Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- 3D-Printed Stretchable Electrodes Enabled by a Titanium/Acrylamide-Based Hydrogel Nanocomposite
- Se Jin Choi, Han Eol Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):67-72. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00465
- 847 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
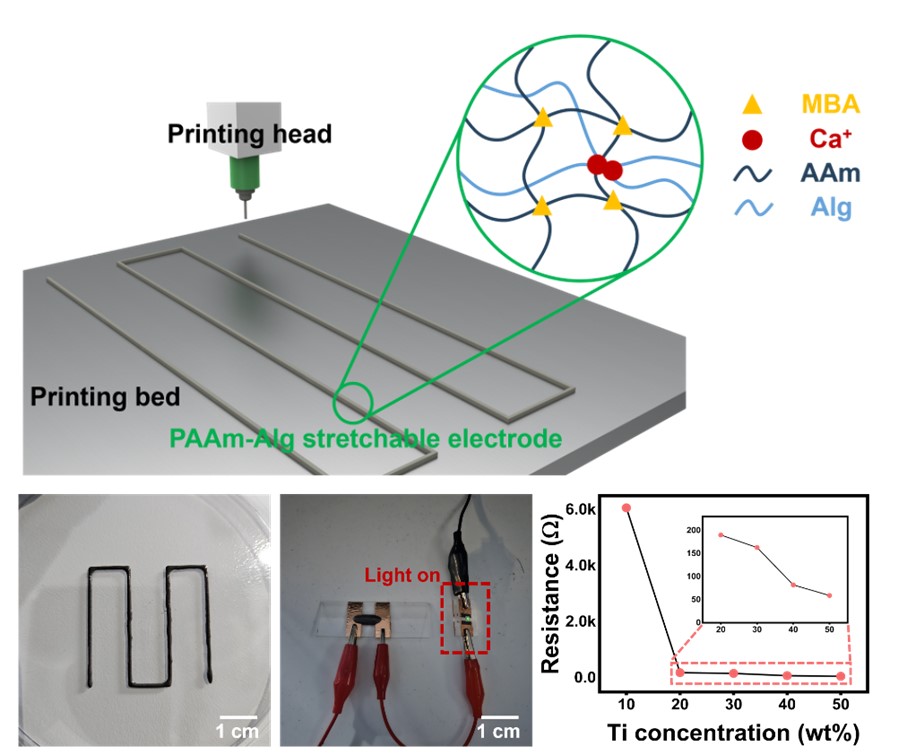
PDF - Wearable electronics have been the focus of considerable interest in various fields, such as human-machine interfaces, soft robotics, and medical treatments, due to their flexibility, stretchability, and light weight. To address the shortcomings of existing metal thin film-based wearable devices, stretchable conductive polymers have been developed. In particular, double networking hydrogels are being actively studied as a polymer with a three-dimensional stereoscopic structure that can be patterned. Nonetheless, they have shortcomings such as poor electrical properties and cumbersome manufacturing processes, making it difficult to apply them in electronic devices. Herein, we report 3D-printed stretchable electrodes enabled by a titanium/polyacrylamide-alginate-based hydrogel nanocomposite. This research suggests the strategy for resolving the challenges of high costs and complex fabrication processes associated with stretchable electrode, providing a solution to accelerate the commercialization of wearable electronic devices.
- [Korean]
- Optimized Process and Mechanical and Electrical Analysis of Polyimide/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Composites
- Junki Lee, Sang-il Yoon, Hyunseung Kim, Chang Kyu Jeong
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):16-22. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00444
- 977 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
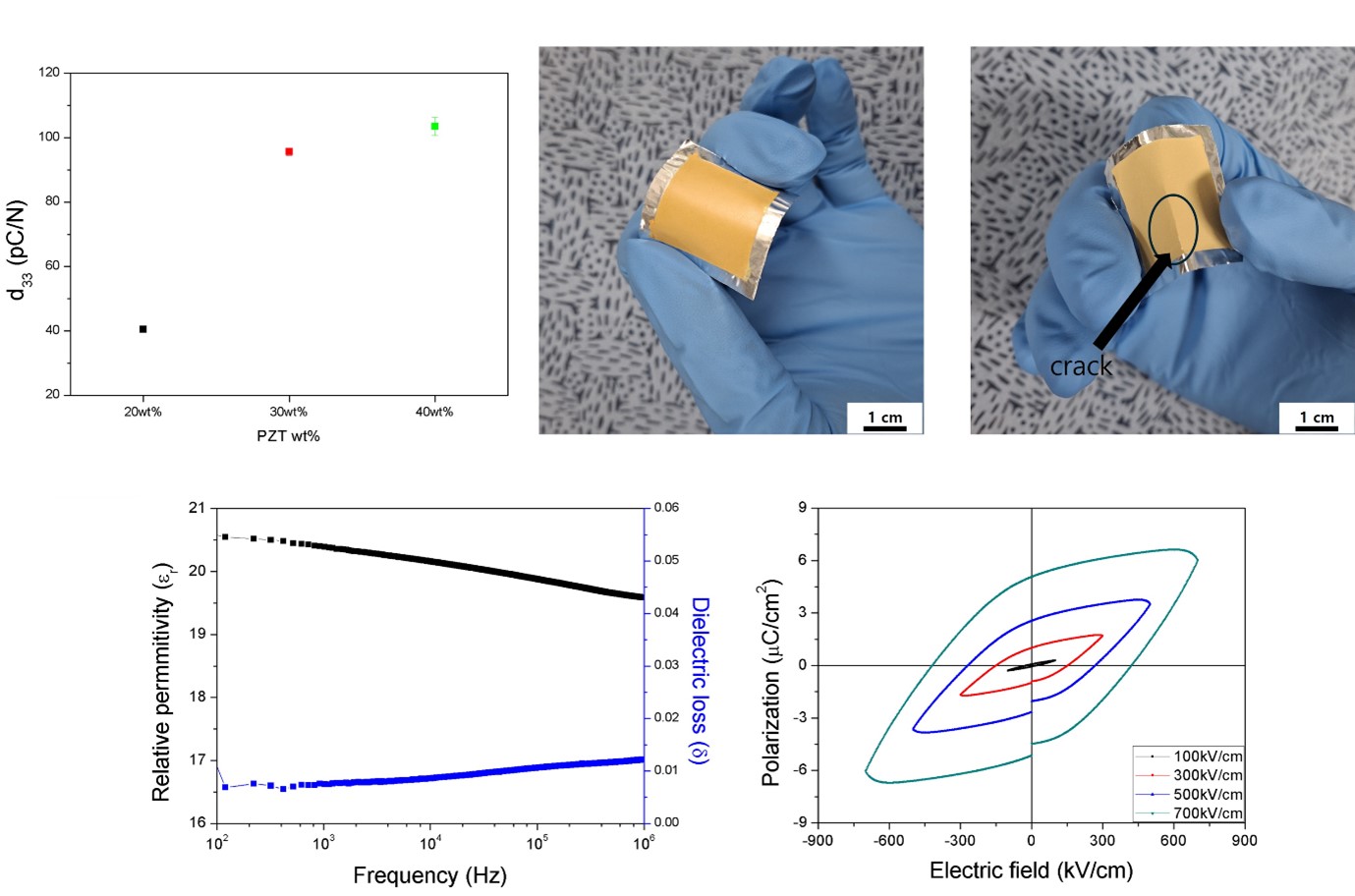
PDF - Piezoelectric composites have attracted significant research interest as sustainable power sources for electronic devices due to their high mechanical stability and electrical output characteristics. This study investigated the optimal processing conditions for fabricating a flexible piezoelectric energy harvester based on Pb(Zr,Ti)O₃ (PZT) powder and a polyimide (PI) matrix composite. Various parameters, including the optimal mixing ratio of PI/PZT, ultrasonic treatment, homogenization, vacuum oven, and UV/O₃ treatment, were optimized to achieve a uniform piezoelectric composite. A PZT content of 30 wt% and 20 minutes of homogenization were identified as the most effective conditions for increasing the uniformity of the composite. The optimized composite exhibited a high piezoelectric coefficient, a typical P-E hysteresis loop, and dielectric properties, exhibiting a voltage output that adjusts in response to variations in the applied touch force. This study provides foundational data for the uniform fabrication of flexible piezoelectric energy harvesters and next-generation miniaturized electronic devices.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of SiCf/SiC Composites with a BN Interphase Prepared by the Wet Method
- Kyung Ho Kim, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):530-536. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00339
- 981 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
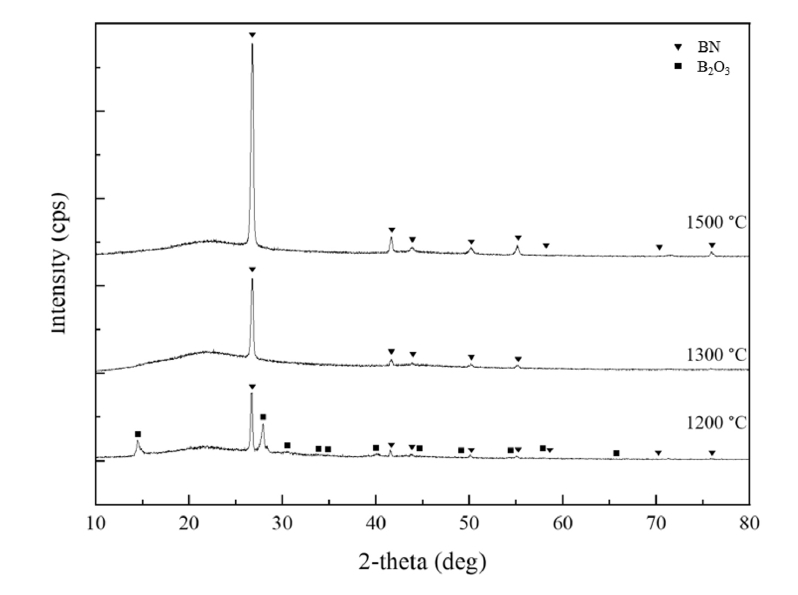
PDF - This study presents a cost-effective wet chemical coating process for fabricating a boron nitride (BN) interphase on silicon carbide (SiC) fibers, increasing the oxidation resistance and performance of SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composites. Using urea as a precursor, optimal nitriding conditions were determined by adjusting the composition, concentration, and immersion time. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed distinct BN phase formation at 1300°C and 1500°C, while a mixture of BN and B₂O₃ was observed at 1200°C. HF treatment improved coating uniformity by removing SiO₂ layers formed during the de-sizing process. Optimization of the boric acid-to-urea molar ratio resulted in a uniform, 130-nm-thick BN layer. This study demonstrates that the wet coating process offers a viable and economical alternative to chemical vapor deposition for fabricating high-performance BN interphases in SiCf/SiC composites that are suitable for high-temperature applications.
- [Korean]
- Inter-laminar Strength of NITE-SiC/SiC Composites With Various Fiber Reinforcing Architecture
- Jong-il Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):437-444. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00248
- 893 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
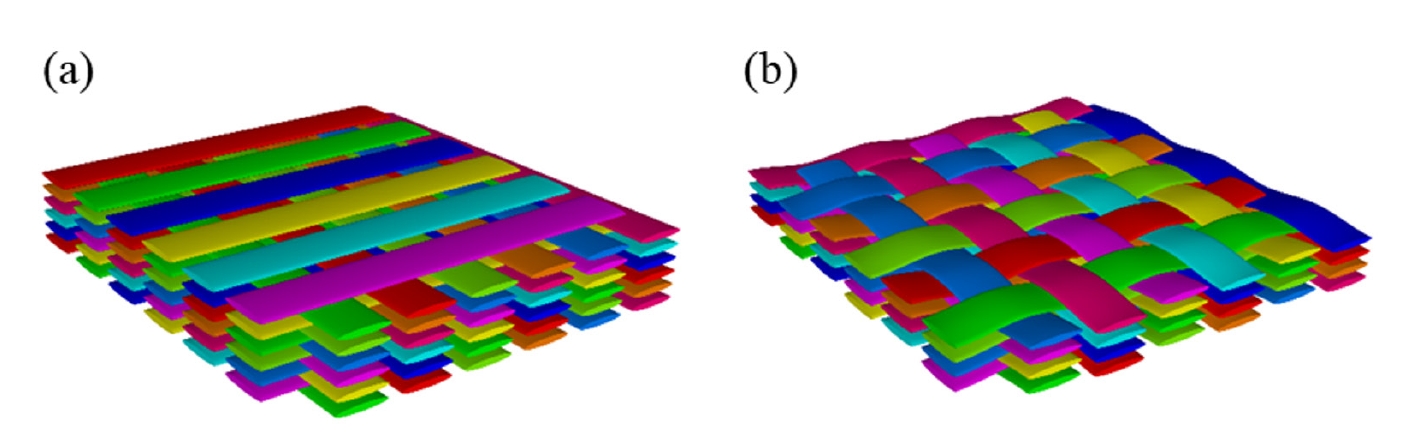
PDF - The mechanical performance of SiC/SiC composites is significantly influenced by the architecture of fiber reinforcement. Among the various fabrication methods, the nano-powder infiltration transition/eutectic (NITE) process is a promising technique that is capable of achieving a dense and stoichiometric SiC matrix. The reinforcement architecture, such as cross-ply (CP) or woven prepreg (WP), is determined during the preform stage of the NITE process, which is crucial in determining the mechanical properties of SiC/SiC composites. In this study, the tensile test and double notch shear (DNS) test were conducted using NITE-SiC/SiC composites to investigate the effect of the fiber reinforcing architecture on the fracture mechanism of SiC/SiC composites. The tensile strength and maximum shear strength of both CP and WP specimens were nearly identical. However, other mechanical properties, particularly those of CP specimens, exhibited significant variability. A comparison of fracture surfaces and load-displacement curve analyses from the DNS tests revealed that the cross points of the longitudinal or transverse fibers act as obstacles to both deformation and crack propagation. These obstacles were found to be more densely distributed in WP specimens than in CP specimens. The variability observed in the mechanical properties of CP specimens is likely due to size effects caused by the sparser distribution of these obstacles compared to the WP specimens.
- [English]
- Machine Learning Modeling of the Mechanical Properties of Al2024-B4C Composites
- Maurya A. K., Narayana P. L., Wang X.-S., Reddy N. S.
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):382-389. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00234
- 1,562 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
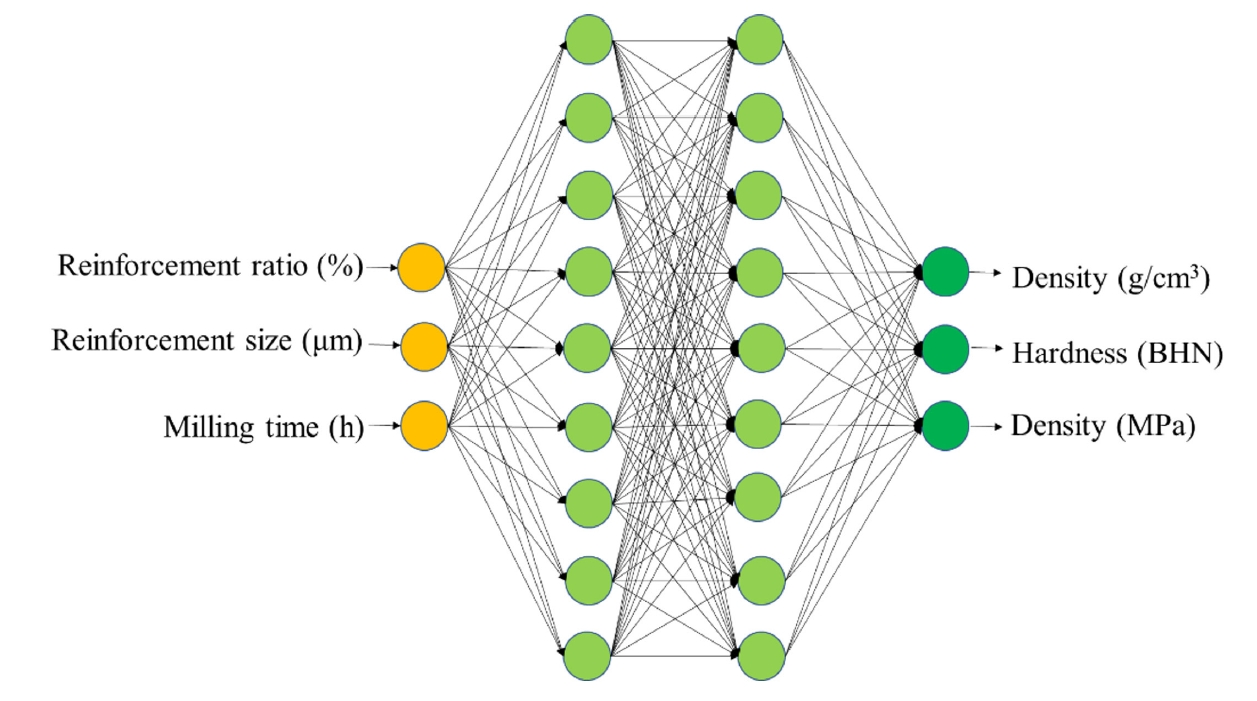
PDF - Aluminum-based composites are in high demand in industrial fields due to their light weight, high electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Due to its unique advantages for composite fabrication, powder metallurgy is a crucial player in meeting this demand. However, the size and weight fraction of the reinforcement significantly influence the components' quality and performance. Understanding the correlation of these variables is crucial for building high-quality components. This study, therefore, investigated the correlations among various parameters—namely, milling time, reinforcement ratio, and size—that affect the composite’s physical and mechanical properties. An artificial neural network model was developed and showed the ability to correlate the processing parameters with the density, hardness, and tensile strength of Al2024-B4C composites. The predicted index of relative importance suggests that the milling time has the most substantial effect on fabricated components. This practical insight can be directly applied in the fabrication of high-quality Al2024-B4C composites.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of 3D Aligned h-BN based Polymer Composites with Enhanced Mechanical Properties for Battery Housing
- Kiho Song, Hyunseung Song, Sang In Lee, Changui Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(4):329-335. Published online August 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00220
- 1,395 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
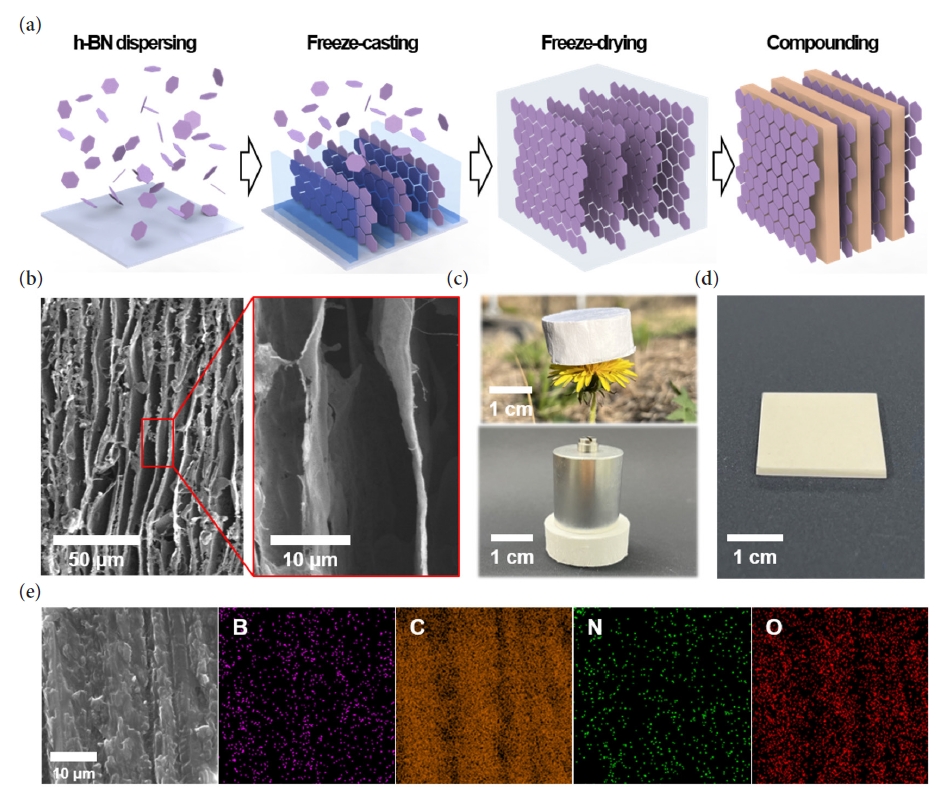
Supplementary Material - As the demand for electric vehicles increases, the stability of batteries has become one of the most significant issues. The battery housing, which protects the battery from external stimuli such as vibration, shock, and heat, is the crucial element in resolving safety problems. Conventional metal battery housings are being converted into polymer composites due to their lightweight and improved corrosion resistance to moisture. The transition to polymer composites requires high mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and thermal stability. In this paper, we proposes a high-strength nanocomposite made by infiltrating epoxy into a 3D aligned h-BN structure. The developed 3D aligned h-BN/epoxy composite not only exhibits a high compressive strength (108 MPa) but also demonstrates excellent electrical insulation and thermal stability, with a stable electrical resistivity at 200 °C and a low thermal expansion coefficient (11.46ⅹppm/℃), respectively.
- [English]
- Research Trends in Electromagnetic Shielding using MXene-based Composite Materials
- Siyeon Kim, Jongmin Byun
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):57-76. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.57
- 8,304 View
- 163 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
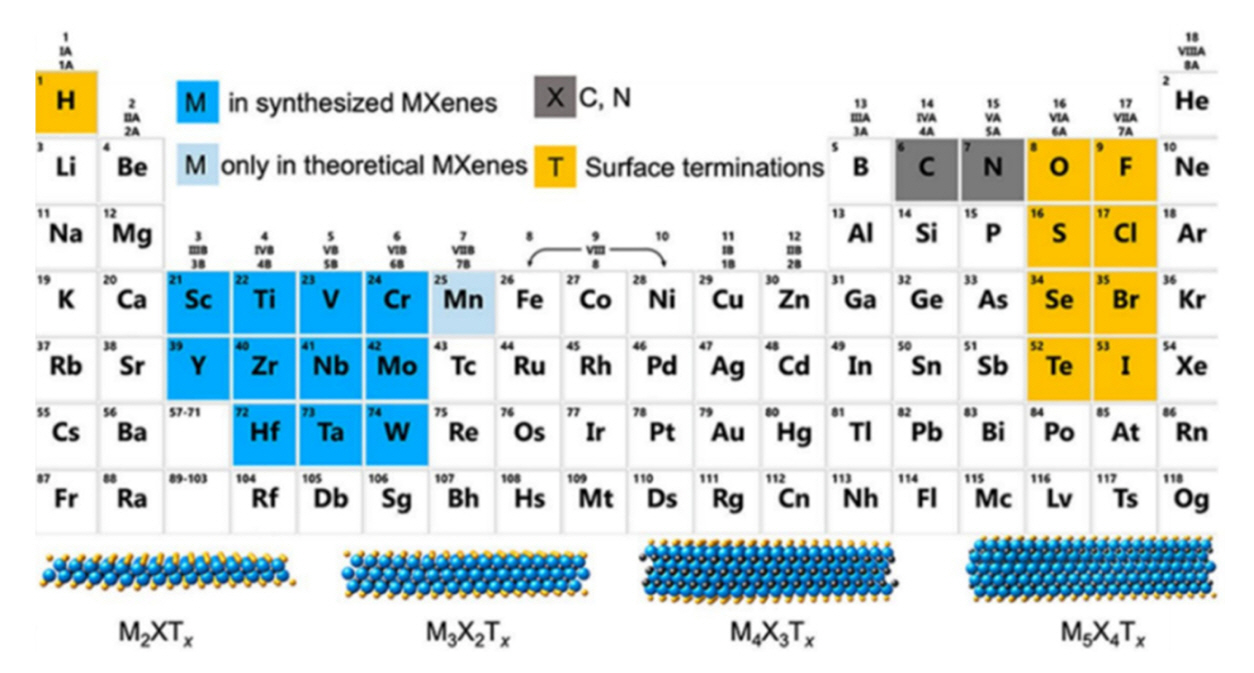
PDF Recent advancements in electronic devices and wireless communication technologies, particularly the rise of 5G, have raised concerns about the escalating electromagnetic pollution and its potential adverse impacts on human health and electronics. As a result, the demand for effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials has grown significantly. Traditional materials face limitations in providing optimal solutions owing to inadequacy and low performance due to small thickness. MXene-based composite materials have emerged as promising candidates in this context owing to their exceptional electrical properties, high conductivity, and superior EMI shielding efficiency across a broad frequency range. This review examines the recent developments and advantages of MXene-based composite materials in EMI shielding applications, emphasizing their potential to address the challenges posed by electromagnetic pollution and to foster advancements in modern electronics systems and vital technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
Pramod D. Mhase, Varsha C. Pujari, Santosh S. Jadhav, Abdullah G. Al-Sehemi, Sarah Alsobaie, Sunil M. Patange
Composites Communications.2025; 54: 102284. CrossRef - Microstructure tailoring of Nb-based MAX phase by low temperature synthesis with layer-structured Nb2C powder and molten salt method
Chaehyun Lim, Wonjune Choi, Jongmin Byun
Materials Characterization.2025; 225: 115106. CrossRef - Fabrication of MOF@MXene composites via surface modification of MXene under acidic conditions
Ji-Haeng Jeong, Woong-Ryeol Yu
Functional Composites and Structures.2025; 7(2): 025006. CrossRef - V2CTx MXene@ZIF-8 composite as an efficient adsorbent for Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution
Sarina Khojasteh Fard, Golshan Mazloom, Manoochehr Sobhani, Mohsen Tamtaji
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2025; 13(6): 120099. CrossRef
- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
- [Korean]
- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
- Jin-Kwon Kim, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Nahm Sahn, Sung-Soo Ryu, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(5):409-414. Published online October 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.5.409
- 589 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
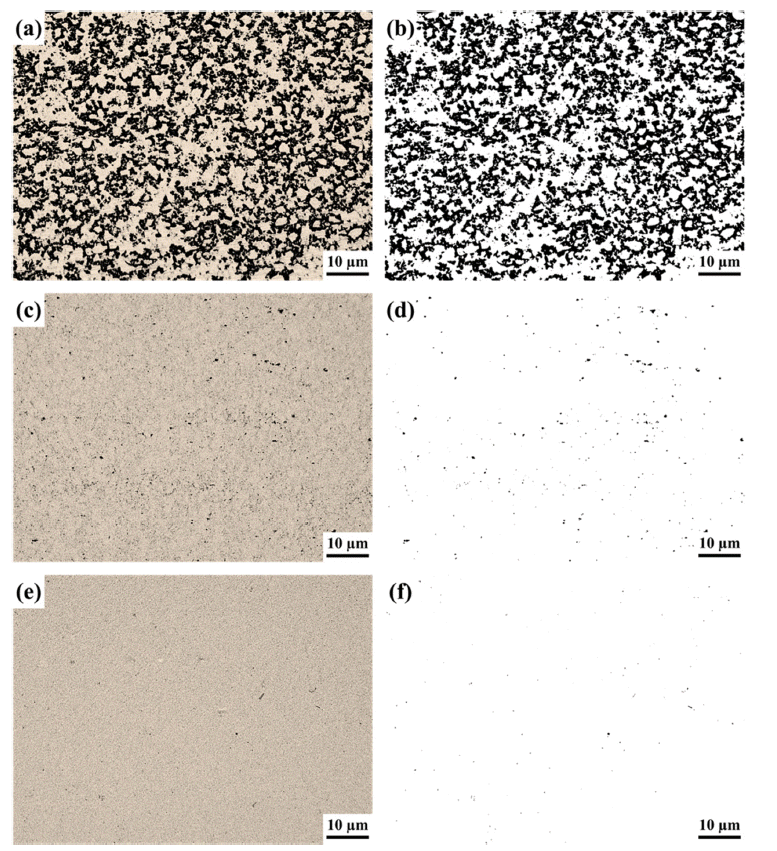
PDF YSZ (Y2O3-stabilized zirconia)-based ceramics have excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength and wear resistance. In the application, YSZ is utilized in the bead mill, a fine-grinding process. YSZ-based parts, such as the rotor and pin, can be easily damaged by continuous application with high rpm in the bead mill process. In that case, adding WC particles improves the tribological and mechanical properties. YSZ-30 vol.% WC composite ceramics are manufactured via hot pressing under different pressures (10/30/60 MPa). The hot-pressed composite ceramics measure the physical properties, such as porosity and bulk density values. In addition, the phase formation of these composite ceramics is analyzed and discussed with those of physical properties. For the increased applied pressure of hot pressing, the tetragonality of YSZ and the crystallinity of WC are enhanced. The mechanical properties indicate an improved tendency with the increase in the applied pressure of hot pressing.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Polymer Composite with Enhanced Insulation and Mechanical Properties using Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
- Junhyeok Choi, Sangin Lee, Kiho Song, Taekyung Kim, Changui Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):356-362. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.356
- 957 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
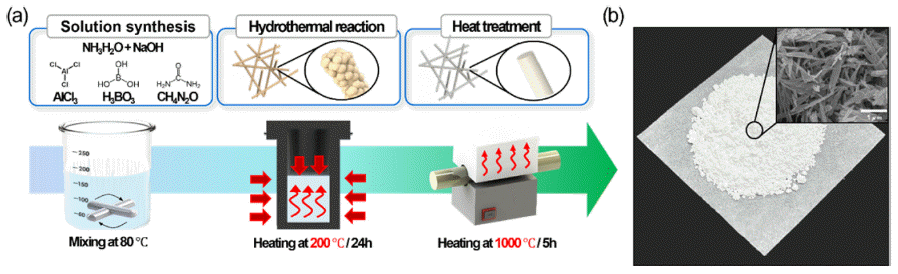
PDF Inorganic-organic composites find extensive application in various fields, including electronic devices and light-emitting diodes. Notably, encapsulation technologies are employed to shield electronic devices (such as printed circuit boards and batteries) from stress and moisture exposure while maintaining electrical insulation. Polymer composites can be used as encapsulation materials because of their controllable mechanical and electrical properties. In this study, we propose a polymer composite that provides good electrical insulation and enhanced mechanical properties. This is achieved by using aluminum borate nanowhiskers (ABOw), which are fabricated using a facile synthesis method. The ABOw fillers are created via a hydrothermal method using aluminum chloride and boric acid. We confirm that the synthesis occurs in various morphologies based on the molar ratio. Specifically, nanowhiskers are synthesized at a molar ratio of 1:3 and used as fillers in the composite. The fabricated ABOw/epoxy composites exhibit a 48.5% enhancement in mechanical properties, similar to those of pure epoxy, while maintaining good electrical insulation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Al18B4O33 Spherical Powder with Increased Fluidity via Control of B2O3 Particle Size and Distribution
Kiho Song, Sang in Lee, Hyunseung Song, Changui Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(6): 513. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Al18B4O33 Spherical Powder with Increased Fluidity via Control of B2O3 Particle Size and Distribution
- [Korean]
- Epoxy-Based Siloxane/Silica Composites for Electronic Packaging by Composition and Molecular Structure of Siloxane, and Analysis of Changes in Properties
- Junho Jang, Dong Jun Kang, Hyeon-Gyun Im
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):346-355. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.346
- 1,160 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
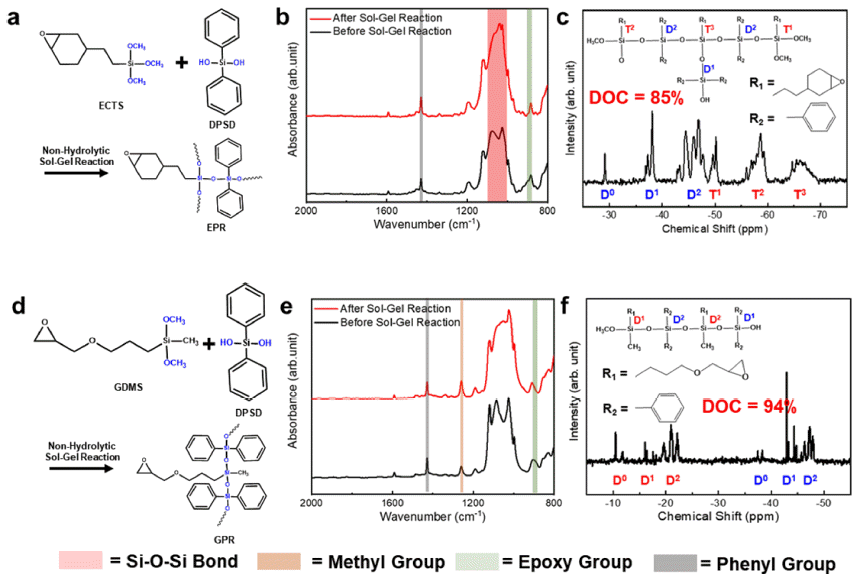
PDF Epoxy-based composites find extensive application in electronic packaging due to their excellent processability and insulation properties. However, conventional epoxy-based polymers exhibit limitations in terms of thermal properties and insulation performance. In this study, we develop epoxy-based siloxane/silica composites that enhance the thermal, mechanical, and insulating properties of epoxy resins. This is achieved by employing a sol–gelsynthesized siloxane hybrid and spherical fused silica particles. Herein, we fabricate two types of epoxy-based siloxane/ silica composites with different siloxane molecular structures (branched and linear siloxane networks) and investigate the changes in their properties for different compositions (with or without silica particles) and siloxane structures. The presence of a branched siloxane structure results in hardness and low insulating properties, while a linear siloxane structure yields softness and highly insulating properties. Both types of epoxy-based siloxane/silica composites exhibit high thermal stability and low thermal expansion. These properties are considerably improved by incorporating silica particles. We expect that our developed epoxy-based composites to hold significant potential as advanced electronic packaging materials, offering high-performance and robustness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Toughening epoxy matrices via elastomeric blending for enhanced compatibility with auxetic reinforcements in composites
Usama Khalid, Shiza Shahid, Muhammad Bilal Qadir, Mumtaz Ali, Zubair Khaliq, Aamir Naseem Satti, Zaheer Anwar Randhawa, Danish Umer
Mechanics Based Design of Structures and Machines.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Enhanced Epoxy Composites Reinforced by 3D-Aligned Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
Hyunseung Song, Kiho Song, Haejin Hwang, Changui Ahn
Materials.2024; 17(19): 4727. CrossRef
- Toughening epoxy matrices via elastomeric blending for enhanced compatibility with auxetic reinforcements in composites
- [Korean]
- Experimental Study on Improving Thermal Shock Resistance of Cement Composite Incorporating Hollow Glass Microspheres
- Yomin Choi, Hyun‐Gyoo Shin
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(6):505-510. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.6.505

- 759 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The thermal shock resistance of cement composites with hollow glass microspheres (HGM) is investigated. Cement composites containing various concentrations of HGM are prepared and their properties studied. The density, thermal conductivity, and coefficient of thermal expansion of the composites decrease with increasing HGM concentration. A thermal shock test is performed by cycling between -60 and 50ºC. After the thermal shock test, the compressive strength of the cement composite without HGM decreases by 28.4%, whereas the compressive strength of the cement composite with 30 wt% HGM decreases by 5.7%. This confirms that the thermal shock resistance of cement is improved by the incorporation of HGM. This effect is attributed to the reduction of the thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal expansion of the cement composite because of the incorporation of HGM, thereby reducing the occurrence of defects due to external temperature changes.
- [Korean]
- Comparison of Properties with Different Sintering Process of 3Y-TZP/WC Composites
- Min-Soo Nam, Jae-Hyung Choi, Sahn Nahm, Seongwon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):424-431. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.424
- 889 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
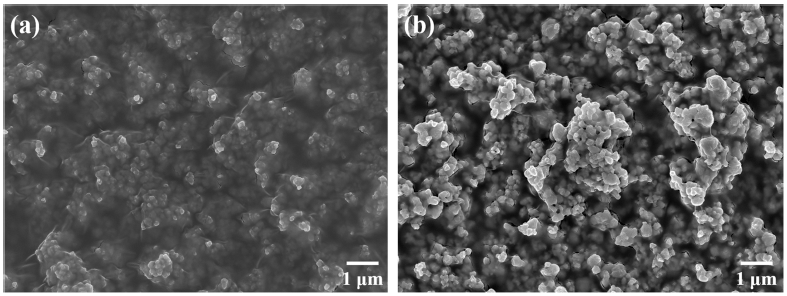
PDF 3Y-TZP ceramics obtained by doping 3 mol.% of Y2O3 to ZrO2 to stabilize the phase transition are widely used in the engineering ceramic industry due to their excellent mechanical properties such as high strength, fracture toughness, and wear resistance. An additional increase in mechanical properties is possible by manufacturing a composite in which a high-hardness material such as oxide or carbide is added to the 3Y-TZP matrix. In this study, composite powder was prepared by dispersing a designated percentage of WC in the 3Y-TZP matrix, and the results were compared after manufacturing the composite using the different processes of spark plasma sintering and HP. The difference between the densification behavior and porosity with the process mechanism was investigated. The correlation between the process conditions and phase formation was examined based on the crystalline phase formation behavior. Changes to the microstructure according to the process conditions were compared using field-emission scanning electron microscopy. The toughness-strengthening mechanism of the composite with densification and phase formation was also investigated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
Jin-Kwon Kim, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Nahm Sahn, Sung-Soo Ryu, Seongwon Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(5): 409. CrossRef
- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
- [Korean]
- Interfacial Reaction between Spark Plasma Sintered High-entropy Alloys and Cast Aluminum
- Min-Sang Kim, Hansol Son, Cha Hee Jung, Juyeon Han, Jung Joon Kim, Young-Do Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Se Hoon Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):213-218. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.213

- 889 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study investigates the interfacial reaction between powder-metallurgy high-entropy alloys (HEAs) and cast aluminum. HEA pellets are produced by the spark plasma sintering of Al0.5CoCrCu0.5FeNi HEA powder. These sintered pellets are then placed in molten Al, and the phases formed at the interface between the HEA pellets and cast Al are analyzed. First, Kirkendall voids are observed due to the difference in the diffusion rates between the liquid Al and solid HEA phases. In addition, although Co, Fe, and Ni atoms, which have low mixing enthalpies with Al, diffuse toward Al, Cu atoms, which have a high mixing enthalpy with Al, tend to form Al–Cu intermetallic compounds. These results provide guidelines for designing Al matrix composites containing high-entropy phases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Simultaneous enhancement of strength and ductility of Al matrix composites enabled by submicron-sized high-entropy alloy phases
Chahee Jung, Seungin Nam, Hansol Son, Juyeon Han, Jaewon Jeong, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Seok Su Sohn, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2024; 33: 1470. CrossRef
- Simultaneous enhancement of strength and ductility of Al matrix composites enabled by submicron-sized high-entropy alloy phases
- [Korean]
- Preparation of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticle Decorated on Electrospun Carbon Nanofiber Composite Electrodes for Supercapacitors
- Hyewon Hwang, Seoyeon Yuk, Minsik Jung, Dongju Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):470-477. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.470
- 749 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
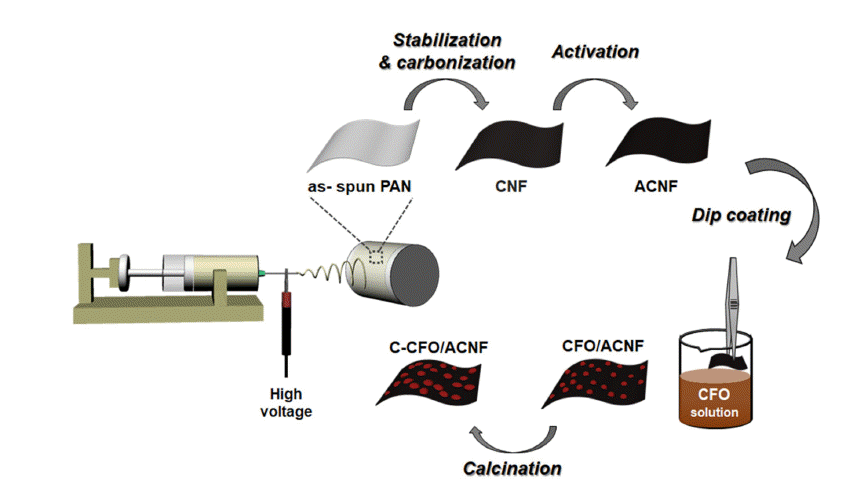
PDF Energy storage systems should address issues such as power fluctuations and rapid charge-discharge; to meet this requirement, CoFe2O4 (CFO) spinel nanoparticles with a suitable electrical conductivity and various redox states are synthesized and used as electrode materials for supercapacitors. In particular, CFO electrodes combined with carbon nanofibers (CNFs) can provide long-term cycling stability by fabricating binder-free three-dimensional electrodes. In this study, CFO-decorated CNFs are prepared by electrospinning and a low-cost hydrothermal method. The effects of heat treatment, such as the activation of CNFs (ACNFs) and calcination of CFO-decorated CNFs (C-CFO/ACNFs), are investigated. The C-CFO/ACNF electrode exhibits a high specific capacitance of 142.9 F/g at a scan rate of 5 mV/s and superior rate capability of 77.6% capacitance retention at a high scan rate of 500 mV/s. This electrode also achieves the lowest charge transfer resistance of 0.0063 Ω and excellent cycling stability (93.5% retention after 5,000 cycles) because of the improved ion conductivity by pathway formation and structural stability. The results of our work are expected to open a new route for manufacturing hybrid capacitor electrodes containing the C-CFO/ACNF electrode that can be easily prepared with a low-cost and simple process with enhanced electrochemical performance.
- [Korean]
- Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ti-20Mo-0.5EB Composites
- Suhyun Bae, Wonki Jeong, Se-Eun Shin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):403-409. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.403
- 650 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, Ti-Mo-EB composites are prepared by ball milling and spark plasma sintering (SPS) to obtain a low elastic modulus and high strength and to evaluate the microstructure and mechanical properties as a function of the process conditions. As the milling time and sintering temperature increased, Mo, as a β-Ti stabilizing element, diffused, and the microstructure of β-Ti increased. In addition, the size of the observed phase was small, so the modulus and hardness of α-Ti and β-Ti were measured using nanoindentation equipment. In both phases, as the milling time and sintering temperature increased, the modulus of elasticity decreased, and the hardness increased. After 12 h of milling, the specimen sintered at 1000°C showed the lowest values of modulus of elasticity of 117.52 and 101.46 GPa for α-Ti and β-Ti, respectively, confirming that the values are lower compared to the that in previously reported studies.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characteristics of YSZ-TiC Ceramics Composite by Using Hot Pressing
- Jae-Hyung Choi, Ji-Young Choi, Seongwon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):381-388. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.381
- 1,515 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Zirconia has excellent mechanical properties, such as high fracture toughness, wear resistance, and flexural strength, which make it a candidate for application in bead mills as milling media as well as a variety of components. In addition, enhanced mechanical properties can be attained by adding oxide or non-oxide dispersing particles to zirconia ceramics. In this study, the densification and mechanical properties of YSZ-TiC ceramic composites with different TiC contents and sintering temperatures are investigated. YSZ - x vol.% TiC (x=10, 20, 30) system is selected as compositions of interest. The mixed powders are sintered using hot pressing (HP) at different temperatures of 1300, 1400, and 1500°C. The densification behavior and mechanical properties of sintered ceramics, such as hardness and fracture toughness, are examined.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
Jin-Kwon Kim, Jae-Hyeong Choi, Nahm Sahn, Sung-Soo Ryu, Seongwon Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(5): 409. CrossRef
- Phase Formation and Mechanical Property of YSZ‒30 vol.% WC Composite Ceramics Fabricated by Hot Pressing
- [Korean]
- Experimental Study on Improving Compressive Strength of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Reinforced Cement Composite
- Yomin Choi, Hyun‐Gyoo Shin
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(6):503-508. Published online December 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.6.503

- 643 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The mechanical properties and microstructures of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN)-reinforced cement composites are experimentally studied for three and seven curing days. Various sizes (5, 10, and 18 μm) and concentrations (0.1%, 0.25%, 0.5%, and 1.0%) of h-BN are dispersed by the tip ultrasonication method in water and incorporated into the cement composite. The compressive strength of the h-BN reinforced cements increases by 40.9%, when 0.5 wt% of 18 μm-sized h-BN is added. However, the compressive strength decreases when the 1.0 wt% cement composite is added, owing to the aggregation of the h-BNs in the cement composite. The microstructural characterization of the h-BN-reinforced cement composite indicates that the h-BNs act as bridges connecting the cracks, resulting in improved mechanical properties for the reinforced cement composite.
- [Korean]
- The Effects of Kaolin Addition on the Properties of Reticulated Porous Diatomite-kaolin Composites
- Chae-Young Lee, Sujin Lee, Jang-Hoon Ha, Jongman Lee, In-Hyuck Song, Kyoung-Seok Moon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(4):325-332. Published online August 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.4.325
- 925 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, the effects of kaolin addition on the properties of reticulated porous diatomite-kaolin composites are investigated. A reticulated porous diatomite-kaolin composite is prepared using the replica template method. The microstructure and pore characteristics of the reticulated porous diatomite-kaolin composites are analyzed by controlling the PPI value (45, 60, and 80 PPI) of the polyurethane foam (which are used as the polymer template), the ball-milling time (8 and 24 h), and the amount of kaolin (0–50 wt. %). The average pore size decreases as the amount of kaolin increases in the reticulated porous diatomite-kaolin composite. As the amount of kaolin increases, it can be determined that the amount of inter-connected pore channels is reduced because the plate-shaped kaolin particles connect the gaps between irregular diatomite particles. Consequently, a higher kaolin percentage affects the overall mechanical properties by improving the pore channel connectivity. The effect of kaolin addition on the basic properties of the reticulated porous diatomite-kaolin composite is further discussed with characterization data such as pore size distribution, scanning electron microscopy images, and compressive strength.
- [Korean]
- Recent Development in Performance Enhancement of PVDF-Nanopowder Composite-based Energy Harvesting Devices
- Geon-Ju Choi, Il-Kyu Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):247-255. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.247
- 1,150 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Recently, interest in technology for eco-friendly energy harvesting has been increasing. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is one of the most fascinating materials that has been used in energy harvesting technology as well as micro-filters by utilizing an electrostatic effect. To enhance the performance of the electrostatic effect-based nanogenerator, most studies have focused on enlarging the contact surface area of the pair of materials with different triboelectric series. For this reason, one-dimensional nanofibers have been widely used recently. In order to realize practical energy-harvesting applications, PVDF nanofibers are modified by enlarging their contact surface area, modulating the microstructure of the surface, and maximizing the fraction of the β-phase by incorporating additives or forming composites with inorganic nanoparticles. Among them, nanocomposite structures incorporating various nanoparticles have been widely investigated to increase the β-phase through strong hydrogen bonding or ion-dipole interactions with -CF2/CH2- of PVDF as well as to enhance the mechanical strength. In this study, we report the recent advances in the nanocomposite structure of PVDF nanofibers and inorganic nanopowders.
- [Korean]
- Development of Fe-Mn-based Hybrid Materials Containing Nano-scale Oxides by a Powder Metallurgical Route
- Jonggyu Jeon, Jungjoon Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(3):203-209. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.3.203

- 893 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The automotive industry has focused on the development of metallic materials with high specific strength, which can meet both fuel economy and safety goals. Here, a new class of ultrafine-grained high-Mn steels containing nano-scale oxides is developed using powder metallurgy. First, high-energy mechanical milling is performed to dissolve alloying elements in Fe and reduce the grain size to the nanometer regime. Second, the ball-milled powder is consolidated using spark plasma sintering. During spark plasma sintering, nanoscale manganese oxides are generated in Fe-15Mn steels, while other nanoscale oxides (e.g., aluminum, silicon, titanium) are produced in Fe-15Mn-3Al-3Si and Fe-15Mn-3Ti steels. Finally, the phases and resulting hardness of a variety of high-Mn steels are compared. As a result, the sintered pallets exhibit superior hardness when elements with higher oxygen affinity are added; these elements attract oxygen from Mn and form nanoscale oxides that can greatly improve the strength of high-Mn steels.
- [Korean]
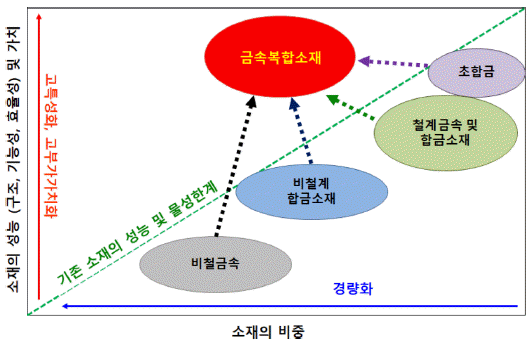
- Recent Trends and Application Status of the Metal Matrix Composites (MMCs)
- Hyo-Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):164-173. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.164
- 1,409 View
- 38 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metal matrix composites (MMCs), which are a combination of two or more constituents with different physical or chemical properties, are today receiving great attention in various areas, as they have high specific strength, corrosion resistance, fatigue strength, and good tribological properties. This paper presents a research review on the combination of matrix and reinforced materials, fabrication processes, and application status of metal matrix composites. In this paper, we aim to discuss and review the importance of metal composite materials as advanced materials that can be used in various applications such as transportation, defense, sports, and extreme environments. In addition, the applicability and technology development trends in new process technology fields such as additive manufacturing of metal composites will be described.
- [English]
- Spark Plasma Sintering of the Ni-graphite Composite Powder Prepared by Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid and Its Properties
- Minh Thuyet-Nguyena, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):14-24. Published online February 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.14

- 983 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this work, the electrical explosion of wire in liquid and subsequent spark plasma sintering (SPS) was introduced for the fabrication of Ni-graphite nanocomposites. The fabricated composite exhibited good enhancements in mechanical properties, such as yield strength and hardness, but reduced the ductility in comparison with that of nickel. The as-synthesized Ni-graphite (5 vol.% graphite) nanocomposite exhibited a compressive yield strength of 275 MPa (about 1.6 times of SPS-processed monolithic nickel ~170 MPa) and elongation to failure ~22%. The hardness of Nigraphite composite had a value of 135.46 HV, which is about 1.3 times higher than that of pure SPS-processed Ni (105.675 HV). In terms of processing, this work demonstrated that this processing route is a novel, simple, and low-cost method for the synthesis of nickel-graphite composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Top-down strategies for achieving high-quality graphene: Recent advancements
Arpana Agrawal
Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry.2025; 142: 103. CrossRef - Electrodeposition of nickel-titanium dioxide coatings and powders from aqueous sulfate solutions
Tazhibayeva Aigerim Shotaevna, Bayeshova Azhar Kospanovna, Bayeshov Abduali, Osińska Małgorzata
Polyhedron.2025; 277: 117571. CrossRef
- Top-down strategies for achieving high-quality graphene: Recent advancements
- [Korean]
- Effect of High Frequency Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Wear Properties of Ni based Self Fluxing Composite Coating Layer Manufactured by HVOF Spray Process
- Dong-Yeol Wi, Gi-Su Ham, Sun-Hong Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):421-431. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.421

- 804 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, the formation, microstructure, and wear properties of Colmonoy 88 (Ni-17W-15Cr-3B-4Si wt.%) + Stellite 1 (Co-32Cr-17W wt.%) coating layers fabricated by high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) spraying are investigated. Colmonoy 88 and Stellite 1 powders were mixed at a ratio of 1:0 and 5:5 vol.%. HVOF sprayed selffluxing composite coating layers were fabricated using the mixed powder feedstocks. The microstructures and wear properties of the composite coating layers are controlled via a high-frequency heat treatment. The two coating layers are composed of γ-Ni, Ni3B, W2B, and Cr23C6 phases. Co peaks are detected after the addition of Stellite 1 powder. Moreover, the WCrB2 hard phase is detected in all coating layers after the high-frequency heat treatment. Porosities were changed from 0.44% (Colmonoy 88) to 3.89% (Colmonoy 88 + ST#1) as the content of Stellite 1 powder increased. And porosity is denoted as 0.3% or less by inducing high-frequency heat treatment. The wear results confirm that the wear property significantly improves after the high-frequency heat treatment, because of the presence of wellcontrolled defects in the coating layers. The wear surfaces of the coated layers are observed and a wear mechanism for the Ni-based self-fluxing composite coating layers is proposed.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Graphene Coated Aluminum Powders by Self-assemble Reaction
- Jin Uk Hwang, Woo Seong Tak, Sang Yong Nam, Woo Sik Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):383-388. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.383

- 950 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF To improve the mechanical properties of aluminum, graphene has been used as a reinforcing material, yielding graphene-reinforced aluminum matrix composites (GRAMCs). Dispersion of graphene materials is an important factor that affects the properties of GRAMCs, which are mainly manufactured by mechanical mixing methods such as ball milling. However, the use of only mechanical mixing process is limited to achieve homogeneous dispersion of graphene. To overcome this problem, in this study, we have prepared composite materials by coating aluminum particles with graphene by a self-assembly reaction using poly vinylalcohol and ethylene diamine as coupling agents. The scanning electron microscopy and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy results confirm the coating of graphene on the Al surface. Bulk density of the sintered composites by spark plasma sintering achieved a relative density of over 99% up to 0.5 wt.% graphene oxide content.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 492. CrossRef
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- [Korean]
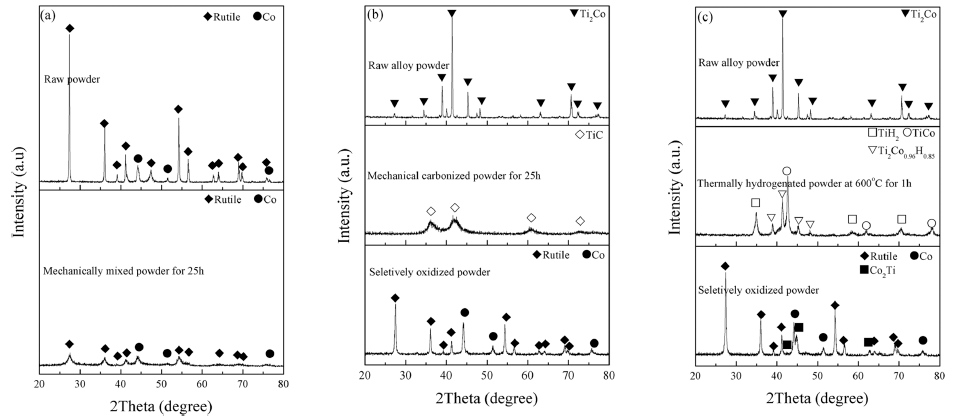
- The Microstructure and the Mechanical Properties of Sintered TiO2-Co Composite Prepared Via Thermal Hydrogenation Method
- Myeongsun Ko, Ilsong Park, Jeshin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):290-298. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.290
- 396 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF TiO2-particles containing Co grains are fabricated via thermal hydrogenation and selective oxidation of Ti-Co alloy. For comparison, TiO2-Co composite powders are prepared by two kinds of methods which were the mechanical carbonization and oxidation process, and the conventional mixing process. The microstructural characteristics of the prepared composites are analyzed by X-ray diffraction, field-emission scattering electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. In addition, the composite powders are sintered at 800°C by spark plasma sintering. The flexural strength and fracture toughness of the sintered samples prepared by thermal hydrogenation and mechanical carbonization are found to be higher than those of the samples prepared by the conventional mixing process. Moreover, the microstructures of sintered samples prepared by thermal hydrogenation and mechanical carbonization processes are found to be similar. The difference in the mechanical properties of sintered samples prepared by thermal hydrogenation and mechanical carbonization processes is attributed to the different sizes of metallic Co particles in the samples.
- [English]
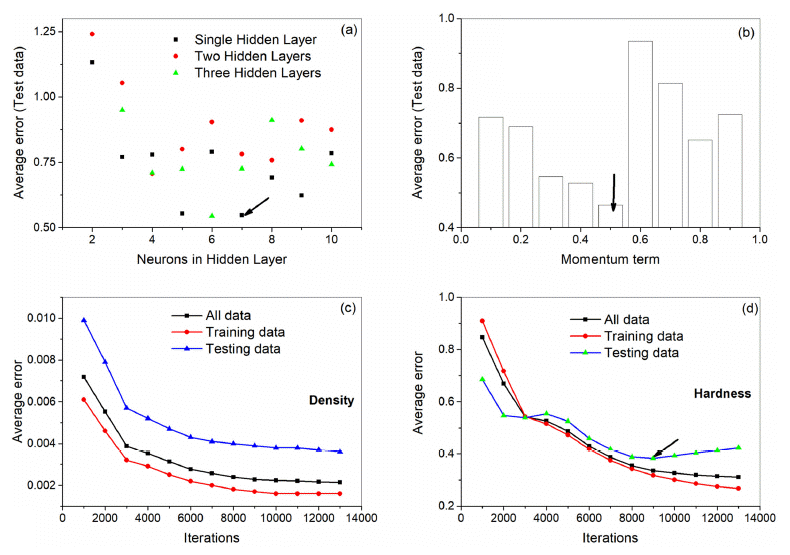
- Modeling the Density and Hardness of AA2024-SiC Nanocomposites
- A-Hyun Jeon, Hong In Kim, Hyokyung Sung, N. S. Reddy
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(4):275-281. Published online August 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.4.275
- 1,010 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF An artificial neural network (ANN) model is developed for the analysis and simulation of correlation between flake powder metallurgy parameters and properties of AA2024-SiC nanocomposites. The input parameters of the model are AA 2024 matrix size, ball milling time, and weight percentage of SiC nanoparticles and the output parameters are density and hardness. The model can predict the density and hardness of the unseen test data with a correlation of 0.986 beyond the experimental data. A user interface is designed to predict properties at new instances. We have used the model to simulate the individual as well as the combined influence of parameters on the properties. Moreover, we have analyzed the calculated results from the powder metallurgical point of view. The developed model can be used as a guide for further composite development.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Highly Reactive Al/CuO Nano-composite using Graphene Oxide
- YeSeul Lim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):220-224. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.220

- 808 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The aluminum (Al)/copper oxide (CuO) complex is known as the most promising material for thermite reactions, releasing a high heat and pressure through ignition or thermal heating. To improve the reaction rate and wettability for handling safety, nanosized primary particles are applied on Al/CuO composite for energetic materials in explosives or propellants. Herein, graphene oxide (GO) is adopted for the Al/CuO composites as the functional supporting materials, preventing a phase-separation between solvent and composites, leading to a significantly enhanced reactivity. The characterizations of Al/CuO decorated on GO(Al/CuO/GO) are performed through scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy mapping analysis. Moreover, the functional bridging between Al/CuO and GO is suggested by identifying the chemical bonding with GO in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis. The reactivity of Al/CuO/GO composites is evaluated by comparing the maximum pressure and rate of the pressure increase of Al/CuO and Al/CuO/GO. The composites with a specific concentration of GO (10 wt%) demonstrate a well-dispersed mixture in hexane solution without phase separation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Controlling Particle Size of Recycled Copper Oxide Powder for Copper Thermite Welding Characteristics
Hansung Lee, Minsu Kim, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 332. CrossRef
- Controlling Particle Size of Recycled Copper Oxide Powder for Copper Thermite Welding Characteristics
- [Korean]
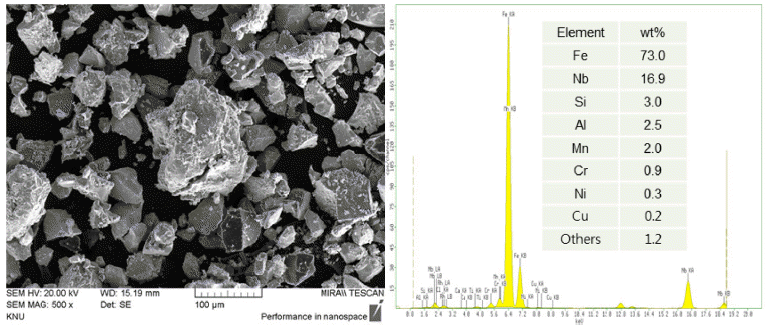
- Microstructure and Characterization of Overlay Welding Layer using Fe-based Composite Powders
- Hong Min, Jong-Jae Lee, Jin Kyu Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):214-219. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.214
- 757 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, the microstructure and characterization of an overlay welding layer using Fe-based composite powders are reported. The effects of the number of passes and composition of powders on the microstructure and mechanical properties are investigated in detail. The welding wire and powders are deposited twice on a stainless-steel rod using a laser overlay welding process. The microstructure and structural characterization are performed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The mechanical properties of the first and second overlay layers are analyzed through the micro-Vickers-hardness tester and abrasion wear tester. In the second overlay layer, the hardness and specific wear are approximately 840 Hv and 2.0 × 10−5 mm3/Nm, respectively. It is suggested that the increase of the volume fractions of (Cr,Fe)7C3 and NbC phases in the second welding layer enhances the hardness and wear resistance.
- [Korean]
- A Comparison Study of Output Performance of Organic-Inorganic Piezoelectric Nanocomposite Made of Piezoelectric/Non-piezoelectric Polymers and BaTiO3 Nanoparticles
- Dong Yeol Hyeon, Kwi-Il Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):119-125. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.119
- 958 View
- 3 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
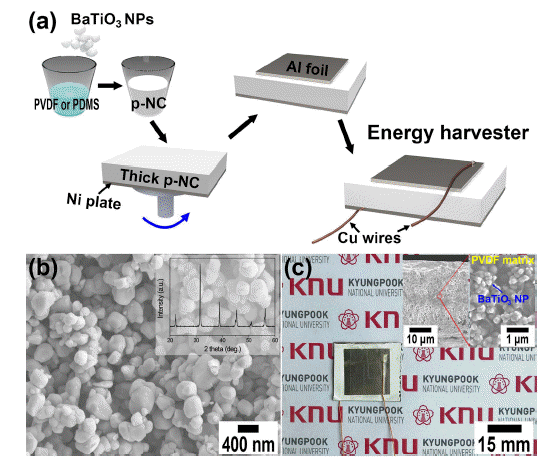
PDF Piezoelectric energy harvesting technology is attracting attention, as it can be used to convert more accessible mechanical energy resources to periodic electricity. Recent developments in the field of piezoelectric energy harvesters (PEHs) are associated with nanocomposites made from inorganic piezoelectric nanomaterials and organic elastomers. Here, we used the BaTiO3 nanoparticles and piezoelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) polymeric matrix to fabricate the nanocomposites-based PEH to improve the output performance of PEHs. The piezoelectric nanocomposite is produced by dispersing the inorganic piezo-ceramic nanoparticles inside an organic piezo-polymer and subsequently spin-coat it onto a metal plate. The fabricated organic-inorganic piezoelectric nanocomposite-based PEH harvested the output voltage of ~1.5 V and current signals of ~90 nA under repeated mechanical pushings: these values are compared to those of energy devices made from non-piezoelectric polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomers and supported by a multiphysics simulation software.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and Characterization of Hafnium-Doped BaTiO3 Nanoparticle-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Devices
HakSu Jang, Hyeon Jun Park, Gwang Hyeon Kim, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Jae-Hoon Ji, Donghun Lee, Young Hwa Jung, Min-Ku Lee, Changyeon Baek, Kwi-Il Park
JOURNAL OF SENSOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY.2024; 33(1): 34. CrossRef - Enhanced energy harvesting of fibrous composite membranes via plasma-piezopolymer interaction
Hyeon Jun Park, Bitna Bae, HakSu Jang, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Dong Hun Lee, Gwang Hyun Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Nano Energy.2024; 131: 110299. CrossRef - Effects of Mixing Ratio and Poling on Output Characteristics of BaTiO3-Poly Vinylidene Fluoride Composite Piezoelectric Generators
Hee-Tae Kim, Sang-Shik Park
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2023; 33(12): 517. CrossRef - Stretchable Sensor Array Based on Lead-Free Piezoelectric Composites Made of BaTiO3 Nanoparticles and Polymeric Matrix
Jun Ho Bae, Seong Su Ham, Sung Cheol Park, Kwi-Il Park
JOURNAL OF SENSOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY.2022; 31(5): 312. CrossRef - Flexible Energy Harvester Made of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Piezoelectric Nanocomposite
Yu Jeong Kwon, Dong Yeol Hyeon, Kwi-Il Park
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2019; 29(6): 371. CrossRef
- Development and Characterization of Hafnium-Doped BaTiO3 Nanoparticle-Based Flexible Piezoelectric Devices
- [Korean]
- Development of Metal Composite Powder Non-corrosive Flux for Low Temperature Forming of the Aluminum Brazing Filler Material
- Dae-Young Kim, Ha-Neul Jang, Dae-Ho Yoon, Yun-Ho Shin, Seong-Ho Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):16-21. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.16
- 792 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
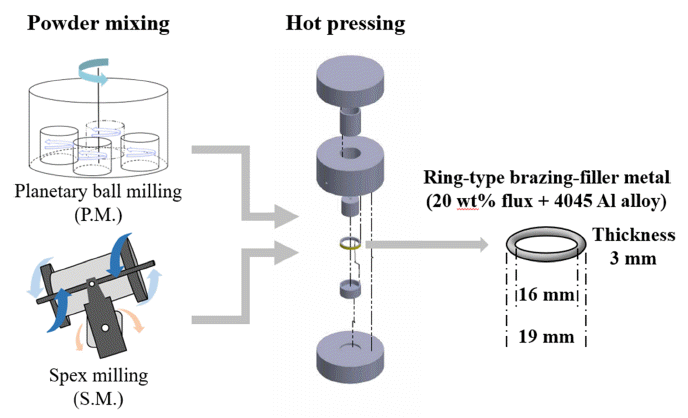
PDF In aluminum brazing processes, corrosive flux, which is used in preventing oxidation, is currently raising environmental concerns because it generates many pollutants such as dioxin. The brazing process involving noncorrosive flux is known to encounter difficulties because the melting temperature of the flux is similar to that of the base material. In this study, a new brazing filler material is developed based on aluminum and non-corrosive flux composite powder. To minimize the interference of consolidation aluminum alloy powder by the flux, the flux is intentionally embedded in the aluminum alloy powder using a mechanical milling process. This study demonstrates that the morphology of the composite powder can be varied according to the mixing process, and this significantly affects the relative density and mechanical properties of the final filler samples.
- [Korean]
- Development of Novel Composite Powder Friction Modifier for Improving Wheel-rail Adhesion in High-speed Train
- Min Chul Oh, Byungmin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):501-506. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.501
- 630 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
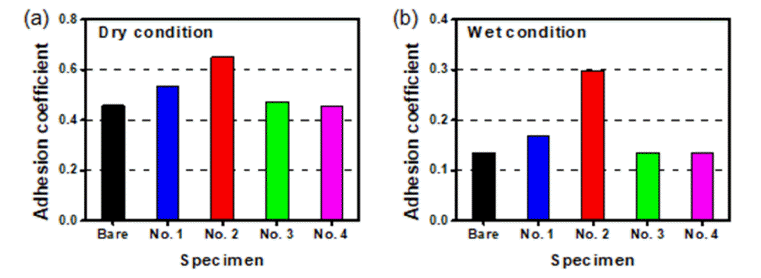
PDF With the recent remarkable improvements in the average speeds of contemporary trains, a necessity has arisen for the development of new friction modifiers to improve adhesion characteristics at the wheel-rail interface. The friction modifier must be designed to reduce slippage or sliding of the trains’ wheels on the rails under conditions of rapid acceleration or braking without excessive rolling contact wear. In this study, a novel composite material consisting of metal, ceramic, and polymer is proposed as a friction modifier to improve adhesion between wheels and rails. A blend of Al-6Cu-0.5Mg metallic powder, Al2O3 ceramic powder, and Bakelite-based polymer in various weight-fractions is hot-pressed at 150°C to form a bulk composite material. Variation in the adhesion coefficient is evaluated using a high-speed wheel-rail friction tester, with and without application of the composite friction modifier, under both dry and wet conditions. The effect of varying the weighting fractions of metal and ceramic friction powders is detailed in the paper.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Molybdenum Silicide-based Composites with Uniformly Dispersed Silicon Carbide
- Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim, Jong Min Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):402-407. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.402
- 483 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
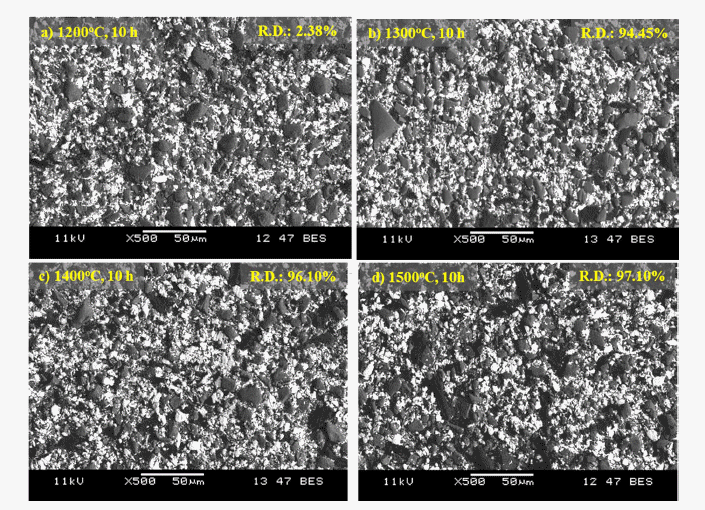
PDF Molybdenum silicide has gained interest for high temperature structural applications. However, poor fracture toughness at room temperatures and low creep resistance at elevated temperatures have hindered its practical applications. This study uses a novel powder metallurgical approach applied to uniformly mixed molybdenum silicidebased composites with silicon carbide. The degree of powder mixing with different ball milling time is also demonstrated by Voronoi diagrams. Core-shell composite powder with Mo nanoparticles as the shell and β-SiC as the core is prepared via chemical vapor transport. Using this prepared core-shell composite powder, the molybdenum silicide-based composites with uniformly dispersed β-SiC are fabricated using pressureless sintering. The relative density of the specimens sintered at 1500°C for 10 h is 97.1%, which is similar to pressure sintering owing to improved sinterability using Mo nanoparticles.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Mo-Cu Powders by Ball Milling and Hydrogen Reduction of MoO3-CuO Powder Mixtures
- Hyunji Kang, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):322-326. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.322
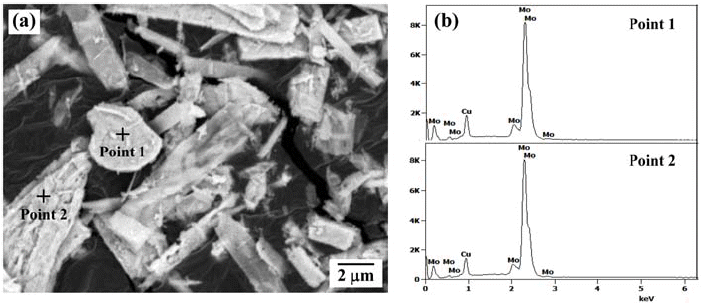
- 924 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The hydrogen reduction behavior of MoO3-CuO powder mixture for the synthesis of homogeneous Mo-20 wt% Cu composite powder is investigated. The reduction behavior of ball-milled powder mixture is analyzed by XRD and temperature programmed reduction method at various heating rates in Ar-10% H2 atmosphere. The XRD analysis of the heat-treated powder at 300°C shows Cu, MoO3, and Cu2MoO5 phases. In contrast, the powder mixture heated at 400°C is composed of Cu and MoO2 phases. The hydrogen reduction kinetic is evaluated by the amount of peak shift with heating rates. The activation energies for the reduction, estimated by the slope of the Kissinger plot, are measured as 112.2 kJ/mol and 65.2 kJ/mol, depending on the reduction steps from CuO to Cu and from MoO3 to MoO2, respectively. The measured activation energy for the reduction of MoO3 is explained by the effect of pre-reduced Cu particles. The powder mixture, hydrogen-reduced at 700°C, shows the dispersion of nano-sized Cu agglomerates on the surface of Mo powders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis of Mo-Cu nanocomposite powder by hydrogen reduction of copper nitrate coated MoO3 powder mixture
Ji Won Choi, Ji Young Kim, Youngmin Kim, Eui Seon Lee, Sung-Tag Oh
Materials Letters.2024; 377: 137565. CrossRef - Fabrication of Porous Mo-Cu by Freeze Drying and Hydrogen Reduction of Metal Oxide Powders
Hyunji Kang, Ju-Yeon Han, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - Hydrogen Reduction Behavior and Microstructure Characteristics of Ball-milled CuO-Co3O4 Powder Mixtures
Ju-Yeon Han, Gyuhwi Lee, Hyunji Kang, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(5): 410. CrossRef
- Synthesis of Mo-Cu nanocomposite powder by hydrogen reduction of copper nitrate coated MoO3 powder mixture
- [Korean]
- Photocatalysis of TiO2/WO3 Composites Synthesized by Ball Milling
- Su-Yeol Yu, Chunghee Nam
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):316-321. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.316
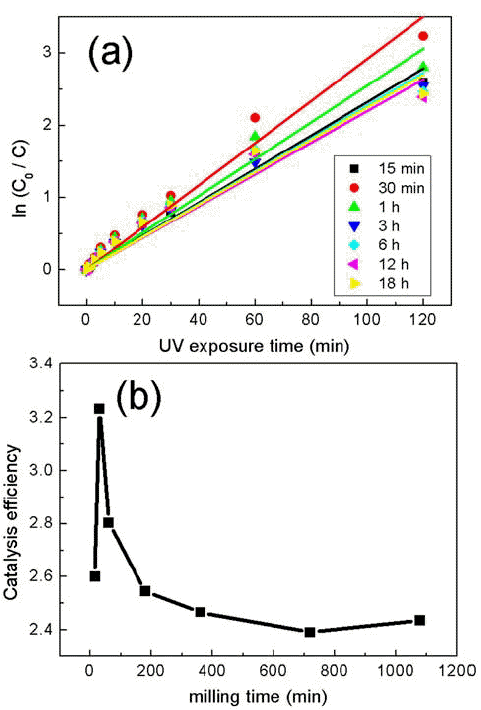
- 786 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Composites of P25 TiO2 and hexagonal WO3 nanorods are synthesized through ball-milling in order to study photocatalytic properties. Various composites of TiO2/WO3 are prepared by controlling the weight percentages (wt%) of WO3, in the range of 1–30 wt%, and milling time to investigate the effects of the composition ratio on the photocatalytic properties. Scanning electron microscopy, x-ray diffraction, and transmission electron microscopy are performed to characterize the structure, shape and size of the synthesized composites of TiO2/WO3. Methylene blue is used as a test dye to analyze the photocatalytic properties of the synthesized composite material. The photocatalytic activity shows that the decomposition efficiency of the dye due to the photocatalytic effect is the highest in the TiO2/WO3 (3 wt%) composite, and the catalytic efficiency decreases sharply when the amount of WO3 is further increased. As the amount of WO3 added increases, dye-removal by adsorption occurs during centrifugation, instead of the decomposition of dyes by photocatalysts. Finally, TiO2/WO3 (3 wt%) composites are synthesized with various milling times. Experimental results show that the milling time has the best catalytic efficiency at 30 min, after which it gradually decreases. There is no significant change after 1 hour.
- [English]
- Preparation of the MnO2/Macroporous Carbon for PET Glycolysis
- Bong Gill Choi, MinHo Yang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):203-207. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.25.3.203
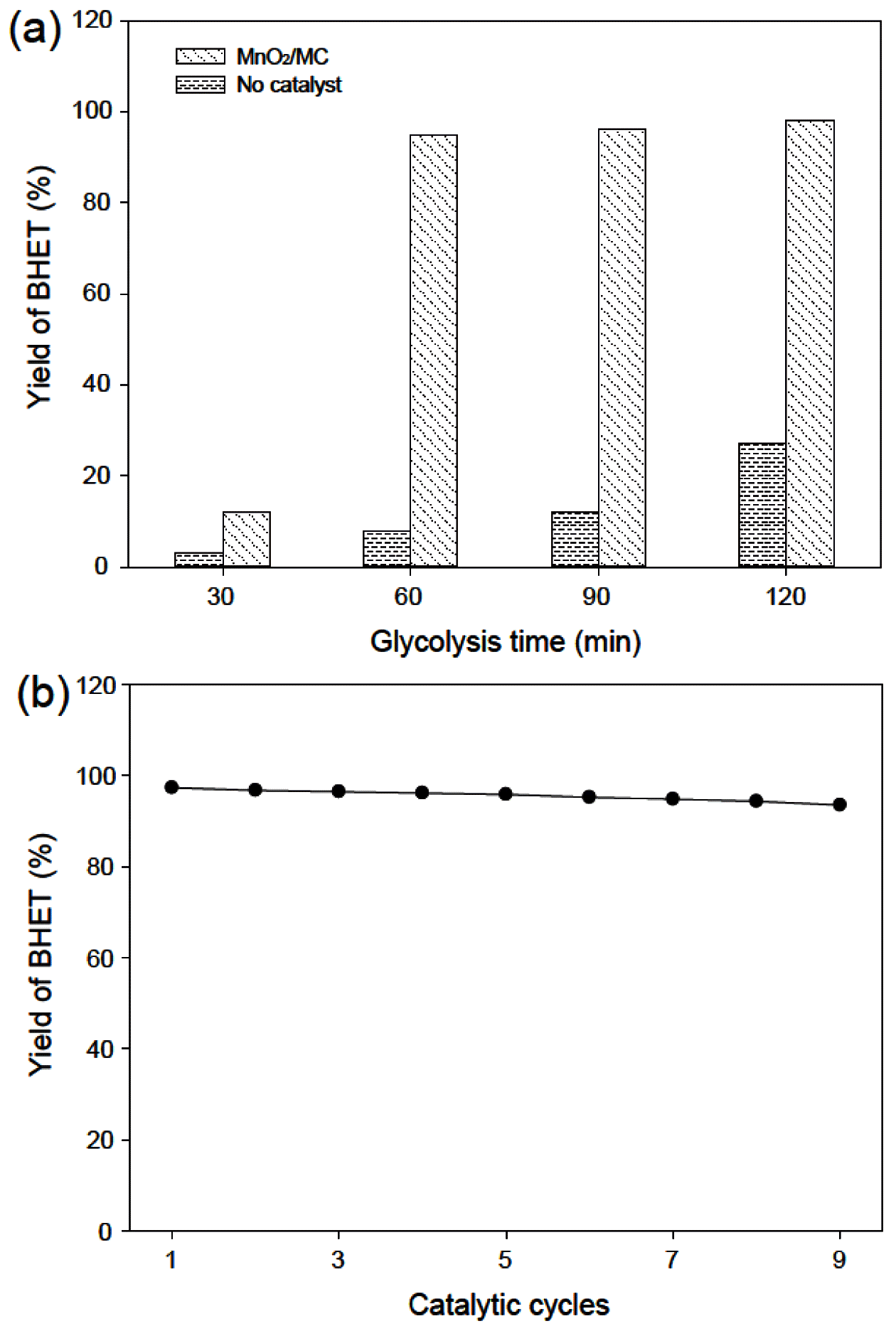
- 627 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Plastic pollution is threatening human health and ecosystems, resulting in one of the biggest challenges that humanity has ever faced. Therefore, this study focuses on the preparation of macroporous carbon from biowaste (MC)-supported manganese oxide (MnO2) as an efficient, reusable, and robust catalyst for the recycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) waste. As-prepared MnO2/MC composites have a hierarchical pore network and a large surface area (376.16 m2/g) with a narrow size distribution. MnO2/MC shows a maximum yield (98%) of bis(2-hydroxyethyl)terephthalate (BHET) after glycolysis reaction for 120 min. Furthermore, MnO2/MC can be reused at least nine times with a negligible decrease in BHET yield. Based on this remarkable catalytic performance, we expect that MnO2-based heterogeneous catalysts have the potential to be introduced into the PET recycling industry.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of CNT dispersed Cu matrix composites by wet mixing and spark plasma sintering process
- Seungchan Cho, Ilguk Jo, Sang-Bok Lee, Sang-Kwan Lee, Moonhee Choi, Jehong Park, Hansang Kwon, Yangdo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):158-164. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.158

- 967 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)–copper (Cu) composites are successfully fabricated by a combination of a binder-free wet mixing and spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. The SPS is performed under various conditions to investigate optimized processing conditions for minimizing the structural defects of CNTs and densifying the MWCNT–Cu composites. The electrical conductivities of MWCNT–Cu composites are slightly increased for compositions containing up to 1 vol.% CNT and remain above the value for sintered Cu up to 2 vol.% CNT. Uniformly dispersed CNTs in the Cu matrix with clean interfaces between the treated MWCNT and Cu leading to effective electrical transfer from the treated MWCNT to the Cu is believed to be the origin of the improved electrical conductivity of the treated MWCNT–Cu composites. The results indicate the possibility of exploiting CNTs as a contributing reinforcement phase for improving the electrical conductivity and mechanical properties in the Cu matrix composites.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Proposing Machine Learning Models Suitable for Predicting Open Data Utilization
Junyoung Jeong, Keuntae Cho
Sustainability.2024; 16(14): 5880. CrossRef
- Proposing Machine Learning Models Suitable for Predicting Open Data Utilization
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Wear Properties of Oxide Dispersion Strengthened Steel Powder Added Steel-Based Composite Material for Automotive Part
- Young-Kyun Kim, Jong-Kwan Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):36-42. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.1.36
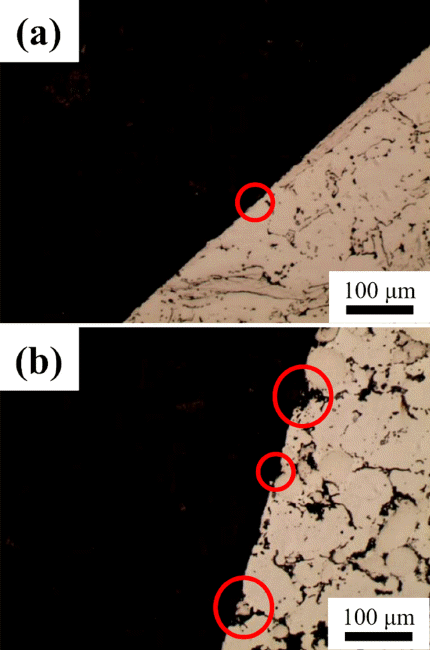
- 834 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In order to expand the application of oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel, a composite material is manufactured by adding mechanically alloyed ODS steel powder to conventional steel and investigated in terms of microstructure and wear properties. For comparison, a commercial automobile part material is also tested. Initial microstructural observations confirm that the composite material with added ODS steel contains i) a pearlitic Fe matrix area and ii) an area with Cr-based carbides and ODS steel particles in the form of a Fe-Fe3C structure. In the commercial material, various hard Co-, Fe-Mo-, and Cr-based particles are present in a pearlitic Fe matrix. Wear testing using the VSR engine simulation wear test confirms that the seatface widths of the composite material with added ODS steel and the commercial material are increased by 24% and 47%, respectively, with wear depths of 0.05 mm and 0.1 mm, respectively. The ODS steel-added composite material shows better wear resistance. Post-wear-testing surface and cross-sectional observations show that particles in the commercial material easily fall off, while the ODS steel-added material has an even, smooth wear surface.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- First principles determination of formation of a Cr shell on the interface between Y–Ti–O nanoparticles and a ferritic steel matrix
Ki-Ha Hong, Jae Bok Seol, Jeoung Han Kim
Applied Surface Science.2019; 481: 69. CrossRef - Thermal Properties and Microstructural Changes of Fe-Co System Valve Seat Alloy by High Densification Process
In-Shup Ahn, Dong-Kyu Park, Kwang-Bok Ahn, Seoung-Mok Shin
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(2): 112. CrossRef
- First principles determination of formation of a Cr shell on the interface between Y–Ti–O nanoparticles and a ferritic steel matrix
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Al2O3 Dispersed Porous Cu by Freeze Drying of CuO-Al2O3/Camphene Slurry
- Hyunji Kang, Doh-Hyung Riu, Sung-Tag Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(1):25-29. Published online February 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.1.25

- 633 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Porous Cu with a dispersion of nanoscale Al2O3 particles is fabricated by freeze-drying CuO-Al2O3/camphene slurry and sintering. Camphene slurries with CuO-Al2O3 contents of 5 and 10 vol% are unidirectionally frozen at -30°C, and pores are generated in the frozen specimens by camphene sublimation during air drying. The green bodies are sintered for 1 h at 700°C and 800°C in H2 atmosphere. The sintered samples show large pores of 100 μm in average size aligned parallel to the camphene growth direction. The internal walls of the large pores feature relatively small pores of ~10 μm in size. The size of the large pores decreases with increasing CuO-Al2O3 content by the changing degree of powder rearrangement in the slurry. The size of the small pores decreases with increasing sintering temperature. Microstructural analysis reveals that 100-nm Al2O3 particles are homogeneously dispersed in the Cu matrix. These results suggest that a porous composite body with aligned large pores could be fabricated by a freeze-drying and H2 reducing process.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Deposition Parameter and Mixing Process of Raw Materials on the Phase and Structure of Ytterbium Silicate Environmental Barrier Coatings by Suspension Plasma Spray Method
- Ho-lim Ryu, Seon-A Choi, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Soo Han, Kyun Choi, Sahn Nahm, Yoon-Suk Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):437-443. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.437

- 832 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF SiC-based composite materials with light weight, high durability, and high-temperature stability have been actively studied for use in aerospace and defense applications. Moreover, environmental barrier coating (EBC) technologies using oxide-based ceramic materials have been studied to prevent chemical deterioration at a high temperature of 1300°C or higher. In this study, an ytterbium silicate material, which has recently been actively studied as an environmental barrier coating because of its high-temperature chemical stability, is fabricated on a sintered SiC substrate. Yb2O3 and SiO2 are used as the raw starting materials to form ytterbium disilicate (Yb2Si2O7). Suspension plasma spraying is applied as the coating method. The effect of the mixing method on the particle size and distribution, which affect the coating formation behavior, is investigated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), an energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. It is found that the originally designed compounds are not effectively formed because of the refinement and vaporization of the raw material particles, i.e., SiO2, and the formation of a porous coating structure. By changing the coating parameters such as the deposition distance, it is found that a denser coating structure can be formed at a closer deposition distance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
Seong-June Youn, Young-Kyun Kim, Jae-Sung Park, Joo-Hyun Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(4): 333. CrossRef
- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
- [Korean]
- Characteristics of WO3-CuO Powder Mixture Prepared by High-Energy Ball Milling in a Bead Mill for the Synthesis of W-Cu Nanocomposite Powder
- Hae-Ryong Park, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):406-413. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.406
- 1,045 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF A Nanosized WO3 and CuO powder mixture is prepared using novel high-energy ball milling in a bead mill to obtain a W-Cu nanocomposite powder, and the effect of milling time on the structural characteristics of WO3-CuO powder mixtures is investigated. The results show that the ball-milled WO3-CuO powder mixture reaches at steady state after 10 h milling, characterized by the uniform and narrow particle size distribution with primary crystalline sizes below 50 nm, a specific surface area of 37 m2/g, and powder mean particle size (D50) of 0.57 μm. The WO3-CuO powder mixtures milled for 10 h are heat-treated at different temperatures in H2 atmosphere to produce W-Cu powder. The XRD results shows that both the WO3 and CuO phases can be reduced to W and Cu phases at temperatures over 700°C. The reduced W-Cu nanocomposite powder exhibits excellent sinterability, and the ultrafine W-Cu composite can be obtained by the Cu liquid phase sintering process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Morphological Characteristics of W/Cu Composite Nanoparticles with Complex Phase Structure Synthesized via Reactive Radio Frequency (RF) Thermal Plasma
Chulwoong Han, Song-Yi Kim, Soobin Kim, Ji-Woon Lee
Metals.2024; 14(9): 1070. CrossRef
- Morphological Characteristics of W/Cu Composite Nanoparticles with Complex Phase Structure Synthesized via Reactive Radio Frequency (RF) Thermal Plasma
- [Korean]
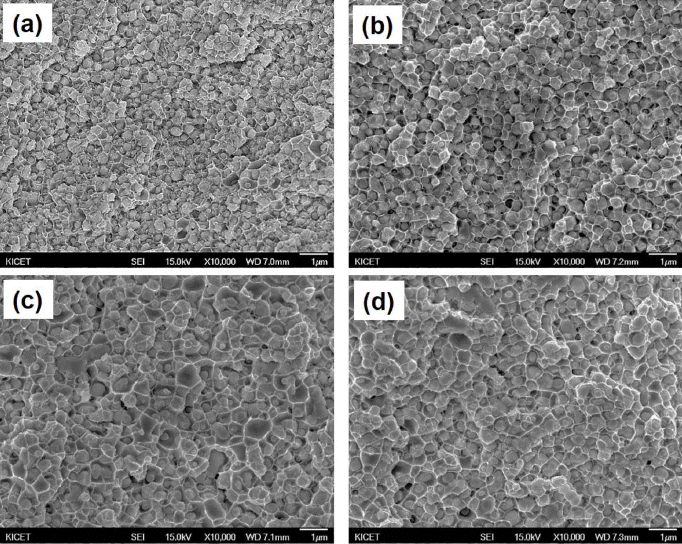
- Microstructure and Electric Contact Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered Ta-Cu Composite
- Won Ju, Young Do Kim, Jae Jin Sim, Sang-Hoon Choi, Soong Keun Hyun, Kyoung Mook Lim, Kyoung-Tae Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):377-383. Published online October 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.377
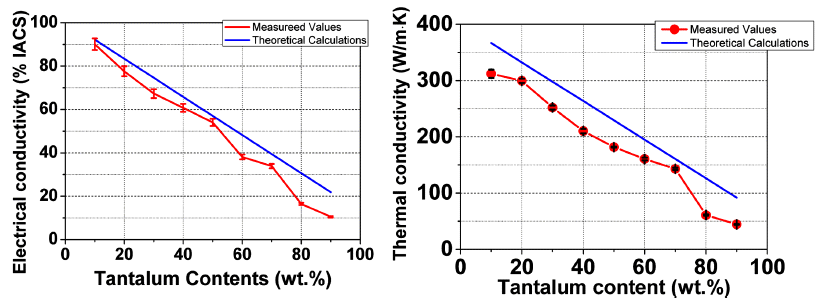
- 1,198 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Microstructure, electric, and thermal properties of the Ta-Cu composite is evaluated for the application in electric contact materials. This material has the potential to be used in a medium for a high current range of current conditions, replacing Ag-MO, W, and WC containing materials. The optimized SPS process conditions are a temperature of 900°C for a 5 min holding time under a 30 MPa mechanical pressure. Comparative research is carried out for the calculated and actual values of the thermal and electric properties. The range of actual thermal and electric properties of the Ta-Cu composite are 50~300W/mk and 10~90 %IACS, respectively, according to the compositional change of the 90 to 10 wt% Ta-Cu system. The results related to the electric contact properties, suggest that less than 50 wt% of Ta compositions are possible in applications of electric contact materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Formation mechanism, microstructural features and dry-sliding behaviour of “Bronze/WC carbide” composite synthesised by atmospheric pulsed-plasma deposition
V.G. Efremenko, Yu.G. Chabak, V.I. Fedun, K. Shimizu, T.V. Pastukhova, I. Petryshynets, A.M. Zusin, E.V. Kudinova, B.V. Efremenko
Vacuum.2021; 185: 110031. CrossRef
- Formation mechanism, microstructural features and dry-sliding behaviour of “Bronze/WC carbide” composite synthesised by atmospheric pulsed-plasma deposition
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Fe3O4/Fe/Graphene nanocomposite powder by Electrical Wire Explosion in Liquid Media and its Electrochemical Properties
- Yoo-Young Kim, Ji-Seub Choi, Hoi-Jin Lee, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):308-314. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.308
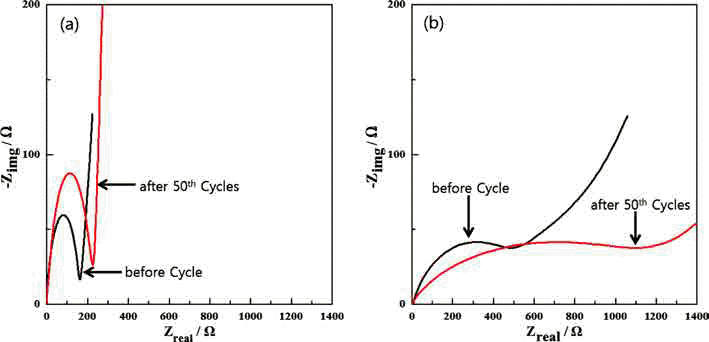
- 1,022 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is synthesized by electrical wire explosion of Fe wire and dispersed graphene in deionized water at room temperature. The structural and electrochemical characteristics of the powder are characterized by the field-emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, field-emission transmission electron microscopy, cyclic voltammetry, and galvanometric discharge-charge method. For comparison, Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposites are fabricated under the same conditions. The Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite particles, around 15-30 nm in size, are highly encapsulated in a graphene matrix. The Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder exhibits a high initial charge specific capacity of 878 mA/g and a high capacity retention of 91% (798 mA/g) after 50 cycles. The good electrochemical performance of the Fe3O4/Fe/graphene nanocomposite powder is clearly established by comparison of the results with those obtained for Fe3O4/Fe nanocomposite powder and is attributed to alleviation of volume change, good distribution of electrode active materials, and improved electrical conductivity upon the addition of graphene.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
Kyunbae Lee, Joonsik Lee, Byung Mun Jung, Byeongjin Park, Taehoon Kim, Sang Bok Lee
Applied Surface Science.2019; 478: 733. CrossRef
- Preparation of magnetic metal and graphene hybrids with tunable morphological, structural and magnetic properties
- [English]
- The Synthesis and Photocatalytic activity of Carbon Nanotube-mixed TiO2 Nanotubes
- Chun Woong Park, Young Do Kim, Tohru Sekino, Se Hoon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):279-284. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.279
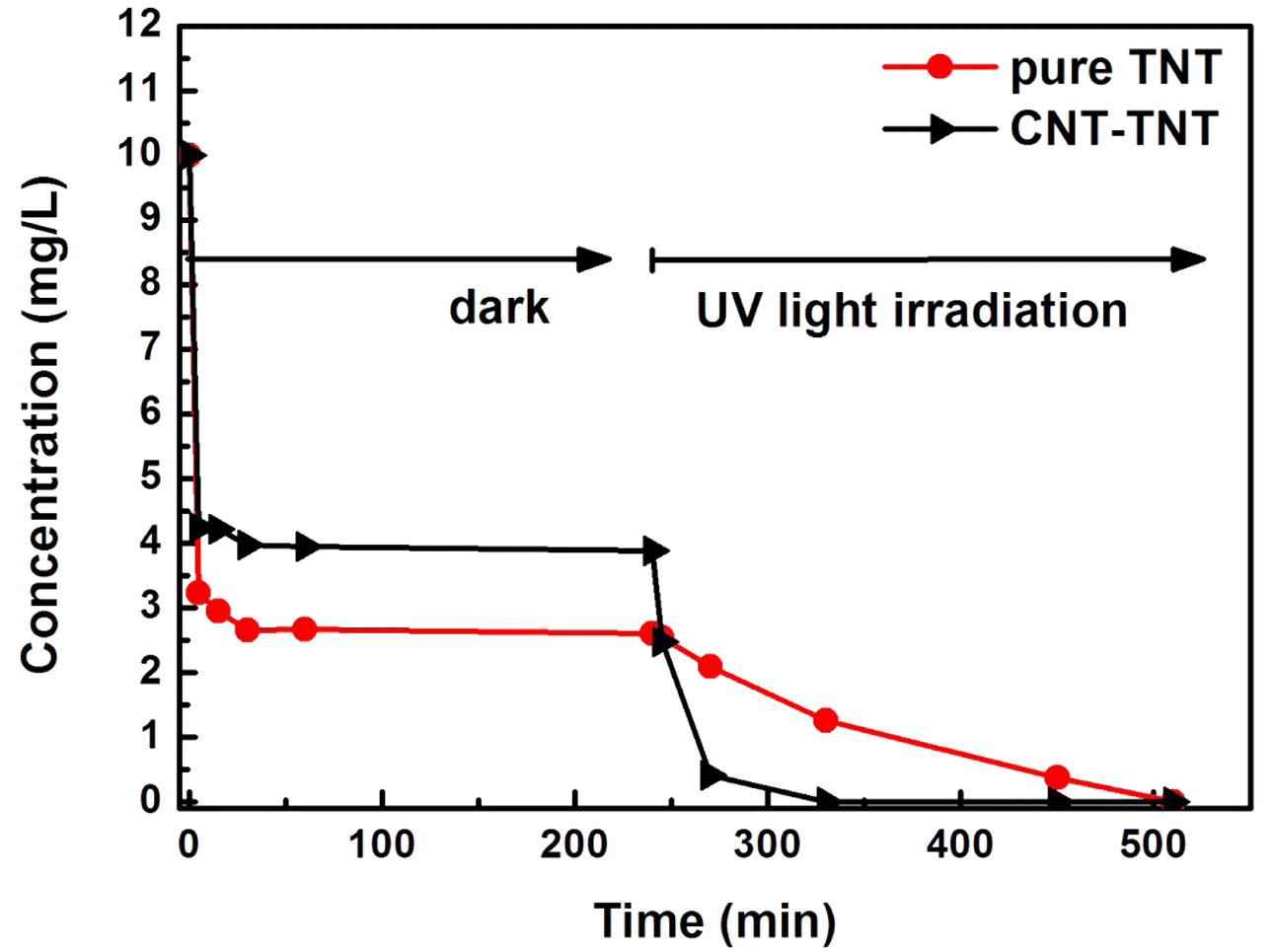
- 1,543 View
- 11 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The formation mechanism and photocatalytic properties of a multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)/TiO2- based nanotube (TNTs) composite are investigated. The CNT/TNT composite is synthesized via a solution chemical route. It is confirmed that this 1-D nanotube composite has a core-shell nanotubular structure, where the TNT surrounds the CNT core. The photocatalytic activity investigated based on the methylene blue degradation test is superior to that of with pure TNT. The CNTs play two important roles in enhancing the photocatalytic activity. One is to act as a template to form the core-shell structure while titanate nanosheets are converted into nanotubes. The other is to act as an electron reservoir that facilitates charge separation and electron transfer from the TNT, thus decreasing the electronhole recombination efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carbon-based photocatalysis in organic transformation
Md Razu Ahmed, Yuta Nishina
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Low-Dimensional Carbon and Titania Nanotube Composites via a Solution Chemical Process and Their Nanostructural and Electrical Properties for Electrochemical Devices
Sunghun Eom, Sung Hun Cho, Tomoyo Goto, Myoung Pyo Chun, Tohru Sekino
ACS Applied Nano Materials.2019; 2(10): 6230. CrossRef
- Carbon-based photocatalysis in organic transformation
- [English]
- Synthesis of Carbonyl Iron-reinforced Polystyrene by High Energy Ball Milling
- Hong-Hai Nguyen, Minh-Thuyet Nguyen, Won Joo Kim, Jin-Chun Kim, Young-Soo Kim, Young-Hyuk Kim, Olga B. Nazarenko
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(4):276-281. Published online August 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.4.276
- 1,257 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Carbonyl iron (CI) is successfully incorporated as an additive into a polystyrene (PS) matrix via a highenergy ball milling method, under an n-hexane medium with volume fractions between 1% and 5% for electromagnetic interference shielding applications by the combination of magnetic CI and an insulating PS matrix. The morphology and the dispersion of CI are investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy, which indicates a uniform distribution of CI in the PS matrix after 2 h of milling. The thermal behavior results indicate no significant degradation of the PS when there is a slight increase in the onset temperature with the addition of CI powder, when compared to the as-received PS pellet. After milling, there are no interactions between the CI and the PS matrix, as confirmed by Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy. In this study, the milled CI-PS powder is extruded to make filaments, and can have potential applications in the 3-D printing industry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Progress toward sustainable polymer technologies with ball-mill grinding
Antonio Rizzo, Gregory I. Peterson
Progress in Polymer Science.2024; 159: 101900. CrossRef
- Progress toward sustainable polymer technologies with ball-mill grinding
- [English]
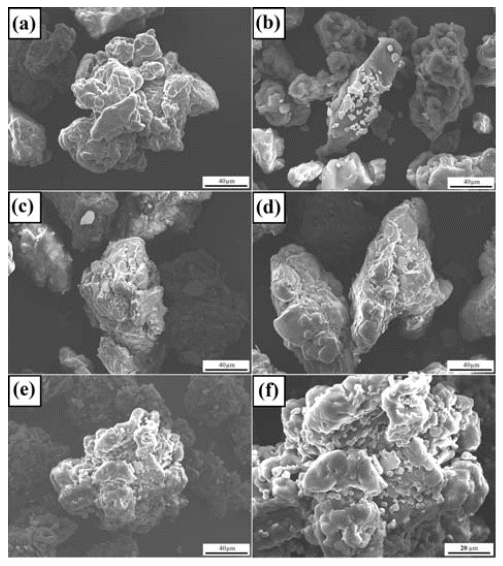
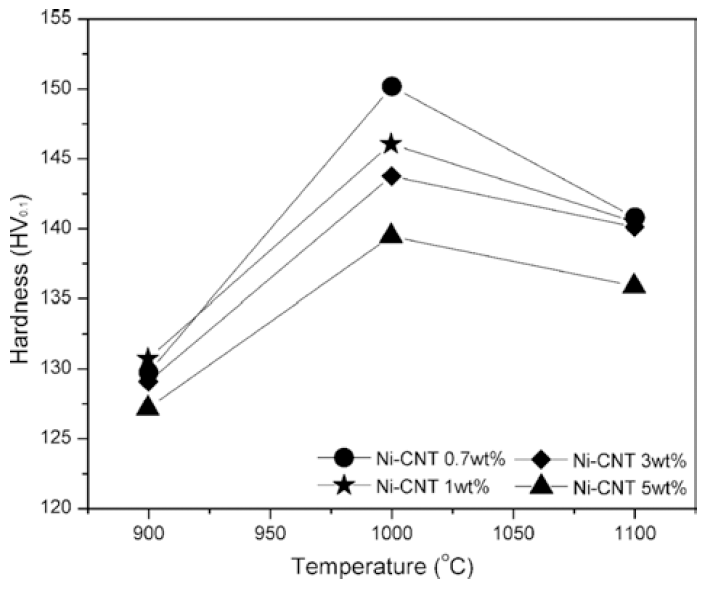
- Fabrication and Mechanical Characteristics of Bulk Nickel/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites via the Electrical Explosion of Wire in Liquid and Spark Plasma Sintering Method
- Thuyet-Nguyen Minh, Hai-Nguyen Hong, Won Joo Kim, Ho Yoon Kim, Jin-Chun Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):213-220. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.213
- 1,278 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, bulk nickel-carbon nanotube (CNT) nanocomposites are synthesized by a novel method which includes a combination of ultrasonication, electrical explosion of wire in liquid and spark plasma sintering. The mechanical characteristics of the bulk Ni-CNT composites synthesized with CNT contents of 0.7, 1, 3 and 5 wt.% are investigated. X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy techniques are used to observe the different phases, morphologies and structures of the composite powders as well as the sintered samples. The obtained results reveal that the as-synthesized composite exhibits substantial enhancement in the microhardness and values more than 140 HV are observed. However an empirical reinforcement limit of 3 wt.% is determined for the CNT content, beyond which, there is no significant improvement in the mechanical properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of nanocomposites by electric explosion of stainless steel capillaries filled with carbon nanotubes
Tao Jiang, Zhongyu Hou
Applied Surface Science.2020; 513: 145824. CrossRef - Effect of a nano-sized TiC particle addition on the flow-assisted corrosion resistance of SA 106B carbon steel
Jin-Ju Park, Eun-Kwang Park, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Chang-Kyu Rhee, Min-Ku Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 143. CrossRef
- Fabrication of nanocomposites by electric explosion of stainless steel capillaries filled with carbon nanotubes
- [Korean]
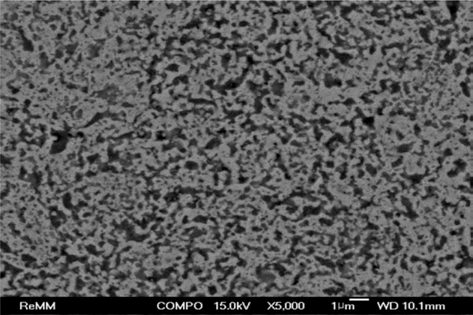
- Sintering of Fe-30 wt% TiC Composite Powders Fabricated from (Fe, TiH2, C) Powder Mixture
- Byunghoon Lee, Ji Soon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(5):356-361. Published online October 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.5.356
- 895 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe-30 wt% TiC composite powders are fabricated by in situ reaction synthesis after planetary ball milling of (Fe, TiH2, Carbon) powder mixture. Two sintering methods of a pressureless sintering and a spark-plasma sintering are tested to densify the Fe-30 wt% TiC composite powder compacts. Pressureless sintering is performed at 1100, 1200 and 1300°C for 1-3 hours in a tube furnace under flowing argon gas atmosphere. Spark-plasma sintering is carried out under the following condition: sintering temperature of 1050°C, soaking time of 10 min, sintering pressure of 50 MPa, heating rate of 50°C/min, and in a vacuum of 0.1 Pa. The curves of shrinkage and its derivative (shrinkage rate) are obtained from the data stored automatically during sintering process. The densification behaviors are investigated from the observation of fracture surface and cross-section of the sintered compacts. The pressureless-sintered powder compacts are not densified even after sintering at 1300°C for 3 h, which shows a relative denstiy of 66.9%. Spark-plasma sintering at 1050°C for 10 min exhibits nearly full densification of 99.6% relative density under the sintering pressure of 50 MPa.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Abrasive Wear Performance of Spherical Hierarchical Structured TiC/High-Manganese Steel Composites
Tao He, Shengnian Zhao, Dehong Lu, Yehua Jiang, Mojin Zhou
Materials.2024; 18(1): 130. CrossRef - Effect of TiC particle size on high temperature oxidation behavior of TiC reinforced stainless steel
Yeong-Hwan Lee, Sungmin Ko, Hyeonjae Park, Donghyun Lee, Sangmin Shin, Ilguk Jo, Sang-Bok Lee, Sang-Kwan Lee, Yangdo Kim, Seungchan Cho
Applied Surface Science.2019; 480: 951. CrossRef - Effect of TiC addition on surface oxidation behavior of SKD11 tool steel composites
Seungchan Cho, Ilguk Jo, Heebong Kim, Hyuk-Tae Kwon, Sang-Kwan Lee, Sang-Bok Lee
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 155. CrossRef
- Abrasive Wear Performance of Spherical Hierarchical Structured TiC/High-Manganese Steel Composites
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of WS2-W-WC Embedded Carbon Nanofiber Composites for Supercapacitors
- Yu-Jin Lee, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):116-121. Published online April 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.116
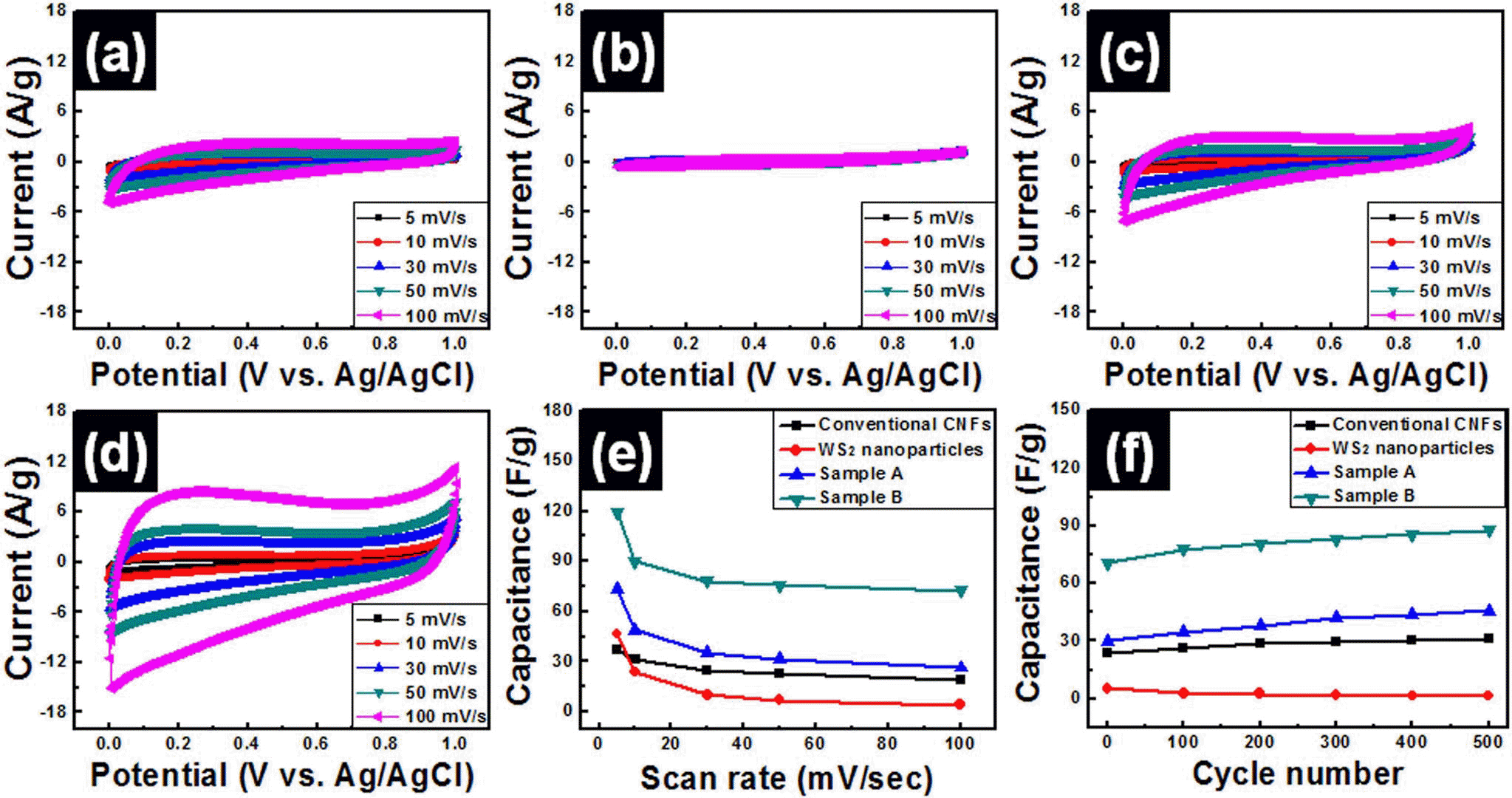
- 848 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF WS2-W-WC embedded carbon nanofiber composites were fabricated by using electrospinning method for use in high-performance supercapacitors. In order to obtain optimum electrochemical properties for supercapacitors, WS2 nanoparticles were used as precursors and the amounts of WS2 precursors were controlled to 4 wt% (sample A) and 8 wt% (sample B). The morphological, structural, and chemical properties of all samples were investigated by means of field emission photoelectron spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. These results demonstrated that the embedded phases of samples A and B were changed from WS2 to WS2-W-WC through carbothermal reaction during carbonization process. In particular, sample B presented high specific capacitance (~119.7 F/g at 5 mV/s), good high-rate capacitance (~60.5%), and superb cycleability. The enhanced electrochemical properties of sample B were explained by the synergistic effect of the using 1-D structure supports, increase of specific surface area, and improved conductivity from formation of W and WC phases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- WS2 Nanoparticles Embedded in Carbon Nanofibers for a Pseudocapacitor
Ki-Wook Sung, Jung Soo Lee, Tae-Kum Lee, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2021; 31(8): 458. CrossRef
- WS2 Nanoparticles Embedded in Carbon Nanofibers for a Pseudocapacitor
- [English]
- Preparation and Characterization of Porous Silicon and Carbon Composite as an Anode Material for Lithium Rechargeable Batteries
- Junsoo Park, Jae-won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(1):15-20. Published online February 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.1.15
- 790 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The composite of porous silicon (Si) and amorphous carbon (C) is prepared by pyrolysis of a nano-porous Si + pitch mixture. The nano-porous Si is prepared by mechanical milling of magnesium powder with silicon monoxide (SiO) followed by removal of MgO with hydrochloric acid (etching process). The Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area of porous Si (64.52 m2g−1) is much higher than that before etching Si/MgO (4.28 m2g−1) which indicates pores are formed in Si after the etching process. Cycling stability is examined for the nano-porous Si + C composite and the result is compared with the composite of nonporous Si + C. The capacity retention of the former composite is 59.6% after 50 charge/discharge cycles while the latter shows only 28.0%. The pores of Si formed after the etching process is believed to accommodate large volumetric change of Si during charging and discharging process.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Elevated Temperature Strength of W-ZrC Composites with Micrometric and Nanosized ZrC Particles
- Yoon Soo Han, Sung-Soo Ryu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(6):415-421. Published online December 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.415
- 660 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF W-10vol.%ZrC composites reinforced by micrometric and nanosized ZrC particles were prepared by hot-pressing of 25 MPa for 2 h at 1900°C. The effect of ZrC particle size on microstructure and mechanical properties at room temperature and elevated temperatures was investigated by X-ray diffraction analysis, scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscope observations and the flexural strength test of the W-ZrC composite. Microstructural analysis of the W-ZrC composite revealed that nanosized ZrC particles were homogeneously dispersed in the W matrix inhibiting W grain growth compared to W specimen with micrometric ZrC particle. As a result, its flexural strength was significantly improved. The flexural strength at room temperature for W-ZrC composite using nanosized ZrC particle being 740 MPa increased by around 2 times than that of specimen using micrometric ZrC particle which was 377 MPa. The maximum strength of 935 MPa was tested at 1200°C on the W composite specimen containing nanosized ZrC particle.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Characterization of SnO2-CoO/carbon-coated CoO Core/shell Nanowire Composites
- Yu-Jin Lee, Bon-Ryul Koo, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):360-365. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.360
- 730 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF SnO2-CoO/carbon-coated CoO core/shell nanowire composites were synthesized by using electrospinning and hydrothermal methods. In order to obtain SnO2-CoO/carbon-coated CoO core/shell nanowire composites, SnO2-Co3O4 nanowire composites and SnO2-Co3O4/polygonal Co3O4 core/shell nanowire composites are also synthesized. To demonstrate their structural, chemical bonding, and morphological properties, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy were carried out. These results indicated that the morphologies and structures of the samples were changed from SnO2-Co3O4 nanowires having cylindrical structures to SnO2-Co3O4/Co3O4 core/shell nanowires having polygonal structures after a hydrothermal process. At last, SnO2-CoO/carbon-coated CoO core/shell nanowire composites having irregular and high surface area are formed after carbon coating using a polypyrrole (PPy). Also, there occur phases transformation of cobalt phases from Co3O4 to CoO during carbon coating using a PPy under a argon atmosphere.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Co-Embedded Graphitic Porous Carbon Nanofibers for Pt-Free Counter Electrode in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
혜란 안, 혜린 강, 효정 선, 지호 한, 효진 안
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2015; 25(12): 672~677. CrossRef - Synthesis of Perforated Polygonal Cobalt Oxides usinga Carbon Nanofiber Template
Dong-Yo Sin, Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(5): 350. CrossRef
- Co-Embedded Graphitic Porous Carbon Nanofibers for Pt-Free Counter Electrode in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


