Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
- So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):529-541. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00493
- 695 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Magneto-mechano-electric (MME) energy harvesters have emerged as a promising solution for maintenance-free power generation in rapidly expanding Internet of Things (IoT) environments, where replacing or wiring batteries is impractical. MME devices convert weak alternating magnetic fields, ubiquitous around power infrastructures, into useful electrical energy through sequential magnetic, mechanical, and electrical transduction processes. This review summarizes recent advances across triboelectric-, piezoelectric-, and hybrid MME architectures. Triboelectric MME generators employing nano-engineered polymer surfaces, flash-induced surface modification, and nanoscale pattern replication demonstrate low-cost fabrication routes while achieving significantly enhanced voltage and current outputs. Piezoelectric MME systems based on Mn-doped PMN-PZT single crystals highlight strategies for improving mechanical quality factors and resonance-driven power generation. Further, hybrid MME designs that integrate piezoelectric and electromagnetic induction mechanisms enable high-power outputs exceeding tens of milliwatts, sufficient to operate multifunctional IoT platforms and charge practical energy-storage devices. Collectively, these studies illustrate a transition of MME harvesting technologies from laboratory concepts to application-ready self-powered systems. Future opportunities lie in broadband resonance design, modular harvester integration, advanced power management, and multi-source hybridization for robust long-term operation in real environments.
- [Korean]
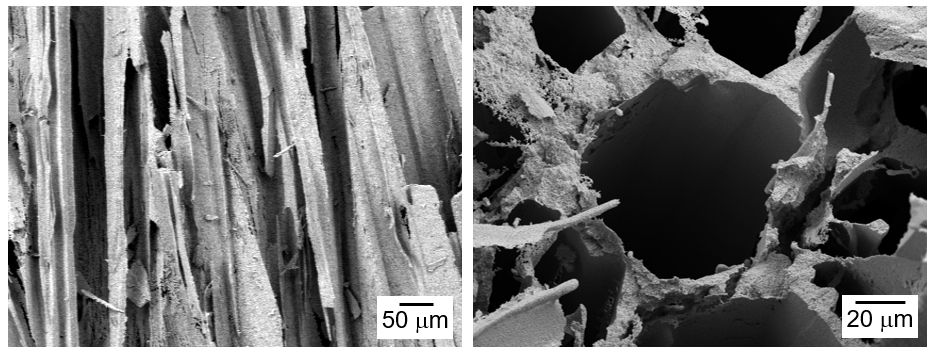
- Preparation of Porous W-Cu by Freeze Casting of Tert-butyl Alcohol Slurry Mixed with WO3-CuO Powder
- Youngmin Kim, Ji Young Kim, Minju Son, Wonyong Kwon, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):466-471. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00437
- 613 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The influence of process conditions on the microstructure of porous W-Cu, fabricated by freeze casting using tert-butyl alcohol as the freezing agent, was investigated. The slurries containing 10 vol% of WO3-CuO powder were prepared by milling with a small amount of citric acid and polyethylene glycol as dispersants. The slurries with dispersion stability were frozen in a mold with the lower part cooled to -25°C, followed by sublimation in a vacuum to remove the freezing agent. The sintered W-1 vol% Cu in a hydrogen atmosphere exhibited aligned pores with the size of 50 μm, which were generated by sublimation of directionally solidified tert-butyl alcohol crystals. In the cross-section of the specimen, hexagonal pores corresponding to the crystal structure of tert-butyl alcohol was observed. Microstructure analysis of the struts revealed that Cu was distributed non-uniformly due to the mutual insolubility and low wettability of the W-Cu system.
- [Korean]
- Comparison of the Properties of Rare-Earth Zirconate Thermal Barrier Coatings for Hydrogen-Fueled Gas Turbines
- Gun-Woong Lee, Min-Soo Nam, Min-Ji Kim, HyunSuk Jung, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):472-480. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00423

- 664 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) for hydrogen-fueled gas turbines withstand higher combustion temperatures and increased steam concentrations compared to conventional natural-gas systems. These harsh operating conditions significantly accelerate the thermal degradation of widely used YSZ coatings, emphasizing the need for alternative top-coat materials with improved phase stability and reduced thermal conductivity. In this study, rare-earth zirconate ceramics, Gd2Zr2O7 (GdZO), Tm2Zr2O7 (TmZO), and a mixed composition (Gd0.5Tm0.5)2Zr2O7 (Gd/TmZO), are synthesized and investigated as potential next-generation TBC candidates. Each material was comparatively examined with a focus on crystal structure, thermophysical properties, and thermal conductivity. Furthermore, high-temperature steam exposure experiments were performed to simulate hydrogen combustion environments. Microstructural analyses, high-temperature degradation behavior, and phase stability evaluations were carried out to obtain fundamental experimental data. This study provides essential baseline information for the design and development of high-performance TBC materials suitable for the hydrogen-fueled gas turbine systems.
- [English]
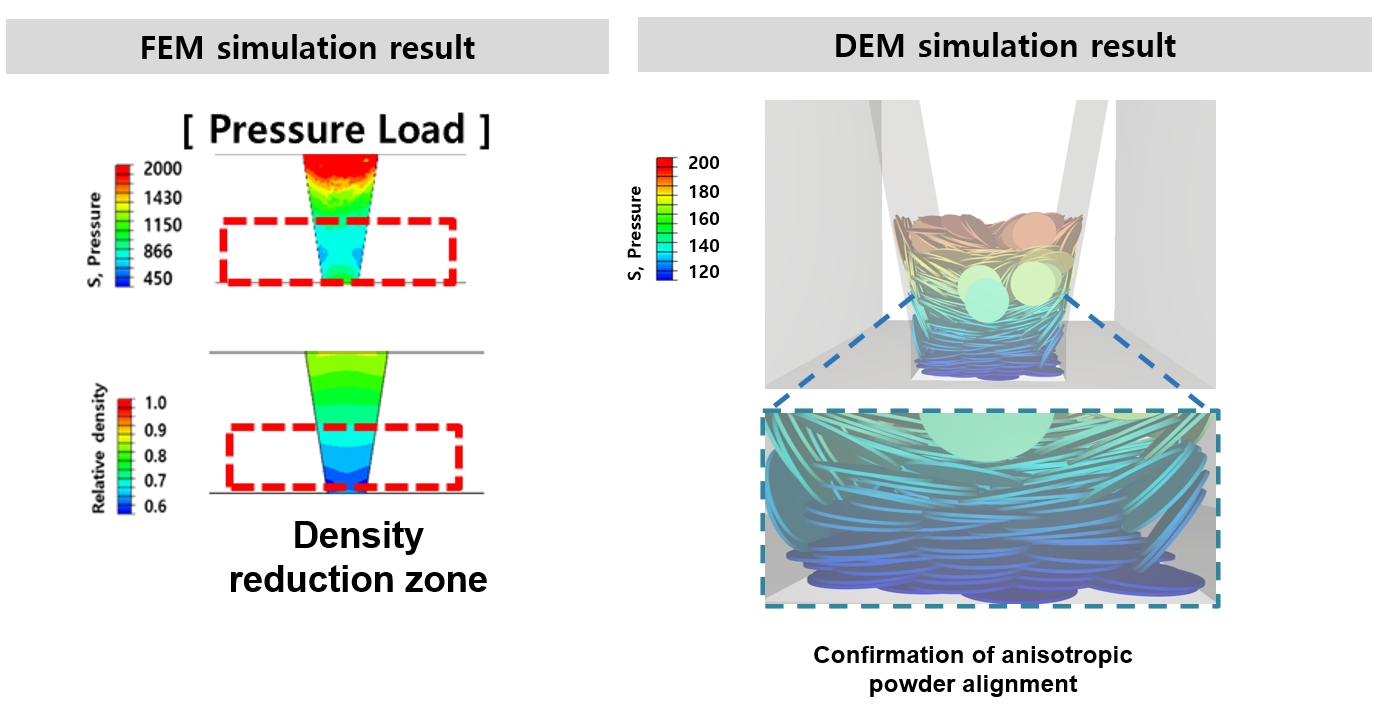
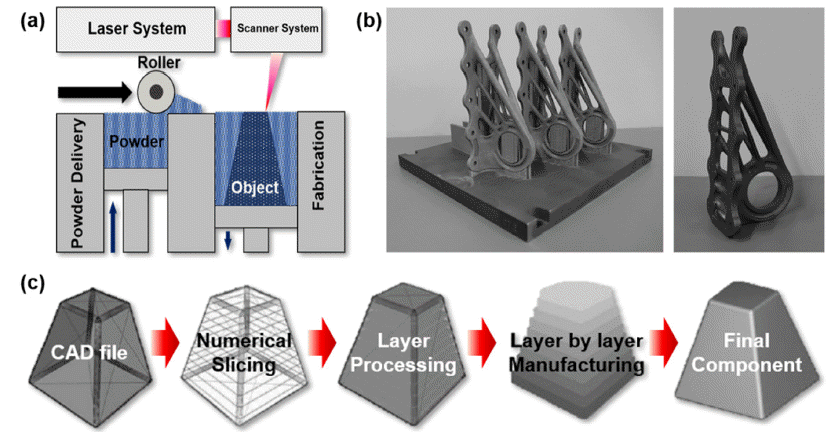
- Finite Element and Discrete Element Analyses of Anisotropic Powder Compaction for Axial Flux Motor Cores
- Jeong Ah Lee, Do Won Lee, , Hyojeong Ha, Ki Hyuk Kwon, Eon Byeong Park, Taeyoung Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):451-458. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00409
- 752 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigates the compaction behavior of anisotropic, plate-like powders used in axial flux motor cores through a combined FEM–DEM approach. A porous continuum FEM model captures stress and density evolution during die pressing, revealing strong gradients along the compaction direction, with higher stress and densification near the upper punch and reduced compaction in the lower region. Guided by these results, DEM simulations examine particle packing, orientation, and contact pressure in representative zones. The DEM analysis shows that higher local pressure promotes denser packing and in-plane particle alignment near the upper punch, while the lower region exhibits more random orientations and lower contact forces. As a result, the multi-scale FEM–DEM framework clarifies how anisotropic particle behavior governs local densification and offers practical guidance for die design and process optimization to achieve more uniform density and controlled magnetic-property-relevant particle alignment in axial flux motor cores.
- [Korean]
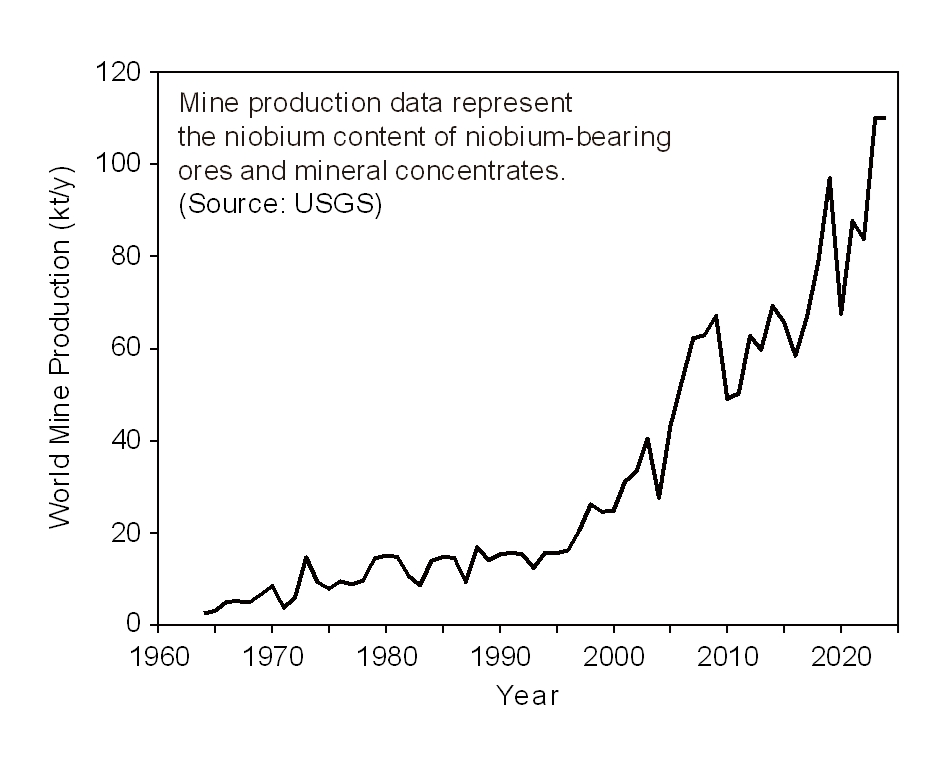
- Smelting and Recycling of Niobium
- Ho-Sang Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):517-528. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00367
- 596 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Global annual production of niobium is only around 100,000 tonnes; however, it is a critical metal for modern industry and is mined in only a limited number of regions. This study reviews the current status of niobium smelting and recycling technologies. Approximately 90% of niobium is produced as ferroniobium (FeNb) for use in steel alloys, although niobium is also utilized in superalloys, superconductors, capacitors, semiconductors, and other applications. Niobium coexists with tantalum in columbite and tantalite ores. These ores are decomposed by hydrofluoric acid digestion or alkali fusion, followed by solvent extraction to separate Nb2O5 and Ta2O5. Niobium metal and FeNb are produced from Nb2O5 primarily via aluminothermic reduction, although metallic niobium can also be manufactured by thermal reduction using Mg, Ca, or C, as well as by molten salt electrolysis. Crude niobium is subsequently refined into high-purity niobium through molten salt electrolytic refining, high-temperature vacuum treatment, and electron beam melting. Because most niobium is used as an alloying element in stainless steel and high-strength low-alloy steel, recycling practices for niobium remain poorly documented.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AA3003 Tube for Heat Exchanger Processed by Floating Plug Drawing
- Hyeon-Jun Heo, Sung Jun Oh, Seong-Hee Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):459-465. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00346

- 623 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An AA3003 tube was severely deformed by cold floating plug drawing, and then annealed at temperatures from 210 to 460℃. The as drawn Al tube exhibited a typical deformation structure in which the grains were greatly elongated along the drawing direction. The hardness increased with increasing the reduction of cross-sectional area (RA), became 68Hv after RA= 99%. Up to 310℃, the Al tube still mainly exhibited a deformed structure. While complete recrystallization occurred at temperatures above 360℃. The hardness decreased with increasing the annealing temperature, and it became 33Hv after annealing at 410℃. Both the tensile and yield strengths also decreased with increasing the annealing temperature, but the decrease was larger in yield strength than in tensile strength. The elongation increased with increasing the annealing temperature. The changes in the strength and the elongation with the annealing temperature were the largest at 360℃, in which the complete recrystallization occurred.
- [Korean]
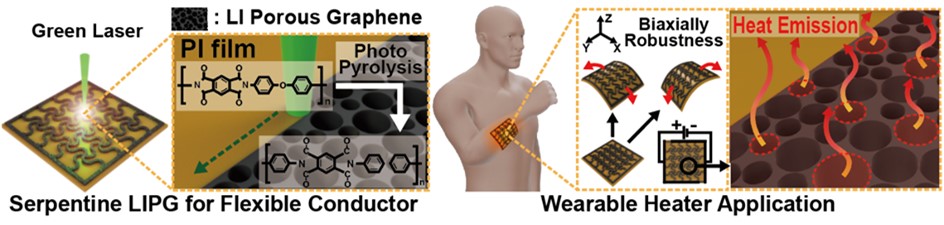
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):492-500. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00332
- 640 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A flexible heater with high thermal efficiency and mechanical durability was developed by fabricating laser-induced porous graphene (LIPG) electrodes on polyimide films using a 532 nm green laser. Laser power, scan speed, and line distance were precisely optimized based on photothermal simulations to generate uniform porous graphene structures with large surface area and excellent heat dissipation characteristics. Raman, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analyses confirmed that the optimized LIPG exhibited highly graphitized features with low oxygen defects. Scanning electron microscope analysis revealed that porous morphologies formed only within a specific laser scan speed range, whereas excessive or insufficient irradiation resulted in collapsed or absent porosity. The serpentine-patterned LIPG heater maintained stable electrical resistance under repeated multidirectional bending, demonstrating excellent flexibility and mechanical stability. The heater also achieved rapid and uniform heating up to 80 °C within seconds, maintaining consistent temperature distribution even on curved surfaces.
- [Korean]
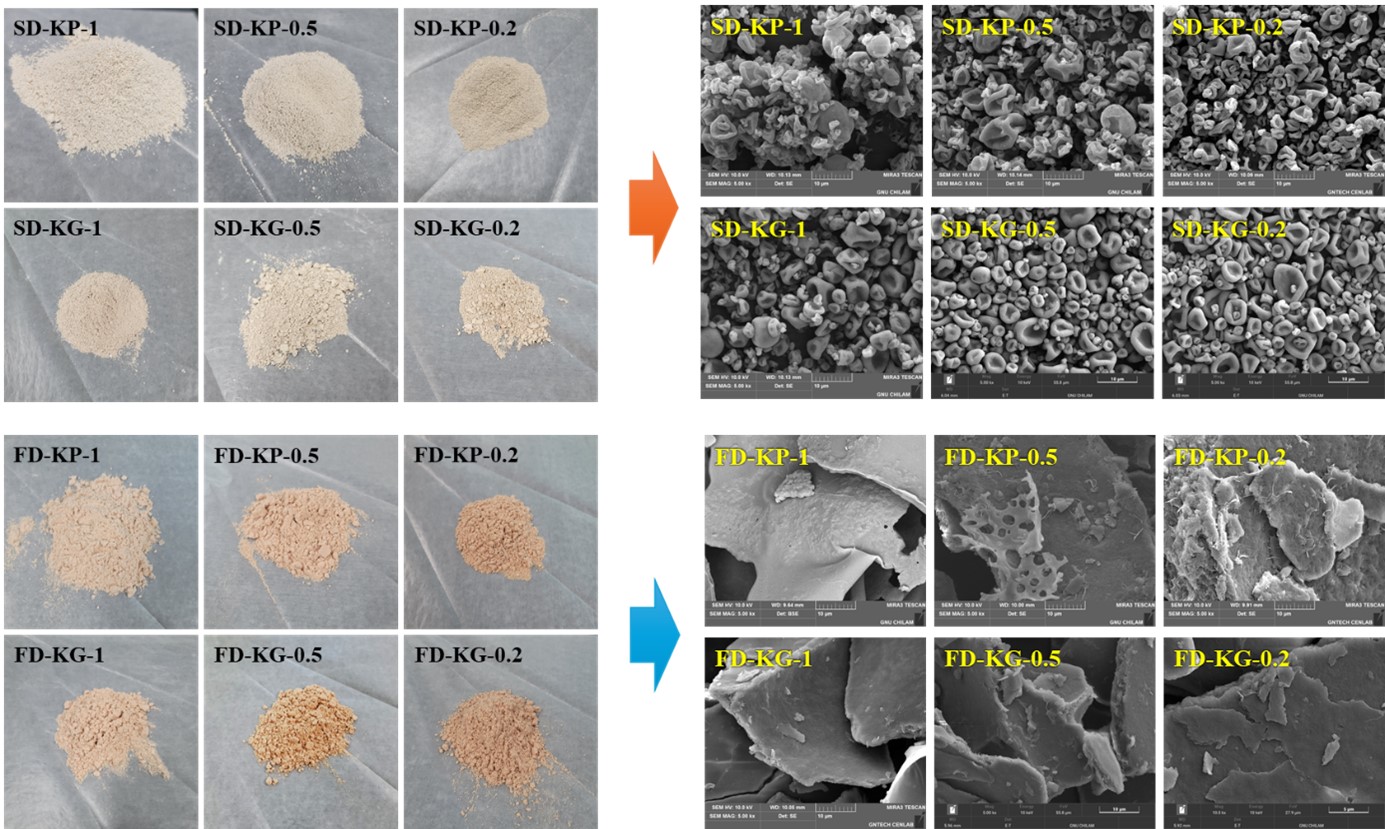
- Powderization Strategy for Porcine Organ By-Products: A Comparative Study on the Effects of Drying Method and Polymer Additives
- Seo Wan Yun, Eun Ju Jeong, Eui-Cheol Shin, Hyun-Wook Kim, Kyeong Soo Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):416-427. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00269
- 469 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study aimed to develop a powderization strategy using porcine by-products (kidney, liver, and heart) by evaluating the effects of raw material type, pretreatment, and additives (hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose P645 and gelatin) on powder characteristics. Powders from kidney tissue were analyzed for yield, particle structure, compressibility, and size distribution, based on the drying method and additive composition. The spray-dried sample with gelatin at 1:0.5 (w/w) showed 20.4% compressibility and the smallest, most uniform particles, indicating excellent flowability. Due to its superior structural stability, gelatin was selected over HPMC P645. Liver and heart samples that underwent enzymatic hydrolysis and the Maillard reaction were spray-dried with gelatin and assessed for yield and microstructure. The Alcalase-treated liver sample showed the highest yield. Surface analysis confirmed that gelatin formed a protective film enhancing particle stability. These findings suggest gelatin-based spray drying is effective for producing high-quality powders from protein-rich by-products.
- [Korean]
- The Manufacturing Process of Clean Ni-Cr-Co-Based Superalloy Powder Using a Plasma Rotating Electrode
- Kyu-Sik Kim, Dae Woong Kim, Yeontae Kim, Jung Hyo Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):222-231. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00171

- 725 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ni-based superalloys are widely used for critical components in aerospace, defense, industrial power generation systems, and other applications. Clean superalloy powders and manufacturing processes, such as compaction and hot isostatic pressing, are essential for producing superalloy discs used in turbine engines, which operate under cyclic rotating loads and high-temperature conditions. In this study, the plasma rotating electrode process (PREP), one of the most promising methods for producing clean metallic powders, is employed to fabricate Ni-based superalloy powders. PREP leads to a larger powder size and narrower distribution compared to powders produced by vacuum induction melt gas atomization. An important finding is that highly spheroidized powders almost free of satellites, fractured, and deformed particles can be obtained by PREP, with significantly low oxygen content (approximately 50 ppm). Additionally, large grain size and surface inclusions should be further controlled during the PREP process to produce high-quality powder metallurgy parts.
- [English]
- SnF2-Induced LiF Interphase for Stable Lithium Metal Anodes with Suppressed Dendrite Growth
- Yeong Hoon Jeon, Seul Ki Choi, Yun Seung Nah, Wonil Shin, Yong-Ho Choa, Minho Yang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):212-221. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00164

- 1,692 View
- 50 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Lithium (Li) metal is a promising anode for next-generation batteries due to its high capacity, low redox potential, and low density. However, dendrite growth and interfacial instability limit its use. In this study, an artificial solid electrolyte interphase layer of LiF and Li-Sn (LiF@Li-Sn) was fabricated by spray-coating SnF2 onto Li. The LiF@Li-Sn anode exhibited improved air stability and electrochemical performance. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy indicated a charge transfer resistance of 25.2 Ω after the first cycle. In symmetric cells, it maintained a low overpotential of 27 mV after 250 cycles at 2 mA/cm2, outperforming bare Li. In situ microscopy confirmed dendrite suppression during plating. Full cells with NMC622 cathodes and LiF@Li-Sn anodes delivered 130.8 mAh/g with 79.4% retention after 300 cycles at 1 C and 98.8% coulombic efficiency. This coating effectively stabilized the interface and suppressed dendrites, with promising implications for practical lithium metal batteries.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Cellulose Fiber Density Variation on Energy Harvesting Performance in a Hydrovoltaic Generator
- Seung-Hwan Lee, So Hyun Baek, Hyun-Woo Lee, Yongbum Kwon, Kanghyuk Lee, Kee-Ryung Park, Yoseb Song, Bum Sung Kim, Ji Young Park, Yong-Ho Choa, Da-Woon Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(2):113-121. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00052

- 1,202 View
- 34 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Energy harvesting has become a crucial technology for sustainable energy solutions; in particular, the utilization of ambient water movement in hydrovoltaic generators has emerged as a promising approach. However, optimizing performance requires an understanding of structural factors affecting energy harvesting, particularly capillary effects. This study aimed to improve hydrovoltaic generator performance by adjusting internal fiber density, which influences water transport and ion mobility. Using cold isostatic pressing, cellulose acetate (CA) loading in a urethane mold was varied to optimize internal density. As CA loading increased, the fiber arrangement became denser, narrowing capillary pathways and reducing proton mobility. While open-circuit voltage (VOC) remained stable, short-circuit current (ISC) decreased with higher CA mass. The sample with a loading of 0.3 g exhibited the highest energy harvesting efficiency, achieving ISC = 107.2 μA, VOC = 0.15 V, and power (P) = 16.7 μW. This study provides insights into methods of improving hydrovoltaic generator efficiency through internal structural modifications.
- [Korean]
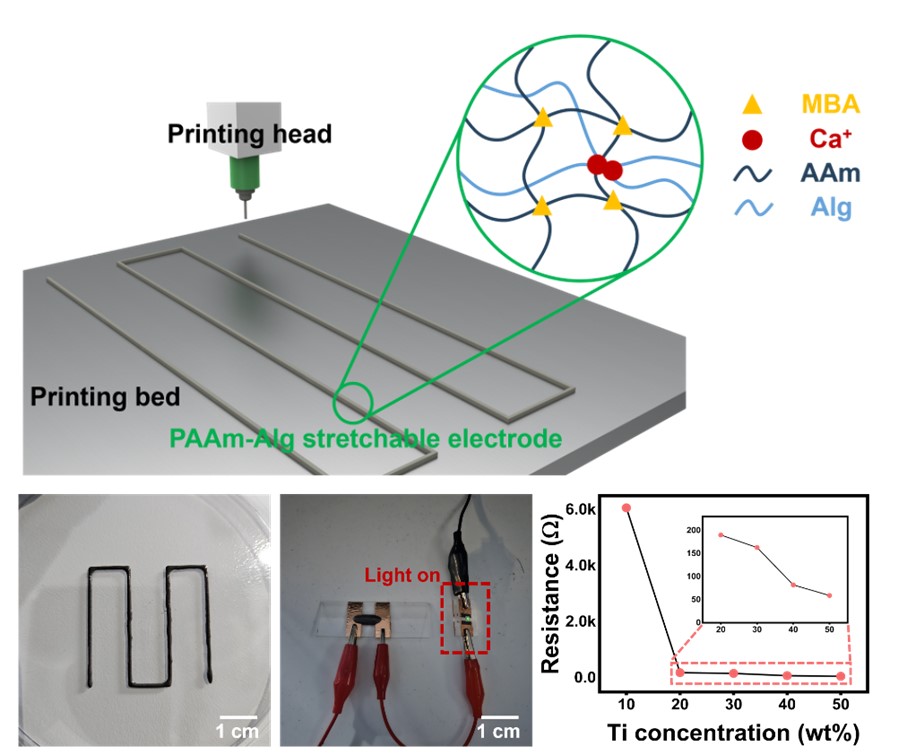
- 3D-Printed Stretchable Electrodes Enabled by a Titanium/Acrylamide-Based Hydrogel Nanocomposite
- Se Jin Choi, Han Eol Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):67-72. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00465
- 794 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Wearable electronics have been the focus of considerable interest in various fields, such as human-machine interfaces, soft robotics, and medical treatments, due to their flexibility, stretchability, and light weight. To address the shortcomings of existing metal thin film-based wearable devices, stretchable conductive polymers have been developed. In particular, double networking hydrogels are being actively studied as a polymer with a three-dimensional stereoscopic structure that can be patterned. Nonetheless, they have shortcomings such as poor electrical properties and cumbersome manufacturing processes, making it difficult to apply them in electronic devices. Herein, we report 3D-printed stretchable electrodes enabled by a titanium/polyacrylamide-alginate-based hydrogel nanocomposite. This research suggests the strategy for resolving the challenges of high costs and complex fabrication processes associated with stretchable electrode, providing a solution to accelerate the commercialization of wearable electronic devices.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Optimization of Al2O3 Microchannels Using DLP-Based 3D Printing
- Jun-Min Cho, Yong-Jun Seo, Yoon-Soo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):59-66. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00346
- 994 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study focused on optimizing the digital light processing (DLP) 3D printing process for high-precision ceramic components using alumina-based slurries. Key challenges, such as cracking during debinding and precision loss due to slurry sedimentation, were addressed by evaluating the exposure time and the nano-to-micro alumina powder ratios. The optimal conditions—exposure time of 15 seconds and a 1:9 mixing ratio—minimized cracking, improved gas flow during debinding, and increased structural precision. Microchannels with diameters above 1.2 mm were successfully fabricated, but channels below 0.8 mm faced challenges due to slurry accumulation and over-curing. These results establish a reliable process for fabricating complex ceramic components with improved precision and structural stability. The findings have significant potential for applications in high-value industries, including aerospace, energy, and healthcare, by providing a foundation for the efficient and accurate production of advanced ceramic structures.
- [Korean]
- Development of Highly Transparent and Thermo-Shielding Flexible Film via Colloidal ITO Nanocrystals
- Hyoin Bae, Hyeyeon Jung, Juna Lee, Dahye Shin, Sungyeon Heo
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):508-512. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00423
- 931 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
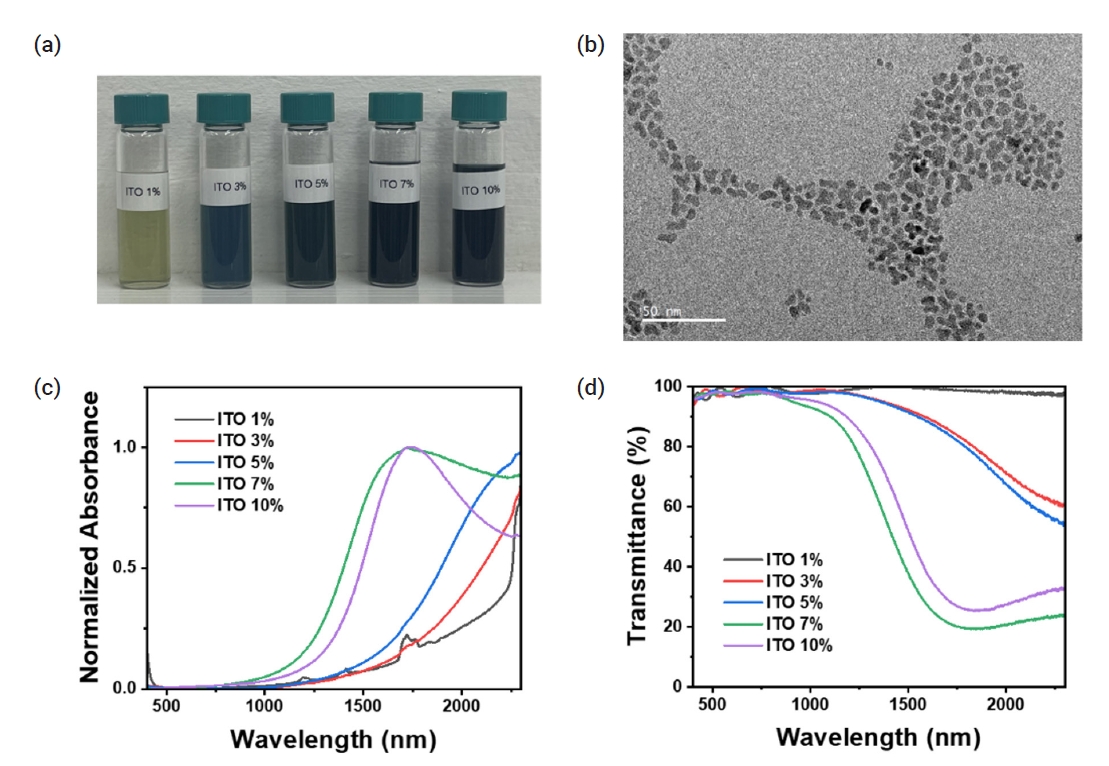
PDF - Infrared radiation accounts for approximately 50% of the solar spectrum. Specifically, the near-infrared (NIR) spectrum, ranging from 760 nm to 2500 nm, is primarily responsible for solar heat gain, increasing indoor temperatures and reducing heating and cooling efficiency. To address this issue, we developed a highly transparent thermo-shielding flexible film that maintains a high transmittance of the visible region (T = 80%) while reducing the transmittance of the NIR region (T ≈ 0%). NIR-absorbing indium tin oxide (ITO) nanocrystals were coated onto polyethylene terephthalate (PET) films, and both films were sandwiched to improve the NIR absorption properties and protect the nanocrystal film layer. The fabricated films were applied to a model house and decreased the indoor temperature by approximately 8°C. Our study demonstrates that energy consumption can be reduced by ITO nanocrystal-coated flexible films, with potential implications for the smart window and mobility markets.
- [English]
- Design of Conductive Inks Containing Carbon Black and Silver Nanowires for Patternable Screen-Printing on Fabrics
- Seokhwan Kim, Geumseong Lee, Jinwoo Park, Dahye Shin, Ki-Il Park, Kyoung Jin Jung, Yuho Min
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):500-507. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00409
- 1,902 View
- 55 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
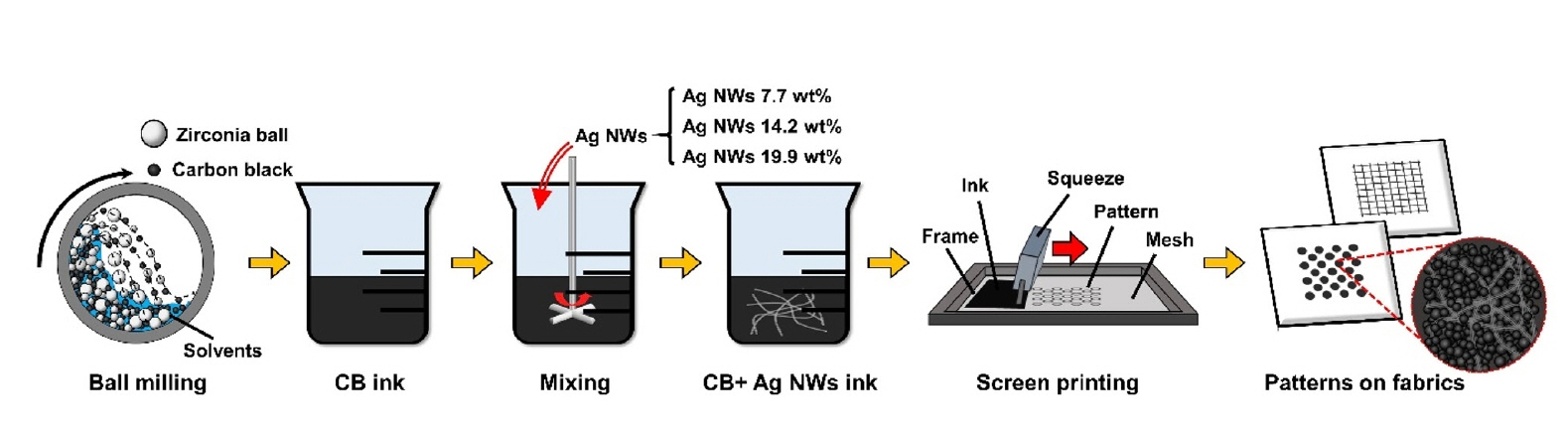
PDF - This study developed conductive inks composed of carbon black (CB) and silver nanowires (Ag NWs) for cost-effective screen-printing on fabrics. The Ag NW density within the CB matrix was precisely controlled, achieving tunable electrical conductivity with minimal Ag NW usage. The resulting inks were successfully patterned into shapes such as square grids and circles on textile surfaces, demonstrating excellent conductivity and fidelity. Adding 19.9 wt% Ag NWs reduced sheet resistance by ~92% compared to CB-only inks, highlighting the effectiveness and potential of this hybrid approach for cost-effective, high-performance textile-based electronics. The one-dimensional morphology of Ag NWs facilitated the formation of conductive percolation networks, creating efficient electron pathways within the CB matrix even at low loadings. This work advances the field of CB-based conductive inks and provides a scalable and practical method for producing functional, patterned electronic textiles.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multifunctional Screen-Printed Conductive Inks: Design Principles, Performance Challenges, and Application Horizons
Nahid Islam, Manisha Das, Bashir Ahmed Johan, Syed Shaheen Shah, Atif Saeed Alzahrani, Md. Abdul Aziz
ACS Applied Electronic Materials.2025; 7(16): 7503. CrossRef
- Multifunctional Screen-Printed Conductive Inks: Design Principles, Performance Challenges, and Application Horizons
- [English]
- High-Temperature Steam Oxidation Behavior of Silicide- or Aluminide- Coated Mo and Nb Refractory Metals
- Woojin Lim, Je-Kyun Baek, JaeJoon Kim, Hyun Gil Kim, Ho Jin Ryu
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):546-555. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00381
- 1,408 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Refractory materials, such as molybdenum and niobium, are potential candidates for cladding material due to their high melting temperatures and desirable mechanical properties at higher temperatures than those of zirconium alloys. However, refractory materials have low resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures. Therefore, this study examined silicide or aluminide surface coatings as protection against rapid oxidation of refractory materials at elevated temperatures for a potential accident-tolerant fuel cladding. Silicide or aluminide layers were formed on refractory metal substrates by using the pack cementation method. The steam oxidation behavior of both coated and uncoated samples was compared by thermogravimetric analysis at 1200°C. The weight changes of the coated samples were greatly reduced than those of uncoated samples. Microstructural analyses demonstrated that the silicide and aluminide layers were oxidized to form a protective surface oxide that prevented rapid oxidation of the refractory substrate at elevated temperatures.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of SiCf/SiC Composites with a BN Interphase Prepared by the Wet Method
- Kyung Ho Kim, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):530-536. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00339
- 886 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
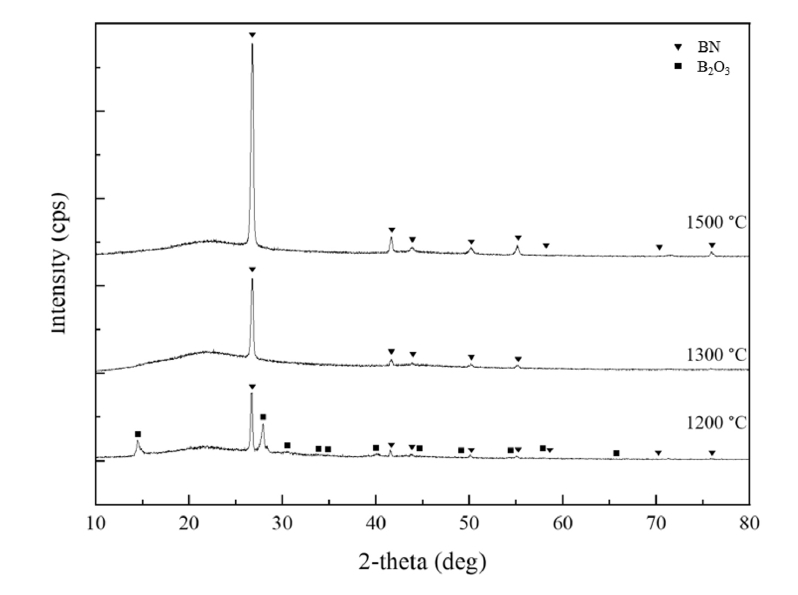
PDF - This study presents a cost-effective wet chemical coating process for fabricating a boron nitride (BN) interphase on silicon carbide (SiC) fibers, increasing the oxidation resistance and performance of SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composites. Using urea as a precursor, optimal nitriding conditions were determined by adjusting the composition, concentration, and immersion time. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed distinct BN phase formation at 1300°C and 1500°C, while a mixture of BN and B₂O₃ was observed at 1200°C. HF treatment improved coating uniformity by removing SiO₂ layers formed during the de-sizing process. Optimization of the boric acid-to-urea molar ratio resulted in a uniform, 130-nm-thick BN layer. This study demonstrates that the wet coating process offers a viable and economical alternative to chemical vapor deposition for fabricating high-performance BN interphases in SiCf/SiC composites that are suitable for high-temperature applications.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and High-Temperature Performance Evaluation of Light-Weight Insulation Materials and Coatings for Reusable Thermal Protection Systems
- Min-Soo Nam, Jong-Il Kim, Jaesung Shin, Hyeonjun Kim, Bum-Seok Oh, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):521-529. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00318
- 1,463 View
- 51 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
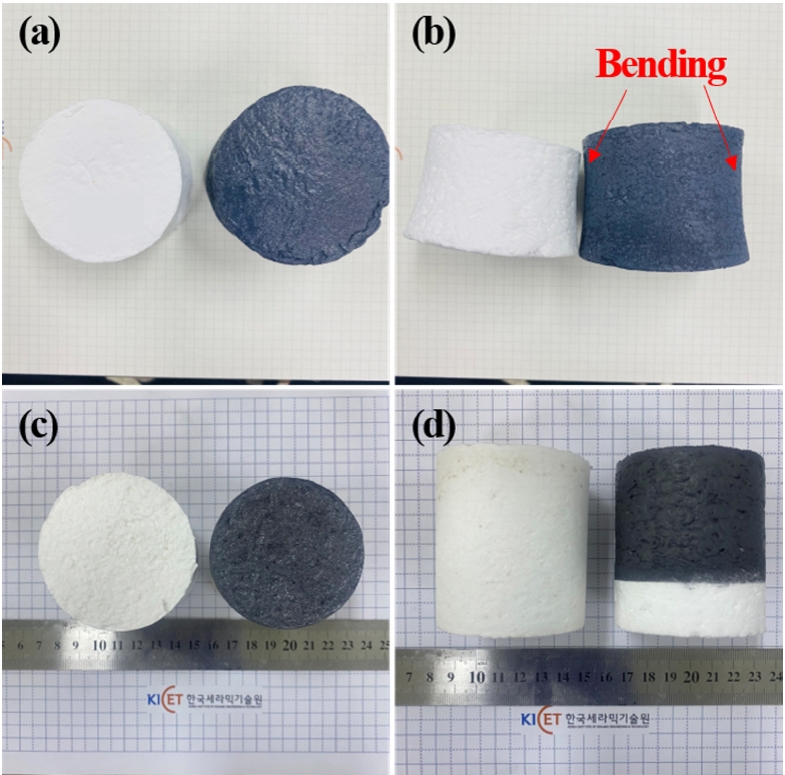
PDF - Light-weight ceramic insulation materials and high-emissivity coatings were fabricated for reusable thermal protection systems (TPS). Alumina-silica fibers and boric acid were used to fabricate the insulation, which was heat treated at 1250 °C. High-emissivity coating of borosilicate glass modified with TaSi2, MoSi2, and SiB6 was applied via dip-and-spray coating methods and heat-treated at 1100°C. Testing in a high-velocity oxygen fuel environment at temperatures over 1100 °C for 120 seconds showed that the rigid structures withstood the flame robustly. The coating effectively infiltrated into the fibers, confirmed by scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction analyses. Although some oxidation of TaSi2 occurred, thereby increasing the Ta2O5 and SiO2 phases, no significant phase changes or performance degradation were observed. These results demonstrate the potential of these materials for reusable TPS applications in extreme thermal environments.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Durability Assessment of Tile-Type Reusable Thermal Protection Materials
Minjeong Kim, Seong Man Choi
Materials.2026; 19(2): 303. CrossRef
- Durability Assessment of Tile-Type Reusable Thermal Protection Materials
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser Powder Bed Fusion 3D-Printed Cu-10Sn Alloy
- Jonggyu Kim, Junghoon Won, Wookjin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):422-430. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00276
- 965 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
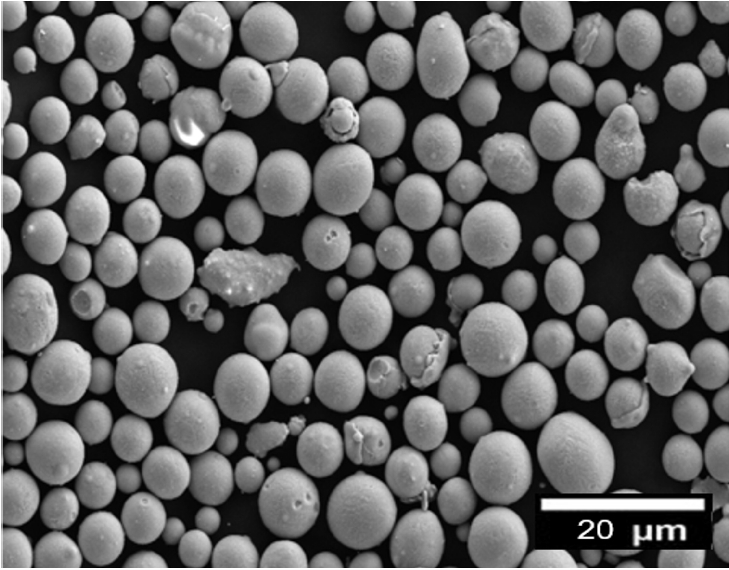
PDF - This study investigated the optimal process conditions and mechanical properties of Cu-10Sn alloys produced by the powder bed fusion (PBF) method. The optimal PBF conditions were explored by producing samples with various laser scanning speeds and laser power. It was found that under optimized conditions, samples with a density close to the theoretical density could be fabricated using PBF without any serious defects. The microstructure and mechanical properties of samples produced under optimized conditions were investigated and compared with a commercial alloy produced by the conventional method. The hardness, maximum tensile strength, and elongation of the samples were significantly higher than those of the commercially available cast alloy with the same chemical composition. Based on these results, it is expected to be possible to use the PBF technique to manufacture Cu-10Sn products with complex 3D shapes that could not be made using the conventional manufacturing method.
- [Korean]
- Effect of TiO2 Content on High-Temperature Degradation Behavior of Nd2O3 and Yb2O3 Doped YSZ Composite Materials
- Gye-Won Lee, Seonung Choi, Tae-jun Park, Jong-il Kim, In-hwan Lee, Yoon-seok Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):431-436. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00269
- 608 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
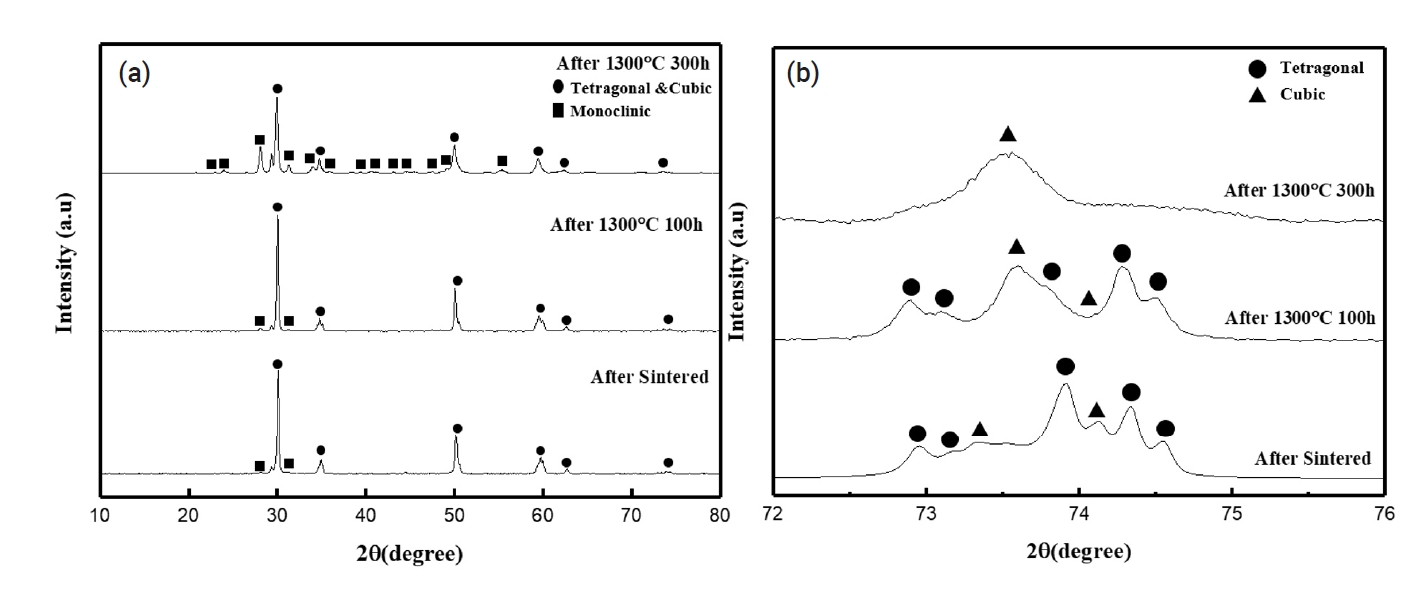
PDF - Hot section components of gas turbines are exposed to a high operating temperature environment. To protect these components, thermal barrier coatings (TBC) are applied to their surfaces. Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ), which is widely used as a TBC material, faces limitations at temperatures above 1200℃. To mitigate these issues, research has focused on adding lanthanide rare earth oxides and tetravalent oxides to prevent the phase-transformation of the monoclinic phase in zirconia. This study investigated the effects of varying TiO2 content in Nd2O3 and Yb2O3 co-doped YSZ composites. Increasing TiO2 content effectively suppressed formation of the monoclinic phase and increased the thermal degradation resistance compared to YSZ in environments over 1200℃. These findings will aid in developing more thermally stable and efficient TBC materials for application in high-temperature environments.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of 3D Aligned h-BN based Polymer Composites with Enhanced Mechanical Properties for Battery Housing
- Kiho Song, Hyunseung Song, Sang In Lee, Changui Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):329-335. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00220
- 1,347 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
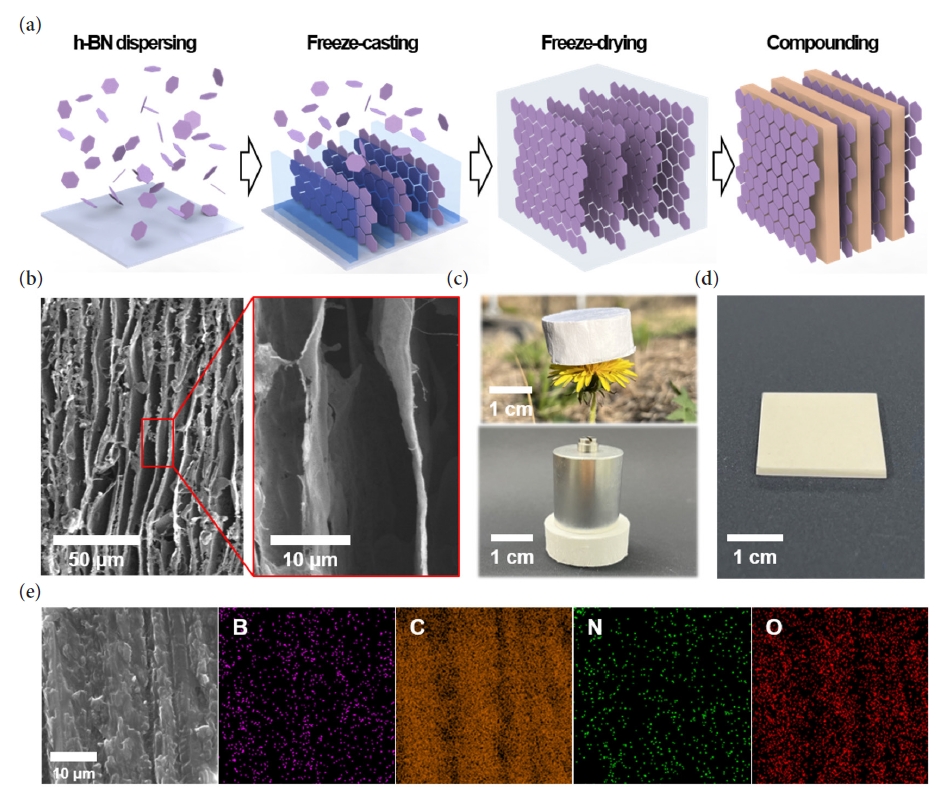
Supplementary Material - As the demand for electric vehicles increases, the stability of batteries has become one of the most significant issues. The battery housing, which protects the battery from external stimuli such as vibration, shock, and heat, is the crucial element in resolving safety problems. Conventional metal battery housings are being converted into polymer composites due to their lightweight and improved corrosion resistance to moisture. The transition to polymer composites requires high mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and thermal stability. In this paper, we proposes a high-strength nanocomposite made by infiltrating epoxy into a 3D aligned h-BN structure. The developed 3D aligned h-BN/epoxy composite not only exhibits a high compressive strength (108 MPa) but also demonstrates excellent electrical insulation and thermal stability, with a stable electrical resistivity at 200 °C and a low thermal expansion coefficient (11.46ⅹppm/℃), respectively.
- [Korean]
- Development of Composite-film-based Flexible Energy Harvester using Lead-free BCTZ Piezoelectric Nanomaterials
- Gwang Hyeon Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, Haksu Jang, Cheol Min Kim, Donghun Lee, Kwi-Il Park
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):16-22. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.16
- 1,719 View
- 31 Download
- 9 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
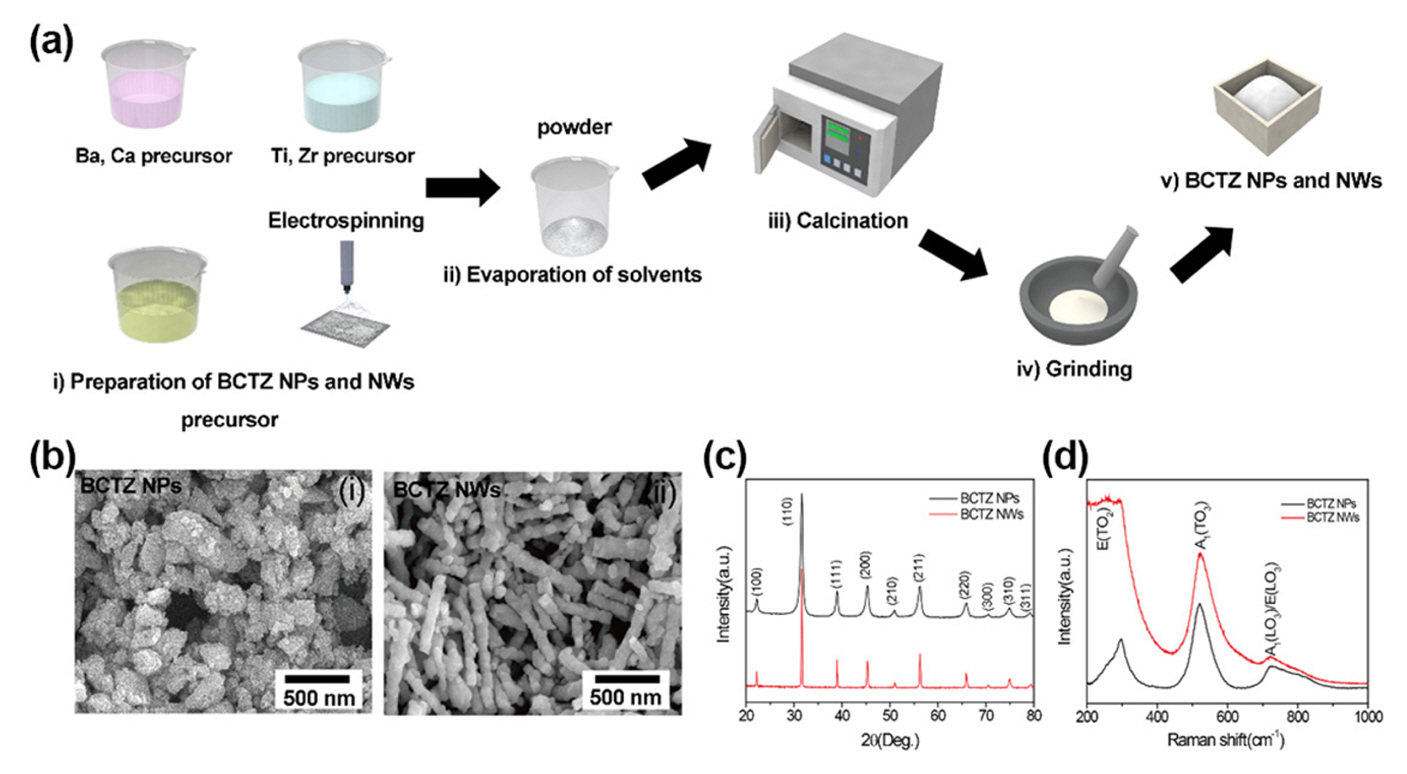
PDF - Composite-based piezoelectric devices are extensively studied to develop sustainable power supply and selfpowered devices owing to their excellent mechanical durability and output performance. In this study, we design a leadfree piezoelectric nanocomposite utilizing (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 (BCTZ) nanomaterials for realizing highly flexible energy harvesters. To improve the output performance of the devices, we incorporate porous BCTZ nanowires (NWs) into the nanoparticle (NP)-based piezoelectric nanocomposite. BCTZ NPs and NWs are synthesized through the solidstate reaction and sol-gel-based electrospinning, respectively; subsequently, they are dispersed inside a polyimide matrix. The output performance of the energy harvesters is measured using an optimized measurement system during repetitive mechanical deformation by varying the composition of the NPs and NWs. A nanocomposite-based energy harvester with 4:1 weight ratio generates the maximum open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current of 0.83 V and 0.28 A, respectively. In this study, self-powered devices are constructed with enhanced output performance by using piezoelectric energy harvesting for application in flexible and wearable devices.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Unidirectional porous PVDF Piezoelectrets fabricated via gradient ice-templating for enhanced energy harvesting performance
HyoMin Jeon, Seo Young Yoon, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, HakSu Jang, Changyeon Baek, Tiandong Zhang, Geon-Tae Hwang, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Sustainable Materials and Technologies.2026; 47: e01888. CrossRef - Long‐Lasting, Steady and Enhanced Energy Harvesting by Inserting a Conductive Layer into the Piezoelectric Polymer
HakSu Jang, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Dong Won Jeon, Hyeon Jun Park, BitNa Bae, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Cheol Min Kim, Changyeon Baek, Min‐Ku Lee, Sung Beom Cho, Gyoung‐Ja Lee, Kwi‐Il Park
Advanced Functional Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Flexible hybrid thermoelectric films made of bismuth telluride-PEDOT:PSS composites enabled by freezing-thawing process and simple chemical treatment
Cheol Min Kim, Seoha Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Bitna Bae, Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Gwang Hyun Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Haksu Jang, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Chemistry.2025; 44: 102532. CrossRef - Dual-controlled piezoelectric composite film with enhanced crystallinity and defect-free via solvent vapor treatment
HakSu Jang, Hyeon Jun Park, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, BitNa Bae, HyoMin Jeon, DongHun Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Nano Energy.2025; 136: 110705. CrossRef - Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(1): 16. CrossRef - Flexible Hybrid Energy Harvester based on Thermoelectric Composite Film and Electrospun Piezopolymer Membranes
Hyomin Jeon, Cheol Min Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, Hyejeong Choi, HakSu Jang, Kwi-Il Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(2): 104. CrossRef - Flexible Thermoelectric Energy Harvester with Stacked Structure of Thermoelectric Composite Films Made of PVDF and Bi2Te3-Based Particles
Da Eun Shin, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Kwi-Il Park
ACS Applied Energy Materials.2024; 7(19): 8288. CrossRef - Enhanced energy harvesting of fibrous composite membranes via plasma-piezopolymer interaction
Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, HakSu Jang, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Dong Hun Lee, Gwang Hyun Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Nano Energy.2024; 131: 110299. CrossRef - CoFe2O4-BaTiO3 core-shell-embedded flexible polymer composite as an efficient magnetoelectric energy harvester
Bitna Bae, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Cheol Min Kim, Jungho Ryu, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Geon-Tae Hwang, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Physics.2024; 48: 101567. CrossRef
- Unidirectional porous PVDF Piezoelectrets fabricated via gradient ice-templating for enhanced energy harvesting performance
- [English]
- Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy through Selective Laser Melting: Comprehensive Study on the Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
- Gargi Roy, Raj Narayan Hajra, Woo Hyeok Kim, Jongwon Lee, Sangwoo Kim, Jeoung Han Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):1-7. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.1
- 5,902 View
- 133 Download
- 9 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study explores the profound impact of varying oxygen content on microstructural and mechanical properties in specimens HO and LO. The higher oxygen concentration in specimen HO is found to significantly influence alpha lath sizes, resulting in a size of 0.5-1 μm, contrasting with the 1-1.5 μm size observed in specimen LO. Pore fraction, governed by oxygen concentration, is high in specimen HO, registering a value of 0.11%, whereas specimen LO exhibits a lower pore fraction (0.02%). Varied pore types in each specimen further underscore the role of oxygen concentration in shaping microstructural morphology. Despite these microstructural variations, the average hardness remains consistent at ~370 HV. This study emphasizes the pivotal role of oxygen content in influencing microstructural features, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the intricate interplay between elemental composition and material properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V based oxide dispersion strengthened alloy using in-situ oxide-dispersed powders and bound metal deposition
Woo Hyeok Kim, Raj Narayan Hajra, Hyung-Ki Park, Jung-Yeul Yun, Jeoung Han Kim
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2026; 1050: 185574. CrossRef - Mechanical response and microstructural evolution of a composite joint fabricated by green laser dissimilar welding of VCoNi medium entropy alloy and 17-4PH stainless steel
Hadiseh Esmaeilpoor, Mahdi Aghaahmadi, Hyun Jong Yoo, Chan Woong Park, Tae Jin Jang, Seok Su Sohn, Jeoung Han Kim
Journal of Materials Science & Technology.2025; 213: 223. CrossRef - High-integrity diffusion bonding of laser powder bed fused, forged, and rolled Ti–6Al–4V alloys
Seoyeon Jeon, Hyunjong Ha, Dong Jun Lee, Hyeonil Park, Yong Nam Kwon, Hyunjoo Choi, Hyokyung Sung
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 35: 2108. CrossRef - Removal of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants from Titanium Turning Scrap via Alkali and Acid Two-Step Cleaning
Seong Min An, Raj Narayan Hajra, Chan Hee Park, Jin-Ho Yoon, Jinsung Rho, Chang-Min Yoon, Jeoung Han Kim
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(7): 855. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Obtaining functionally-graded metal-matrix materials Ti‒6Al‒4V + WC in the process of 3D printing by the method of additive plasma-arc deposition
V. Korzhyk, A. Grynyuk, O. Babych, O. Berdnikova, Ye. Illiashenko, O. Bushma
The Paton Welding Journal.2025; 2025(8): 29. CrossRef - Obtaining functionally-graded metal-matrix materials ti‒6al‒4v + wc by the method of additive plasma-arc deposition
V.M. Korzhyk, A.A. Grynyuk, O.A. Babych, O.M. Berdnikova, Ye.V. Illiashenko, O.I. Bushma
Avtomatičeskaâ svarka (Kiev).2025; 2025(5): 48. CrossRef - Comparative Review of the Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Fabricated via Wrought and Powder Metallurgy Processes
Raj Narayan Hajra, Gargi Roy, An Seong Min, Hyunseok Lee, Jeoung Han Kim
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 365. CrossRef - A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef
- Additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V based oxide dispersion strengthened alloy using in-situ oxide-dispersed powders and bound metal deposition
- [English]
- Eco-Friendly Powder and Particles-Based Triboelectric Energy Harvesters
- Rayyan Ali Shaukat, Jihun Choi, Chang Kyu Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):528-535. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.528
- 1,957 View
- 38 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
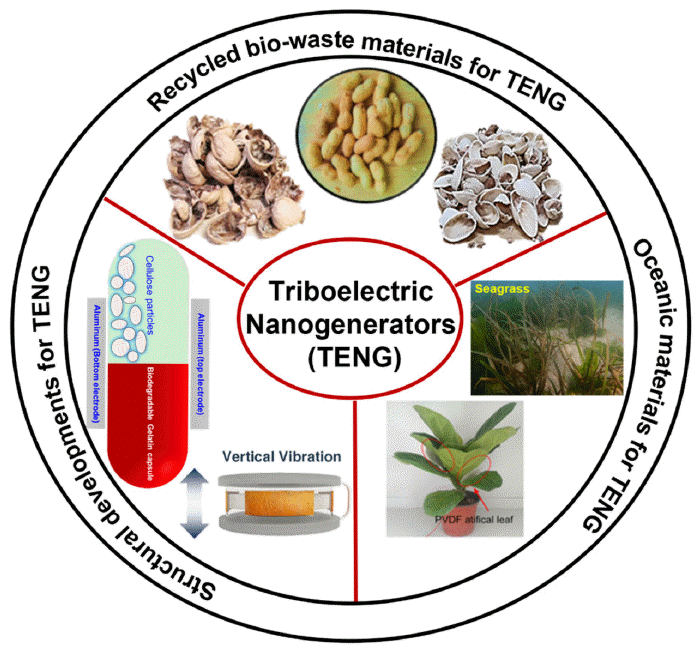
PDF Since their initial development in 2012, triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) have gained popularity worldwide as a desired option for harnessing energy. The urgent demand for TENGs is attributed to their novel structural design, low cost, and use of large-scale materials. The output performance of a TENG depends on the surface charge density of the friction layers. Several recycled and biowaste materials have been explored as friction layers to enhance the output performance of TENGs. Natural and oceanic biomaterials have also been investigated as alternatives for improving the performance of TENG devices. Moreover, structural innovations have been made in TENGs to develop highly efficient devices. This review summarizes the recent developments in recycling and biowaste materials for TENG devices. The potential of natural and oceanic biowaste materials is also discussed. Finally, future outlooks for the structural developments in TENG devices are presented.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Future Space Missions
Rayyan Ali Shaukat, Muhammad Muqeet Rehman, Maryam Khan, Rui Chang, Carlo Saverio Iorio, Yarjan Abdul Samad, Yijun Shi
Nano-Micro Letters.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Fabrication and Characterization of a Flexible Polyurethane-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for a Harvesting Energy System
Saba Ejaz, Imran Shah, Shahid Aziz, Gul Hassan, Ahmed Shuja, Muhammad Asif Khan, Dong-Won Jung
Micromachines.2025; 16(2): 230. CrossRef - Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(1): 16. CrossRef - Sustainable Triboelectric Nanogenerator from Abalone Shell Powder for Self-Powered Humidity Sensing
Yunsook Yang, Farhan Akhtar, Shahzad Iqbal, Muhammad Muqeet Rehman, Woo Young Kim
Sensors.2025; 25(24): 7584. CrossRef - Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 529. CrossRef
- Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Future Space Missions
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Flexible Energy Harvester Based on BaTiO3 Piezoelectric Nanotube Arrays
- Seo Young Yoon, Cheol Min Kim, Bitna Bae, Yujin Na, Haksu Jang, Kwi-Il Park
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):521-527. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.521
- 960 View
- 15 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
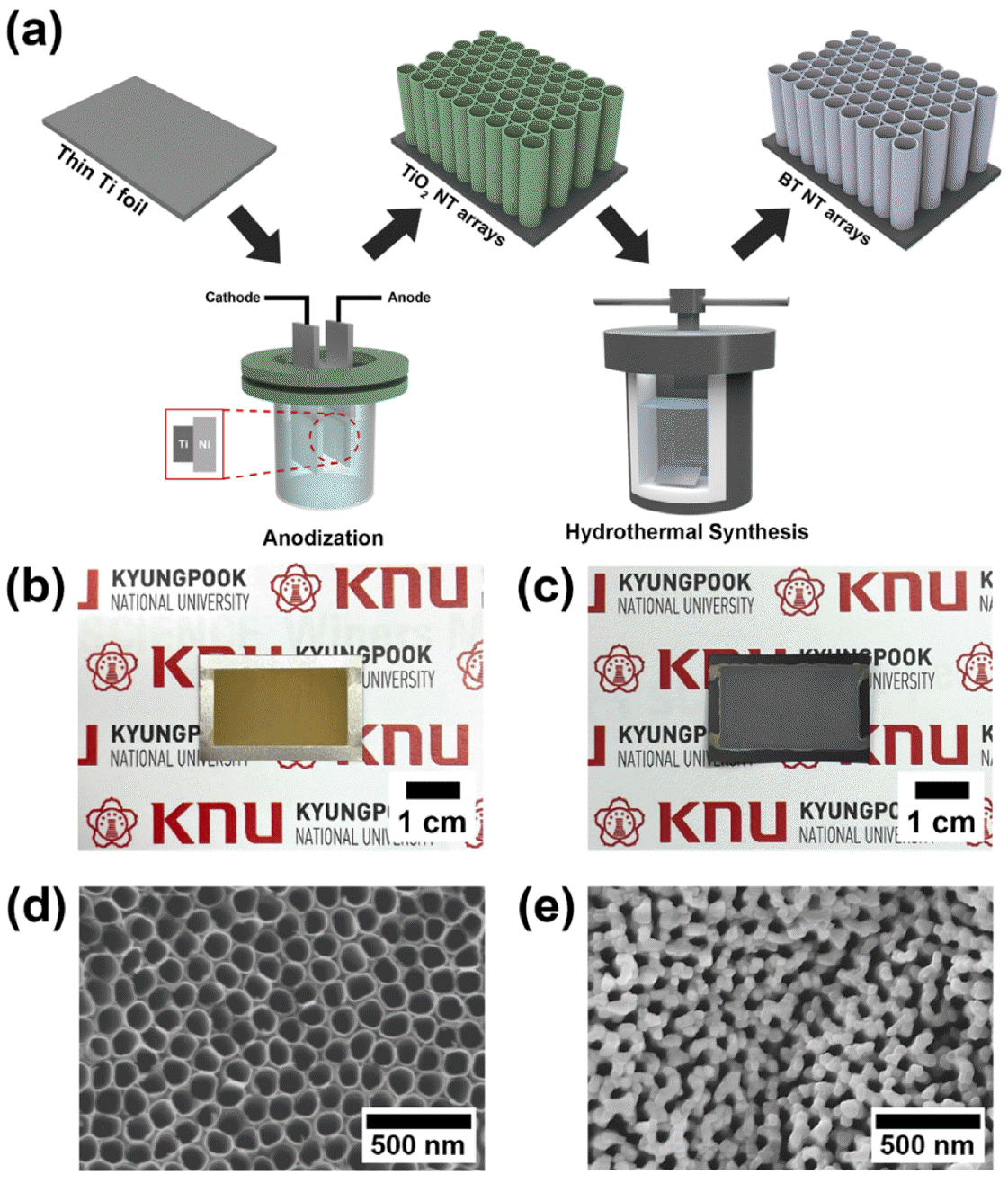
PDF Piezoelectric technology, which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, has recently attracted drawn considerable attention in the industry. Among the many kinds of piezoelectric materials, BaTiO3 nanotube arrays, which have outstanding uniformity and anisotropic orientation compared to nanowire-based arrays, can be fabricated using a simple synthesis process. In this study, we developed a flexible piezoelectric energy harvester (f-PEH) based on a composite film with PVDF-coated BaTiO3 nanotube arrays through sequential anodization and hydrothermal synthesis processes. The f-PEH fabricated using the piezoelectric composite film exhibited excellent piezoelectric performance and high flexibility compared to the previously reported BaTiO3 nanotube array-based energy harvester. These results demonstrate the possibility for widely application with high performance by our advanced f-PEH technique based on BaTiO3 nanotube arrays.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Flexible Thermoelectric Energy Harvester with Stacked Structure of Thermoelectric Composite Films Made of PVDF and Bi2Te3-Based Particles
Da Eun Shin, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Kwi-Il Park
ACS Applied Energy Materials.2024; 7(19): 8288. CrossRef - CoFe2O4-BaTiO3 core-shell-embedded flexible polymer composite as an efficient magnetoelectric energy harvester
Bitna Bae, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Cheol Min Kim, Jungho Ryu, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Geon-Tae Hwang, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Physics.2024; 48: 101567. CrossRef
- Flexible Thermoelectric Energy Harvester with Stacked Structure of Thermoelectric Composite Films Made of PVDF and Bi2Te3-Based Particles
- [Korean]
- Irradiation Hardening Property of Inconel 718 Alloy produced by Selective Laser Melting
- Joowon Suh, Sangyeob Lim, Hyung-Ha Jin, Young-Bum Chun, Suk Hoon Kang, Heung Nam Han
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):431-435. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.431
- 1,123 View
- 14 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
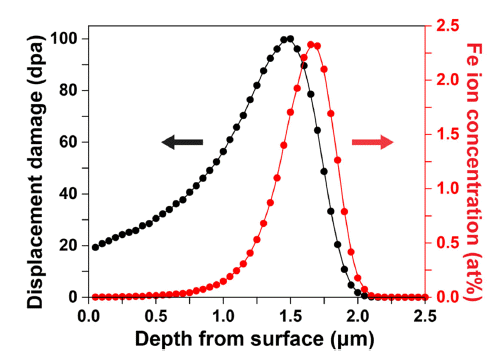
PDF An irradiation hardening of Inconel 718 produced by selective laser melting (SLM) was studied based on the microstructural observation and mechanical behavior. Ion irradiation for emulating neutron irradiation has been proposed owing to advantages such as low radiation emission and short experimental periods. To prevent softening caused by the dissolution of γ' and γ'' precipitates due to irradiation, only solution annealing (SA) was performed. SLM SA Inconel 718 specimen was ion irradiated to demonstrate the difference in microstructure and mechanical properties between the irradiated and non-irradiated specimens. After exposing specimens to Fe3+ ions irradiation up to 100 dpa (displacement per atom) at an ambient temperature, the hardness of irradiated specimens was measured by nanoindentation as a function of depth. The depth distribution profile of Fe3+ and dpa were calculated by the Monte Carlo SRIM (Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter)-2013 code under the assumption of the displacement threshold energy of 40 eV. A transmission electron microscope was utilized to observe the formation of irradiation defects such as dislocation loops. This study reveals that the Frank partial dislocation loops induce irradiation hardening of SLM SA Inconel 718 specimens.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(5): 390. CrossRef
- A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
- [Korean]
- Tribological Behavior Analysis of WC-Ni-Cr + Cr3C2 and WC-Ni-Cr + YSZ Coatings Sprayed by HVOF
- Tae-Jun Park, Gye-Won Lee, Yoon-Suk Oh
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):415-423. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.415
- 948 View
- 9 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
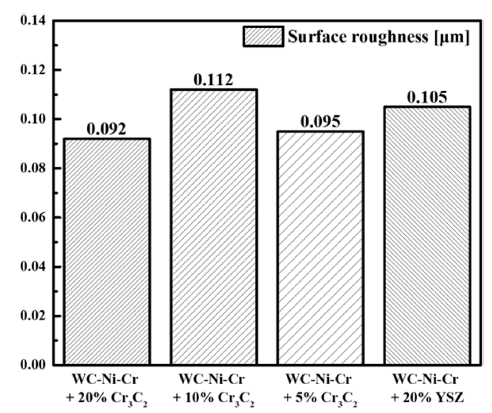
PDF With the increasing attention to environmental pollution caused by particulate matter globally, the automotive industry has also become increasingly interested in particulate matter, especially particulate matter generated by automobile brake systems. Here, we designed a coating composition and analyzed its mechanical properties to reduce particulate matter generated by brake systems during braking of vehicles. We designed a composition to check the mechanical properties change by adding Cr3C2 and YSZ to the WC-Ni-Cr composite composition. Based on the designed composition, coating samples were manufactured, and the coating properties were analyzed by Vickers hardness and ball-on-disk tests. As a result of the experiments, we found that the hardness and friction coefficient of the coating increased as the amount of Cr3C2 added decreased. Furthermore, we found that the hardness of the coating layer decreased when YSZ was added at 20vol%, but the friction coefficient was higher than the composition with Cr3C2 addition.
- [English]
- Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
- Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):318-323. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.318
- 1,686 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
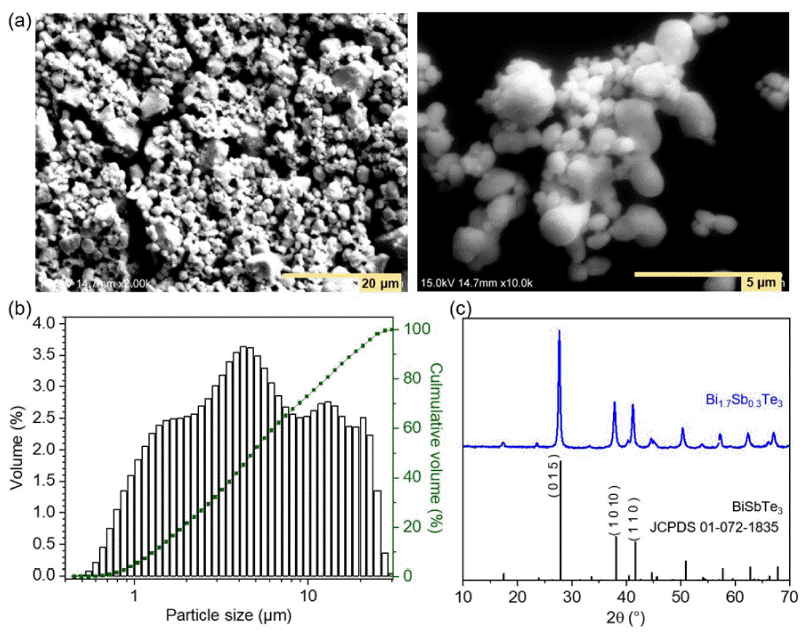
PDF The thermoelectric effect, which converts waste heat into electricity, holds promise as a renewable energy technology. Recently, bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3)-based alloys are being recognized as important materials for practical applications in the temperature range from room temperature to 500 K. However, conventional sintering processes impose limitations on shape-changeable and tailorable Bi2Te3 materials. To overcome these issues, three-dimensional (3D) printing (additive manufacturing) is being adopted. Although some research results have been reported, relatively few studies on 3D printed thermoelectric materials are being carried out. In this study, we utilize extrusion 3D printing to manufacture n-type Bi1.7Sb0.3Te3 (N-BST). The ink is produced without using organic binders, which could negatively influence its thermoelectric properties. Furthermore, we introduce graphene oxide (GO) at the crystal interface to enhance the electrical properties. The formed N-BST composites exhibit significantly improved electrical conductivity and a higher Seebeck coefficient as the GO content increases. Therefore, we propose that the combination of the extrusion 3D printing process (Direct Ink Writing, DIW) and the incorporation of GO into N-BST offers a convenient and effective approach for achieving higher thermoelectric efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef
- Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
- [Korean]
- Research on the Manufacturing Technology for a PDMS Structure-Based Transpiration Generator Using Biomimetic Capillary Phenomenon
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Jeungjai Yun, So Hyun Baek, Yongbum Kwon, Yoseb Song, Bum Sung Kim, Yong-Ho Choa, Da-Woon Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):268-275. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.268
- 1,121 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
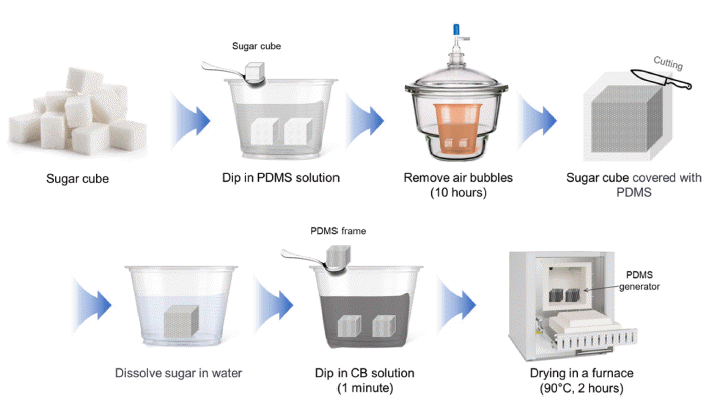
PDF The demand for energy is steadily rising because of rapid population growth and improvements in living standards. Consequently, extensive research is being conducted worldwide to enhance the energy supply. Transpiration power generation technology utilizes the vast availability of water, which encompasses more than 70% of the Earth's surface, offering the unique advantage of minimal temporal and spatial constraints over other forms of power generation. Various principles are involved in water-based energy harvesting. In this study, we focused on explaining the generation of energy through the streaming potential within the generator component. The generator was fabricated using sugar cubes, PDMS, carbon black, CTAB, and DI water. In addition, a straightforward and rapid manufacturing method for the generator was proposed. The PDMS generator developed in this study exhibits high performance with a voltage of 29.6 mV and a current of 8.29 μA and can generate power for over 40h. This study contributes to the future development of generators that can achieve high performance and long-term power generation.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Acid Leaching Conditions on the Properties of Cr Powder Produced by Self-propagating High-temperature Synthesis
- YongKwan Lee, YeongWoo Cho, ShinYoung Choi, SungGue Heo, Ju Won, KyoungTae Park, MiHye Lee, JaeJin Sim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):233-241. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.233
- 731 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
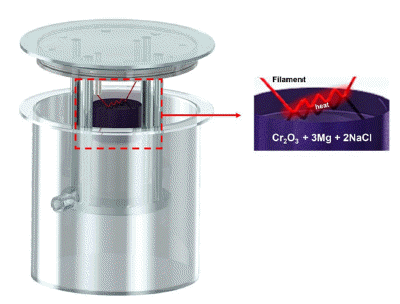
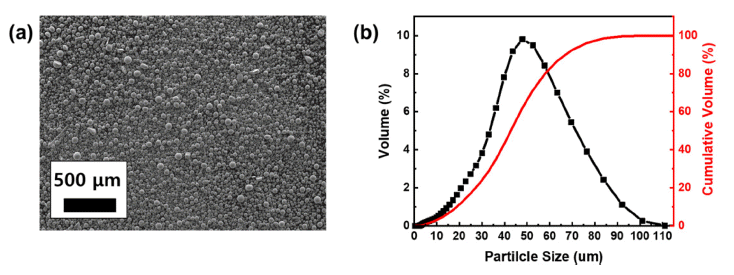
PDF In this study, we evaluated the effects of acid leaching on the properties of Cr powder synthesized using self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS). Cr powder was synthesized from a mixture of Cr2O3 and magnesium (Mg) powders using the SHS Process, and the byproducts after the reaction were removed using acid leaching. The properties of the recovered Cr powder were analyzed via X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), particle size analysis (PSA), and oxygen content analysis. The results show that perfect selective leaching of Cr is challenging because of various factors such as incomplete reaction, reaction kinetics, the presence of impurities, and incompatibility between the acid and metal mixture. Therefore, this study provides essential information on the properties under acidic conditions during the production of high-quality Cr powder using a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis method.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Substrate Pre-heating on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnet Manufactured by L-PBF
- Yeon Woo Kim, Haeum Park, Tae-Hoon Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):116-122. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.116
- 1,099 View
- 17 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Because magnets fabricated using Nd-Fe-B exhibit excellent magnetic properties, this novel material is used in various high-tech industries. However, because of the brittleness and low formability of Nd-Fe-B magnets, the design freedom of shapes for improving the performance is limited based on conventional tooling and postprocessing. Laserpowder bed fusion (L-PBF), the most famous additive manufacturing (AM) technique, has recently emerged as a novel process for producing geometrically complex shapes of Nd-Fe-B parts owing to its high precision and good spatial resolution. However, because of the repeated thermal shock applied to the materials during L-PBF, it is difficult to fabricate a dense Nd-Fe-B magnet. In this study, a high-density (>96%) Nd-Fe-B magnet is successfully fabricated by minimizing the thermal residual stress caused by substrate heating during L-PBF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef - Linkage between process-induced microstructure and magnetic property of Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Yeon Woo Kim, Sujin Lee, Yoona Lee, Jae Bok Seol, Namhyun Kang, Yoon Suk Choi, Ji-Hun Yu, Jung-Goo Lee, Tae-Hoon Kim, Jeong Min Park
Materials & Design.2025; 259: 114929. CrossRef
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- [English]
- Selective Laser Sintering of Co-Cr Alloy Powders and Sintered Products Properties
- Dong-Wan Lee, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):7-12. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.7

- 1,387 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal-additive manufacturing techniques, such as selective laser sintering (SLS), are increasingly utilized for new biomaterials, such as cobalt-chrome (Co-Cr). In this study, Co-Cr gas-atomized powders are used as charge materials for the SLS process. The aim is to understand the consolidation of Co-Cr alloy powder and characterization of samples sintered using SLS under various conditions. The results clearly suggest that besides the matrix phase, the second phase, which is attributed to pores and oxidation particles, is observed in the sintered specimens. The as-built samples exhibit completely different microstructural features compared with the casting or wrought products reported in the literature. The microstructure reveals melt pools, which represent the characteristics of the scanning direction, in particular, or of the SLS conditions, in general. It also exposes extremely fine grain sizes inside the melt pools, resulting in an enhancement in the hardness of the as-built products. Thus, the hardness values of the samples prepared by SLS under all parameter conditions used in this study are evidently higher than those of the casting products.
- [Korean]
- A Study on Rinsing Effects of Sn Sensitization and Pd Activation Processes for Uniform Electroless Plating
- Seong-Jae Jeong, Mi-Se Chang, Jae-Won Jeong, Sang-Sun Yang, Young-Tae Kwon
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):511-516. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.511
- 1,670 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
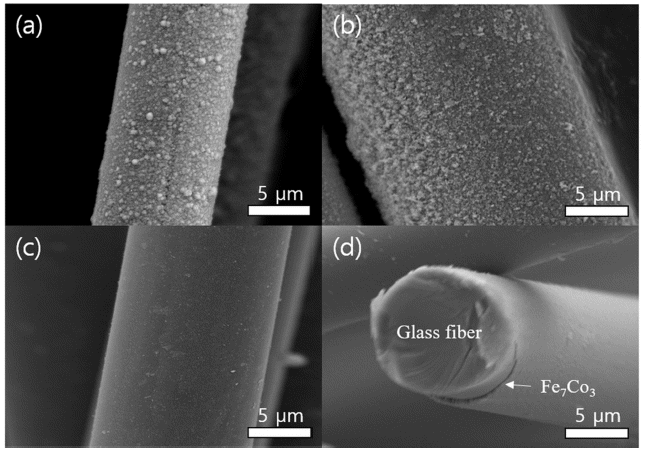
PDF Electroless plating is widely utilized in engineering for the metallization of insulator substrates, including polymers, glass, and ceramics, without the need for the application of external potential. Homogeneous nucleation of metals requires the presence of Sn-Pd catalysts, which significantly reduce the activation energy of deposition. Therefore, rinsing conducted during Sn sensitization and Pd activation is a key variable for the formation of a uniform seed layer without the lack or excess of catalysts. Herein, we report the optimized rinsing process for the functionalization of Sn-Pd catalysts, which enables the uniform FeCo metallization of the glass fibers. Rinsing enables good deposition of the FeCo alloy because of the removal of excess catalysts from the glass fiber. Concurrently, excessive rinsing results in a complete removal of the Sn–Pd nucleus. Collectively, the comprehensive study of the proposed nanomaterial preparation and surface science show that the metallization of insulators is a promising technology for electronics, solar cells, catalysts, and mechanical parts.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of NiCo2O4/Ni Foam Electrode for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Water Splitting
- Minsol Kwon, Jaeseong Go, Yesol Lee, Sungmin Lee, Jisu Yu, Hyowon Lee, Sung Ho Song, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):411-417. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.411
- 1,092 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
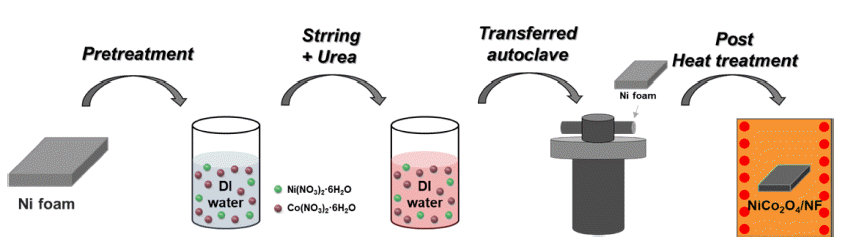
PDF Environmental issues such as global warming due to fossil fuel use are now major worldwide concerns, and interest in renewable and clean energy is growing. Of the various types of renewable energy, green hydrogen energy has recently attracted attention because of its eco-friendly and high-energy density. Electrochemical water splitting is considered a pollution-free means of producing clean hydrogen and oxygen and in large quantities. The development of non-noble electrocatalysts with low cost and high performance in water splitting has also attracted considerable attention. In this study, we successfully synthesized a NiCo2O4/NF electrode for an oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline water splitting using a hydrothermal method, which was followed by post-heat treatment. The effects of heat treatment on the electrochemical performance of the electrodes were evaluated under different heat-treatment conditions. The optimized NCO/NF-300 electrode showed an overpotential of 416 mV at a high current density of 50 mA/cm2 and a low Tafel slope (49.06 mV dec-1). It also showed excellent stability (due to the large surface area) and the lowest charge transfer resistance (12.59 Ω). The results suggested that our noble-metal free electrodes have great potential for use in developing alkaline electrolysis systems.
- [Korean]
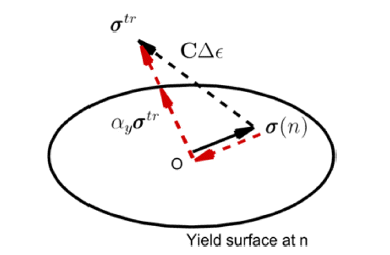
- Analysis of Anisotropic Plasticity of Additively Manufactured Structure using Modified Return Mapping Method
- Seung-Yong Yang, Doo-Han Jin, Jeoung-Han Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):303-308. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.303
- 839 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The plastic deformation behavior of additively manufactured anisotropic structures are analyzed using the finite element method (FEM). Hill’s quadratic anisotropic yield function is used, and a modified return-mapping method based on dual potential is presented. The plane stress biaxial loading condition is considered to investigate the number of iterations required for the convergence of the Newton-Raphson method during plastic deformation analysis. In this study, incompressible plastic deformation is considered, and the associated flow rule is assumed. The modified returnmapping method is implemented using the ABAQUS UMAT subroutine and effective in reducing the number of iterations in the Newton-Raphson method. The anisotropic tensile behavior is computed using the 3-dimensional FEM for two tensile specimens manufactured along orthogonal additive directions.
- [Korean]
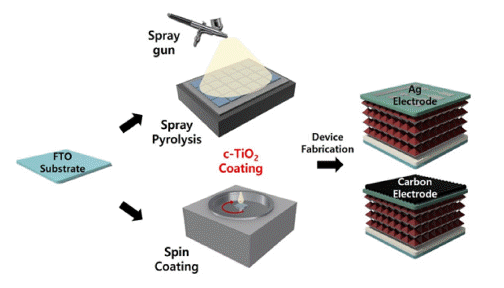
- Comparison Study of Compact Titanium Oxide (c-TiO2) Powder Electron Transport Layer Fabrication for Carbon Electrode-based Perovskite Solar Cells
- Chae Young Woo, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):297-302. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.297
- 792 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study compares the characteristics of a compact TiO2 (c-TiO2) powdery film, which is used as the electron transport layer (ETL) of perovskite solar cells, based on the manufacturing method. Additionally, its efficiency is measured by applying it to a carbon electrode solar cell. Spin-coating and spray methods are compared, and spraybased c-TiO2 exhibits superior optical properties. Furthermore, surface analysis by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) exhibits the excellent surface properties of spray-based TiO2. The photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) is 14.31% when applied to planar perovskite solar cells based on metal electrodes. Finally, carbon nanotube (CNT) film electrode-based solar cells exhibits a 76% PCE compared with that of metal electrodebased solar cells, providing the possibility of commercialization.
- [Korean]
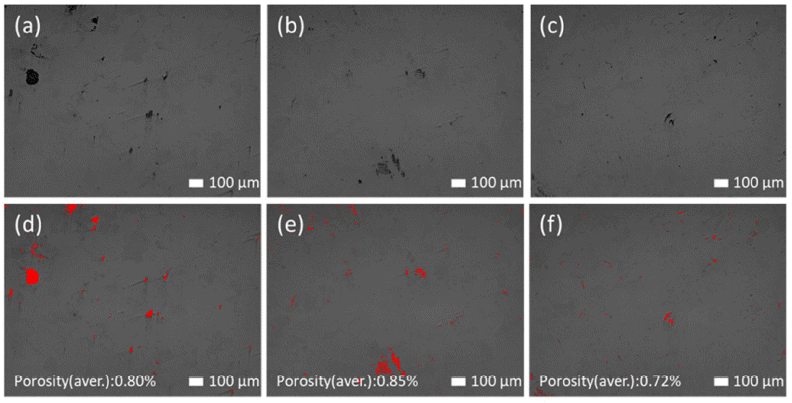
- Improvement of the Mechanical Property and Corrosion Resistivity of the Ni-/Fe-based Hybrid Coating Layer using High-velocity Oxygen Fuel Spraying by Heat Treatment
- Jungjoon Kim, Yeonjoo Lee, Song-Yi Kim, Jong-Jae Lee, Jae-hun Kim, Seok-Jae Lee, Hyunkyu Lim, Min-Ha Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):240-246. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.240
- 875 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Novel Ni- and Fe-based alloys are developed to impart improved mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The designed alloys are manufactured as a powder and deposited on a steel substrate using a high-velocity oxygen-fuel process. The coating layer demonstrates good corrosion resistance, and the thus-formed passive film is beneficial because of the Cr contained in the alloy system. Furthermore, during low-temperature heat treatment, factors that deteriorate the properties and which may arise during high-temperature heat treatment, are avoided. For the heattreated coating layers, the hardness increases by up to 32% and the corrosion resistance improves. The influence of the heat treatment is investigated through various methods and is considered to enhance the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the coating layer.
- [Korean]
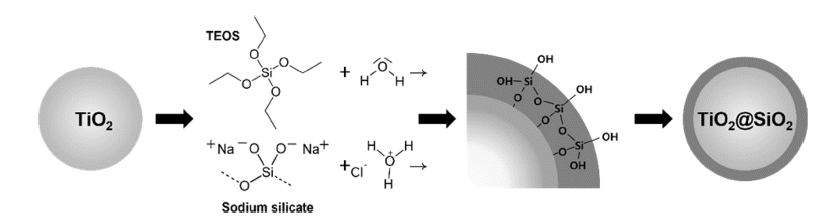
- A Study of Various SiO2 Coating Control on White TiO2 Pigment for Cosmetic Applications
- Minsol Park, Wooyoung Shim, YooJin Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):207-212. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.207
- 1,044 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nanosized rutile titanium dioxide (TiO2) is used in inorganic pigments and cosmetics because of its high whiteness and duality. The high quality of the white pigments depends on their surface coating technique via the solgel process. SiO2 coatings are required to improve the dispersibility, UV-blocking, and whiteness of TiO2. Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) is an important coating precursor owing to its ability to control various thicknesses and densities. In addition, we use Na2SiO3 (sodium silicate) as a precursor because of its low cost. Compared to TEOS, which controls the pH using a basic catalyst, Na2SiO3 controls the pH using an acid catalyst, giving a uniform coating. The coating thickness of TiO2 is controlled using a surface modifier, cetrimonium bromide, which is used in various applications. The shape and thickness of the nanosized coating layer on TiO2 are analyzed using transmission electron microscopy, and the SiO2 nanoparticle behavior in terms of the before-and-after size distribution is measured using a particle size analyzer. The color measurements of the SiO2 pigment are performed using UV-visible spectroscopy.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeMnNi-type High-entropy Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting: A Review
- Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):132-151. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.132
- 2,516 View
- 37 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy (HEA), which is the most widely known HEA with a single facecentered cubic structure, has attracted significant academic attention over the past decade owing to its outstanding multifunctional performance. Recent studies have suggested that CoCrFeMnNi-type HEAs exhibit excellent printability for selective laser melting (SLM) under a wide range of process conditions. Moreover, it has been suggested that SLM can not only provide great topological freedom of design but also exhibit excellent mechanical properties by overcoming the strength–ductility trade-off via producing a hierarchical heterogeneous microstructure. In this regard, the SLM-processed CoCrFeMnNi HEA has been extensively studied to comprehensively understand the mechanisms of microstructural evolution and resulting changes in mechanical properties. In this review, recent studies on CoCrFeMnNi-type HEAs produced using SLM are discussed with respect to process-induced microstructural evolution and the relationship between hierarchical heterogeneous microstructure and mechanical properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Investigation of effects of process parameters on microstructure and fracture toughness of SLM CoCrFeMnNi
Joseph Agyapong, Diego Mateos, Aleksander Czekanski, Solomon Boakye-Yiadom
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2024; 987: 173998. CrossRef - Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 8. CrossRef - Data-driven Approach to Explore the Contribution of Process Parameters for Laser Powder Bed Fusion of a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
Jeong Min Park, Jaimyun Jung, Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Yeon Woo Kim, Ji-Hun Yu
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 137. CrossRef - Cryogenic tensile behavior of carbon-doped CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Hyeonseok Kwon, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Jungho Choe, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jung Gi Kim, Jeong Min Park
Additive Manufacturing.2024; 86: 104223. CrossRef - Microstructural evolution and high strain rate deformation response of SLM-printed CoCrFeMnNi after annealing and deep-cryogenic treatment
Joseph Agyapong, Aleksander Czekanski, Solomon Boakye Yiadom
Materials Characterization.2024; 218: 114506. CrossRef - High-speed manufacturing-driven strength-ductility improvement of H13 tool steel fabricated by selective laser melting
Yeon Woo Kim, Haeum Park, Young Seong Eom, Dong Gill Ahn, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-hun Yu, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 582. CrossRef
- Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Roll Manufacturing Technology Applying Powder Flame Spray Coating Technology of Ni-Based Alloy Powder
- Ji Woong Park, Soon Kook Kim, Gye Bum Ban
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):123-131. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.123

- 1,030 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The purpose of this study is to improve the mechanical properties and develop manufacturing technology through self-soluble alloy powder flame spray coating on the surface of a run-out table roller for hot rolling. The roller surface of the run-out table should maintain high hardness at high temperatures and possess high wear, corrosion, and heat resistances. In addition, sufficient bonding strength between the thermal spray coating layer and base material, which would prevent the peel-off of the coating layer, is also an important factor. In this study, the most suitable powder and process for roll manufacturing technology are determined through the initial selection of commercial alloy powder for roll manufacturing, hardness, component analysis, and bond strength analysis of the powder and thermal spray coating layer according to the powder.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of rare earth oxides on microstructure and mechanical properties of nickel-based superalloys fabricated by high energy beam processing: A review
Lianjie Bi, Hua Yan, Peilei Zhang, Haichuan Shi, Zhiyuan Li, Ruidi Li
Journal of Rare Earths.2024; 42(9): 1629. CrossRef
- Influence of rare earth oxides on microstructure and mechanical properties of nickel-based superalloys fabricated by high energy beam processing: A review
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Tungsten by Freeze Casting and Vacuum Drying of WO3/Tert-butyl Alcohol Slurry
- Youn Ji Heo, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh, Young-Keun Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):118-122. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.118

- 895 View
- 11 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The synthesis of porous W by freeze-casting and vacuum drying is investigated. Ball-milled WO3 powders and tert-butyl alcohol were used as the starting materials. The tert-butyl alcohol slurry is frozen at –25°C and dried under vacuum at –25 and –10°C. The dried bodies are hydrogen-reduced at 800°C and sintered at 1000°C. The XRD analysis shows that WO3 is completely reduced to W without any reaction phases. SEM observations reveal that the struts and pores aligned in the tert-butyl alcohol growth direction, and the change in the powder content and drying temperature affects the pore structure. Furthermore, the struts of the porous body fabricated under vacuum are thinner than those fabricated under atmospheric pressure. This behavior is explained by the growth mechanism of tert-butyl alcohol and rearrangement of the powders during solidification. These results suggest that the pore structure of a porous body can be controlled by the powder content, drying temperature, and pressure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
Fabrication of porous W by freeze-casting and hydrogen reduction of camphene-based WO
3
suspension
Ji Won Choi, Youngmin Kim, Ji Young Kim, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(3): 283. CrossRef - Preparation of Porous W-Cu by Freeze Casting of Tert-butyl Alcohol Slurry Mixed with WO3-CuO Powder
Youngmin Kim, Ji Young Kim, Minju Son, Wonyong Kwon, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 466. CrossRef - Fabrication of Porous TiO2 with Aligned Pores Using Tert-Butyl Alcohol Based Freeze Casting
Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2024; 62(12): 929. CrossRef
-
Fabrication of porous W by freeze-casting and hydrogen reduction of camphene-based WO
3
suspension
- [Korean]
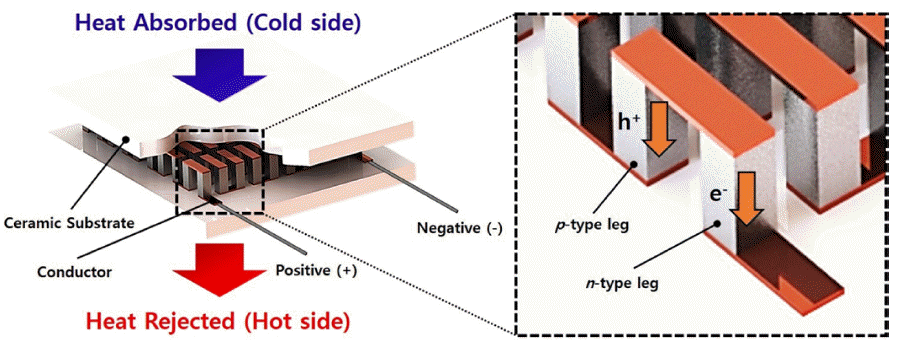
- Recent progress on Performance Improvements of Thermoelectric Materials using Atomic Layer Deposition
- Seunghyeok Lee, Tae Joo Park, Seong Keun Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):56-62. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.56
- 1,496 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a promising technology for the uniform deposition of thin films. ALD is based on a self-limiting mechanism, which can effectively deposit thin films on the surfaces of powders of various sizes. Numerous studies are underway to improve the performance of thermoelectric materials by forming core-shell structures in which various materials are deposited on the powder surface using ALD. Thermoelectric materials are especially relevant as clean energy storage materials due to their ability to interconvert between thermal and electrical energy by the Seebeck and Peltier effects. Herein, we introduce a surface and interface modification strategy based on ALD to control the performance of thermoelectric materials. We also discuss the properties of the interface between various deposition materials and thermoelectric materials.
- [Korean]
- Recycling of Hardmetal Tool through Alkali Leaching Process and Fabrication Process of Nano-sized Tungsten Carbide Powder using Self-propagation High-temperature Synthesis
- Hee-Nam Kang, Dong Il Jeong, Young Il Kim, In Yeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Cheol Woo Nam, Seok-Jun Seo, Jin Yeong Lee, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):47-55. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.47

- 1,384 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten carbide is widely used in carbide tools. However, its production process generates a significant number of end-of-life products and by-products. Therefore, it is necessary to develop efficient recycling methods and investigate the remanufacturing of tungsten carbide using recycled materials. Herein, we have recovered 99.9% of the tungsten in cemented carbide hard scrap as tungsten oxide via an alkali leaching process. Subsequently, using the recovered tungsten oxide as a starting material, tungsten carbide has been produced by employing a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) method. SHS is advantageous as it reduces the reaction time and is energy-efficient. Tungsten carbide with a carbon content of 6.18 wt % and a particle size of 116 nm has been successfully synthesized by optimizing the SHS process parameters, pulverization, and mixing. In this study, a series of processes for the highefficiency recycling and quality improvement of tungsten-based materials have been developed.
- [Korean]
- The Effects of TiC Content on Microstructure of Modified A6013-3wt.%Si Alloy Powder Compact
- Hyo-Sang Yoo, Yong-Ho Kim, Hyeon-Taek Son
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):28-33. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.28

- 897 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Aluminum-based powders have attracted attention as key materials for 3D printing owing to their low density, high specific strength, high corrosion resistance, and formability. This study describes the effects of TiC addition on the microstructure of the A6013 alloy. The alloy powder was successfully prepared by gas atomization and further densified using an extrusion process. We have carried out energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDS) and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) in order to investigate the effect of TiC addition on the microstructure and texture evolution of the A6013 alloy. The atomized A6013-xTiC alloy powder is fine and spherical, with an initial powder size distribution of approximately 73 μm which decreases to 12.5, 13.9, 10.8, and 10.0 μm with increments in the amount of TiC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Curing Agent Amount on Properties of Dynamic Vulcanized Phenyl Silicone Rubber-SEBS-SBS System
Chunxu Zhao, Bobing He, Xian Chen
Polymers.2022; 14(24): 5443. CrossRef
- Influence of Curing Agent Amount on Properties of Dynamic Vulcanized Phenyl Silicone Rubber-SEBS-SBS System
- [Korean]
- A Study on Powder Size Dependence of Additive Manufactured AlCrFeNi HEA on Its Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
- Jong Woo Choi, Hae Jin Park, Gyeol Chan Kang, Min Seob Jung, Ki Tae Oh, Sung Hwan Hong, Hyun Gil Kim, Ki Buem Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):22-27. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.22
- 756 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Conventionally, metal materials are produced by subtractive manufacturing followed by melting. However, there has been an increasing interest in additive manufacturing, especially metal 3D printing technology, which is relatively inexpensive because of the absence of complicated processing steps. In this study, we focus on the effect of varying powder size on the synthesis quality, and suggest optimum process conditions for the preparation of AlCrFeNi high-entropy alloy powder. The SEM image of the as-fabricated specimens show countless, fine, as-synthesized powders. Furthermore, we have examined the phase and microstructure before and after 3D printing, and found that there are no noticeable changes in the phase or microstructure. However, it was determined that the larger the powder size, the better the Vickers hardness of the material. This study sheds light on the optimization of process conditions in the metal 3D printing field.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 254. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
- [Korean]
- Effect of Process Stopping and Restarting on the Microstructure and Local Property of 316L Stainless Steel Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting Process
- Hyunjin Joo, Jeongmin Woo, Yongho Sohn, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):1-7. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.1

- 741 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the effect of process stopping and restarting on the microstructure and local nanoindentation properties of 316L stainless steel manufactured via selective laser melting (SLM). We find that stopping the SLM process midway, exposing the substrate to air having an oxygen concentration of 22% or more for 12 h, and subsequently restarting the process, makes little difference to the density of the restarted area (~ 99.8%) as compared to the previously melted area of the substrate below. While the microstructure and pore distribution near the stop/restart area changes, this modified process does not induce the development of unusual features, such as an inhomogeneous microstructure or irregular pore distribution in the substrate. An analysis of the stiffness and hardness values of the nano-indented steel also reveals very little change at the joint of the stop/restart area. Further, we discuss the possible and effective follow-up actions of stopping and subsequently restarting the SLM process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- On the Fabrication of Functionally Graded Prototypes with Laser Powder Bed Fusion from Reused Ni-625 and 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Powder
Bharat Kalia, Rupinder Singh, B. S. Pabla
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2025; 34(22): 27160. CrossRef - Additive Manufacturing of SS316L/IN718 Bimetallic Structure via Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Asif Mahmud, Nicolas Ayers, Thinh Huynh, Yongho Sohn
Materials.2023; 16(19): 6527. CrossRef
- On the Fabrication of Functionally Graded Prototypes with Laser Powder Bed Fusion from Reused Ni-625 and 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Powder
- [Korean]
- A Comparative Study on Characteristics of Cutting Tool Materials Based on SiAlON Ceramics
- Seongwon Kim, Jae-Hyung Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):502-508. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.502
- 1,122 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF SiAlON-based ceramics are a type of oxynitride ceramics, which can be used as cutting tools for heatresistant super alloys (HRSAs). These ceramics are derived from Si3N4 ceramics. SiAlON can be densified using gaspressure reactive sintering from mixtures of oxides and nitrides. In this study, we prepare an α-/β-SiAlON ceramic composite with a composition of Yb0.03Y0.10Si10.6Al1.4O1.0N15.0. The structure and mechanical/thermal properties of the densified SiAlON specimen are characterized and compared with those of a commercial SiAlON cutting tool. By observing the crystallographic structures and microstructures, the constituent phases of each SiAlON ceramic, such as α- SiAlON, β-SiAlON, and intergranular phases, are identified. By evaluating the mechanical and thermal properties, the contribution of the constituent phases to these properties is discussed as well.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation and cutting performance of textured SiAlON ceramic brazing composite tool
Run-Ping Liu, Yi Zhou, Yang You, Wei-Ming Guo, Shi-Kuan Sun, Yu-jin Wang, Hua-Tay Lin
Ceramics International.2025; 51(20): 30931. CrossRef
- Preparation and cutting performance of textured SiAlON ceramic brazing composite tool
- [Korean]
- Development of Amorphous Iron Based Coating Layer using High-velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) Spraying
- Jungjoon Kim, Song-Yi Kim, Jong-Jae Lee, Seok-Jae Lee, Hyunkyu Lim, Min-Ha Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):483-490. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.483
- 682 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A new Fe-Cr-Mo-B-C amorphous alloy is designed, which offers high mechanical strength, corrosion resistance as well as high glass-forming ability and its gas-atomized amorphous powder is deposited on an ASTM A213-T91 steel substrate using the high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) process. The hybrid coating layer, consisting of nanocrystalline and amorphous phases, exhibits strong bonding features with the substrate, without revealing significant pore formation. By the coating process, it is possible to obtain a dense structure in which pores are hardly observed not only inside the coating layer but also at the interface between the coating layer and the substrate. The coating layer exhibits good adhesive strength as well as good wear resistance, making it suitable for coating layers for biomass applications.
- [Korean]
- Electrochemical Properties of Ball-milled Tin-Graphite Composite Anode Materials for Lithium-Ion Battery
- Tae-Hui Lee, Hyeon-A Hong, Kwon-Koo Cho, Yoo-Young Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):462-469. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.462

- 1,169 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tin/graphite composites are prepared as anode materials for Li-ion batteries using a dry ball-milling process. The main experimental variables in this work are the ball milling time (0–8 h) and composition ratio (tin:graphite=5:95, 15:85, and 30:70 w/w) of graphite and tin powder. For comparison, a tin/graphite composite is prepared using wet ball milling. The morphology and structure of the different tin/graphite composites are investigated using X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and scanning and transmission electron microscopy. The electrochemical properties of the samples are also examined. The optimal dry ball milling time for the uniform mixing of graphite and tin is 6 h in a graphite-30wt.%Sn sample. The electrode prepared from the composite that is dry-ballmilled for 6 h exhibits the best cycle performance (discharge capacity after 50th cycle: 308 mAh/g and capacity retention: 46%). The discharge capacity after the 50th cycle is approximately 112 mAh/g, higher than that when the electrode is composed of only graphite (196 mAh/g after 50th cycle). This result indicates that it is possible to manufacture a tin/graphite composite anode material that can effectively buffer the volume change that occurs during cycling, even using a simple dry ball-milling process.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of the Multi-layered SnO Nanoparticles and Enhanced Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries by Heat treatment
- So Yi Lee, Yoon Myung, Kyu-Tae Lee, Jaewon Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):455-461. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.455

- 1,676 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, multilayered SnO nanoparticles are prepared using oleylamine as a surfactant at 165°C. The physical and chemical properties of the multilayered SnO nanoparticles are determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Interestingly, when the multilayered SnO nanoparticles are heated at 400°C under argon for 2 h, they become more efficient anode materials, maintaining their morphology. Heat treatment of the multilayered SnO nanoparticles results in enhanced discharge capacities of up to 584 mAh/g in 70 cycles and cycle stability. These materials exhibit better coulombic efficiencies. Therefore, we believe that the heat treatment of multilayered SnO nanoparticles is a suitable approach to enable their application as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and electrochemical properties of multi-layered SnO/rGO composite as anode materials for sodium ion batteries
So Yi Lee, Honggyu Seong, Geongil Kim, Youngho Jin, Joon Ha Moon, Wonbin Nam, Sung Kuk Kim, MinHo Yang, Jaewon Choi
Applied Surface Science.2023; 612: 155859. CrossRef
- Synthesis and electrochemical properties of multi-layered SnO/rGO composite as anode materials for sodium ion batteries
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


