Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Enhanced H2S Gas Sensing Using ZnO Porous Nanorod Synthesized via a Rotational Hydrothermal Method
- Jimyeong Park, Changyu Kim, Minseo Kim, Jiyeon Shin, Jae-Hyoung Lee, Myung Sik Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):406-415. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00262
- 123 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
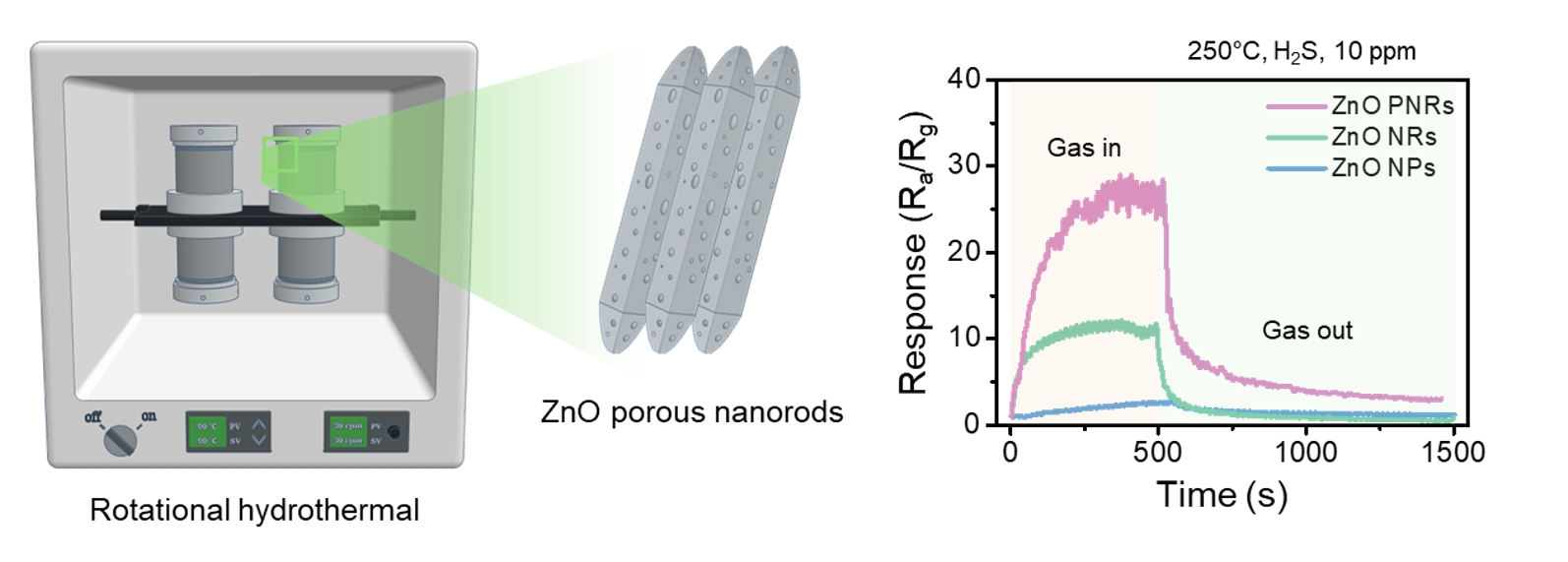
PDF - In this study, ZnO porous nanorods were synthesised using a rotational hydrothermal process, and their performance as hydrogen sulphide (H2S) gas sensors was analysed. Compared to commercial ZnO nanoparticles and conventionally hydrothermally synthesised ZnO nanorods, the ZnO porous nanorods exhibited a more uniform structure and improved crystal growth in the (002) plane, with surfaces rich in porosity and oxygen vacancies. These structural and chemical characteristics significantly improved the sensitivity toward H2S, showing high detection performance at 250°C across various concentrations of H2S gas. Additionally, the sensor demonstrated excellent selectivity against other gases such as C2H5OH, C6H6, C7H8, and NH3. This study indicated that the rotational hydrothermal process is an effective method for developing high-performance ZnO-based gas sensors and suggests its applicability to other metal oxide materials.
- [English]
- Enhancing the Dispersion Stability of Exfoliated MoS2 Nanoflakes for Na⁺ Intercalation
- Jae Min Sung, Dong-Won Kyung, Ammad Ali, Kee-Ryung Park, Mi Hye Lee, Da-Woon Jeong, Bum Sung Kim, Haejin Hwang, Leeseung Kang, Yoseb Song
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):390-398. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00255
- 127 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
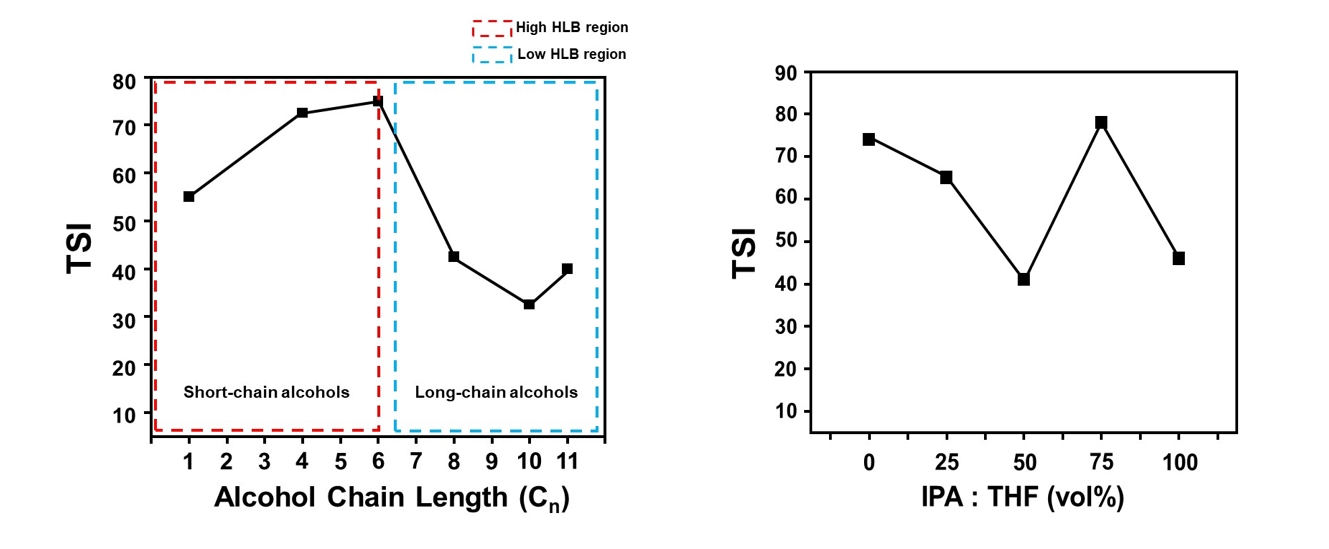
PDF - This study investigated the dispersion stability of exfoliated MoS₂ nanoflakes in various organic solvents and binary mixtures using a Turbiscan optical analyzer. Sedimentation behavior was quantitatively evaluated via transmittance variation (ΔT), backscattering variation (ΔBS), and the Turbiscan stability index (TSI). Alcohol-based solvents were categorized by hydrophilic-lipophilic balance values. Long-chain alcohols, such as 1-undecanol, showed increased stability due to high viscosity and strong hydrophobic affinity with MoS2 basal planes, while short-chain alcohols exhibited poor stabilization. Binary mixtures of isopropanol (IPA) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) were also assessed, with the 5:5 volume ratio showing the best stability profile, including the lowest TSI and minimal ΔT and ΔBS values. This improvement is attributed to synergistic interactions, as IPA stabilizes hydrophilic edge sites, while THF engages with hydrophobic basal surfaces. These findings highlight the importance of balancing physicochemical properties when selecting solvents to improve MoS2 dispersion for structural modification and electrocatalytic applications.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Fe and Cr on ω Phase Formation in Metastable β-Ti Alloy
- Sun-Young Park, Young-Bum Chun
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):354-360. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00220

- 754 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the effects of Fe and Cr contents on ω phase formation and transformation during solution treatment and the subsequent aging process, for which four model alloys with varying Fe and Cr contents but keeping Mo equivalent of ~ 12.6 were prepared by plasma arc melting and fabricated into plates by hot forging followed by hot-rolling. The atherrmal ω phase was observed in all Ti alloys after solution treatment followed by water quenching through XRD and TEM analysis. The largest volume fraction of athermal ω phase is formed in Ti alloy with only Fe 4 wt.% among all Ti alloys, leading to the highest Vickers value due to hardening effect ω phase. It was found that not only Mo equivalent but also each characteristic of β stabilizing elements should be considered to understand a microstructure evolution and mechanical properties.
- [English]
- Laser Processing of an Al0.1CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy + Cu Composite Powders via Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Kwangtae Son, Ji-Woon Lee, Soon-Jik Hong, Somayeh Pasebani
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):277-287. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00101

- 822 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study examined process–structure relationships in laser powder bed fusion of Al₀.₁CoCrFeNi + Cu composites, focusing on densification, elemental distribution, and solidification cracking. Mechanically mixed Al₀.₁CoCrFeNi and Cu powders were processed across a range of laser powers (100–250 W) and scan speeds (200–800 mm/s). Increased volumetric energy density (VED) improved densification, with a plateau near 200 J/mm³ yielding ~96% relative density; however, this value was still below application-grade thresholds. At low VED, insufficient thermal input and short melt pool residence times promoted Cu segregation, while higher VED facilitated improved elemental mixing. Elemental mapping showed partial co-segregation of Ni with Cu at low energies. Solidification cracks were observed across all processing conditions. In high VED regimes, cracking exhibited a minimal correlation with segregation behavior and was primarily attributed to steep thermal gradients, solidification shrinkage, and residual stress accumulation. In contrast, at low VED, pronounced Cu segregation appeared to exacerbate cracking through localized thermal and mechanical mismatch.
- [English]
- Effect of the Cross-rolling Process on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of 9Cr-1W ODS Steel
- Bu-An Kim, Sanghoon Noh
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):37-42. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00332
- 722 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
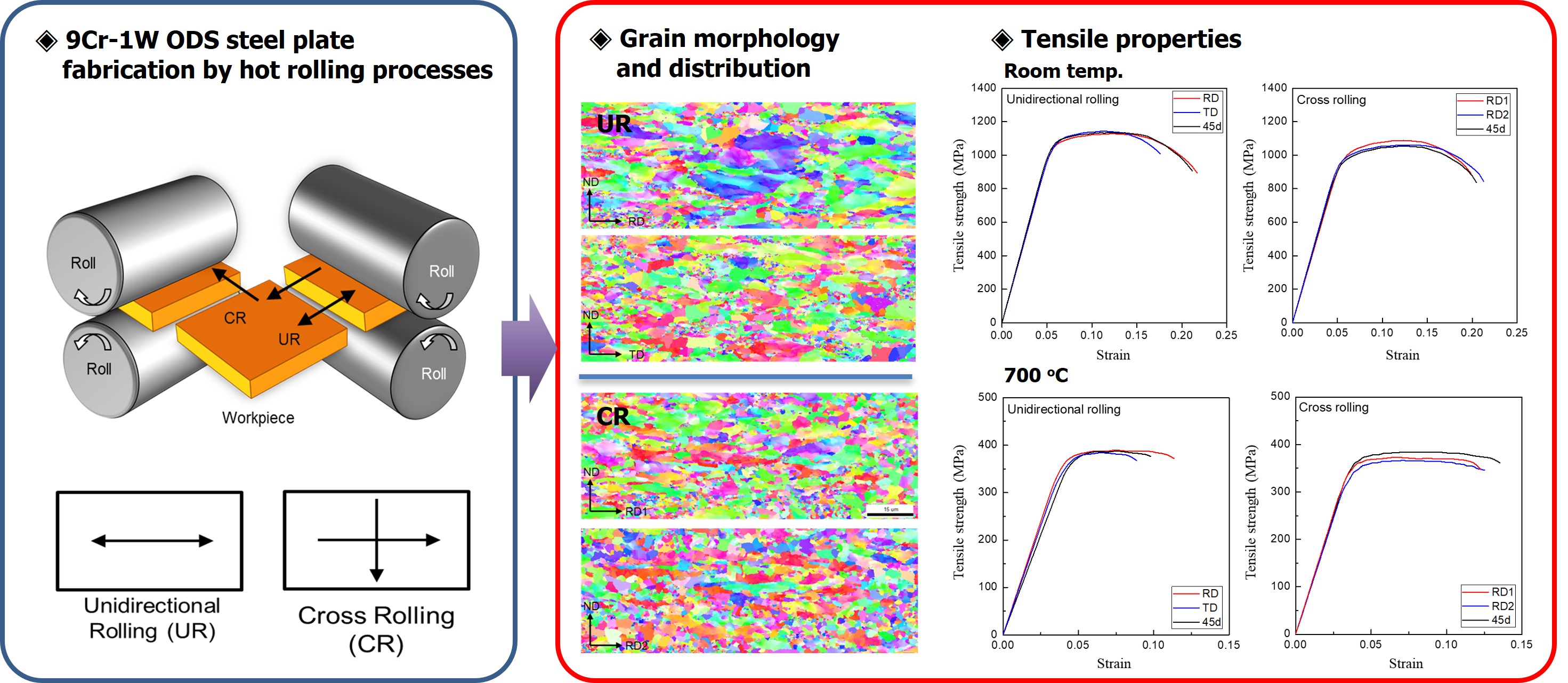
PDF - This study employed a cross-rolling process to fabricate oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel plates and investigated their microstructures and mechanical properties. The 9Cr-1W ODS ferritic steel was fabricated using mechanical alloying and hot isostatic pressing. The hot cross-rolling process produced thick ODS ferritic steel plates with a well-extended rectangular shape. The working direction greatly affected the grain structure and crystal texture of the ODS ferritic steel. Cross-rolled plates showed fine micro-grains with random crystal orientation, while unidirectionally rolled plates exhibited a strong orientation with larger, elongated grains. Transmission electron microscopy revealed a uniform distribution of nano-oxide particles in both rolling methods, with no major differences. Tensile tests of the ODS ferritic steel plates showed that the unidirectional rolled plates had anisotropic elongation, while cross-rolled plates exhibited isotropic behavior with uniform elongation. Cross-rolling produced finer, more uniform grains, reducing anisotropy and improving mechanical properties, making it ideal for manufacturing wide ODS steel components.
- [English]
- Hot-Cracking Behaviors in (CoNi)85Mo15 Medium-Entropy Alloys Manufactured via Powder Bed Fusion
- Seungjin Nam, Heechan Jung, Haeum Park, Chahee Jung, Jeong Min Park, Hyoung Seop Kim, Seok Su Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):537-545. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00262
- 959 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
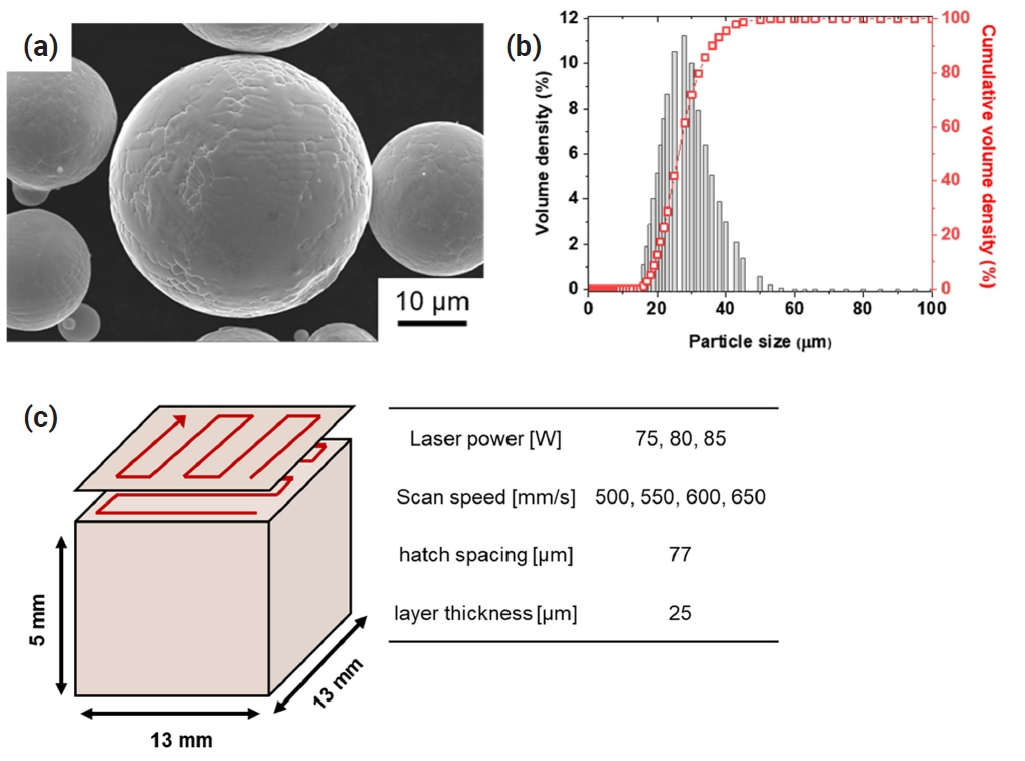
PDF - Additive manufacturing makes it possible to improve the mechanical properties of alloys through segregation engineering of specific alloying elements into the dislocation cell structure. In this study, we investigated the mechanical and microstructural characteristics of CoNi-based medium-entropy alloys (MEAs), including the refractory alloying element Mo with a large atomic radius, manufactured via laser-powder bed fusion (L-PBF). In an analysis of the printability depending on the processing parameters, we achieved a high compressive yield strength up to 653 MPa in L-PBF for (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs. However, severe residual stress remained at high-angle grain boundaries, and a brittle µ phase was precipitated at Mo-segregated dislocation cells. These resulted in hot-cracking behaviors in (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs during L-PBF. These findings highlight the need for further research to adjust the Mo content and processing techniques to mitigate cracking behaviors in L-PBF-manufactured (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- [Korean]
- Recent Developments in Quantum Dot Patterning Technology for Quantum Dot Display
- Yeong Jun Jin, Kyung Jun Jung, Jaehan Jung
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):169-179. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00073
- 6,283 View
- 143 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
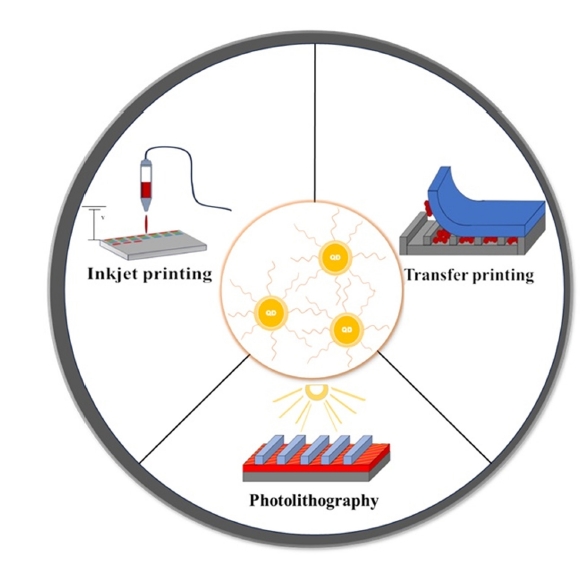
PDF - Colloidal quantum dot (QDs) have emerged as a crucial building block for LEDs due to their size-tunable emission wavelength, narrow spectral line width, and high quantum efficiency. Tremendous efforts have been dedicated to improving the performance of quantum dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs) in the past decade, primarily focusing on optimization of device architectures and synthetic procedures for high quality QDs. However, despite these efforts, the commercialization of QLEDs has yet to be realized due to the absence of suitable large-scale patterning technologies for high-resolution devices., This review will focus on the development trends associated with transfer printing, photolithography, and inkjet printing, and aims to provide a brief overview of the fabricated QLED devices. The advancement of various quantum dot patterning methods will lead to the development of not only QLED devices but also solar cells, quantum communication, and quantum computers.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Acid Leaching Conditions on the Properties of Cr Powder Produced by Self-propagating High-temperature Synthesis
- YongKwan Lee, YeongWoo Cho, ShinYoung Choi, SungGue Heo, Ju Won, KyoungTae Park, MiHye Lee, JaeJin Sim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):233-241. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.233
- 624 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
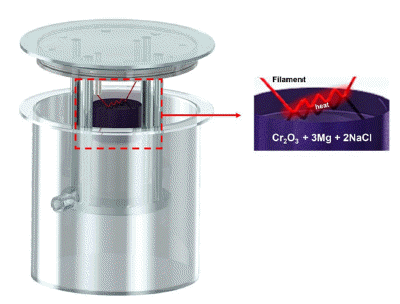
PDF In this study, we evaluated the effects of acid leaching on the properties of Cr powder synthesized using self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS). Cr powder was synthesized from a mixture of Cr2O3 and magnesium (Mg) powders using the SHS Process, and the byproducts after the reaction were removed using acid leaching. The properties of the recovered Cr powder were analyzed via X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), particle size analysis (PSA), and oxygen content analysis. The results show that perfect selective leaching of Cr is challenging because of various factors such as incomplete reaction, reaction kinetics, the presence of impurities, and incompatibility between the acid and metal mixture. Therefore, this study provides essential information on the properties under acidic conditions during the production of high-quality Cr powder using a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis method.
- [Korean]
- Prediction of Crack Density in additive manufactured AA7075 Alloy Reinforced with ZrH2 inoculant via Response Surface Method
- Jeong Ah Lee, Jungho Choe, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):203-209. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.203

- 1,050 View
- 8 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Aluminum alloy-based additive manufacturing (AM) has emerged as a popular manufacturing process for the fabrication of complex parts in the automotive and aerospace industries. The addition of an inoculant to aluminum alloy powder has been demonstrated to effectively reduce cracking by promoting the formation of equiaxed grains. However, the optimization of the AM process parameters remains challenging owing to their variability. In this study, the response surface methodology (RSM) was used to predict the crack density of AM-processed Al alloy samples. RSM was performed by setting the process parameters and equiaxed grain ratio, which influence crack propagation, as independent variables and designating crack density as a response variable. The RSM-based quadratic polynomial models for crack-density prediction were found to be highly accurate. The relationship among the process parameters, crack density, and equiaxed grain fraction was also investigated using RSM. The findings of this study highlight the efficacy of RSM as a reliable approach for optimizing the properties of AM-processed parts with limited experimental data. These results can contribute to the development of robust AM processing strategies for the fabrication of highquality Al alloy components for various applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synergistic strengthening of crack-free Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys with hierarchical microstructures achieved via laser powder bed fusion
Jungho Choe, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park, Hyomoon Joo, Sang Guk Jeong, Eun Seong Kim, Soung Yeoul Ahn, Gang Hee Gu, Hyoung Seop Kim
Materials Research Letters.2024; 12(8): 598. CrossRef
- Synergistic strengthening of crack-free Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys with hierarchical microstructures achieved via laser powder bed fusion
- [English]
- Selective Laser Sintering of Co-Cr Alloy Powders and Sintered Products Properties
- Dong-Wan Lee, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):7-12. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.7

- 1,039 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal-additive manufacturing techniques, such as selective laser sintering (SLS), are increasingly utilized for new biomaterials, such as cobalt-chrome (Co-Cr). In this study, Co-Cr gas-atomized powders are used as charge materials for the SLS process. The aim is to understand the consolidation of Co-Cr alloy powder and characterization of samples sintered using SLS under various conditions. The results clearly suggest that besides the matrix phase, the second phase, which is attributed to pores and oxidation particles, is observed in the sintered specimens. The as-built samples exhibit completely different microstructural features compared with the casting or wrought products reported in the literature. The microstructure reveals melt pools, which represent the characteristics of the scanning direction, in particular, or of the SLS conditions, in general. It also exposes extremely fine grain sizes inside the melt pools, resulting in an enhancement in the hardness of the as-built products. Thus, the hardness values of the samples prepared by SLS under all parameter conditions used in this study are evidently higher than those of the casting products.
- [English]
- Investigation on Microstructure and Flowability of Gas Atomized Heat-resistant KHR45A Alloy Powders for Additive Manufacturing
- Geonwoo Baek, Mohsen Saboktakin Rizi, Yeeun Lee, SungJae Jo, Joo-Hyun Choi, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):13-21. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.13

- 2,113 View
- 766 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In additive manufacturing, the flowability of feedstock particles determines the quality of the parts that are affected by different parameters, including the chemistry and morphology of the powders and particle size distribution. In this study, the microstructures and flowabilities of gas-atomized heat-resistant alloys for additive manufacturing applications are investigated. A KHR45A alloy powder with a composition of Fe-30Cr-40Mn-1.8Nb (wt.%) is fabricated using gas atomization process. The microstructure and effect of powder chemistry and morphology on the flow behavior are investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and revolution powder analysis. The results reveal the formation of spherical particles composed of single-phase FCC dendritic structures after gas atomization. SEM observations show variations in the microstructures of the powder particles with different size distributions. Elemental distribution maps, line scans, and high-resolution XPS results indicate the presence of a Si-rich oxide accompanied by Fe, Cr, and Nb metal oxides in the outer layer of the powders. The flowability behavior is found to be induced by the particle size distribution, which can be attributed to the interparticle interactions and friction of particles with different sizes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Engineering heterogeneous microstructure for enhancing mechanical properties of multicomponent alloys via powder metallurgy route
Min Woo Shin, Sung-Jae Jo, Sourabh Kumar Soni, Ji-Woon Lee, Jongun Moon, Hyoung Seop Kim, Soon-Jik Hong
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2025; 941: 148599. CrossRef - Al-based amorphous coatings by warm spraying: Numerical simulation and experimental validation
Deming Wang, Nianchu Wu, Peng Cao
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2024; 1008: 176674. CrossRef
- Engineering heterogeneous microstructure for enhancing mechanical properties of multicomponent alloys via powder metallurgy route
- [English]
- Optimization of VIGA Process Parameters for Power Characteristics of Fe-Si-Al-P Soft Magnetic Alloy using Machine Learning
- Sung-Min Kim, Eun-Ji Cha, Do-Hun Kwon, Sung-Uk Hong, Yeon-Joo Lee, Seok-Jae Lee, Kee-Ahn Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):459-467. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.459

- 675 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Soft magnetic powder materials are used throughout industries such as motors and power converters. When manufacturing Fe-based soft magnetic composites, the size and shape of the soft magnetic powder and the microstructure in the powder are closely related to the magnetic properties. In this study, Fe-Si-Al-P alloy powders were manufactured using various manufacturing process parameter sets, and the process parameters of the vacuum induction melt gas atomization process were set as melt temperature, atomization gas pressure, and gas flow rate. Process variable data that records are converted into 6 types of data for each powder recovery section. Process variable data that recorded minute changes were converted into 6 types of data and used as input variables. As output variables, a total of 6 types were designated by measuring the particle size, flowability, apparent density, and sphericity of the manufactured powders according to the process variable conditions. The sensitivity of the input and output variables was analyzed through the Pearson correlation coefficient, and a total of 6 powder characteristics were analyzed by artificial neural network model. The prediction results were compared with the results through linear regression analysis and response surface methodology, respectively.
- [Korean]
- Aqueous Synthesis and Luminescent Characteristics of Cu:ZnSe Quantum Dots by Internal Doping Method
- Geum Ji Back, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):370-375. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.370
- 710 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
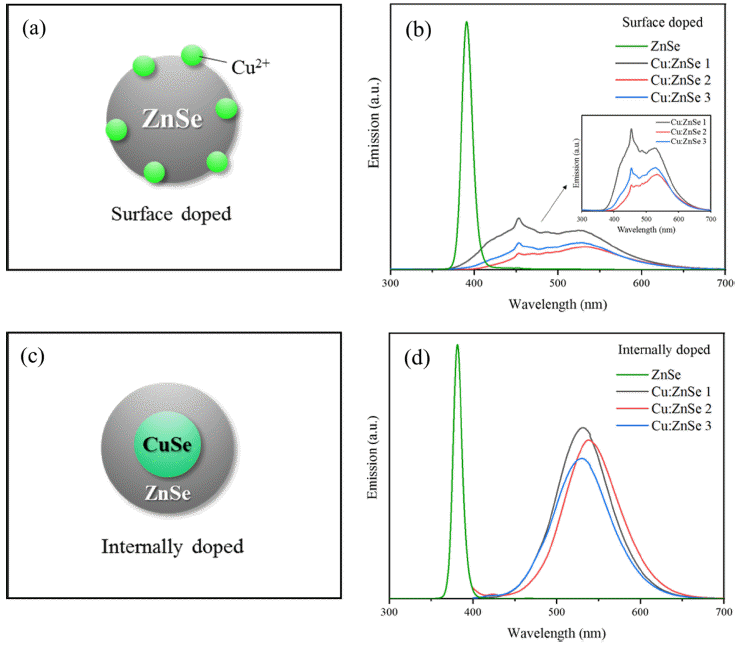
PDF Cu-doped ZnSe quantum dots were successfully synthesized in an aqueous solution using an internal doping method. The effects of ligand type, CuSe synthesis temperature, and heating time on Cu-doped ZnSe synthesis were systematically investigated. Of MPA, GSH, TGA, and NAC used as ligands, MPA was the optimal ligand as determined by PL spectrum analysis. In addition, the emission wavelength was found to depend on the synthesis temperature of the internal doping core of CuSe. As the temperature increased, the doping of Cu2+ was enhanced, and the emission wavelength band was redshifted; accordingly, the emission peaks moved from blue to green (up to 550 nm). Thus, the synthesis of Cu:ZnSe using internal doping in aqueous solutions is a potential method for ecomanufacturing of colortuned ZnSe quantum dots for display applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and luminescence characteristics of manganese-doped ZnSe quantum dots synthesized in aqueous solution through internal doping
Hyun Seon Hong, Yerin Kim, Jea Hyung Kim, Hyeon Seon Ryu, Dahye Song
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2025; 62(3): 472. CrossRef
- Synthesis and luminescence characteristics of manganese-doped ZnSe quantum dots synthesized in aqueous solution through internal doping
- [Korean]
- Recycling of Hardmetal Tool through Alkali Leaching Process and Fabrication Process of Nano-sized Tungsten Carbide Powder using Self-propagation High-temperature Synthesis
- Hee-Nam Kang, Dong Il Jeong, Young Il Kim, In Yeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Cheol Woo Nam, Seok-Jun Seo, Jin Yeong Lee, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):47-55. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.47

- 1,172 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten carbide is widely used in carbide tools. However, its production process generates a significant number of end-of-life products and by-products. Therefore, it is necessary to develop efficient recycling methods and investigate the remanufacturing of tungsten carbide using recycled materials. Herein, we have recovered 99.9% of the tungsten in cemented carbide hard scrap as tungsten oxide via an alkali leaching process. Subsequently, using the recovered tungsten oxide as a starting material, tungsten carbide has been produced by employing a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) method. SHS is advantageous as it reduces the reaction time and is energy-efficient. Tungsten carbide with a carbon content of 6.18 wt % and a particle size of 116 nm has been successfully synthesized by optimizing the SHS process parameters, pulverization, and mixing. In this study, a series of processes for the highefficiency recycling and quality improvement of tungsten-based materials have been developed.
- [Korean]
- The Effects of TiC Content on Microstructure of Modified A6013-3wt.%Si Alloy Powder Compact
- Hyo-Sang Yoo, Yong-Ho Kim, Hyeon-Taek Son
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):28-33. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.28

- 751 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Aluminum-based powders have attracted attention as key materials for 3D printing owing to their low density, high specific strength, high corrosion resistance, and formability. This study describes the effects of TiC addition on the microstructure of the A6013 alloy. The alloy powder was successfully prepared by gas atomization and further densified using an extrusion process. We have carried out energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS) and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) in order to investigate the effect of TiC addition on the microstructure and texture evolution of the A6013 alloy. The atomized A6013-xTiC alloy powder is fine and spherical, with an initial powder size distribution of approximately 73 μm which decreases to 12.5, 13.9, 10.8, and 10.0 μm with increments in the amount of TiC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Curing Agent Amount on Properties of Dynamic Vulcanized Phenyl Silicone Rubber-SEBS-SBS System
Chunxu Zhao, Bobing He, Xian Chen
Polymers.2022; 14(24): 5443. CrossRef
- Influence of Curing Agent Amount on Properties of Dynamic Vulcanized Phenyl Silicone Rubber-SEBS-SBS System
- [Korean]
- A Study on Morphology Control of (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) Nanofibers according to the Composition and Crystallinity of Oxide Nanofibers Synthesized by Electrospinning
- Jeong Hyun Kim, Sung-Tag Oh, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):259-266. Published online June 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.259
- 497 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
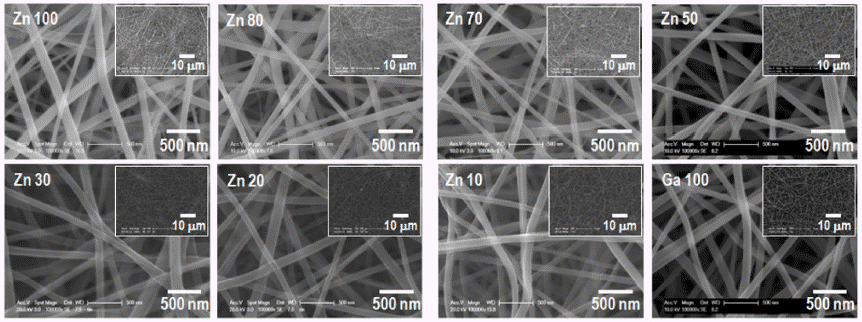
PDF The (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) solid solution is attracting extensive attention for photocatalytic water splitting and wastewater treatment owing to its narrow and controllable band gap. To optimize the photocatalytic performance of the solid solution, the key points are to decrease its band gap and recombination rate. In this study, (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) nanofibers with various Zn fractions are prepared by electrospinning followed by calcination and nitridation. The effect of the composition and crystallinity of electrospun oxide nanofibers on the morphology and optical properties of the obtained solid-solution nanofibers are systematically investigated. The results show that the final shape of the (Ga1-xZnx) (N1-xOx) material is greatly affected by the crystallinity of the oxide nanofibers before nitridation. The photocatalytic properties of (Ga1-xZnx)(N1-xOx) with different Ga:Zn atomic ratios are investigated by studying the degradation of rhodamine B under visible light irradiation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Nanowire by Electrospinning Process Using Nickel Oxide Particle Recovered from MLCC
Haein Shin, Jongwon Bae, Minsu Kang, Kun-Jae Lee
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 502. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Nanowire by Electrospinning Process Using Nickel Oxide Particle Recovered from MLCC
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Optical Property of (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x Nanoparticles Using an Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process and Subsequent Chemical Transformation
- Jeong Hyun Kim, Cheol-Hui Ryu, Myungjun Ji, Yomin Choi, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):143-149. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.143
- 618 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
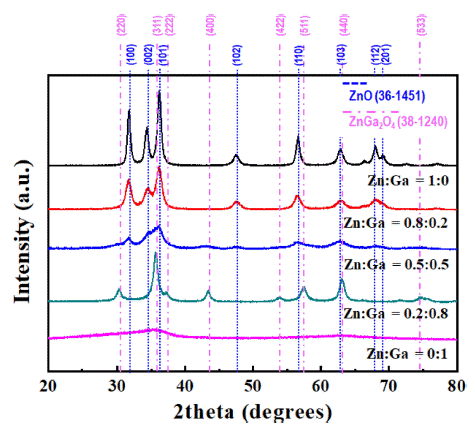
PDF In this study, (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x solid solution nanoparticles with a high zinc content are prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis and subsequent nitridation. The structure and morphology of the samples are investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field-emission scanning electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The characterization results show a phase transition from the Zn and Ga-based oxides (ZnO or ZnGa2O4) to a (GaN)1-x (ZnO)x solid solution under an NH3 atmosphere. The effect of the precursor solution concentration and nitridation temperature on the final products are systematically investigated to obtain (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x nanoparticles with a high Zn concentration. It is confirmed that the powder synthesized from the solution in which the ratio of Zn and Ga was set to 0.8:0.2, as the initial precursor composition was composed of about 0.8-mole fraction of Zn, similar to the initially set one, through nitriding treatment at 700°C. Besides, the synthesized nanoparticles exhibited the typical XRD pattern of (GaN)1-x(ZnO)x, and a strong absorption of visible light with a bandgap energy of approximately 2.78 eV, confirming their potential use as a hydrogen production photocatalyst.
- [Korean]
- Manufacture of AlSi10Mg Alloy Powder for Powder Bed Fusion(PBF) Process using Gas Atomization Method
- Weon Bin Im, Seung Joon Park, Yeo Chun Yun, Byeong Cheol Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):120-126. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.120

- 1,181 View
- 11 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, AlSi10Mg alloy powders are synthesized using gas atomization and sieving processes for powder bed fusion (PBF) additive manufacturing. The effect of nozzle diameter (ø = 4.0, 4.5, 5.0 and 8.0 mm) on the gas atomization and sieving size on the properties of the prepared powder are investigated. As the nozzle diameter decreases, the size of the manufactured powder decreases, and the uniformity of the particle size distribution improves. Therefore, the ø 4.0 mm nozzle diameter yields powder with superior properties. Spherically shaped powders can be prepared at a scale suitable for the PBF process with a particle size distribution of 10–45 μm. The Hausner ratio value of the powder is measured to be 1.24. In addition, the yield fraction of the powder prepared in this study is 26.6%, which is higher than the previously reported value of 10–15%. These results indicate that the nozzle diameter and the post-sieve process simultaneously influence the shape of the prepared powder as well as the satellite powder on its surface.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
SiO
2
nanoparticle-coated Ti-6Al-4V spherical powder for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process
Jongik Lee, Taehoo Kang, Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Sanghee Jung, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 333. CrossRef - Effect of thermal debinding conditions on microstructure and mechanical properties of a biomedical Ti-15Nb-5Sn alloy prepared by material extrusion additive manufacturing (MEAM) process
Jin-hwan Lim, Soo-yeong Kim, Tae-gyun Gu, Shuanglei Li, Tae-hyun Nam
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1044: 184366. CrossRef - Effect of Phase Composition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Biomedical Ti-15Nb-5Sn Alloy Prepared by Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
Jin-hwan Lim, Gyeong-ho Kang, Shuanglei Li, Tae-hyun Nam
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of a Laboratory-Scale Gas-Atomized AlSi10Mg Powder and a Commercial-Grade Counterpart for Laser Powder Bed Fusion Processing
Fabrizio Marinucci, Alberta Aversa, Diego Manfredi, Mariangela Lombardi, Paolo Fino
Materials.2022; 15(21): 7565. CrossRef
-
SiO
2
nanoparticle-coated Ti-6Al-4V spherical powder for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process
- [Korean]
- Photophysical Properties of Guest Molecules Confined in Nanopores
- Suhyeon Park, Juyeong Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):477-483. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.477
- 406 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
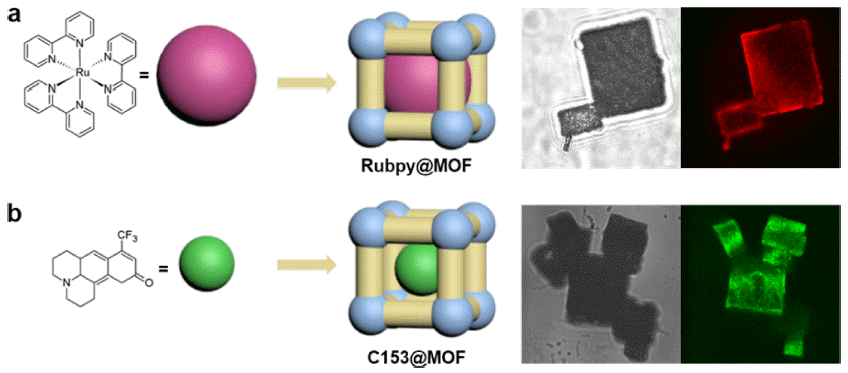
PDF Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are of significant interest because of their high porosity, which facilitates their utilization in gas storage and catalysis. To enhance their current properties in these applications, it is necessary to elucidate the interactions between molecules in a confined environment that differ from those in bulk conditions. Herein, we study the confined molecular interaction by investigating the solvent-dependent photophysical properties of two different-sized molecules inside MOF-5. Ruthenium
tris -bipyridine (Rubpy) and coumarin 153 (C153) are encapsulated in MOF-5. Rubpy with MOF-5 (Rubpy@MOF) is prepared by building MOF-5 around it, resulting in limited space for solvent molecules in the pores. The smaller C153 is encapsulated in the preformed MOF-5 (C153@MOF) by simply soaking the MOF in a concentrated C153 solution. C153@MOF permits more space for solvent molecules in the pore. Their characteristic absorption and emission spectra are examined to elucidate the confined molecular interactions. Rubpy@MOF and C153@MOF exhibit different spectral shifts compared to the guest molecules under bulk conditions. This discrepancy is attributed to the different micro-environments inside the pores, derived from confined host-guest interactions in the interplay of solvent molecules.
- [English]
- Interaction of Detonation Nanodiamonds with Hispidin
- Changkyu Rhee, Whungwhoe Kim, Andrey E. Burov, Alexey P. Puzyr, Vladimir S. Bondar
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):458-463. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.458
- 516 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
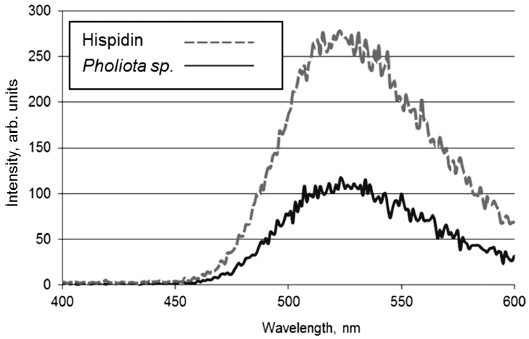
PDF Hispidin is a secondary metabolite found in numerous medicinal mushrooms that has attracted significant attention, owing to its distinct biological effects, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and cytoprotective properties. Experiments are being carried out to study the interaction of detonation nanodiamonds (DNDs) with synthetic and natural hispidin sourced from extracts of
Pholiota sp. fungus. The bioluminescence method is used to determine the adsorption/ desorption properties of DNDs toward hispidin. It is found that hispidin forms strong conjugates with DNDs, and the use of various eluents does not result in a significant release of the adsorbed hispidin molecules. DND-bovine serum albumin (BSA) complex, where DNDs serve as a carrier for the protein and the latter acts as a hispidin sorbent, has been developed and applied in hispidin adsorption/desorption tests. The results support the use of the DNDs as a carrier for hispidin in medical applications. They also advocate the application of the DND-BSA complex for isolating the substance from fungal extracts.
- [Korean]
- Partially Dry-Transferred Graphene Electrode with Zinc Oxide Nanopowder and Its Application on Organic Solar Cells
- Yeongsu Jo, Chae Young Woo, Soon Kyu Hong, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):305-310. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.305
- 400 View
- 1 Download
-
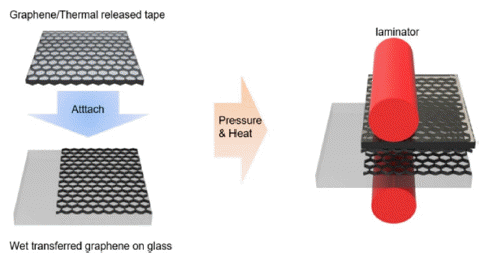
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, partially dry transfer is investigated to solve the problem of fully dry transfer. Partially dry transfer is a method in which multiple layers of graphene are dry-transferred over a wet-transferred graphene layer. At a wavelength of 550 nm, the transmittance of the partially dry-transferred graphene is seen to be about 3% higher for each layer than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene. Furthermore, the sheet resistance of the partially drytransferred graphene is relatively lower than that of the fully dry-transferred graphene, with the minimum sheet resistance being 179 Ω/sq. In addition, the fully dry-transferred graphene is easily damaged during the solution process, so that the performance of the organic photovoltaics (OPV) does not occur. In contrast, the best efficiency achievable for OPV using the partially dry-transferred graphene is 2.37% for 4 layers.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of
Gastrodia elata -loaded Particles for Increased Moisture Stability - Jae Hwan Jung, Sung Giu Jin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):241-246. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.241
- 658 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To develop
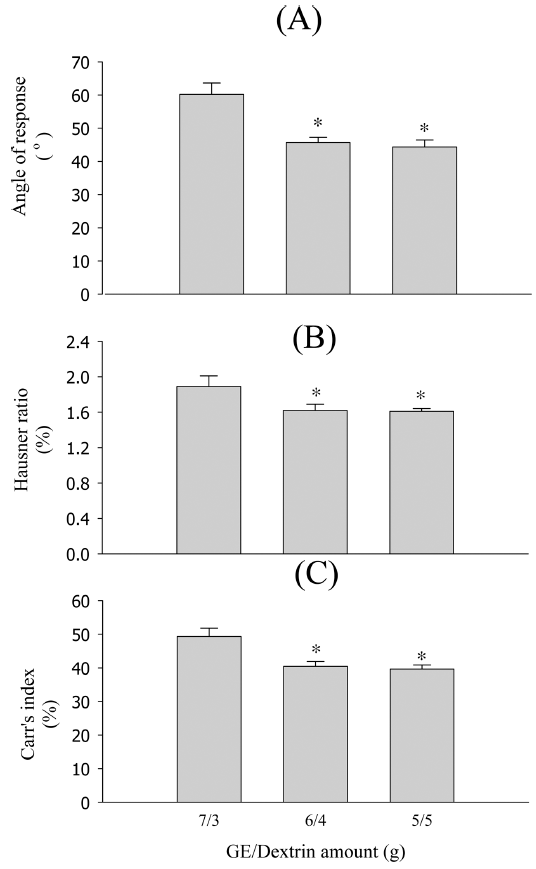
Gastrodia elata (GE)-loaded particles for herbal extract dosage forms, various GE-loaded particles containing dextrin, isomalt, maltodextrin, and silicon dioxide as solidifying carriers in the GE water extract are prepared using the spray drying method. Their physical properties are evaluated using the repose angle, Hausner ratio, Carr’s index, weight increase rate at 40°C/75% RH condition, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Particles made of dextrin improve the fluidity, compressibility, and water stability. In addition, 2% silicon dioxide increases the fluidity and moisture stability. The best flowability and compressibility of GE-loaded particles are observed with TP, dextrin, and silicon dioxide amounts in the ratio of 6/4/0.2 (34.29 ± 2.86°, 1.48 ± 0.03, and 38.29 ± 2.39%, repose angle, Hausner Ratio, and Carr’s index, respectively) and moisture stability with a 2% weight increase rate for 14 h at 40°C/75% RH condition. Therefore, our results suggest that the particles prepared by the spray drying method with dextrin and 2% silicon dioxide can be used as powerful particles to improve the flowability, compressibility, and moisture stability of GE.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Sn Addition on Microstructure of Al Alloy Powder for Brazing Process
- Yong-Ho Kim, Hyo-Sang Yoo, Sang-Su Na, Hyeon-Taek Son
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):139-145. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.139
- 517 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
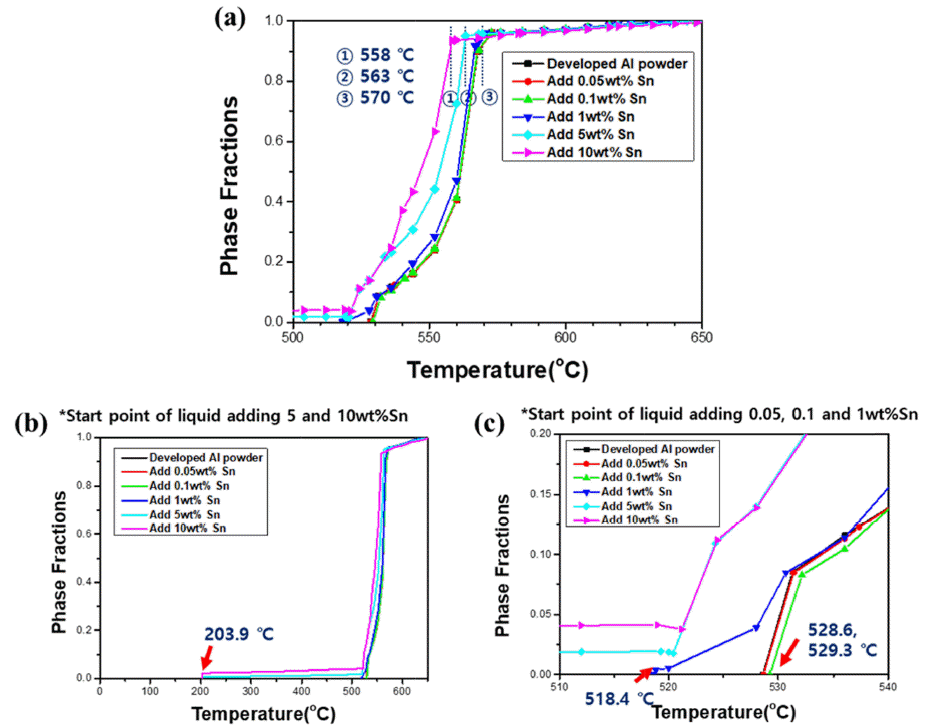
PDF The powder manufacturing process using the gas atomizer process is easy for mass production, has a fine powder particle size, and has excellent mechanical properties compared to the existing casting process, so it can be applied to various industries such as automobiles, electronic devices, aviation, and 3D printers. In this study, a modified A4032-xSn (x = 0, 1, 3, 5, and 10 wt.%) alloy with low melting point properties is investigated. After maintaining an argon (Ar) gas atmosphere, the main crucible is tilted; containing molten metal at 1,000°C by melting the master alloy at a high frequency, and Ar gas is sprayed at 10 bar gas pressure after the molten metal inflow to the tundish crucible, which is maintained at 800°C. The manufactured powder is measured using a particle size analyzer, and FESEM is used to observe the shape and surface of the alloy powder. DSC is performed to investigate the change in shape, according to the melting point and temperature change. The microstructure of added tin (Sn) was observed by heat treatment at 575°C for 10 min. As the content of Sn increased, the volume fraction increased to 1.1, 3.1, 6.4, and 10.9%.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of C3S, C2S, C3A Powders using Ultra-fine Calcium Oxide Powder Synthesized from Eggshell and Effect of C3A Content on Hardened Mixed Aggregates
- Heon Kong, Ki-Beom Kwon, Sang-Jin Park, Whyo-Sub Noh, Sang-Jin Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(6):493-501. Published online December 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.6.493
- 766 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this work, ultra-fine calcium oxide (CaO) powder derived from eggshells is used as the starting material to synthesize mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA). The prepared CaO powder is confirmed to have an average particle size of 500 nm. MTAs are synthesized with three types of fine CaO-based powders, namely, tricalcium silicate (C3S), dicalcium silicate (C2S), and tricalcium aluminate (C3A). The synthesis behavior of C3S, C2S and C3A with ultra-fine CaO powder and the effects of C3A content and curing time on the properties of MTA are investigated. The characteristics of the synthesized MTA powders are examined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission-scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), and a universal testing machine (UTM). The microstructure and compressive strength characteristics of the synthesized MTA powders are strongly dependent on the C3A wt.% and curing time. Furthermore, MTA with 5 wt.% C3A is found to increase the compressive strength and shorten the curing time.
- [Korean]
- Analysis on Milling Behavior of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Ni-based Atomizing Powder with Ni5Y Intermetallic Phase
- Chun Woong Park, Jong Min Byun, Won June Choi, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):101-106. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.101
- 822 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
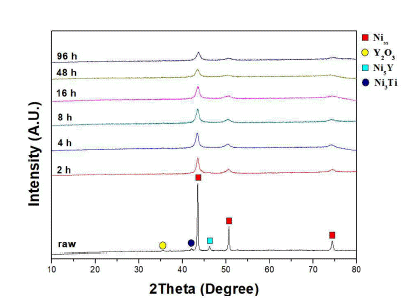
PDF Ni-based oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) alloys have a higher usable temperature and better hightemperature mechanical properties than conventional superalloys. They are therefore being explored for applications in various fields such as those of aerospace and gas turbines. In general, ODS alloys are manufactured from alloy powders by mechanical alloying of element powders. However, our research team produces alloy powders in which the Ni5Y intermetallic phase is formed by an atomizing process. In this study, mechanical alloying was performed using a planetary mill to analyze the milling behavior of Ni-based oxide dispersions strengthened alloy powder in which the Ni5Y is the intermetallic phase. As the milling time increased, the Ni5Y intermetallic phase was refined. These results are confirmed by SEM and EPMA analysis on microstructure. In addition, it is confirmed that as the milling increased, the mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloy powder improve due to grain refinement by plastic deformation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficient prediction of corrosion behavior in ternary Ni-based alloy systems: Theoretical calculations and experimental verification
Xuelian Xiao, Keke Chang, Kai Xu, Ming Lou, Liping Wang, Qunji Xue
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2023; 167: 94. CrossRef - Effect of high-energy ball milling on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni-based ODS alloys fabricated using gas-atomized powder
Chun Woong Park, Won June Choi, Jongmin Byun, Young Do Kim
Journal of Materials Science.2022; 57(38): 18195. CrossRef
- Efficient prediction of corrosion behavior in ternary Ni-based alloy systems: Theoretical calculations and experimental verification
- [Korean]
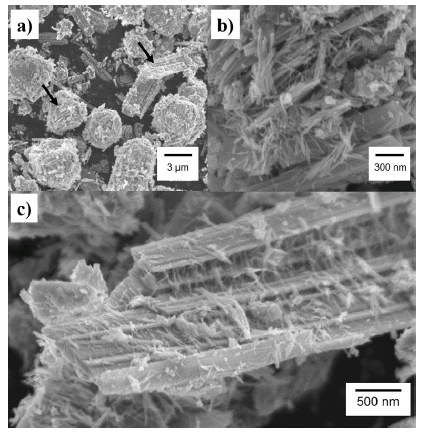
- Fabrication and Characterization of Hexagonal Tungsten Oxide Nanopowders for High Performance Gas Sensing Application
- Jinsoo Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):28-33. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.28
- 619 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The gas sensor is essential to monitoring dangerous gases in our environment. Metal oxide (MO) gas sensors are primarily utilized for flammable, toxic and organic gases and O3 because of their high sensitivity, high response and high stability. Tungsten oxides (WO3) have versatile applications, particularly for gas sensor applications because of the wide bandgap and stability of WO3. Nanosize WO3 are synthesized using the hydrothermal method. Asprepared WO3 nanopowders are in the form of nanorods and nanorulers. The crystal structure is hexagonal tungsten bronze (MxWO3, x =< 0.33), characterized as a tunnel structure that accommodates alkali ions and the phase stabilizer. A gas detection test reveals that WO3 can detect acetone, butanol, ethanol, and gasoline. This is the first study to report this capability of WO3.
- [Korean]
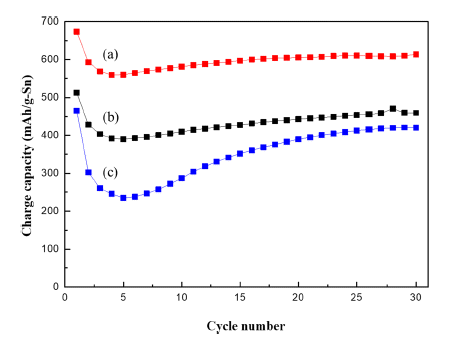
- Effect of Auxetic Structure of PVdF on Tin Anode Stability for Na-ion Batteries
- Jinsoo Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):507-513. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.507
- 765 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the viability of using a Na-ion battery with a tin(Sn) anode to mitigate the vulnerability caused by volume changes during discharge and charge cycling. In general, the volume changes of carbon material do not cause any instability during intercalation into its layer structure. Sn has a high theoretical capacity of 847 mAh g−1. However, it expands dramatically in the discharge process by alloying Na-Sn, placing the electrode under massive internal stress, and particularly straining the binder over the elastic limit. The repeating strain results in loss of active material and its electric contact, as well as capacity decrease. This paper expands the scope of fabrication of Na-ion batteries with Sn by fabricating the binder as an auxetic structure with a unique feature: a negative Poisson ratio (NPR), which increases the resistance to internal stress in the Na-Sn alloying/de-alloying processes. Electrochemical tests and micrograph images of auxetic and common binders are used to compare dimensional and structural differences. Results show that the capacity of an auxetic-structured Sn electrode is much larger than that of a Sn electrode with a common-structured binder. Furthermore, using an auxetic structured Sn electrode, stability in discharge and charge cycling is obtained.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Highly Flexible and Conductive Electrodes through Combining Honeycomb and Butterfly Pattern Bio‐Inspired Structure for ECG Signal Recording
Qi Hou, Min Wang, Chunyang Han, Kuiyang Gao, Ruiyao Liu, Guofeng Yao
Advanced Materials Interfaces.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Highly Flexible and Conductive Electrodes through Combining Honeycomb and Butterfly Pattern Bio‐Inspired Structure for ECG Signal Recording
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Optical Property of GaN Powder Using an Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process and Subsequent Nitridation Treatment
- Myeong-Jun Ji, Jae-Hyun Yoo, Young-In Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):482-486. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.482

- 603 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Despite numerous advances in the preparation and use of GaN, and many leading-edge applications in lighting technologies, the preparation of high-quality GaN powder remains a challenge. Ammonolytic preparations of polycrystalline GaN have been studied using various precursors, but all were time-consuming and required high temperatures. In this study, an efficient and low-temperature method to synthesize high-purity hexagonal GaN powder is developed using sub-micron Ga2O3 powder as a starting material. The sub-micron Ga2O3 powder was prepared by an ultrasonic spray pyrolysis process. The GaN powder is synthesized from the sub-micron Ga2O3 powder through a nitridation treatment in an NH3 flow at 800°C. The characteristics of the synthesized powder are systematically examined by X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, and UV-vis spectrophotometer.
- [Korean]
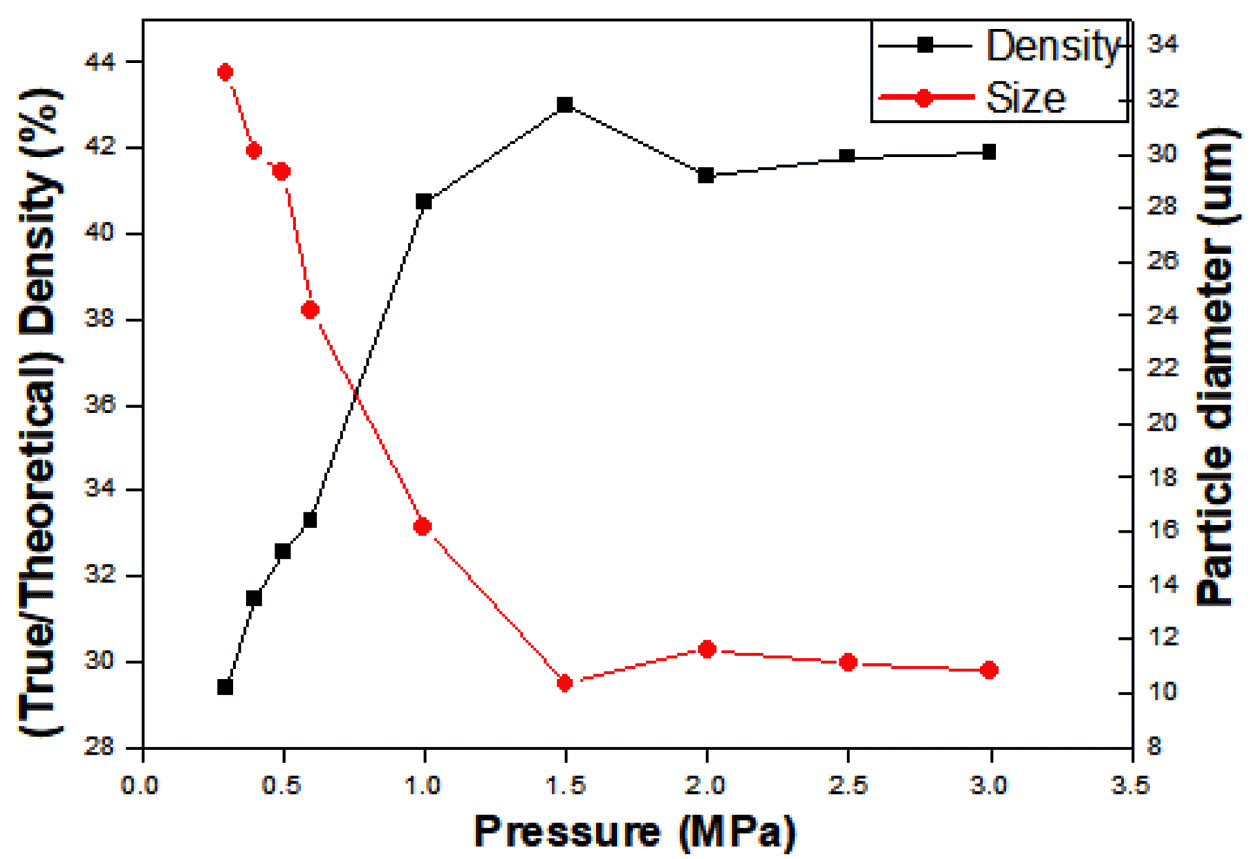
- Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
- Jae Jin Sim, Sang Hoon Choi, Ji Hwan Park, Il Kyu Park, Jae Hong Lim, Kyoung Tae Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):251-256. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.251
- 761 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We report the feasibility of TaC production via self-propagating high temperature synthesis, and the influence of the initial green compact density on the final composite particle size. Experiments are carried out from a minimum pressure of 0.3 MPa, the pressure at which the initial green body becomes self-standing, up to 3 MPa, the point at which no further combustion occurs. The green density of the pellets varies from 29.99% to 42.97%, as compared with the theoretical density. The increase in green density decreases the powder size of TaC, and the smallest particle size is observed with 1.5 MPa, at 10.36 μm. Phase analysis results confirm the presence of the TaC phase only. In the range of 0.3-0.5 MPa, traces of unreacted Ta and C residues are detected. However, results also show the presence of only C residue in the matrix within the pressure range of 0.6-3.0 MPa.
- [Korean]
- Trends and Implications of International Standardization for Rare Earths
- Sardar Farhat Abbas, Sang-Hyun lee, Bin Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):165-169. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.165
- 819 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare earth elements (REEs) are considered to be vital to modern industry due to their important roles in applications such as permanent magnets, automobile production, displays, and many more. The imbalance between demand and supply of REEs can be solved by recycling processes. Regarding the needs of industry and society, the International Organization for Standardization, Technical Committee 298 (ISO/TC298) Rare Earths has been recently launched for developing international standards on rare earth elements. In accordance with the suggestion of its constituents, it is tentatively working to develop the appropriate standards under five working groups (WG) on terms and definitions (WG1), element recycling (WG2), environmental stewardship (WG3), packaging, labelling, marking, transport, and storage (WG4), and testing analysis (WG5). The scope and structure of ISO/TC298 on the topic of rare earths is discussed in this document.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and magnetic properties of Sm2Co17 particles using salt-assisted spray pyrolysis and a reduction-diffusion process
Tae-Yeon Hwang, Jimin Lee, Min Kyu Kang, Gyutae Lee, Jongryoul Kim, Yong-Ho Choa
Applied Surface Science.2019; 475: 986. CrossRef - Worker Safety in the Rare Earth Elements Recycling Process From the Review of Toxicity and Issues
Seo-Ho Shin, Hyun-Ock Kim, Kyung-Taek Rim
Safety and Health at Work.2019; 10(4): 409. CrossRef
- Synthesis and magnetic properties of Sm2Co17 particles using salt-assisted spray pyrolysis and a reduction-diffusion process
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of CNT dispersed Cu matrix composites by wet mixing and spark plasma sintering process
- Seungchan Cho, Ilguk Jo, Sang-Bok Lee, Sang-Kwan Lee, Moonhee Choi, Jehong Park, Hansang Kwon, Yangdo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):158-164. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.158

- 787 View
- 17 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)–copper (Cu) composites are successfully fabricated by a combination of a binder-free wet mixing and spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. The SPS is performed under various conditions to investigate optimized processing conditions for minimizing the structural defects of CNTs and densifying the MWCNT–Cu composites. The electrical conductivities of MWCNT–Cu composites are slightly increased for compositions containing up to 1 vol.% CNT and remain above the value for sintered Cu up to 2 vol.% CNT. Uniformly dispersed CNTs in the Cu matrix with clean interfaces between the treated MWCNT and Cu leading to effective electrical transfer from the treated MWCNT to the Cu is believed to be the origin of the improved electrical conductivity of the treated MWCNT–Cu composites. The results indicate the possibility of exploiting CNTs as a contributing reinforcement phase for improving the electrical conductivity and mechanical properties in the Cu matrix composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Proposing Machine Learning Models Suitable for Predicting Open Data Utilization
Junyoung Jeong, Keuntae Cho
Sustainability.2024; 16(14): 5880. CrossRef
- Proposing Machine Learning Models Suitable for Predicting Open Data Utilization
- [English]
- Microstructural Characterization of Gas Atomized Copper-Iron Alloys with Composition and Powder Size
- Sardar Farhat Abbas, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):19-24. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.25.1.19

- 506 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Cu-Fe alloys (CFAs) are much anticipated for use in electrical contacts, magnetic recorders, and sensors. The low cost of Fe has inspired the investigation of these alloys as possible replacements for high-cost Cu-Nb and Cu-Ag alloys. Here, alloys of Cu and Fe having compositions of Cu100-xFex (x = 10, 30, and 50 wt.%) are prepared by gas atomization and characterized microstructurally and structurally based on composition and powder size with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Grain sizes and Fe-rich particle sizes are measured and relationships among composition, powder size, and grain size are established. Same-sized powders of different compositions yield different microstructures, as do differently sized powders of equal composition. No atomic-level alloying is observed in the CFAs under the experimental conditions.
- [Korean]
- Phase Formation and Physical Properties of SiAlON Ceramics Fabricated by Gas-Pressure Reactive Sintering
- Soyul Lee, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Yoonsoo Han, Sung-Min Lee, Seongwon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):431-436. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.431
- 795 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
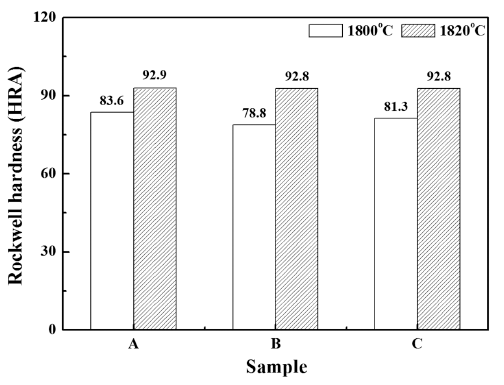
PDF SiAlON-based ceramics are some of the most typical oxynitride ceramic materials, which can be used as cutting tools for heat-resistant super-alloys (HRSA). SiAlON can be fabricated by using gas-pressure reactive sintering from the raw materials, nitrides and oxides such as Si3N4, AlN, Al2O3, and Yb2O3. In this study, we fabricate Ybm/3Si12-(m+n)Alm+nOnN16-n (m=0.3, n=1.9, 2.3, 2.7) ceramics by using gas-pressure sintering at different sintering temperatures. Then, the densification behavior, phase formation, microstructure, and hardness of the sintered specimens are characterized. We obtain a fully densified specimen with β- SiAlON after gas-pressure sintering at 1820°C for 90 min. under 10 atm N2 pressure. These SiAlON ceramic materials exhibited hardness values of ~92.9 HRA. The potential of these SiAlON ceramics for cutting tool application is also discussed.
- [English]
- The Synthesis Method of Tin Dioxide Nanoparticles by Plasma-Assisted Electrolysis Process and Gas Sensing Property
- Tae Hyung Kim, Yoseb Song, Chan-Gi Lee, Yong-Ho Choa
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):351-356. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.351
- 1,027 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
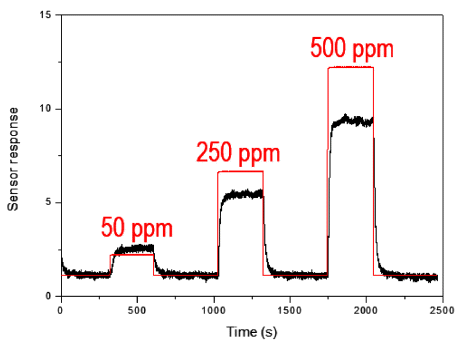
PDF Tin dioxide nanoparticles are prepared using a newly developed synthesis method of plasma-assisted electrolysis. A high voltage is applied to the tin metal plate to apply a high pressure and temperature to the synthesized oxide layer on the metal surface, producing nanoparticles in a low concentration of sulfuric acid. The particle size, morphology, and size distribution is controlled by the concentration of electrolytes and frequency of the power supply. The as-prepared powder of tin dioxide nanoparticles is used to fabricate a gas sensor to investigate the potential application. The particle-based gas sensor exhibits a short response and recovery time. There is sensitivity to the reduction gas for the gas flowing at rates of 50, 250, and 500 ppm of H2S gas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of porosity and particle size on the gas sensing properties of SnO2 films
Min Ah Han, Hyun-Jong Kim, Hee Chul Lee, Jin-Seong Park, Ho-Nyun Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 133. CrossRef
- Effects of porosity and particle size on the gas sensing properties of SnO2 films
- [English]
- Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
- Jin-Koo Han, Dong-won Shin, Babu Madavali, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):115-121. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.115

- 1,045 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this work, p-type Bi−Sb−Te alloys powders are prepared using gas atomization, a mass production powder preparation method involving rapid solidification. To study the effect of the sintering temperature on the microstructure and thermoelectric properties, gas-atomized powders are consolidated at different temperatures (623, 703, and 743 K) using spark plasma sintering. The crystal structures of the gas-atomized powders and sintered bulks are identified using an X-ray diffraction technique. Texture analysis by electron backscatter diffraction reveals that the grains are randomly oriented in the entire matrix, and no preferred orientation in any unique direction is observed. The hardness values decrease with increasing sintering temperature owing to a decrease in grain size. The conductivity increases gradually with increasing sintering temperature, whereas the Seebeck coefficient decreases owing to increases in the carrier mobility with grain size. The lowest thermal conductivity is obtained for the bulk sintered at a low temperature (603 K), mainly because of its fine-grained microstructure. A peak ZT of 1.06 is achieved for the sample sintered at 703 K owing to its moderate electrical conductivity and sustainable thermal conductivity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of the SPS heating rate on the optical and mechanical properties of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites
Seok-Min Yong
Journal of Ceramic Processing Research.2019; 20(1): 59. CrossRef
- Influence of the SPS heating rate on the optical and mechanical properties of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposites
- [English]
- Optimization of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature Conditions for Enhancement of Thermoelectric Performance in Gas-Atomized Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Compound
- Kwang-yong Jeong, Chul Hee Lee, Peyala Dharmaiah, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):108-114. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.108
- 935 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
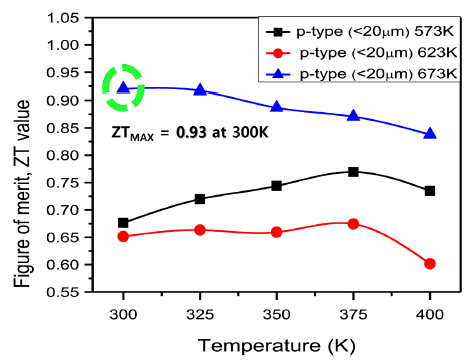
PDF We fabricate fine (<20 μm) powders of Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 alloys using a large-scale production method and subsequently consolidate them at temperatures of 573, 623, and 673 K using a spark plasma sintering process. The microstructure, mechanical properties, and thermoelectric properties are investigated for each sintering temperature. The microstructural features of both the powders and bulks are characterized by scanning electron microscopy, and the crystal structures are analyzed by X-ray diffraction analysis. The grain size increases with increasing sintering temperature from 573 to 673 K. In addition, the mechanical properties increase significantly with decreasing sintering temperature owing to an increase in grain boundaries. The results indicate that the electrical conductivity and Seebeck coefficient (217 μV/K) of the sample sintered at 673 K increase simultaneously owing to decreased carrier concentration and increased mobility. As a result, a high
ZT value of 0.92 at 300 K is achieved. According to the results, a sintering temperature of 673 K is preferable for consolidation of fine (<20 μm) powders.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Complex microstructure induced high thermoelectric performances of p-type Bi–Sb–Te alloys
Eun-Ha Go, Babu Madavali, Min-Woo Shin, Sung Ho Song, Soon-Jik Hong
Materials Chemistry and Physics.2023; 307: 128156. CrossRef - Role of sintering temperature on electronic and mechanical properties of thermoelectric material: A theoretical and experimental study of TiCoSb half-Heusler alloy
Ajay Kumar Verma, Kishor Kumar Johari, Kriti Tyagi, Durgesh Kumar Sharma, Pawan Kumar, Sudhir Kumar, Sivaiah Bathula, S.R. Dhakate, Bhasker Gahtori
Materials Chemistry and Physics.2022; 281: 125854. CrossRef - Enhanced thermoelectric properties of Li and Mg co−substituted Bi2Sr2Co2O fabricated by combined conventional sintering and spark plasma sintering
K. Park, H.Y. Hong, S.Y. Gwon
Inorganic Chemistry Communications.2022; 145: 110005. CrossRef
- Complex microstructure induced high thermoelectric performances of p-type Bi–Sb–Te alloys
- [Korean]
- Investigation on Fe-Hf-B-Nb-P-C Soft Magnetic Powders Prepared by High-Pressure Gas Atomization
- Jae Won Jeong, Dong-Yeol Yang, Ki Bong Kim, Junhong Lee, Young Ja Kim, Tae-Soo Lim, Sangsun Yang, Min Ha Lee, Hwi Jun Kim, Yong-Jin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):391-396. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.391
- 623 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
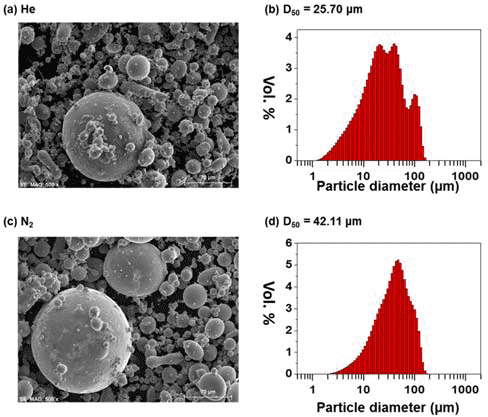
PDF In this study, ultra-fine soft-magnetic micro-powders are prepared by high-pressure gas atomization of an Fe-based alloy, Fe-Hf-B-Nb-P-C. Spherical powders are successfully obtained by disintegration of the alloy melts under high-pressure He or N2 gas. The mean particle diameter of the obtained powders is 25.7 μm and 42.1 μm for He and N2 gas, respectively. Their crystallographic structure is confirmed to be amorphous throughout the interior when the particle diameter is less than 45 μm. The prepared powders show excellent soft magnetic properties with a saturation magnetization of 164.5 emu/g and a coercivity of 9.0 Oe. Finally, a toroidal core is fabricated for measuring the magnetic permeability, and a μr of up to 78.5 is obtained. It is strongly believed that soft magnetic powders prepared by gas atomization will be beneficial in the fabrication of high-performance devices, including inductors and motors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimization of Densification Behavior of a Soft Magnetic Powder by Discrete Element Method and Machine Learning
Jungjoon Kim, Dongchan Min, Suwon Park, Junhyub Jeon, Seok-Jae Lee, Youngkyun Kim, Hwi-Jun Kim, Youngjin Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2022; 63(10): 1304. CrossRef - Optimizing the magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous powder by adjusting atomic structures from vitrification at different temperatures
Song-Yi Kim, Hye-Ryeong Oh, Hyeon-Ah Kim, A-Young Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Sang-Sun Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi, Il-Hyun Kim, Hyun-Gil Kim, Jürgen Eckert, Jong-Ryoul Kim, Min-Ha Lee
Journal of Applied Physics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline hybrid materials
Yeonjoo Lee, Jonggyu Jeon, Seungjin Nam, Teasuk Jang, Hwijun Kim, Minwoo Lee, Yongjin Kim, Dongyeol Yang, Kyeongsik Min, Hyunjoo Choi
Powder Technology.2018; 339: 440. CrossRef
- Optimization of Densification Behavior of a Soft Magnetic Powder by Discrete Element Method and Machine Learning
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Solid State Electrolyte Li7La3Zr2O12 thick Film by Tape Casting
- Ran-Hee Shin, Samick Son, Sung-Soo Ryu, Hyung-Tae Kim, Yoon-Soo Han
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):379-383. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.379
- 774 View
- 10 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
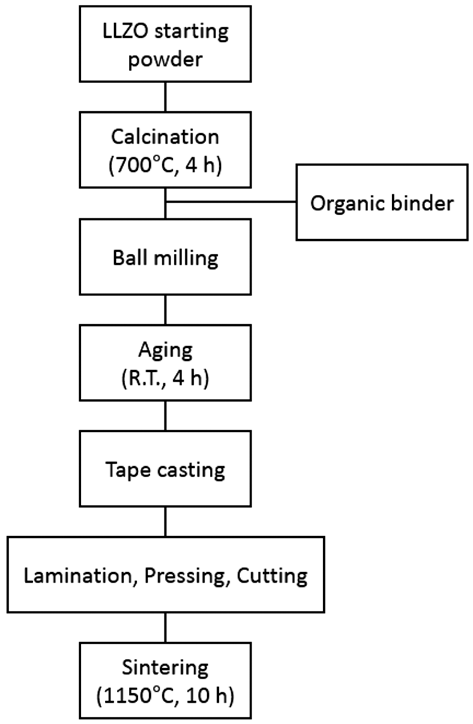
PDF A thick film of Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO) solid-state electrolyte is fabricated using the tape casting process and is compared to a bulk specimen in terms of the density, microstructure, and ion conductivity. The final thickness of LLZO film after sintering is 240 μm which is stacked up with four sheets of LLZO green films including polymeric binders. The relative density of the LLZO film is 83%, which is almost the same as that of the bulk specimen. The ion conductivity of a LLZO thick film is 2.81 × 10−4 S/cm, which is also similar to that of the bulk specimen, 2.54 × 10−4 S/ cm. However, the microstructure shows a large difference in the grain size between the thick film and the bulk specimen. Although the grain boundary area is different between the thick film and the bulk specimen, the fact that both the ion conductivities are very similar means that no secondary phase exists at the grain boundary, which is thought to originate from nonstoichiometry or contamination.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Waste minimization in all-solid-state battery production via re-lithiation of the garnet solid electrolyte LLZO
Vivien Kiyek, Martin Hilger, Melanie Rosen, Jürgen Peter Gross, Markus Mann, Dina Fattakhova-Rohlfing, Ruth Schwaiger, Martin Finsterbusch, Olivier Guillon
Journal of Power Sources.2024; 609: 234709. CrossRef - Powder Aerosol Deposition as a Method to Produce Garnet‐Type Solid Ceramic Electrolytes: A Study on Electrochemical Film Properties and Industrial Applications
Tobias Nazarenus, Yanyan Sun, Jörg Exner, Jaroslaw Kita, Ralf Moos
Energy Technology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Synthesize of Nd2Fe14B Powders from 1-D Nd2Fe14B Wires using Electrospinning Process
Nu Si A Eom, Su Noh, Muhammad Aneeq Haq, Bum Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(6): 477. CrossRef
- Waste minimization in all-solid-state battery production via re-lithiation of the garnet solid electrolyte LLZO
- [Korean]
- The Effect of Surface Defects on the Optical Properties of ZnSe:Eu Quantum Dots
- Da-Woon Jeong, Ji Young Park, Han Wook Seo, Kyoung-Mook Lim, Tae-Yeon Seong, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):348-352. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.348
- 1,134 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
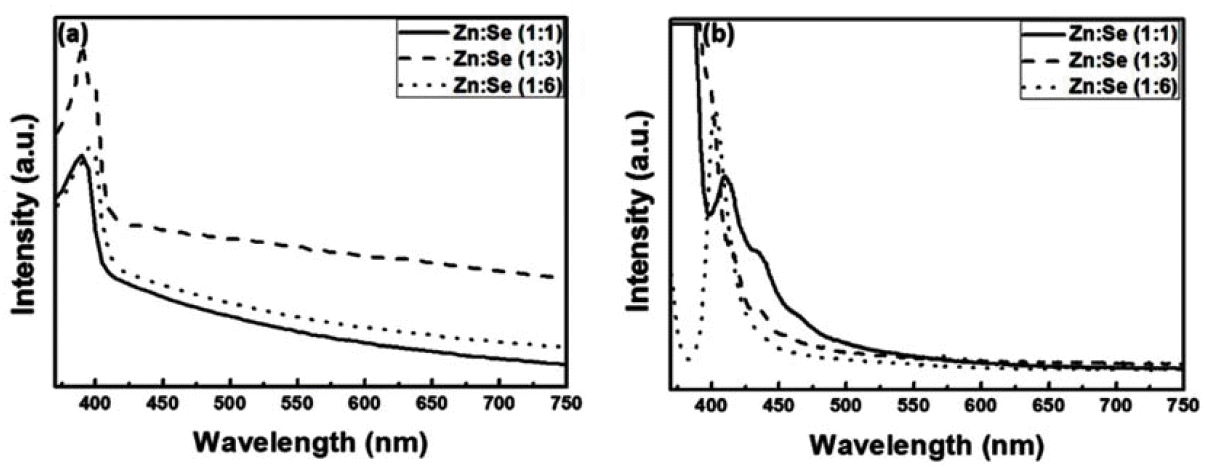
PDF Quantum dots (QDs) are capable of controlling the typical emission and absorption wavelengths because of the bandgap widening effect of nanometer-sized particles. These phosphor particles have been used in optical devices, photovoltaic devices, advanced display devices, and several biomedical complexes. In this study, we synthesize ZnSe QDs with controlled surface defects by a heating-up method. The optical properties of the synthesized particles are analyzed using UV-visible and photoluminescence (PL) measurements. Calculations indicate nearly monodisperse particles with a size of about 5.1 nm at 260°C (full width at half maximum = 27.7 nm). Furthermore, the study results confirm that successful doping is achieved by adding Eu3+ preparing the growth phase of the ZnSe:Eu QDs when heating-up method. Further, we investigate the correlation between the surface defects and the luminescent properties of the QDs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An investigation into the effective surface passivation of quantum dots by a photo-assisted chemical method
So-Yeong Joo, Hyun-Su Park, Do-yeon Kim, Bum-Sung Kim, Chan Gi Lee, Woo-Byoung Kim
AIP Advances.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Multimodal luminescence properties of surface-treated ZnSe quantum dots by Eu
Ji Young Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Kyoung-Mook Lim, Yong-Ho Choa, Woo-Byoung Kim, Bum Sung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 8. CrossRef
- An investigation into the effective surface passivation of quantum dots by a photo-assisted chemical method
- [Korean]
- Analyses of Creep Properties of Ni-base Superalloy Powders as Cooling Rate after Solid Solution Heat Treatment
- Chan Jun, Youngseon Lee, Byeong Beom Bae, Hong-Kyu Kim, Seong Suk Hong, Donghoon Kim, Jondo Yun, Eun Yoo Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):247-253. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.247
- 752 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
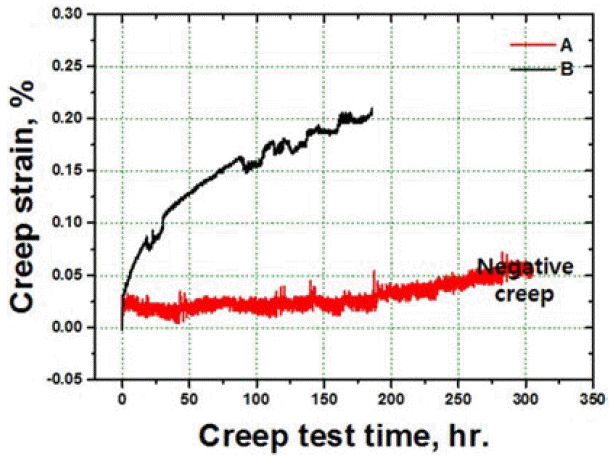
PDF In this study, solid solution heat treatment of consolidated nickel-based superalloy powders is carried out by hot isotactic pressing. The effects of the cooling rate of salt quenching, and air cooling on the microstructures and the mechanical properties of the specimens are analyzed . The specimen that is air cooled shows the formation of serrated grain boundaries due to their obstruction by the carbide particles. Moreover, the specimen that is salt quenched shows higher strength than the one that is air cooled due to the presence of fine and close-packed tertiary gamma prime phase. The tensile elongation at high temperatures improves due to the presence of grain boundary serrations in the specimen that is air cooled. On the contrary, the specimen that is salt quenched and consists of unserrated grain boundaries shows better creep properties than the air cooled specimen with the serrated grain boundaries, due to the negative creep phenomenon.
- [English]
- Effects of Hydrogen Reduction in Microstructure, Mechanical and Thermoelectric Properties of Gas Atomized
n -type Bi2Te2.7 Se0.3 Material - Pradip Rimal, Sang-Min Yoon, Eun-Bin Kim, Chul-Hee Lee, Soon-Jik Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):126-131. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.126

- 694 View
- 5 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The recent rise in applications of thermoelectric materials has attracted interest in studies toward the fabrication of thermoelectric materials using mass production techniques. In this study, we successfully fabricate
n -type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 material by a combination of mass production powder metallurgy techniques, gas atomization, and spark plasma sintering. In addition, to examine the effects of hydrogen reduction in the microstructure, the thermoelectric and mechanical properties are measured and analyzed. Here, almost 60% of the oxygen content of the powder are eliminated after hydrogen reduction for 4 h at 360°C. Micrographs of the powder show that the reduced powder had a comparatively clean surface and larger grain sizes than unreduced powder. The density of the consolidated bulk using as-atomized powder and reduced atomized powder exceeds 99%. The thermoelectric power factor of the sample prepared by reduction of powder is 20% better than that of the sample prepared using unreduced powder.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tuning of power factor in bismuth selenide through Sn/Te co doping for low temperature thermoelectric applications
Ganesh Shridhar Hegde, Ashwatha Narayana Prabhu, Ramakrishna Nayak, C. F. Yang, Y. K. Kuo
Applied Physics A.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing thermoelectric performance of K-doped polycrystalline SnSe through band engineering tuning and hydrogen reduction
Nan Xin, Yifei Li, Guihua Tang, Longyun Shen
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2022; 899: 163358. CrossRef - The effect of powder pre-treatment on the mechanical and thermoelectric properties of spark plasma sintered N-type bismuth telluride
Ahmed A. Abdelnabi, Vickram Lakhian, Joseph R. McDermid, James S. Cotton
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2021; 874: 159782. CrossRef - Investigation of Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Thermoelectric Properties of p-type Bi-Sb-Te alloys
Jin-Koo Han, Dong-won Shin, Babu Madavali, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 115. CrossRef - The Preparation and Growth Mechanism of the Recovered Bi2Te3 Particles with Respect to Surfactants
Hyeongsub So, Eunpil Song, Yong-Ho Choa, Kun-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 141. CrossRef - Enhanced thermoelectric cooling properties of Bi2Te3−xSex alloys fabricated by combining casting, milling and spark plasma sintering
Seung Tek Han, Pradip Rimal, Chul Hee Lee, Hyo-Seob Kim, Yongho Sohn, Soon-Jik Hong
Intermetallics.2016; 78: 42. CrossRef
- Tuning of power factor in bismuth selenide through Sn/Te co doping for low temperature thermoelectric applications
- [Korean]
- Characterization of Films Sputtered with the Cu-Ga Target Prepared by the Cold Spray Process
- Youngji Cho, Jung Ho Yoo, Jun-Mo Yang, Dong-Yong Park, Jong-Kyun Kim, Gang-Bo Choi, Jiho Chang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):21-25. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.21
- 435 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
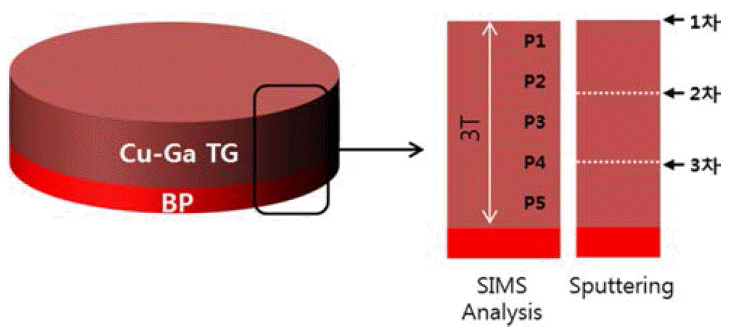
PDF The microstructural properties and electrical characteristics of sputtering films deposited with a Cu-Ga target are analyzed. The Cu-Ga target is prepared using the cold spray process and shows generally uniform composition distributions, as suggested by secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS) data. Characteristics of the sputtered Cu-Ga films are investigated at three positions (top, center and bottom) of the Cu-Ga target by X-ray diffraction (XRD), SIMS, 4-point probe and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis methods. The results show that the Cu-Ga films are composed of hexagonal and unknown phases, and they have similar distributions of composition and resistivity at the top, center, and bottom regions of the Cu-Ga target. It demonstrates that these films have uniform properties regardless of the position on the Cu-Ga target. In conclusion, the cold spray process is expected to be a useful method for preparing sputter targets.
- [Korean]
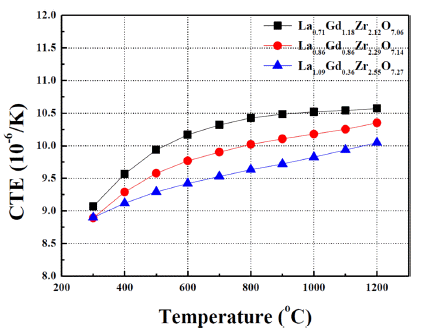
- Phase Formation and Thermo-physical Properties of Lanthanum/Gadolinium Zirconate with Reduced Rare-earth Contents for Thermal Barrier Coatings
- Sujin Lee, Chang-Sup Kwon, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):420-425. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.420
- 907 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare-earth zirconates, such as lanthanum zirconates and gadolinium zirconates, have been intensively investigated due to their excellent properties of low thermal conductivity as well as chemical stability at high temperature, which can make these materials ones of the most promising candidates for next-generation thermal barrier coating applications. In this study, three compositions, lanthanum/gadolinium zirconates with reduced rare-earth contents from stoichiometric RE2Zr2O7 compositions, are fabricated via solid state reaction as well as sintering at 1600°C for 4 hrs. The phase formation, microstructure, and thermo-physical properties of three oxide ceramics are examined. In particular, each oxide ceramics exhibits composite structures between pyrochlore and fluorite phases. The potential of lanthanum/ gadolinium zirconate ceramics for TBC applications is also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rare earth zirconate nanostructures: Recent development on preparation and photocatalytic applications
Sahar Zinatloo-Ajabshir, Masoud Salavati-Niasari, Azam Sobhani, Zahra Zinatloo-Ajabshir
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2018; 767: 1164. CrossRef - A novel Co-ions complexation method to synthesize pyrochlore La 2 Zr 2 O 7
Chunhui Xu, Hongyun Jin, Qifeng Zhang, Can Huang, Daifeng Zou, Fujian He, Shuen Hou
Journal of the European Ceramic Society.2017; 37(8): 2871. CrossRef - Fabrication and Characteristics of Thermal Barrier Coatings in the La2O3-Gd2O3-ZrO2System by Using Suspension Plasma Spray with Different Suspension Preparations
Soyul Lee, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh, Hyung-Tae Kim, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
Journal of the Korean institute of surface engineering.2016; 49(6): 595. CrossRef
- Rare earth zirconate nanostructures: Recent development on preparation and photocatalytic applications
- [Korean]
- Influence of Oxidation Temperatures on the Structure and the Microstructure of GaN MOCVD Scraps
- Hyun Seon Hong, Joong Woo Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):278-282. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.278

- 815 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The GaN-powder scrap generated in the manufacturing process of LED contains significant amounts of gallium. This waste can be an important resource for gallium through recycling of scraps. In the present study, the influence of annealing temperatures on the structural properties of GaN powder was investigated when the waste was recycled through the mechanochemical oxidation process. The annealing temperature varied from 200°C to 1100°C and the changes in crystal structure and microstructure were studied. The annealed powder was characterized using various analytical tools such as TGA, XRD, SEM, and XRF. The results indicate that GaN structure was fully changed to Ga2O3 structure when annealed above 900°C for 2 h. And, as the annealing temperature increased, crystallinity and particle size were enhanced. The increase in particle size of gallium oxide was possibly promoted by powder-sintering which merged particles to larger than 50 nm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High-temperature thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded materials produced by plasma sprayed coating: Experimental and modeling results
Kang Hyun Choi, Hyun-Su Kim, Chang Hyun Park, Gon-Ho Kim, Kyoung Ho Baik, Sung Ho Lee, Taehyung Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(5): 817. CrossRef
- High-temperature thermo-mechanical behavior of functionally graded materials produced by plasma sprayed coating: Experimental and modeling results
- [Korean]
- Investigation for Microstructure and Hardness of Welded Zone of Cu-Ni Alloy using W92-Ni-Fe Sintering Tool
- Tae-Jin Yoon, Sang-Won Park, Myung-Chang Kang, Joong-Suk Noh, Sung-Wook Chung, Chung-Yun Kang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(3):181-186. Published online June 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.3.181
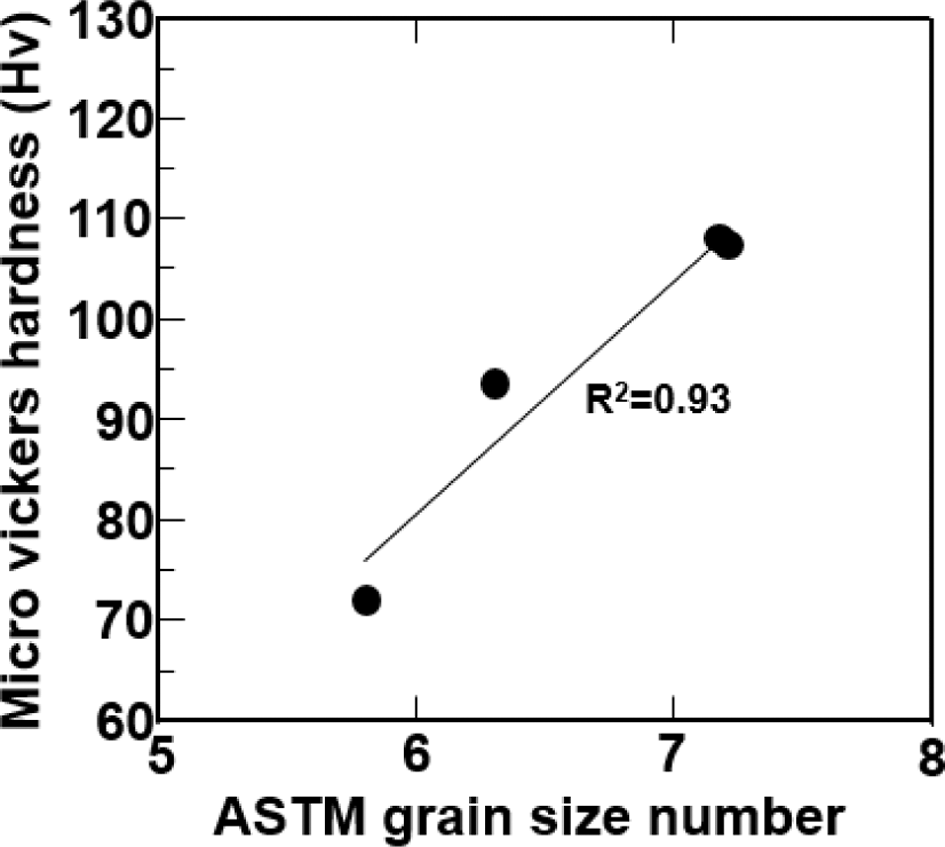
- 539 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, the effect of the friction stir welding (FSW) was compared with that of the gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) on the microstructure and microhardness of Cu-Ni alloy weldment. The weldment of 10 mm thickness was fabricated by FSW and GTAW, respectively. Both weldments were compared with each other by optical microstructure, microhardness test and grain size measurement. Results of this study suggest that the microhardness decreased from the base metal (BM) to the heat affected zone (HAZ) and increased at fusion zone (FZ) of GTAW and stir zone (SZ) of FSW. the minimum Hv value of both weldment was obtained at HAZ, respectively, which represents the softening zone, whereas Hv value of FSW weldment was little higher than that of GTAW weldment. These phenomena can be explained by the grain size difference between HAZs of each weldment. Grain size was increased at the HAZ during FSW and GTAW. Because FSW is a solid-state joining process obtaining the lower heat-input generated by rotating shoulder than heat generated in the arc of GTAW.
- [Korean]
- CNT Growth Behavior on Ti Substrate by Catalytic CVD Process with Temperature Gradient in Tube Furnace
- Ju Hyuk Park, Jong Min Byun, Hyung Soo Kim, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):371-376. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.371
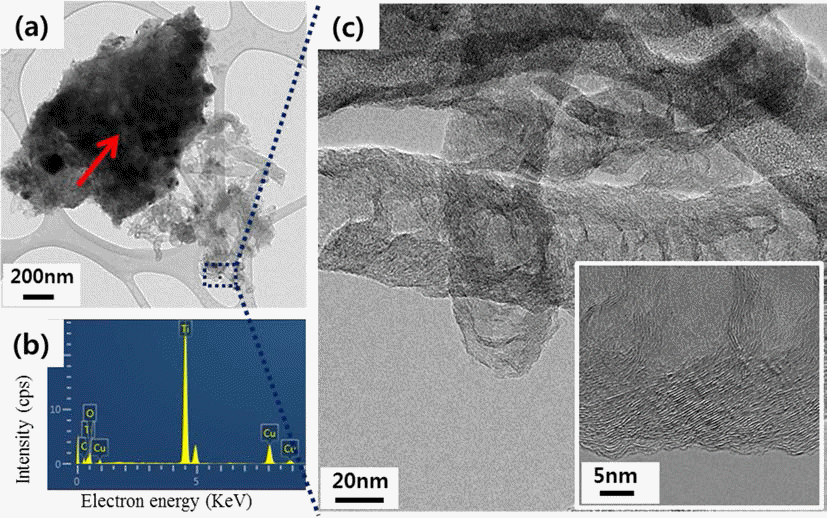
- 805 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, modified catalytic chemical vapor deposition (CCVD) method was applied to control the CNTs (carbon nanotubes) growth. Since titanium (Ti) substrate and iron (Fe) catalysts react one another and form a new phase (Fe2TiO5) above 700°C, the decrease of CNT yield above 800°C where methane gas decomposes is inevitable under common CCVD method. Therefore, we synthesized CNTs on the Ti substrate by dividing the tube furnace into two sections (left and right) and heating them to different temperatures each. The reactant gas flew through from the end of the right tube furnace while the Ti substrate was placed in the center of the left tube furnace. When the CNT growth temperature was set 700/950°C (left/right), CNTs with high yield were observed. Also, by examining the micro-structure of CNTs of 700/950°C, it was confirmed that CNTs show the bamboo-like structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Ti Porous body with Improved Specific Surface Area by Synthesis of CNTs
Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(3): 235. CrossRef - Synthesis of CNT on a Camphene Impregnated Titanium Porous Body by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition
Hogyu Kim, Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(2): 122. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Ti Porous body with Improved Specific Surface Area by Synthesis of CNTs
- [Korean]
- Mechanical Alloying of GaSe and GaTe Systems
- Jung Bo Choi, Jung-Ho Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):338-342. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.338
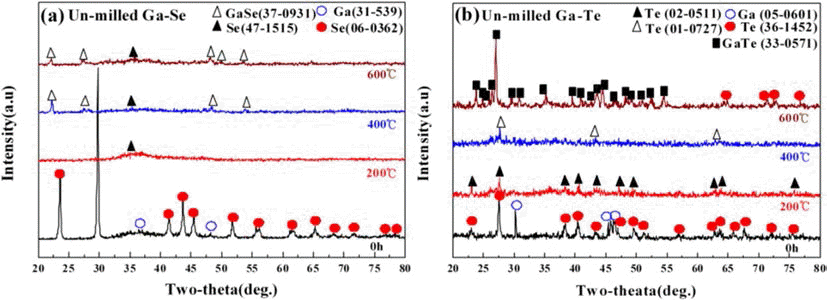
- 552 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the present work, we investigated the mechanical alloying of binary Ga-Se(1:1) and Ga-Te(1;1) sysyems. The high-energy ball-milling was performed at 40°C where one of constituents (Ga) is molten state. The purpose of the work was to see whether reactions between constituent elements are accelerated by the presence of a liquid phase. During the ball-milling, the liquid Ga phase completely disappeared and the resulting powders consist of nanocrystalline grain of ~20 nm with partly amorphized phases. However, no intermetallic compounds formed in spite of the presence of the liquid phases which has much higher diffusivity than solid constituents. By subsequent heat-treatments, the inter-metallic compounds such as GaSe and GaTe formed at relatively low temperatures. The formation temperature of theses compound was much lower than those predicted by equilibrium phase diagram. The comparison of the ball-milled powders with un-milled ones indicated that the easy formation of intermetallic compound or allying occurs at low temperatures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on Synthesis of Ni-Ti-B Alloy by Mechanical Alloying from Elemental Component Powder
Jung Geun Kim, Yong Ho Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(3): 202. CrossRef
- A Study on Synthesis of Ni-Ti-B Alloy by Mechanical Alloying from Elemental Component Powder
- [Korean]
- Manufacturing and Properties of CGI-based Composite Coating Layer Utilizing a Warm Spray Process and Cu-Ga and Cu-In Mixed Powders
- Min-Gwang Jeon, Myeong-Ju Lee, Hyeong-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):229-234. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.229

- 620 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study manufactured a CIG-based composite coating layer utilizing a new warm spray process, and a mixed powder of Cu-20at.%Ga and Cu-20at.%In. In order to obtain the mixed powder with desired composition, the Cu-20at.%Ga and Cu-20at.%In powders were mixed with a 7:1 ratio. The mixed powder had an average particle size of 35.4 μm. Through the utilization of a warm spray process, a CIG-based composite coating layer of 180 μm thickness could be manufactured on a pure Al matrix. To analyze the microstructure and phase, the warm sprayed coating layer underwent XRD, SEM/EDS and EMPA analyses. In addition, to improve the physical properties of the coating layer, an annealing heat treatment was conducted at temperatures of 200°C, 400°C and 600°C for 1 hour each. The microstructure analysis identified α-Cu, Cu4In and Cu3Ga phases in the early mixed powder, while Cu4In disappeared, and additional Cu9In4 and Cu9Ga4 phases were identified in the warm sprayed coating layer. Porosity after annealing heat treatment reduced from 0.75% (warm sprayed coating layer) to 0.6% (after 600°C/1 hr. heat treatment), and hardness reduced from 288 Hv to 190 Hv. No significant phase changes were found after annealing heat treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Microstructure/Properties of Bulk-typeTantalum Material by a Kinetic Spray Process
Ji-Hye Lee, Ji-Won Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(1): 8. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Treatment Environment on the Microstructure and Properties of Kinetic Sprayed Tantalum Coating Layer
Ji-Hye Lee, Hyung-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(1): 32. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Microstructure/Properties of Bulk-typeTantalum Material by a Kinetic Spray Process
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Characterization of a Ceria Based Composite Electrolyte for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells by an Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis Process
- Young-In Lee, Yong-Ho Choa
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):222-228. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.222
- 639 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Much research into fuel cells operating at a temperature below 800°C. is being performed. There are significant efforts to replace the yttria-stabilized zirconia electrolyte with a doped ceria electrolyte that has high ionic conductivity even at a lower temperature. Even if the doped ceria electrolyte has high ionic conductivity, it also shows high electronic conductivity in a reducing environment, therefore, when used as a solid electrolyte of a fuel cell, the powergeneration efficiency and mechanical properties of the fuel cell may be degraded. In this study, gadolinium-doped ceria nanopowder with Al2O3 and Mn2O3 as a reinforcing and electron trapping agents were synthesized by ultrasonic pyrolysis process. After firing, their microstructure and mechanical and electrical properties were investigated and compared with those of pure gadolinium-doped ceria specimen.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- High growth-rate atomic layer deposition process of cerium oxide thin film for solid oxide fuel cell
Jin-Geun Yu, Byung Chan Yang, Jeong Woo Shin, Sungje Lee, Seongkook Oh, Jae-Ho Choi, Jaehack Jeong, Wontae Noh, Jihwan An
Ceramics International.2019; 45(3): 3811. CrossRef - Atomic-layer-deposited ZrO2-doped CeO2 thin film for facilitating oxygen reduction reaction in solid oxide fuel cell
Byung Chan Yang, Dohyun Go, Seongkook Oh, Jeong Woo Shin, Hyong June Kim, Jihwan An
Applied Surface Science.2019; 473: 102. CrossRef
- High growth-rate atomic layer deposition process of cerium oxide thin film for solid oxide fuel cell
- [Korean]
- Leaching behavior of Ga and In from MOCVD dust
- Kyung-Soo Park, Basudev Swain, Lee Seung Kang, Chan Gi Lee, Hyun Seon Hong, Jong-Gil Shim, Jeung-Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):202-206. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.202
- 757 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Leaching of MOCVD dust in the LED industry is an essential stage for hydro-metallurgical recovery of pure Ga and In. To recover Ga and In, the leaching behavior of MOCVD scrap of an LED, which contains significant amounts of Ga, In, Al and Fe in various phases, has been investigated. The leaching process must be performed effectively to maximize recovery of Ga and In metals using the most efficient lixiviant. Crystalline structure and metallic composition of the raw MOCVD dust were analyzed prior to digestion. Subsequently, various mineral acids were tested to comprehensively study and optimize the leaching parameters such as acidity, pulp density, temperature and time. The most effective leaching of Ga and In was observed for a boiling 4 M HCl solution vigorously stirred at 400 rpm. Phase transformation of GaN into gallium oxide by heat treatment also improved the leaching efficiency of Ga. Subsequently high purity Ga and In can be recovered by series of hydro processes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Selective Solvent Extraction of In from Synthesis Solution of MOCVD Dust using D2EHPA
Byoungyong Im, Basudev Swain, Chan Gi Lee, Jae Layng Park, Kyung-Soo Park, Jong-Gil Shim, Jeung-Jin Park
Journal of the Korean Institute of Resources Recycling.2015; 24(5): 80. CrossRef - Fabrication of High Purity Ga-containing Solution using MOCVD dust
Duk-Hee Lee, Jin-Ho Yoon, Kyung-Soo Park, Myung-Hwan Hong, Chan-Gi Lee, Jeung-Jin Park
Journal of the Korean Institute of Resources Recycling.2015; 24(4): 50. CrossRef - Influence of Oxidation Temperatures on the Structure and the Microstructure of GaN MOCVD Scraps
Hyun Seon Hong, Joong Woo Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.1970; 22(4): 278. CrossRef
- Selective Solvent Extraction of In from Synthesis Solution of MOCVD Dust using D2EHPA
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


