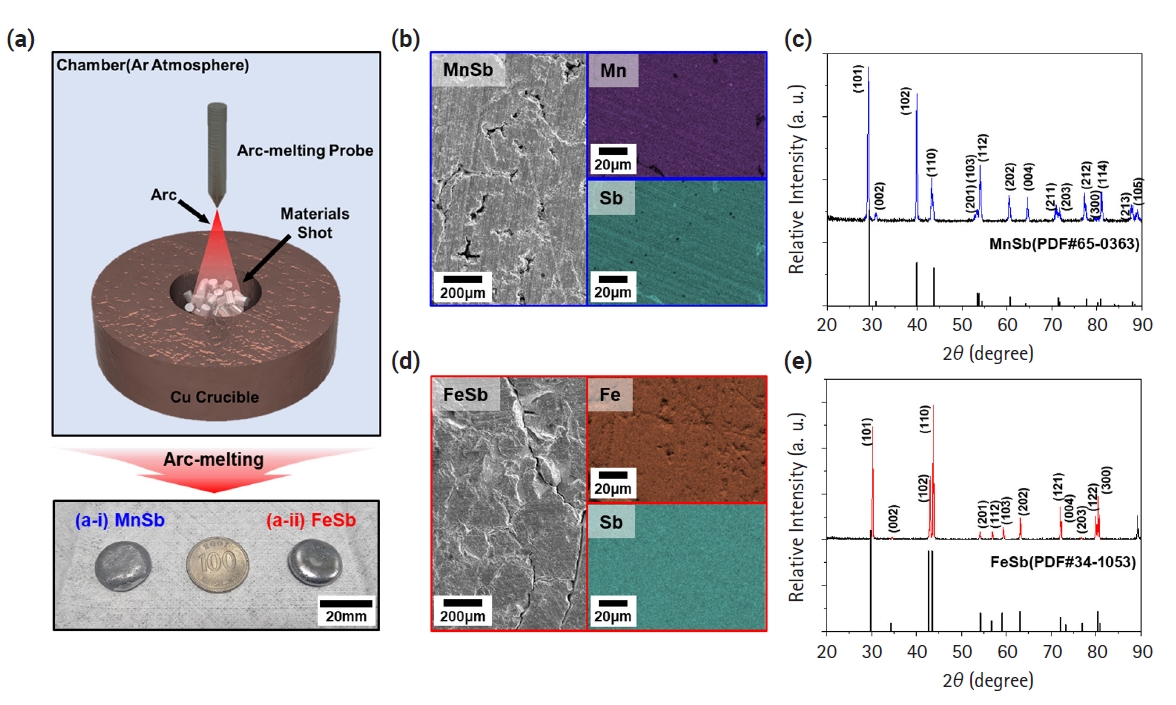
- Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
- Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):236-242. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00031
- 1,781 View
- 44 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The development of thermoelectric (TE) materials to replace Bi2Te3 alloys is emerging as a hot issue with the potential for wider practical applications. In particular, layered Zintl-phase materials, which can appropriately control carrier and phonon transport behaviors, are being considered as promising candidates. However, limited data have been reported on the thermoelectric properties of metal-Sb materials that can be transformed into layered materials through the insertion of cations. In this study, we synthesized FeSb and MnSb, which are used as base materials for advanced thermoelectric materials. They were confirmed as single-phase materials by analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns. Based on electrical conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity of both materials characterized as a function of temperature, the zT values of MnSb and FeSb were calculated to be 0.00119 and 0.00026, respectively. These properties provide a fundamental data for developing layered Zintl-phase materials with alkali/alkaline earth metal insertions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Jihun Yu, Kyung Tae Kim
Materials Letters.2025; 381: 137796. CrossRef - Highly deformable and hierarchical 3D composite sponge for versatile thermoelectric energy conversion
Jong Min Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Kwi-Il Park
Applied Surface Science.2025; 692: 162730. CrossRef
- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
- [English]
- Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):8-15. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.8
- 4,530 View
- 139 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The emergence of ferrous-medium entropy alloys (FeMEAs) with excellent tensile properties represents a potential direction for designing alloys based on metastable engineering. In this study, an FeMEA is successfully fabricated using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), a metal additive manufacturing technology. Tensile tests are conducted on the LPBF-processed FeMEA at room temperature and cryogenic temperatures (77 K). At 77 K, the LPBF-processed FeMEA exhibits high yield strength and excellent ultimate tensile strength through active deformation-induced martensitic transformation. Furthermore, due to the low stability of the face-centered cubic (FCC) phase of the LPBF-processed FeMEA based on nano-scale solute heterogeneity, stress-induced martensitic transformation occurs, accompanied by the appearance of a yield point phenomenon during cryogenic tensile deformation. This study elucidates the origin of the yield point phenomenon and deformation behavior of the FeMEA at 77 K.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stronger weld than base metal in face-centered cubic alloy through multi-scale heterogeneity
Yoona Lee, Sangwon Park, Dongwon Shin, Marcia Myung Hye Ahn, Wei Xiong, Nokeun Park, Hyoung Seop Kim, Je In Lee, Wookjin Lee, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park, Namhyun Kang
Materials Research Letters.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Effect of Building Orientation on Tensile Properties of Hastelloy X alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seong-June Youn, GooWon Noh, Seok Su Sohn, Young-Sang Na, Young-Kyun Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(2): 130. CrossRef - Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Cryogenic tensile behavior of carbon-doped CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Hyeonseok Kwon, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Jungho Choe, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jung Gi Kim, Jeong Min Park
Additive Manufacturing.2024; 86: 104223. CrossRef - Recent progress in high-entropy alloys for laser powder bed fusion: Design, processing, microstructure, and performance
Asker Jarlöv, Zhiguang Zhu, Weiming Ji, Shubo Gao, Zhiheng Hu, Priyanka Vivegananthan, Yujia Tian, Devesh Raju Kripalani, Haiyang Fan, Hang Li Seet, Changjun Han, Liming Tan, Feng Liu, Mui Ling Sharon Nai, Kun Zhou
Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports.2024; 161: 100834. CrossRef
- Stronger weld than base metal in face-centered cubic alloy through multi-scale heterogeneity
- [Korean]
- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
- Jin-Kwon Kim, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Nahm Sahn, Sung-Soo Ryu, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):409-414. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.409
- 589 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF YSZ (Y2O3-stabilized zirconia)-based ceramics have excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength and wear resistance. In the application, YSZ is utilized in the bead mill, a fine-grinding process. YSZ-based parts, such as the rotor and pin, can be easily damaged by continuous application with high rpm in the bead mill process. In that case, adding WC particles improves the tribological and mechanical properties. YSZ-30 vol.% WC composite ceramics are manufactured via hot pressing under different pressures (10/30/60 MPa). The hot-pressed composite ceramics measure the physical properties, such as porosity and bulk density values. In addition, the phase formation of these composite ceramics is analyzed and discussed with those of physical properties. For the increased applied pressure of hot pressing, the tetragonality of YSZ and the crystallinity of WC are enhanced. The mechanical properties indicate an improved tendency with the increase in the applied pressure of hot pressing.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Polymer Composite with Enhanced Insulation and Mechanical Properties using Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
- Junhyeok Choi, Sangin Lee, Kiho Song, Taekyung Kim, Changui Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):356-362. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.356
- 957 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Inorganic-organic composites find extensive application in various fields, including electronic devices and light-emitting diodes. Notably, encapsulation technologies are employed to shield electronic devices (such as printed circuit boards and batteries) from stress and moisture exposure while maintaining electrical insulation. Polymer composites can be used as encapsulation materials because of their controllable mechanical and electrical properties. In this study, we propose a polymer composite that provides good electrical insulation and enhanced mechanical properties. This is achieved by using aluminum borate nanowhiskers (ABOw), which are fabricated using a facile synthesis method. The ABOw fillers are created via a hydrothermal method using aluminum chloride and boric acid. We confirm that the synthesis occurs in various morphologies based on the molar ratio. Specifically, nanowhiskers are synthesized at a molar ratio of 1:3 and used as fillers in the composite. The fabricated ABOw/epoxy composites exhibit a 48.5% enhancement in mechanical properties, similar to those of pure epoxy, while maintaining good electrical insulation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Al18B4O33 Spherical Powder with Increased Fluidity via Control of B2O3 Particle Size and Distribution
Kiho Song, Sang in Lee, Hyunseung Song, Changui Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(6): 513. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Al18B4O33 Spherical Powder with Increased Fluidity via Control of B2O3 Particle Size and Distribution
- [English]
- Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
- Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):318-323. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.318
- 1,799 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
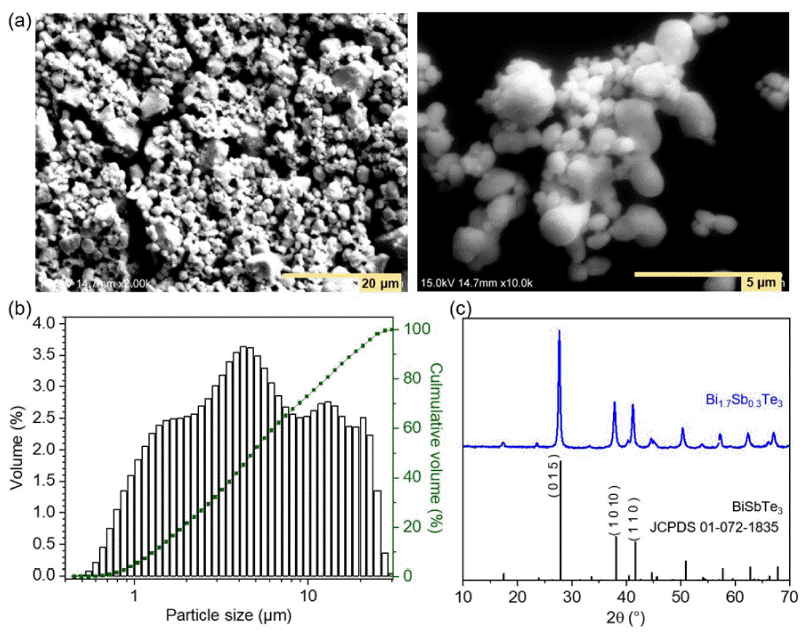
PDF The thermoelectric effect, which converts waste heat into electricity, holds promise as a renewable energy technology. Recently, bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3)-based alloys are being recognized as important materials for practical applications in the temperature range from room temperature to 500 K. However, conventional sintering processes impose limitations on shape-changeable and tailorable Bi2Te3 materials. To overcome these issues, three-dimensional (3D) printing (additive manufacturing) is being adopted. Although some research results have been reported, relatively few studies on 3D printed thermoelectric materials are being carried out. In this study, we utilize extrusion 3D printing to manufacture n-type Bi1.7Sb0.3Te3 (N-BST). The ink is produced without using organic binders, which could negatively influence its thermoelectric properties. Furthermore, we introduce graphene oxide (GO) at the crystal interface to enhance the electrical properties. The formed N-BST composites exhibit significantly improved electrical conductivity and a higher Seebeck coefficient as the GO content increases. Therefore, we propose that the combination of the extrusion 3D printing process (Direct Ink Writing, DIW) and the incorporation of GO into N-BST offers a convenient and effective approach for achieving higher thermoelectric efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 492. CrossRef - Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- [Korean]
- Effect of Bulk Shape on Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Haeum Park, Yeon Woo Kim, Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Jung Gi Kim, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):140-145. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.140
- 2,493 View
- 33 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
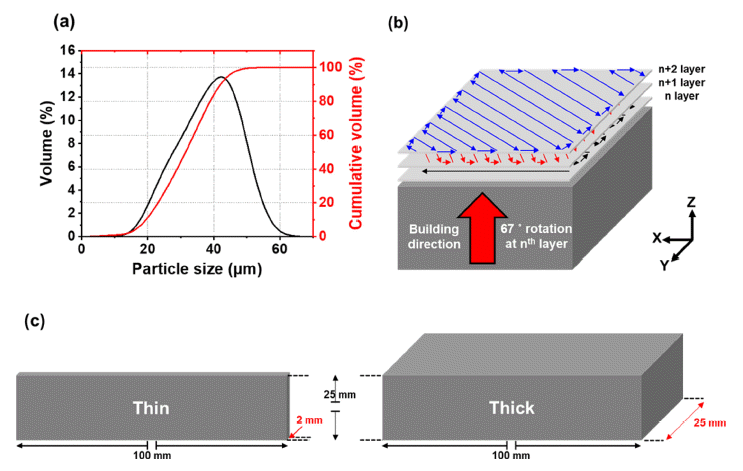
PDF Although the Ti–6Al–4V alloy has been used in the aircraft industry owing to its excellent mechanical properties and low density, the low formability of the alloy hinders broadening its applications. Recently, laser-powder bed fusion (L-PBF) has become a novel process for overcoming the limitations of the alloy (i.e., low formability), owing to the high degree of design freedom for the geometry of products having outstanding performance used in hightech applications. In this study, to investigate the effect of bulk shape on the microstructure and mechanical properties of L-PBFed Ti-6Al-4V alloys, two types of samples are fabricated using L-PBF: thick and thin samples. The thick sample exhibits lower strength and higher ductility than the thin sample owing to the larger grain size and lower residual dislocation density of the thick sample because of the heat input during the L-PBF process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 8. CrossRef - Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy through Selective Laser Melting: Comprehensive Study on the Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Gargi Roy, Raj Narayan Hajra, Woo Hyeok Kim, Jongwon Lee, Sangwoo Kim, Jeoung Han Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Data-driven Approach to Explore the Contribution of Process Parameters for Laser Powder Bed Fusion of a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
Jeong Min Park, Jaimyun Jung, Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Yeon Woo Kim, Ji-Hun Yu
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 137. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef - High-speed manufacturing-driven strength-ductility improvement of H13 tool steel fabricated by selective laser melting
Yeon Woo Kim, Haeum Park, Young Seong Eom, Dong Gill Ahn, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-hun Yu, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 582. CrossRef
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- [Korean]
- Comparison of Properties with Different Sintering Process of 3Y-TZP/WC Composites
- Min-Soo Nam, Jae-Hyung Choi, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):424-431. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.424
- 889 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
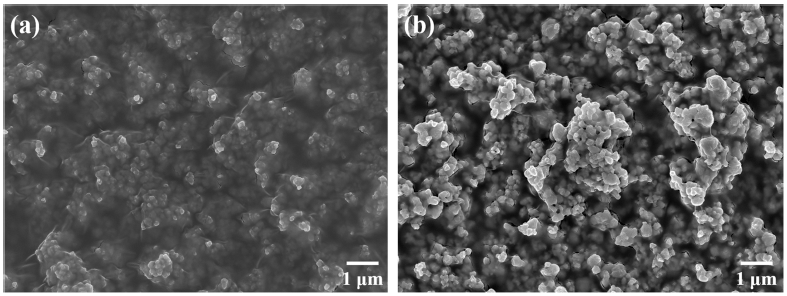
PDF 3Y-TZP ceramics obtained by doping 3 mol.% of Y2O3 to ZrO2 to stabilize the phase transition are widely used in the engineering ceramic industry due to their excellent mechanical properties such as high strength, fracture toughness, and wear resistance. An additional increase in mechanical properties is possible by manufacturing a composite in which a high-hardness material such as oxide or carbide is added to the 3Y-TZP matrix. In this study, composite powder was prepared by dispersing a designated percentage of WC in the 3Y-TZP matrix, and the results were compared after manufacturing the composite using the different processes of spark plasma sintering and HP. The difference between the densification behavior and porosity with the process mechanism was investigated. The correlation between the process conditions and phase formation was examined based on the crystalline phase formation behavior. Changes to the microstructure according to the process conditions were compared using field-emission scanning electron microscopy. The toughness-strengthening mechanism of the composite with densification and phase formation was also investigated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
Jin-Kwon Kim, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Nahm Sahn, Sung-Soo Ryu, Seongwon Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(5): 409. CrossRef
- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
- [Korean]
- Developing Continuous Stabilization Process for Textile-Grade PAN Fiber-Based Carbon Fiber Using UV Irradiation
- Joon Ha Moon, Honggyu Seong, Jiseon Yoo, Se Youn Cho, Jaewon Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):418-423. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.418
- 921 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
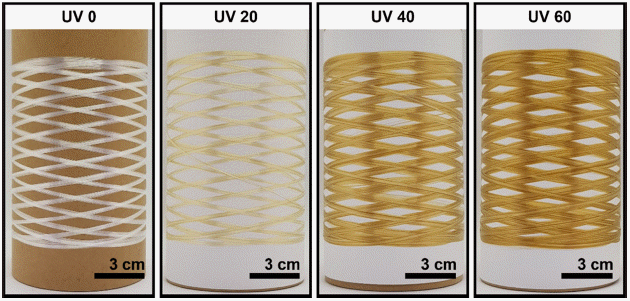
PDF Carbon fibers (CFs) are considered promising composite materials for various applications. However, the high cost of CFs (as much as $26 per kg) limits their practical use in the automobile and energy industries. In this study, we developed a continuous stabilization process for manufacturing low-cost CFs. We employed a textile-grade polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fiber as a low-cost precursor and UV irradiation technique to shorten the thermal stabilization time. We confirmed that UV irradiation on the textile-grade PAN fibers could lower the initial thermal stabilization temperature and also lead to a higher reaction. These resulted in a shorter overall stabilization time and enhancement of the tensile properties of textilegrade PAN-based CFs. Our study found that only 70 min of stabilization time with UV irradiation was required to prepare textile-grade PAN-based low-cost CFs with a tensile strength of 2.37 ± 0.22GPa and tensile modulus of 249 ± 5 GPa.
- [Korean]
- Evaluation of Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Depending on Sintering Heating Rate of IN 939W Alloy
- Junhyub Jeon, Junho Lee, Namhyuk Seo, Seung Bae Son, Jae-Gil Jung, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):399-410. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.399
- 1,682 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
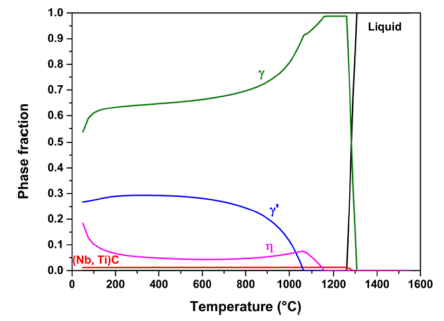
PDF Changes in the mechanical properties and microstructure of an IN 939 W alloy according to the sintering heating rate were evaluated. IN 939 W alloy samples were fabricated by spark plasma sintering. The phase fraction, number density, and mean radius of the IN 939W alloy were calculated using a thermodynamic calculation. A universal testing machine and micro-Vickers hardness tester were employed to confirm the mechanical properties of the IN 939W alloy. X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, Cs-corrected-field emission transmission electron microscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry were used to evaluate the microstructure of the alloy. The rapid sintering heating rate resulted in a slightly dispersed γ' phase and chromium oxide. It also suppressed the precipitation of the η phase. These helped to reinforce the mechanical properties.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Particle Sphericity on the Rheological Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Powders for Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
- T. Y. Kim, M. H. Kang, J. H. Kim, J.K. Hong, J.H. Yu, J.I. Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):99-109. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.99
- 1,765 View
- 36 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Powder flowability is critical in additive manufacturing processes, especially for laser powder bed fusion. Many powder features, such as powder size distribution, particle shape, surface roughness, and chemical composition, simultaneously affect the flow properties of a powder; however, the individual effect of each factor on powder flowability has not been comprehensively evaluated. In this study, the impact of particle shape (sphericity) on the rheological properties of Ti-6Al-4V powder is quantified using an FT4 powder rheometer. Dynamic image analysis is conducted on plasma-atomized (PA) and gas-atomized (GA) powders to evaluate their particle sphericity. PA and GA powders exhibit negligible differences in compressibility and permeability tests, but GA powder shows more cohesive behavior, especially in a dynamic state, because lower particle sphericity facilitates interaction between particles during the powder flow. These results provide guidelines for the manufacturing of advanced metal powders with excellent powder flowability for laser powder bed fusion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A fully computational approach for the prediction of melt pool generation of the directed energy deposition process
Mingyu Chung, Kang-Hyun Lee, Jaeeun Park, Yoon Sun Lee, Gun Jin Yun
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology.2025; 39(11): 6847. CrossRef - Enhanced Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy with Vanadium Carbide Coating via Directed Energy Deposition
Ui Jun Ko, Ju Hyeong Jung, Jung Hyun Kang, Kyunsuk Choi, Jeoung Han Kim
Materials.2024; 17(3): 733. CrossRef - Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy through Selective Laser Melting: Comprehensive Study on the Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Gargi Roy, Raj Narayan Hajra, Woo Hyeok Kim, Jongwon Lee, Sangwoo Kim, Jeoung Han Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 8. CrossRef
- A fully computational approach for the prediction of melt pool generation of the directed energy deposition process
- [Korean]
- Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ti-20Mo-0.5EB Composites
- Suhyun Bae, Wonki Jeong, Se-Eun Shin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):403-409. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.403
- 650 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, Ti-Mo-EB composites are prepared by ball milling and spark plasma sintering (SPS) to obtain a low elastic modulus and high strength and to evaluate the microstructure and mechanical properties as a function of the process conditions. As the milling time and sintering temperature increased, Mo, as a β-Ti stabilizing element, diffused, and the microstructure of β-Ti increased. In addition, the size of the observed phase was small, so the modulus and hardness of α-Ti and β-Ti were measured using nanoindentation equipment. In both phases, as the milling time and sintering temperature increased, the modulus of elasticity decreased, and the hardness increased. After 12 h of milling, the specimen sintered at 1000°C showed the lowest values of modulus of elasticity of 117.52 and 101.46 GPa for α-Ti and β-Ti, respectively, confirming that the values are lower compared to the that in previously reported studies.
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33
x B10.67-0.67x Px Cu0.8 Nanocrystalline Soft Magnetic Alloys with varying P Content - Hyun Ah Im, Kyoung-Hoon Bae, Yeong gyun Nam, Subong An, Sangsun Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jae Won Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(4):293-300. Published online August 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.4.293

- 883 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We investigate the effect of phosphorous content on the microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33
x B10.67-0.67x Px Cu0.8 (x = 1–4 at.%) nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys. The simultaneous addition of Cu and P to nanocrystalline alloys reportedly decreases the nanocrystalline size significantly, to 10–20 nm. In the P-containing nanocrystalline alloy, P atoms are distributed in an amorphous residual matrix, which suppresses grain growth, increases permeability, and decreases coercivity. In this study, nanocrystalline ribbons with a composition of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33x B10.67- 0.67x Px Cu0.8 (x = 1–4 at.%) are fabricated by rapid quenching melt-spinning and thermal annealing. It is demonstrated that the addition of a small amount of P to the alloy improves the glass-forming ability and increases the resistance to undesirable Fex(B,P) crystallization. Among the alloys investigated in this work, an Fe83.2Si5B10P1Cu0.8 nanocrystalline ribbon annealed at 460°C exhibits excellent soft-magnetic properties including low coercivity, low core loss, and high saturation magnetization. The uniform nanocrystallization of the Fe83.2Si5B10P1Cu0.8 alloy is confirmed by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy analysis.
- [Korean]
- Improvement of Mechanical Properties of Nanocrystalline FeCrC Alloy via Strain-Induced Martensitic Transformation
- Gwanghun Kim, Junhyub Jeon, Namhyuk Seo, Jungbin Park, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):246-252. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.246

- 532 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The effect of sintering conditions on the austenite stability and strain-induced martensitic transformation of nanocrystalline FeCrC alloy is investigated. Nanocrystalline FeCrC alloys are successfully fabricated by spark plasma sintering with an extremely short densification time to obtain the theoretical density value and prevent grain growth. The nanocrystallite size in the sintered alloys contributes to increased austenite stability. The phase fraction of the FeCrC sintered alloy before and after deformation according to the sintering holding time is measured using X-ray diffraction and electron backscatter diffraction analysis. During compressive deformation, the volume fraction of strain-induced martensite resulting from austenite decomposition is increased. The transformation kinetics of the strain-induced martensite is evaluated using an empirical equation considering the austenite stability factor. The hardness of the S0W and S10W samples increase to 62.4-67.5 and 58.9-63.4 HRC before and after deformation. The hardness results confirmed that the mechanical properties are improved owing to the effects of grain refinement and strain-induced martensitic transformation in the nanocrystalline FeCrC alloy.
- [Korean]
- Development of Hybrid Insulating Coating for Fe-based Soft Magnetic Powder
- Jungjoon Kim, Sungyeom Kim, Youngkyun Kim, Taesuk Jang, Hwi-jun Kim, Youngjin Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):233-238. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.233
- 625 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Iron-based amorphous powder attracts increasing attention because of its excellent soft magnetic properties and low iron loss at high frequencies. The development of an insulating layer on the surface of the amorphous soft magnetic powder is important for minimizing the eddy current loss and enhancing the energy efficiency of highfrequency devices by further increasing the electrical resistivity of the cores. In this study, a hybrid insulating coating layer is investigated to compensate for the limitations of monolithic organic or inorganic coating layers. Fe2O3 nanoparticles are added to the flexible silicon-based epoxy layer to prevent magnetic dilution; in addition TiO2 nanoparticles are added to enhance the mechanical durability of the coating layer. In the hybrid coating layer with optimal composition, the decrease in magnetic permeability and saturation magnetization is suppressed.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Sintering Condition on Tensile Strength of Fe-based Non-equiatomic High Entropy Alloy
- Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jeon, Gwanghun Kim, Jungbin Park, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):221-226. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.221

- 985 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We fabricate the non-equiatomic high-entropy alloy (NE-HEA) Fe49.5Mn30Co10Cr10C0.5 (at.%) using spark plasma sintering under various sintering conditions. Each elemental pure powder is milled by high-energy ball milling to prepare NE-HEA powder. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the sintered samples are investigated using various methods. We use the X-ray diffraction (XRD) method to investigate the microstructural characteristics. Quantitative phase analysis is performed by direct comparison of the XRD results. A tensile test is used to compare the mechanical properties of small samples. Next, electron backscatter diffraction analysis is performed to analyze the phase fraction, and the results are compared to those of XRD analysis. By combining different sintering durations and temperature conditions, we attempt to identify suitable spark plasma sintering conditions that yield mechanical properties comparable with previously reported values. The samples sintered at 900 and 1000°C with no holding time have a tensile strength of over 1000 MPa.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
- [Korean]
- Influence of Milling Conditions on the Microstructural Characteristics and Mechanical Properties of Non-equiatomic High Entropy Alloy
- Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jeon, Gwanghoon Kim, Jungbin Park, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):103-109. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.103
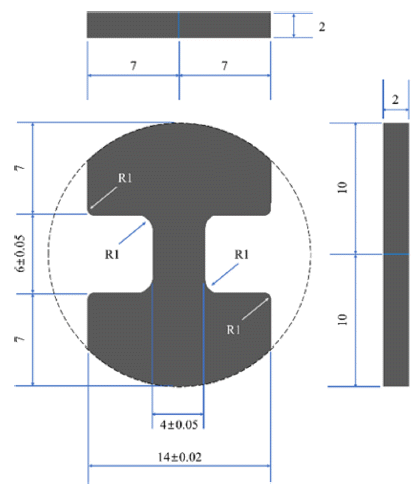
- 864 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF High-entropy alloys have excellent mechanical properties under extreme environments, rendering them promising candidates for next-generation structural materials. It is desirable to develop non-equiatomic high-entropy alloys that do not require many expensive or heavy elements, contrary to the requirements of typical high-entropy alloys. In this study, a non-equiatomic high-entropy alloy powder Fe49.5Mn30Co10Cr10C0.5 (at.%) is prepared by high energy ball milling and fabricated by spark plasma sintering. By combining different ball milling times and ball-topowder ratios, we attempt to find a proper mechanical alloying condition to achieve improved mechanical properties. The milled powder and sintered specimens are examined using X-ray diffraction to investigate the progress of mechanical alloying and microstructural changes. A miniature tensile specimen after sintering is used to investigate the mechanical properties. Furthermore, quantitative analysis of the microstructure is performed using electron backscatter diffraction.
- [Korean]
- Experimental Study on Improving Compressive Strength of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Reinforced Cement Composite
- Yomin Choi, Hyun‐Gyoo Shin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):503-508. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.503

- 643 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The mechanical properties and microstructures of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN)-reinforced cement composites are experimentally studied for three and seven curing days. Various sizes (5, 10, and 18 μm) and concentrations (0.1%, 0.25%, 0.5%, and 1.0%) of h-BN are dispersed by the tip ultrasonication method in water and incorporated into the cement composite. The compressive strength of the h-BN reinforced cements increases by 40.9%, when 0.5 wt% of 18 μm-sized h-BN is added. However, the compressive strength decreases when the 1.0 wt% cement composite is added, owing to the aggregation of the h-BNs in the cement composite. The microstructural characterization of the h-BN-reinforced cement composite indicates that the h-BNs act as bridges connecting the cracks, resulting in improved mechanical properties for the reinforced cement composite.
- [Korean]
- Development of Fe-Mn-based Hybrid Materials Containing Nano-scale Oxides by a Powder Metallurgical Route
- Jonggyu Jeon, Jungjoon Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):203-209. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.203

- 893 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The automotive industry has focused on the development of metallic materials with high specific strength, which can meet both fuel economy and safety goals. Here, a new class of ultrafine-grained high-Mn steels containing nano-scale oxides is developed using powder metallurgy. First, high-energy mechanical milling is performed to dissolve alloying elements in Fe and reduce the grain size to the nanometer regime. Second, the ball-milled powder is consolidated using spark plasma sintering. During spark plasma sintering, nanoscale manganese oxides are generated in Fe-15Mn steels, while other nanoscale oxides (e.g., aluminum, silicon, titanium) are produced in Fe-15Mn-3Al-3Si and Fe-15Mn-3Ti steels. Finally, the phases and resulting hardness of a variety of high-Mn steels are compared. As a result, the sintered pallets exhibit superior hardness when elements with higher oxygen affinity are added; these elements attract oxygen from Mn and form nanoscale oxides that can greatly improve the strength of high-Mn steels.
- [Korean]
- Structural Characteristics, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-Cr-Al Metallic Foam Fabricated by Powder Alloying Process
- Kyu-Sik Kim, Byeong-Hoon Kang, Man-Ho Park, Jung-Yeul Yun, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):37-43. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.37
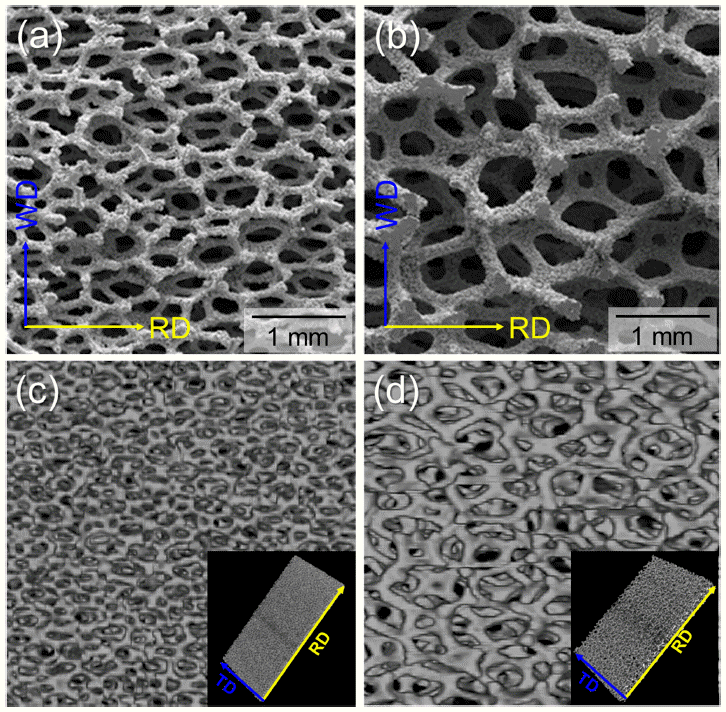
- 651 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The Fe-22wt.%Cr-6wt.%Al foams were fabricated via the powder alloying process in this study. The structural characteristics, microstructure, and mechanical properties of Fe-Cr-Al foams with different average pore sizes were investigated. Result of the structural analysis shows that the average pore sizes were measured as 474 μm (450 foam) and 1220 μm (1200 foam). Regardless of the pore size, Fe-Cr-Al foams had a Weaire-Phelan bubble structure, and α-ferrite was the major constituent phase. Tensile and compressive tests were conducted with an initial strain rate of 10−3 /s. Tensile yield strengths were 3.4 MPa (450 foam) and 1.4 MPa (1200 foam). Note that the total elongation of 1200 foam was higher than that of 450 foam. Furthermore, their compressive yield strengths were 2.5 MPa (450 foam) and 1.1 MPa (1200 foam), respectively. Different compressive deformation behaviors according to the pore sizes of the Fe-Cr-Al foams were characterized: strain hardening for the 450 foam and constant flow stress after a slight stress drop for the 1200 foam. The effect of structural characteristics on the mechanical properties was also discussed.
- [English]
- Spark Plasma Sintering of the Ni-graphite Composite Powder Prepared by Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid and Its Properties
- Minh Thuyet-Nguyena, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):14-24. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.14

- 983 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this work, the electrical explosion of wire in liquid and subsequent spark plasma sintering (SPS) was introduced for the fabrication of Ni-graphite nanocomposites. The fabricated composite exhibited good enhancements in mechanical properties, such as yield strength and hardness, but reduced the ductility in comparison with that of nickel. The as-synthesized Ni-graphite (5 vol.% graphite) nanocomposite exhibited a compressive yield strength of 275 MPa (about 1.6 times of SPS-processed monolithic nickel ~170 MPa) and elongation to failure ~22%. The hardness of Nigraphite composite had a value of 135.46 HV, which is about 1.3 times higher than that of pure SPS-processed Ni (105.675 HV). In terms of processing, this work demonstrated that this processing route is a novel, simple, and low-cost method for the synthesis of nickel-graphite composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Top-down strategies for achieving high-quality graphene: Recent advancements
Arpana Agrawal
Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry.2025; 142: 103. CrossRef - Electrodeposition of nickel-titanium dioxide coatings and powders from aqueous sulfate solutions
Tazhibayeva Aigerim Shotaevna, Bayeshova Azhar Kospanovna, Bayeshov Abduali, Osińska Małgorzata
Polyhedron.2025; 277: 117571. CrossRef
- Top-down strategies for achieving high-quality graphene: Recent advancements
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of the Multifunctional Core/Intermediate/Shell Nanoparticles: Tunable Magnetic and Photoluminescence Properties
- Mun-Kyoung Kim, Seyun Kim, Kyoung-Seok Moon, Weon Ho Shin, Hyung Mo Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):463-470. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.463
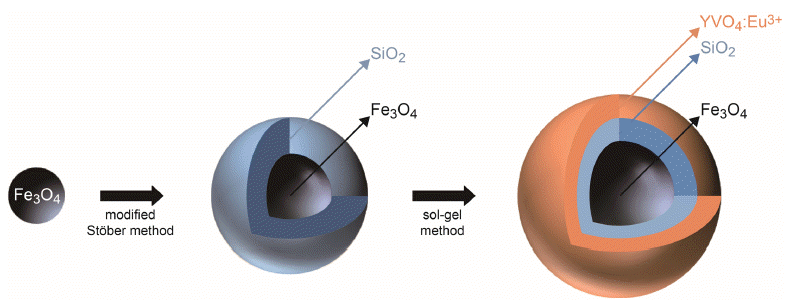
- 752 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe3O4/SiO2/YVO4:Eu3+ multifunctional nanoparticles are successfully synthesized by facile stepwise sol-gel processes. The multifunctional nanoparticles show a spherical shape with narrow size distribution (approximately 40 nm) and the phosphor shells are well crystallized. The Eu3+ shows strong photoluminescence (red emission at 619 nm, absorbance at 290 nm) due to an effective energy transfer from the vanadate group to Eu. Core-shell structured multifunctional nanoparticles have superparamagnetic properties at 300 K. Furthermore, the core-shell nanoparticles have a quick response time for the external magnetic field. These results suggest that the photoluminescence and magnetic properties could be easily tuned by either varying the number of coating processes or changing the phosphor elements. The nanoparticles may have potential applications for appropriate fields such as laser systems, optical amplifiers, security systems, and drug delivery materials.
- [Korean]
- The Influence of Fe Particle Size on the Critical Properties of MgB2 Superconductor
- Hyeondeok Jeong, Dong-Gun Lee, Sung-Soo Ryu, Hai-Woong Park, Chan-Joong Kim, Byung-Hyuk Jun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):432-436. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.432
- 555 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study demonstrates the effect of addition of Fe particles of different sizes on the critical properties of the superconductor MgB2. Bulk MgB2 is synthesized by ball milling Mg and B powders with Fe particles at 900°C. When Fe particles with size less than 10 μm are added in MgB2, they easily react with B and form the FeB phase, resulting in a reduction in the amount of the MgB2 phase and deterioration of the crystallinity. Accordingly, both the critical temperature and the critical current density are significantly reduced. On the other hand, when larger Fe particles are added, the Fe2B phase forms instead of FeB due to the lower reactivity of Fe toward B. Accordingly, negligible loss of B occurs, and the critical properties are found to be similar to those of the intact MgB2.
- [Korean]
- Effects of Sintering Additives on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of AlN by Pressureless Sintering
- Jin Uk Hwang, So Youn Mun, Sang Yong Nam, Hwan Soo Dow
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):395-404. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.395
- 2,277 View
- 53 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
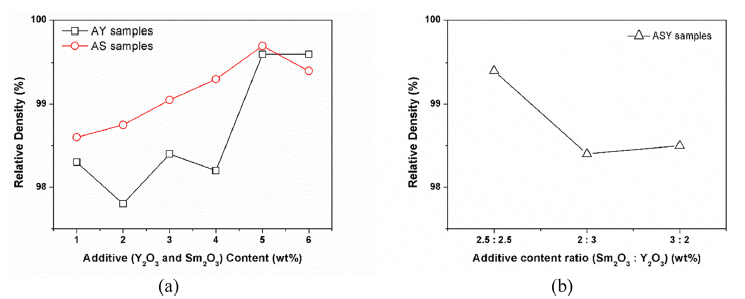
PDF Aluminum nitride (AlN) has excellent electrical insulation property, high thermal conductivity, and a low thermal expansion coefficient; therefore, it is widely used as a heat sink, heat-conductive filler, and heat dissipation substrate. However, it is well known that the AlN-based materials have disadvantages such as low sinterability and poor mechanical properties. In this study, the effects of addition of various amounts (1-6 wt.%) of sintering additives Y2O3 and Sm2O3 on the thermal and mechanical properties of AlN samples pressureless sintered at 1850°C in an N2 atmosphere for a holding time of 2 h are examined. All AlN samples exhibit relative densities of more than 97%. It showed that the higher thermal conductivity as the Y2O3 content increased than the Sm2O3 additive, whereas all AlN samples exhibited higher mechanical properties as Sm2O3 content increased. The formation of secondary phases by reaction of Y2O3, Sm2O3 with oxygen from AlN lattice influenced the thermal and mechanical properties of AlN samples due to the reaction of the oxygen contents in AlN lattice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of YH2 addition on pressureless sintered AlN ceramics
Liang Wang, Wei-Ming Guo, Peng-Fei Sheng, Li-Fu Lin, Xiao Zong, Shang-Hua Wu
Journal of the European Ceramic Society.2023; 43(3): 862. CrossRef
- Effects of YH2 addition on pressureless sintered AlN ceramics
- [Korean]
- The Microstructure and the Mechanical Properties of Sintered TiO2-Co Composite Prepared Via Thermal Hydrogenation Method
- Myeongsun Ko, Ilsong Park, Jeshin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):290-298. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.290
- 396 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
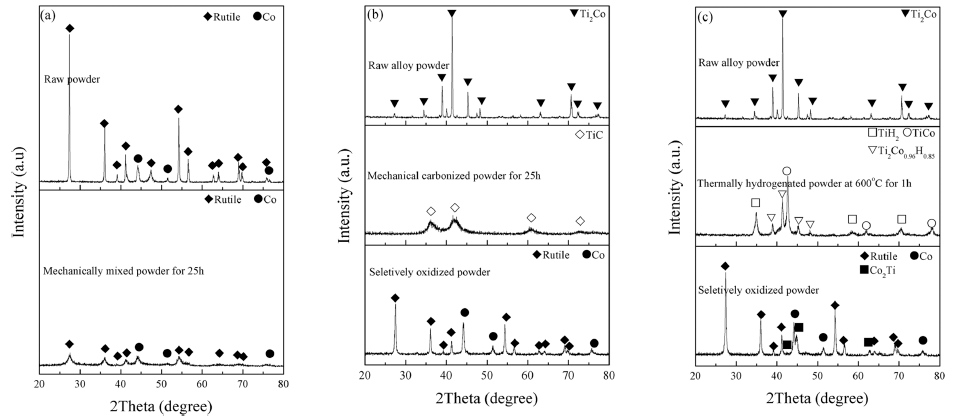
PDF TiO2-particles containing Co grains are fabricated via thermal hydrogenation and selective oxidation of Ti-Co alloy. For comparison, TiO2-Co composite powders are prepared by two kinds of methods which were the mechanical carbonization and oxidation process, and the conventional mixing process. The microstructural characteristics of the prepared composites are analyzed by X-ray diffraction, field-emission scattering electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. In addition, the composite powders are sintered at 800°C by spark plasma sintering. The flexural strength and fracture toughness of the sintered samples prepared by thermal hydrogenation and mechanical carbonization are found to be higher than those of the samples prepared by the conventional mixing process. Moreover, the microstructures of sintered samples prepared by thermal hydrogenation and mechanical carbonization processes are found to be similar. The difference in the mechanical properties of sintered samples prepared by thermal hydrogenation and mechanical carbonization processes is attributed to the different sizes of metallic Co particles in the samples.
- [Korean]
- Property Evaluation of Tungsten-Carbide Hard Materials as a Function of Binder
- Ju-Hun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Jeong-Han Lee, Sung-Kil Hong, Hyun-Kuk Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):132-137. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.132
- 1,074 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten carbide (WC) hard materials are used in various industries and possess a superior hardness compared to other hard materials. They have particularly high melting points, high strength, and abrasion resistance. Accordingly, tungsten carbide hard materials are used for wear-resistant tools, cutting tools, machining tools, and other tooling materials. In this study, the WC-5wt.%Co, Fe, Ni hard materials are densified using the horizontal ball milled WC-Co, WC-Fe, and WC-Ni powders by a spark plasma sintering process. The WC-5Co, WC-5Fe, and WC-5Ni hard materials are almost completely densified with a relative density of up to 99.6% after simultaneous application of a pressure of 60 MPa and an electric current for about 15 min without any significant change in the grain size. The average grain size of WC-5Co, WC-5Fe, and WC-5Ni that was produced through SPS was about 0.421, 0.779, and 0.429 μm, respectively. The hardness and fracture toughness of the dense WC-5Co, WC-5Fe, WC-5Ni hard materials were also investigated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing Mechanical Properties via Grain Growth Suppression and High Densification in WC Compacts
Jong Min Gwak, Min Soo Park, Gook Hyun Ha, Nam Hyun Kang
Metals and Materials International.2025; 31(12): 3733. CrossRef - Synthesis of W2C by Spark Plasma Sintering of W-WC Powder Mixture and Its Etching Property
Gyu-Sang Oh, Sung-Min Lee, Sung-Soo Ryu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(4): 293. CrossRef - Fabrication and Properties of Densified Tungsten by Magnetic Pulse Compaction and Spark Plasma Sintering
Eui Seon Lee, Jongmin Byun, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2020; 30(6): 321. CrossRef
- Enhancing Mechanical Properties via Grain Growth Suppression and High Densification in WC Compacts
- [Korean]
- Thermal Properties and Microstructural Changes of Fe-Co System Valve Seat Alloy by High Densification Process
- In-Shup Ahn, Dong-Kyu Park, Kwang-Bok Ahn, Seoung-Mok Shin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):112-118. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.112

- 892 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Infiltration is a popular technique used to produce valve seat rings and guides to create dense parts. In order to develop valve seat material with a good thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient, Cu-infiltrated properties of sintered Fe-Co-M(M=Mo,Cr) alloy systems are studied. It is shown that the copper network that forms inside the steel alloy skeleton during infiltration enhances the thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient of the steel alloy composite. The hard phase of the CoMoCr and the network precipitated FeCrC phase are distributed homogeneously as the infiltrated Cu phase increases. The increase in hardness of the alloy composite due to the increase of the Co, Ni, Cr, and Cu contents in Fe matrix by the infiltrated Cu amount increases. Using infiltration, the thermal conductivity and thermal expansion coefficient were increased to 29.5 W/mK and 15.9 um/m°C, respectively, for tempered alloy composite.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Single and Dual Doping of Rare Earth Metal Ce and Nd Elements on Electrochemical Properties of LiNi0.83 Co0.11Mn0.06O2 Cathode Lithium-ion Battery Material
- Yoo-Young Kim, Jong-Keun Ha, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):49-57. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.49
- 2,009 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Layered LiNi0.83Co0.11Mn0.06O2 cathode materials single- and dual-doped by the rare-earth elements Ce and Nd are successfully fabricated by using a coprecipitation-assisted solid-phase method. For comparison purposes, nondoping pristine LiNi0.83Co0.11Mn0.06O2 cathode material is also prepared using the same method. The crystal structure, morphology, and electrochemical performances are characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) mapping, and electrochemical techniques. The XRD data demonstrates that all prepared samples maintain a typical α-NaFeO2-layered structure with the
R-3m -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Numerical approach for lithium-ion battery performance considering various cathode active material composition for electric vehicles using 1D simulation
Heewon Choi, Nam-gyu Lim, Seong Jun Lee, Jungsoo Park
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology.2021; 35(6): 2697. CrossRef - Synthesis of CeVO4-V2O5 nanowires by cation-exchange method for high-performance lithium-ion battery electrode
Xueliu Xu, Shiying Chang, Taofang Zeng, Yidan Luo, Dong Fang, Ming Xie, Jianhong Yi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2021; 887: 161237. CrossRef
- Numerical approach for lithium-ion battery performance considering various cathode active material composition for electric vehicles using 1D simulation
- [Korean]
- Effect of Porosity on Mechanical Anisotropy of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Additively Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting
- Jeong Min Park, Jin Myoung Jeon, Jung Gi Kim, Yujin Seong, Sun Hong Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):475-481. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.475
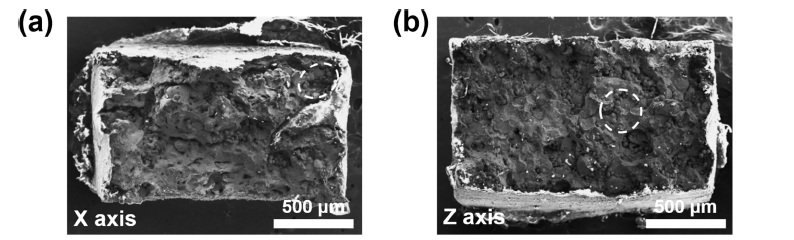
- 1,342 View
- 12 Download
- 12 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Selective laser melting (SLM), a type of additive manufacturing (AM) technology, leads a global manufacturing trend by enabling the design of geometrically complex products with topology optimization for optimized performance. Using this method, three-dimensional (3D) computer-aided design (CAD) data components can be built up directly in a layer-by-layer fashion using a high-energy laser beam for the selective melting and rapid solidification of thin layers of metallic powders. Although there are considerable expectations that this novel process will overcome many traditional manufacturing process limits, some issues still exist in applying the SLM process to diverse metallic materials, particularly regarding the formation of porosity. This is a major processing-induced phenomenon, and frequently observed in almost all SLM-processed metallic components. In this study, we investigate the mechanical anisotropy of SLM-produced 316L stainless steel based on microstructural factors and highly-oriented porosity. Tensile tests are performed to investigate the microstructure and porosity effects on mechanical anisotropy in terms of both strength and ductility.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of temperature and impact loading condition on deformation behavior in 316L austenitic stainless steel manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Tae Hyeong Kim, Haeum Park, Jun Seok Lee, Jeong Min Park, Jae Wung Bae
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 933: 148286. CrossRef - Selective laser melting additive manufactured H13 tool steel for aluminum extrusion die component construction
Evangelos Giarmas, Vasileios Tsakalos, Emmanuel Tzimtzimis, Nikolaos Kladovasilakis, Ioannis Kostavelis, Dimitrios Tzovaras, Dimitrios Tzetzis
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2024; 133(9-10): 4385. CrossRef - Nanoindentation Creep Behavior of Additively Manufactured H13 Steel by Utilizing Selective Laser Melting Technology
Evangelos Giarmas, Emmanouil K. Tzimtzimis, Nikolaos Kladovasilakis, Dimitrios Tzovaras, Dimitrios Tzetzis
Materials.2024; 17(15): 3756. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef - Development of multi-defect diagnosis algorithm for the directed energy deposition (DED) process with in situ melt-pool monitoring
Hyewon Shin, Jimin Lee, Seung-Kyum Choi, Sang Won Lee
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2023; 125(1-2): 357. CrossRef - Corrosion Resistance of Laser Powder Bed Fused AISI 316L Stainless Steel and Effect of Direct Annealing
Kichang Bae, Dongmin Shin, Jonghun Lee, Seohan Kim, Wookjin Lee, Ilguk Jo, Junghoon Lee
Materials.2022; 15(18): 6336. CrossRef - Experimental investigation on the effect of process parameters in additive/subtractive hybrid manufacturing 316L stainless steel
Chengming Tang, Jibin Zhao, Zhiguo Wang, Yuhui Zhao, Tianran Wang
The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology.2022; 121(3-4): 2461. CrossRef - Interface characteristics and mechanical behavior of additively manufactured multi-material of stainless steel and Inconel
Man Jae Sagong, Eun Seong Kim, Jeong Min Park, Gangaraju Manogna Karthik, Byeong-Joo Lee, Jung-Wook Cho, Chong Soo Lee, Takayoshi Nakano, Hyoung Seop Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2022; 847: 143318. CrossRef - Effect of heat treatment on microstructural heterogeneity and mechanical properties of 1%C-CoCrFeMnNi alloy fabricated by selective laser melting
Jeong Min Park, Eun Seong Kim, Hyeonseok Kwon, Praveen Sathiyamoorthi, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim
Additive Manufacturing.2021; 47: 102283. CrossRef - Manufacturing Aluminum/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Composites via Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Eo Ryeong Lee, Se Eun Shin, Naoki Takata, Makoto Kobashi, Masaki Kato
Materials.2020; 13(18): 3927. CrossRef - Effects of microstructure and internal defects on mechanical anisotropy and asymmetry of selective laser-melted 316L austenitic stainless steel
Jin Myoung Jeon, Jeong Min Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Jung Gi Kim, Yujin Seong, Sun Hong Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2019; 763: 138152. CrossRef - Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions
Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Junhyeok Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Im Doo Jung, Hyokyung Sung
Materials Characterization.2019; 155: 109817. CrossRef
- Effect of temperature and impact loading condition on deformation behavior in 316L austenitic stainless steel manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
- [Korean]
- A Study on Pore Properties of SUS316L Powder Porous Metal Fabricated by Electrostatic Powder Coating Process
- Min-Jeong Lee, Yu-Jeong Yi, Hyeon-Ju Kim, Manho Park, Byoung-Kee Kim, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):415-419. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.415
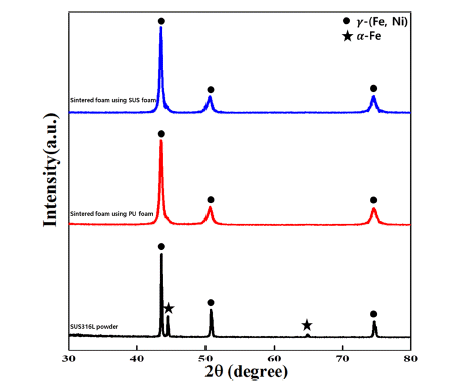
- 798 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Porous metals demonstrate not only excessively low densities, but also novel physical, thermal, mechanical, electrical, and acoustic properties. Thus, porous metals exhibit exceptional performance, which are useful for diesel particulate filters, heat exchangers, and noise absorbers. In this study, SUS316L foam with 90% porosity and 3,000 μm pore size is successfully manufactured using the electrostatic powder coating (ESPC) process. The mean size of SUS316L powders is approximately 12.33 μm. The pore properties are evaluated using SEM and Archimedes. As the quantity of powder coating increases, pore size decreases from 2,881 to 1,356 μm. Moreover, the strut thickness and apparent density increase from 423.7 to 898.3 μm and from 0.278 to 0.840 g/cm3, respectively. It demonstrates that pore properties of SUS316L powder porous metal are controllable by template type and quantity of powder coating.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
Minji Kim, Min-Jeong Lee, Su-Jin Yun, Poong-Yeon Kim, Hyeon Ju Kim, Juyong Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(4): 299. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Pore Characteristics of Metal Powder Filters with a Cross-Sealed Honeycomb Shape Using Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
- [Korean]
- Effect of post heat treatment on fatigue properties of EBM 3D-printed Ti-6Al-4V alloy
- Young-Sin Choi, Ji-Hoon Jang, Gun-Hee Kim, Chang-Woo Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Dong-Geun Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):340-345. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.340
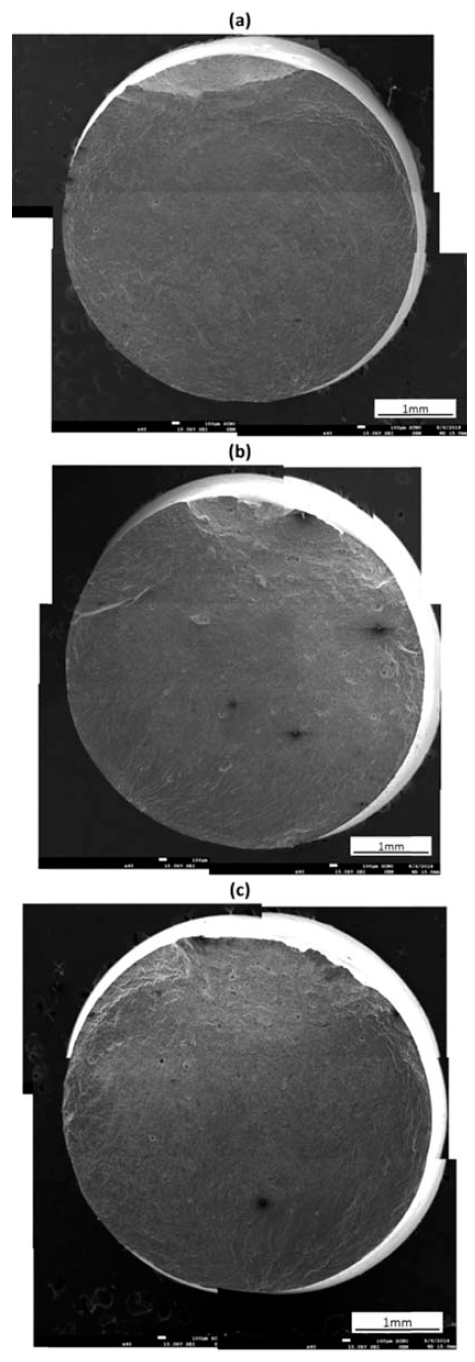
- 1,092 View
- 8 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Additive manufacturing by electron beam melting is an affordable process for fabricating near net shaped parts of titanium and its alloys. 3D additive-manufactured parts have various kinds of voids, lack of fusion, etc., and they may affect crack initiation and propagation. Post process is necessary to eliminate or minimize these defects. Hot isostatic pressing (HIP) is the main method, which is expensive. The objective of this paper is to achieve an optimum and simple post heat treatment process without the HIP process. Various post heat treatments are conducted for the 3Dprinted Ti-6Al-4V specimen below and above the beta transus temperature (996°C). The as-fabricated EBM Ti-6Al-4V alloy has an α‘-martensite structure and transforms into the α+β duplex phase during the post heat treatment. The fatigue strength of the as-fabricated specimen is 400 MPa. The post heat treatment at 1000°C/30 min/AC increases the fatigue strength to 420 MPa. By post heat treatment, the interior pore size and the pore volume fraction are reduced and this can increase the fatigue limit.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Line Energy Conditions on Mechanical and Fatigue Properties of Ti6Al4V Fabricated by Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing
Youngsin Choi, Hwi-Jun Kim, Gun-Hee Kim, Chang-Woo Lee, Dong-Geun Lee
Metals.2021; 11(6): 878. CrossRef - Mechanical and Physical Characteristics Analysis of Radius Trauma Plate by EBM Additive Manufacturing
Kwun-Mook Lim, Sung-Jun Park
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Technology Engineers.2020; 29(2): 147. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Treatments on Fatigue Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by EBM Additive Manufacturing
Dong-Geun Lee, Youngsin Choi, P. Villechaise, B. Appolaire, P. Castany, M. Dehmas, C. Delaunay, J. Delfosse, A. Denquin, E. Gautier, L. Germain, N. Gey, T. Gloriant, J.-Y. Hascoët, S. Hémery, Y. Millet, D. Monceau, F. Pettinari-Sturmel, M. Piellard, F. Pr
MATEC Web of Conferences.2020; 321: 03027. CrossRef - Correlation between surface tension and fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy fabricated by EBM additive manufacturing
Youngsin Choi, Dong-Geun Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 741. CrossRef
- Effect of Line Energy Conditions on Mechanical and Fatigue Properties of Ti6Al4V Fabricated by Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing
- [English]
- Influence of milling atmosphere on thermoelectric properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te based alloys by mechanical alloying
- Suk-min Yoon, Cheenepalli Nagarjuna, Dong-won Shin, Chul-hee Lee, Babu Madavali, Soon-jik Hong, Kap-ho Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):357-363. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.357
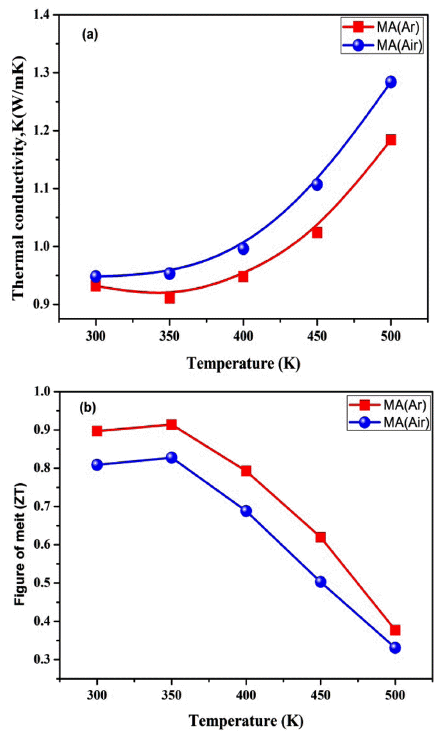
- 1,271 View
- 4 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, Bi-Sb-Te thermoelectric materials are produced by mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). To examine the influence of the milling atmosphere on the microstructure and thermo-electric (TE) properties, a p-type Bi-Sb-Te composite powder is mechanically alloyed in the presence of argon and air atmospheres. The oxygen content increases to 55% when the powder is milled in the air atmosphere, compared with argon. All grains are similar in size and uniformly, distributed in both atmospheric sintered samples. The Seebeck coefficient is higher, while the electrical conductivity is lower in the MA (Air) sample due to a low carrier concentration compared to the MA (Ar) sintered sample. The maximum figure of merit (ZT) is 0.91 and 0.82 at 350 K for the MA (Ar) and MA (Air) sintered samples, respectively. The slight enhancement in the ZT value is due to the decrease in the oxygen content during the MA (Ar) process. Moreover, the combination of mechanical alloying and SPS process shows a higher hardness and density values for the sintered samples.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Grain Size‐Dependent Thermoelectric Performances of Al2O3 Addition into BiSbTe Alloy During Heat Treatment Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying
Ji‐Won Ha, Vasudevan Rathinam, Eun‐Ha Go, Soon‐Jik Hong
Advanced Engineering Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Revealing the improved thermoelectric performances of (BiSb)2Te3 alloy through rapid solidification of cold-water assisted water atomization approach
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Ji-Won Ha, Sung-Jae Jo, GeonWoo Baek, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1010: 177548. CrossRef - Microstructural and Thermoelectric Properties of Heat-treated Al2O3 Doped BiSbTe Alloy
Jiwon Ha, Vasudevan Rathinam, Eunha Go, Soonjik Hong
Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy.2025; 72(Supplement): S983. CrossRef - Advancement of thermoelectric performances through the dispersion of expanded graphene on p-type BiSbTe alloys
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Babu Madavali, Peyala Dharmaiah, Min-Woo Shin, Sung Ho Song, Soon-Jik Hong
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 722. CrossRef - Influence of milling atmosphere on the structure and magnetic properties of mechanically alloyed Fe40Co30Ni30
Alex Abraham Paul, Anuj Rathi, Ganesh Varma Thotakura, Tanjore V. Jayaraman
Materials Chemistry and Physics.2021; 258: 123897. CrossRef - Enhancement of mechanical properties and thermoelectric performance of spark plasma sintered P-type Bismuth Telluride by powder surface oxide reduction
Ahmed A. Abdelnabi, Vickram Lakhian, Joseph R. McDermid, Yu-Chih Tseng, James S. Cotton
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2021; 858: 157657. CrossRef - Solid solution evolution during mechanical alloying in Cu-Nb-Al compounds
Kaouther Zaara, Mahmoud Chemingui, Virgil Optasanu, Mohamed Khitouni
International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials.2019; 26(9): 1129. CrossRef
- Grain Size‐Dependent Thermoelectric Performances of Al2O3 Addition into BiSbTe Alloy During Heat Treatment Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying
- [Korean]
- Stretch-Flangeability of Harmonic Structure Material Manufactured by Powder Metallurgy Method
- Jae Ik Yoon, Hak Hyeon Lee, Hyung Keun Park, Kei Ameyama, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):128-132. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.128
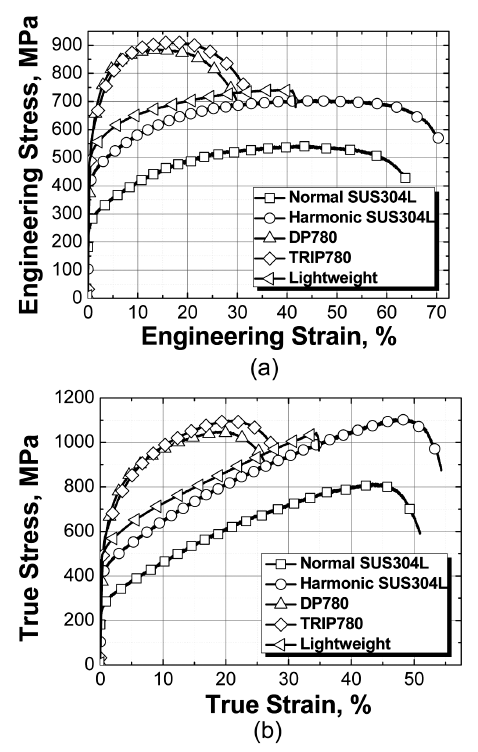
- 858 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Harmonic structure materials are materials with a core–shell structure having a shell with a small grain size and a core with a relatively large grain size. They are in the spotlight because their mechanical properties reportedly feature strength similar to that of a sintered powder with a fine grain size and elongation similar to that of a sintered powder with a coarse grain size at the same time. In this study, the tensile properties, microstructure, and stretchflangeability of harmonic structure SUS304L made using powder metallurgy are investigated to check its suitability for automotive applications. The harmonic powders are made by mechanical milling and sintered using a spark plasma sintering method at 1173 K and a pressure of 50 MPa in a cylindrical die. The sintered powders of SUS304L having harmonic structure (harmonic SUS304L) exhibit excellent tensile properties compared with sintered powders of SUS304L having homogeneous microstructure. In addition, the harmonic SUS304L has excellent stretch-flangeability compared with commercial advanced high-strength steels (AHSSs) at a similar strength grade. Thus, the harmonic SUS304L is more suitable for automotive applications than conventional AHSSs because it exhibits both excellent tensile properties and stretch-flangeability.
- [English]
- Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
- Jin-Koo Han, Dong-won Shin, Babu Madavali, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):115-121. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.115

- 1,380 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this work, p-type Bi−Sb−Te alloys powders are prepared using gas atomization, a mass production powder preparation method involving rapid solidification. To study the effect of the sintering temperature on the microstructure and thermoelectric properties, gas-atomized powders are consolidated at different temperatures (623, 703, and 743 K) using spark plasma sintering. The crystal structures of the gas-atomized powders and sintered bulks are identified using an X-ray diffraction technique. Texture analysis by electron backscatter diffraction reveals that the grains are randomly oriented in the entire matrix, and no preferred orientation in any unique direction is observed. The hardness values decrease with increasing sintering temperature owing to a decrease in grain size. The conductivity increases gradually with increasing sintering temperature, whereas the Seebeck coefficient decreases owing to increases in the carrier mobility with grain size. The lowest thermal conductivity is obtained for the bulk sintered at a low temperature (603 K), mainly because of its fine-grained microstructure. A peak ZT of 1.06 is achieved for the sample sintered at 703 K owing to its moderate electrical conductivity and sustainable thermal conductivity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of the SPS heating rate on the optical and mechanical properties of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites
Seok-Min Yong
Journal of Ceramic Processing Research.2019; 20(1): 59. CrossRef
- Influence of the SPS heating rate on the optical and mechanical properties of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites
- [Korean]
- Effects of Porous Microstructure on the Electrochemical Properties of Si-Ge-Al Base Anode Materials for Li-ion Rechargeable Batteries
- Chung Rae Cho, Myeong Geun Kim, Keun Yong Sohn, Won-Wook Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):24-28. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.24
- 654 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Silicon alloys are considered promising anode active materials to replace Li-ion batteries by graphite powder, because they have a relatively high capacity of up to 4200 mAh/g, and are environmentally friendly and inexpensive ECO-materials. However, its poor charge/discharge properties, induced by cracking during cycles, constitute their most serious problem as anode electrode. In order to solve these problems, Si-Ge-Al alloys with porous structure are designed as anode alloy powders, to improve cycling stability. The alloys are melt-spun to obtain the rapidly solidified ribbons, and then ball-milled to make fine powders. The powders are etched using 1 M HCl solution, which gives the powders a porous structure by removing the element Al. Subsequently, in this study, the microstructures and the characteristics of the etched powders are evaluated for application as anode materials. As a result, the etched porous powder shows better electrochemical properties than as-milled Si-Ge-Al powder.
- [Korean]
- Investigation on the Thermoelectric Properties of Bismuth Telluride Matrix Composites by Addition of Graphene Oxide Powders
- Kyung Tae Kim, Taesik Min, Dong Won Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):263-269. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.263
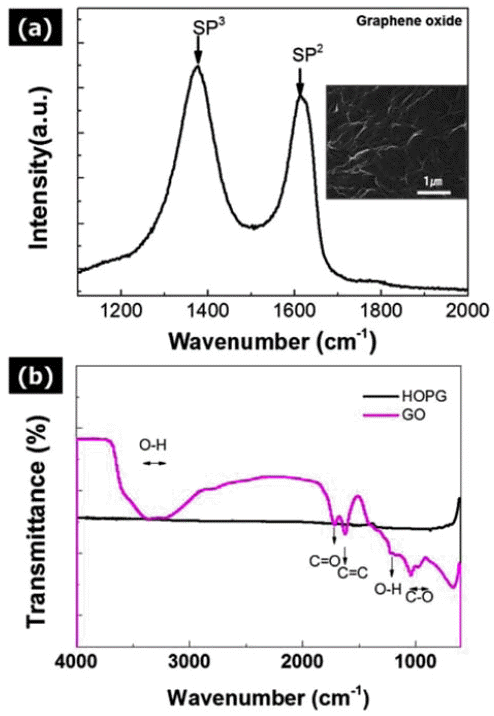
- 787 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Graphene oxide (GO) powder processed by Hummer's method is mixed with p-type Bi2Te3 based thermoelectric materials by a high-energy ball milling process. The synthesized GO-dispersed p-type Bi2Te3 composite powder has a composition of Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 (BSbT), and the powder is consolidated into composites with different contents of GO powder by using the spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. It is found that the addition of GO powder significantly decreases the thermal conductivity of the pure BSbT material through active phonon scattering at the newly formed interfaces. In addition, the electrical properties of the GO/BSbT composites are degraded by the addition of GO powder except in the case of the 0.1 wt% GO/BSbT composite. It is found that defects on the surface of GO powder hinder the electrical transport properties. As a result, the maximum thermoelectric performance (ZT value of 0.91) is achieved from the 0.1% GO/BSbT composite at 398 K. These results indicate that introducing GO powder into thermoelectric materials is a promising method to achieve enhanced thermoelectric performance due to the reduction in thermal conductivity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nanocomposite Strategy toward Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance in Bismuth Telluride
Hua‐Lu Zhuang, Jincheng Yu, Jing‐Feng Li
Small Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef - Advancement of thermoelectric performances through the dispersion of expanded graphene on p-type BiSbTe alloys
Eun-Ha Go, Rathinam Vasudevan, Babu Madavali, Peyala Dharmaiah, Min-Woo Shin, Sung Ho Song, Soon-Jik Hong
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 722. CrossRef - The role of edge-oxidized graphene to improve the thermopower of p-type bismuth telluride-based thick films
Young Min Cho, Kyung Tae Kim, Gi Seung Lee, Soo Hyung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2019; 476: 533. CrossRef - The Preparation and Growth Mechanism of the Recovered Bi2Te3 Particles with Respect to Surfactants
Hyeongsub So, Eunpil Song, Yong-Ho Choa, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 141. CrossRef
- Nanocomposite Strategy toward Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance in Bismuth Telluride
- [Korean]
- Study on Microstructures and Hardness of STS316L Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting
- Gi Hun Shin, Joon Phil Choi, Kyung Tae Kim, Byoung Kee Kim, Ji Hun Yu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;24(3):210-215. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.210

- 975 View
- 2 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, STS316L powders prepared by gas atomization are used to manufacture bulk structures with dimensions of 10 × 10 × 10 mm3 using selective laser melting (SLM). The microstructures and hardness of the fabricated 316L stainless steel has been investigated with the laser beam overlap varied from 10% to 70%. The microstructures of the fabricated STS316L samples show a decrease in the balling and satellite of powders introducing defect in the bulk samples and the porosity caused by the gap between the molten metal pools disappearing as the overlap ratio increases, whereas a low overlap ratio results in significant balling and a large amount of isolated powders due to the increased gap between the melt pools. Furthermore, the highest value in Vickers hardness is obtained for the sample fabricated by 30% overlapped laser beams. These results show that the overlap ratio of laser beams in the SLM process should be considered as an important process parameter.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and mechanical properties of Al–Si-based alloys by selective laser melting process
Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Dong Won Kim, Soo ho Jung, Jung Woo Nam, Dong Yeol Yang, Jungho Choe, Ji Hun Yu, Injoon Son
Powder Metallurgy.2021; 64(3): 198. CrossRef - Effect of laser remelting on the surface characteristics of 316L stainless steel fabricated via directed energy deposition
Seung Yeong Cho, Gwang Yong Shin, Do Sik Shim
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2021; 15: 5814. CrossRef - Investigation on Interfacial Microstructures of Stainless Steel/Inconel Bonded by Directed Energy Deposition of alloy Powders
Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Soo-Ho Jung, Jihun Yu, Dong Yeol Yang, Jungho Choe, Chul Yong Sim, Seung Jun An
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 219. CrossRef - Influence of Powder Size on Properties of Selectively Laser-Melted- AlSi10Mg Alloys
Yeong Seong Eom, Dong Won Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Sang Sun Yang, Jungho Choe, Injoon Son, Ji Hun Yu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(2): 103. CrossRef - Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions
Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Junhyeok Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Im Doo Jung, Hyokyung Sung
Materials Characterization.2019; 155: 109817. CrossRef - Microstructures and Characterization of Al-Si-Mg Alloy Processed by Selective Laser Melting with Post-Heat-treatment
Gi Seung Lee, Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Byoung Kee Kim, Ji Hun Yu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(2): 138. CrossRef - Correlation between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Additive Manufactured H13 Tool Steel
Woojin An, Junhyeok Park, Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Im Doo Jung, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Hyokyung Sung
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(11): 663. CrossRef
- Fabrication and mechanical properties of Al–Si-based alloys by selective laser melting process
- [Korean]
- Influence of Sintering Temperature on Magnetic Properties of Ni-Zn-Cu Ferrites Used for Mangetic Shielding in NFC
- Yo-Han Ryu, Sung-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):132-135. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.132
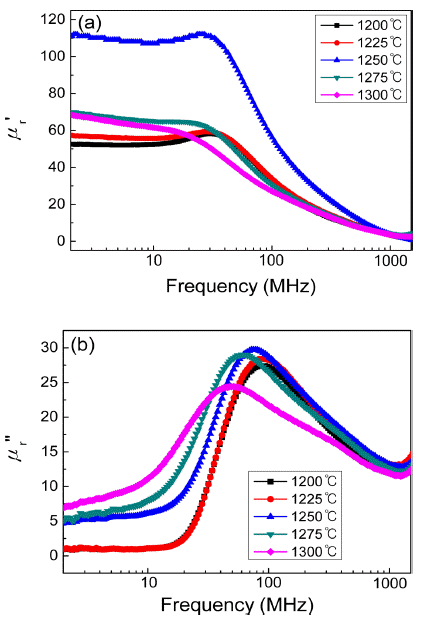
- 513 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the influence of sintering temperature on the magnetic properties and frequency dispersion of the complex permeability of Ni–Zn–Cu ferrites used for magnetic shielding in near-field communication (NFC) systems. Sintered specimens of (Ni0.7Zn0.3)0.96Cu0.04Fe2O4 are prepared by conventional ceramic processing. The complex permeability is measured by an RF impedance analyzer in the range of 1 MHz to 1.8 GHz. The real and imaginary parts of the complex permeability depend sensitively on the sintering temperature, which is closely related to the microstructure, including grain size and pore distribution. In particular, internal pores within grains produced by rapid grain growth decrease the permeability and increase the magnetic loss at the operating frequency of NFC (13.56 MHz). At the optimized sintering temperature (1225-1250°C), the highest permeability and lowest magnetic loss can be obtained.
- [English]
- Effects of Hydrogen Reduction in Microstructure, Mechanical and Thermoelectric Properties of Gas Atomized
n -type Bi2Te2.7 Se0.3 Material - Pradip Rimal, Sang-Min Yoon, Eun-Bin Kim, Chul-Hee Lee, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):126-131. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.126

- 947 View
- 5 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The recent rise in applications of thermoelectric materials has attracted interest in studies toward the fabrication of thermoelectric materials using mass production techniques. In this study, we successfully fabricate
n -type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 material by a combination of mass production powder metallurgy techniques, gas atomization, and spark plasma sintering. In addition, to examine the effects of hydrogen reduction in the microstructure, the thermoelectric and mechanical properties are measured and analyzed. Here, almost 60% of the oxygen content of the powder are eliminated after hydrogen reduction for 4 h at 360°C. Micrographs of the powder show that the reduced powder had a comparatively clean surface and larger grain sizes than unreduced powder. The density of the consolidated bulk using as-atomized powder and reduced atomized powder exceeds 99%. The thermoelectric power factor of the sample prepared by reduction of powder is 20% better than that of the sample prepared using unreduced powder.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tuning of power factor in bismuth selenide through Sn/Te co doping for low temperature thermoelectric applications
Ganesh Shridhar Hegde, Ashwatha Narayana Prabhu, Ramakrishna Nayak, C. F. Yang, Y. K. Kuo
Applied Physics A.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing thermoelectric performance of K-doped polycrystalline SnSe through band engineering tuning and hydrogen reduction
Nan Xin, Yifei Li, Guihua Tang, Longyun Shen
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2022; 899: 163358. CrossRef - The effect of powder pre-treatment on the mechanical and thermoelectric properties of spark plasma sintered N-type bismuth telluride
Ahmed A. Abdelnabi, Vickram Lakhian, Joseph R. McDermid, James S. Cotton
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2021; 874: 159782. CrossRef - Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
Jin-Koo Han, Dong-won Shin, Babu Madavali, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 115. CrossRef - The Preparation and Growth Mechanism of the Recovered Bi2Te3 Particles with Respect to Surfactants
Hyeongsub So, Eunpil Song, Yong-Ho Choa, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 141. CrossRef - Enhanced thermoelectric cooling properties of Bi2Te3−xSex alloys fabricated by combining casting, milling and spark plasma sintering
Seung Tek Han, Pradip Rimal, Chul Hee Lee, Hyo-Seob Kim, Yongho Sohn, Soon-Jik Hong
Intermetallics.2016; 78: 42. CrossRef
- Tuning of power factor in bismuth selenide through Sn/Te co doping for low temperature thermoelectric applications
- [English]
- Investigation of Ball Size Effect on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of
p -type BiSbTe by Mechanical Alloying - May Likha Lwin, Sang-min Yoon, Babu Madavali, Chul-Hee Lee, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):120-125. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.120

- 1,467 View
- 5 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF P -type ternary Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 alloys are fabricated via mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). Different ball sizes are used in the MA process, and their effect on the microstructure; hardness, and thermoelectric properties of thep -type BiSbTe alloys are investigated. The phases of milled powders and bulks are identified using an X-ray diffraction technique. The morphology of milled powders and fracture surface of compacted samples are examined using scanning electron microscopy. The morphology, phase, and grain structures of the samples are not altered by the use of different ball sizes in the MA process. Measurements of the thermoelectric (TE) transport properties including the electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and power factor are measured at temperatures of 300- 400 K for samples treated by SPS. The TE properties do not depend on the ball size used in the MA process.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
Jin-Koo Han, Dong-won Shin, Babu Madavali, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 115. CrossRef - Flexible Thermoelectric Device Using Thick Films for Energy Harvesting from the Human Body
Han Ki Cho, Da Hye Kim, Hye Sun Sin, Churl-Hee Cho, Seungwoo Han
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2017; 54(6): 518. CrossRef - Investigation of the Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of P-Type BiSbTe Alloys by Usage of Different Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) During Mechanical Milling
S.-M. Yoon, B. Madavali, Y.-N. Yoon, S.-J. Hong
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1167. CrossRef - Mechanical and thermoelectric properties of Bi2−xSbxTe3 prepared by using encapsulated melting and hot pressing
Woo-Jin Jung, Il-Ho Kim
Journal of the Korean Physical Society.2016; 69(8): 1328. CrossRef
- Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
- [Korean]
- Phase Formation and Thermo-physical Properties of Lanthanum/Gadolinium Zirconate with Reduced Rare-earth Contents for Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Sujin Lee, Chang-Sup Kwon, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):420-425. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.420
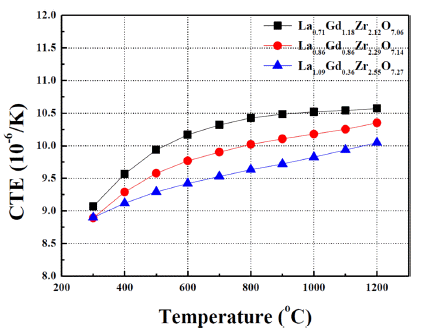
- 1,101 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare-earth zirconates, such as lanthanum zirconates and gadolinium zirconates, have been intensively investigated due to their excellent properties of low thermal conductivity as well as chemical stability at high temperature, which can make these materials ones of the most promising candidates for next-generation thermal barrier coating applications. In this study, three compositions, lanthanum/gadolinium zirconates with reduced rare-earth contents from stoichiometric RE2Zr2O7 compositions, are fabricated via solid state reaction as well as sintering at 1600°C for 4 hrs. The phase formation, microstructure, and thermo-physical properties of three oxide ceramics are examined. In particular, each oxide ceramics exhibits composite structures between pyrochlore and fluorite phases. The potential of lanthanum/ gadolinium zirconate ceramics for TBC applications is also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rare earth zirconate nanostructures: Recent development on preparation and photocatalytic applications
Sahar Zinatloo-Ajabshir, Masoud Salavati-Niasari, Azam Sobhani, Zahra Zinatloo-Ajabshir
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2018; 767: 1164. CrossRef - A novel Co-ions complexation method to synthesize pyrochlore La 2 Zr 2 O 7
Chunhui Xu, Hongyun Jin, Qifeng Zhang, Can Huang, Daifeng Zou, Fujian He, Shuen Hou
Journal of the European Ceramic Society.2017; 37(8): 2871. CrossRef - Fabrication and Characteristics of Thermal Barrier Coatings in the La2O3-Gd2O3-ZrO2System by Using Suspension Plasma Spray with Different Suspension Preparations
Soyul Lee, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
Journal of the Korean institute of surface engineering.2016; 49(6): 595. CrossRef
- Rare earth zirconate nanostructures: Recent development on preparation and photocatalytic applications
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Ceramics and Thermal Barrier Coatings of Lanthanum Zirconate with Reduced Rare-earth Contents in the La2O3-ZrO2 System
- Chang-Sup Kwon, Sujin Lee, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Byung-Koog Jang, Seongwon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):413-419. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.413
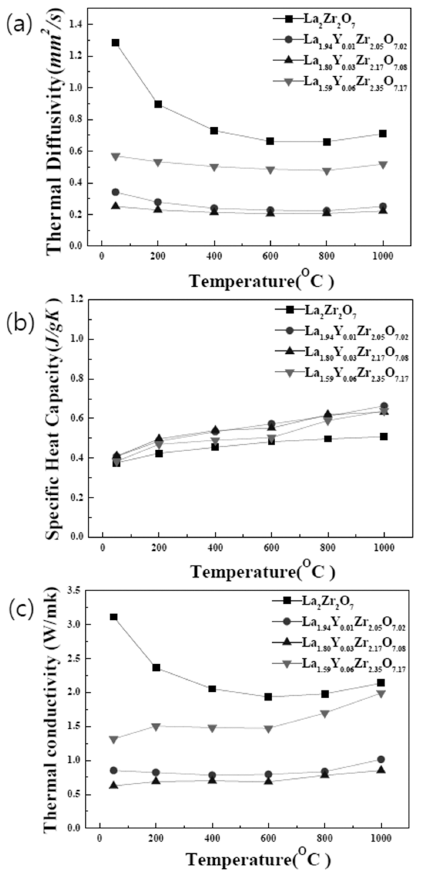
- 837 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Lanthanum zirconate, La2Zr2O7, is one of the most promising candidates for next-generation thermal barrier coating (TBC) applications in high efficient gas turbines due to its low thermal conductivity and chemical stability at high temperature. In this study, bulk specimens and thermal barrier coatings are fabricated via a variety of sintering processes as well as suspension plasma spray in lanthanum zirconates with reduced rare-earth contents. The phase formation, microstructure, and thermo-physical properties of these oxide ceramics and coatings are examined. In particular, lanthanum zirconates with reduced rare-earth contents in a La2Zr2O7-4YSZ composite system exhibit a single phase of fluorite or pyrochlore after fabricated by suspension plasma spray or spark plasma sintering. The potential of lanthanum zirconate ceramics for TBC applications is also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phase Formation and Thermo-physical Properties of Lanthanum/Gadolinium Zirconate with Reduced Rare-earth Contents for Thermal Barrier Coatings
Sujin Lee, Chang-Sup Kwon, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(6): 420. CrossRef
- Phase Formation and Thermo-physical Properties of Lanthanum/Gadolinium Zirconate with Reduced Rare-earth Contents for Thermal Barrier Coatings
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


